How do different levels of women’s lacrosse heads affect gameplay. What are the key features of beginner, intermediate, and advanced lacrosse sticks. How can players choose the best lacrosse stick for their skill level and position.
Understanding the Importance of Lacrosse Stick Selection
Choosing the right lacrosse stick is crucial for players at every level. The design and features of a lacrosse stick can significantly impact a player’s performance, comfort, and ability to develop their skills. While it may seem that all women’s lacrosse sticks look similar at first glance, there are important differences that cater to various skill levels and playing positions.
Beginner Lacrosse Sticks: Features and Benefits
Beginner lacrosse players require sticks that are easy to handle and forgiving in their design. Key features of beginner lacrosse sticks include:
- Lightweight construction for easy maneuverability
- Flat, wide scoop for easier ground ball pickup
- Larger pocket for better ball retention
- More flexible shaft for reduced vibration
Why are these features important for beginners? A lightweight stick with a flat scoop helps new players develop proper technique for scooping ground balls, a fundamental skill in lacrosse. The larger pocket allows for easier catching and carrying of the ball, while the flexible shaft helps absorb impact and reduces fatigue during practice and games.

Choosing the Right Beginner Stick
When selecting a beginner lacrosse stick, focus on comfort and ease of use. Look for sticks labeled as “beginner” or “entry-level” and prioritize those with wider heads and flatter scoops. Many manufacturers offer complete stick packages designed specifically for new players, which can be an excellent starting point.
Intermediate Lacrosse Sticks: Bridging the Gap
As players progress in their lacrosse journey, they often outgrow their beginner sticks. Intermediate lacrosse sticks offer a balance between beginner-friendly features and more advanced design elements. Characteristics of intermediate sticks include:
- Slightly narrower head shape for improved ball control
- More defined scoop angle for quicker ground ball pickups
- Mid-range pocket depth for versatile play
- Stiffer shaft for increased power in passes and shots
How do intermediate sticks differ from beginner models? Intermediate sticks provide a stepping stone for players who have mastered basic skills and are ready to refine their technique. The narrower head and more defined scoop allow for better ball handling and quicker transitions, while the stiffer shaft enables players to generate more power in their passes and shots.

Selecting an Intermediate Stick Based on Position
When choosing an intermediate stick, consider your primary playing position:
- Midfielders and defenders: Opt for sticks with a flatter scoop to facilitate ground ball pickups
- Attackers: Look for sticks with a narrower throat to improve shot accuracy
- Goalies: Choose sticks with wider heads for increased save potential
Advanced Lacrosse Sticks: Precision and Performance
Advanced players require sticks that offer maximum control, power, and customization. Features of advanced lacrosse sticks include:
- Narrower head profile for pinpoint accuracy
- Specialized scoop designs for position-specific play
- Customizable pocket depth and stringing patterns
- High-performance shaft materials (e.g., carbon fiber, titanium alloys)
Why do advanced players prefer these features? The narrow head profile and specialized scoop designs allow for precise ball control and quick release, essential for high-level play. Customizable pockets enable players to fine-tune their stick’s performance to match their playing style, while high-performance shaft materials offer the optimal balance of weight, strength, and flex.
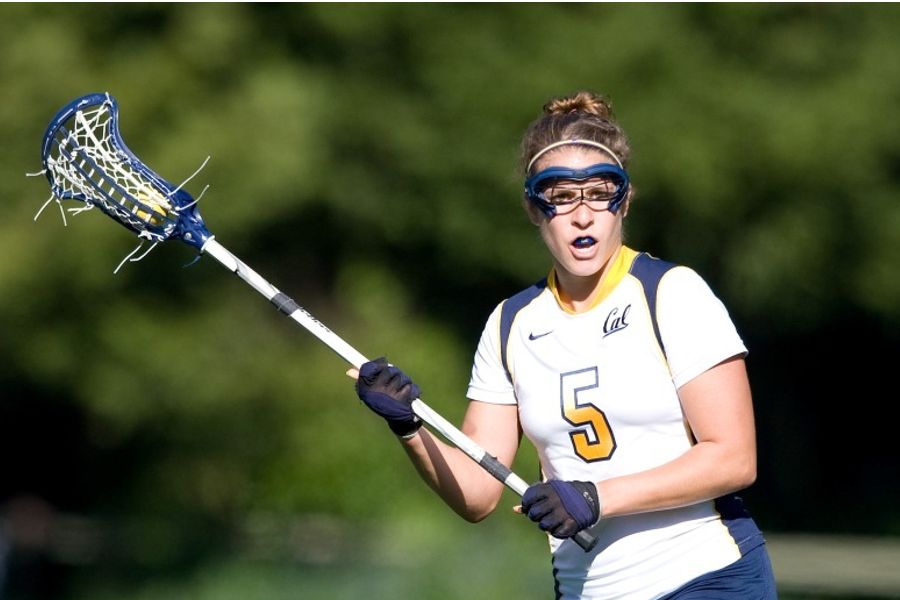

Customizing Advanced Sticks
Many advanced players opt to customize their sticks by restringing the pocket or replacing the shaft. This level of customization allows players to create a stick that perfectly suits their individual needs and preferences. Some popular customization options include:
- Experimenting with different pocket materials (e.g., mesh, traditional)
- Adjusting pocket depth and placement
- Trying various shooting string configurations
- Exploring different shaft materials and lengths
The Evolution of Lacrosse Stick Technology
Lacrosse stick technology has come a long way since the sport’s inception. Modern sticks incorporate advanced materials and design techniques to enhance performance and durability. Some notable advancements include:
- Lightweight composite materials for increased speed and maneuverability
- Ergonomic grip designs for improved control and comfort
- Weather-resistant coatings to maintain consistent performance in all conditions
- Computer-aided design for optimized head shapes and pocket patterns
How have these advancements impacted the game? The evolution of lacrosse stick technology has led to faster gameplay, more precise ball control, and increased scoring opportunities. Players at all levels can now benefit from equipment that enhances their natural abilities and helps them perform at their best.

Maintaining and Caring for Your Lacrosse Stick
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring your lacrosse stick performs optimally and lasts as long as possible. Here are some key tips for caring for your stick:
- Clean your stick regularly with mild soap and water
- Store your stick in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight
- Avoid leaving your stick in extreme temperatures (e.g., hot car)
- Periodically check and tighten screws on the head
- Replace worn strings or mesh to maintain pocket consistency
Why is proper maintenance important? A well-maintained lacrosse stick will perform more consistently and have a longer lifespan. Regular cleaning and inspection can help prevent issues such as warped heads, loose screws, or damaged strings that could negatively impact your game.
Regulations and Rules Regarding Lacrosse Sticks
It’s important to be aware of the regulations governing lacrosse sticks, as using non-compliant equipment can result in penalties or disqualification. Some key rules to keep in mind include:

- Stick length requirements (varies by position and age group)
- Head dimensions and shape restrictions
- Pocket depth limitations
- Shooting string placement guidelines
How can players ensure their sticks are legal? Always check the most recent rules and regulations set by your governing body (e.g., US Lacrosse, NCAA) before purchasing or customizing a stick. Many manufacturers produce sticks that meet standard regulations, but it’s still important to verify compliance, especially if you’ve made any modifications.
Choosing the Right Lacrosse Stick: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the perfect lacrosse stick can be overwhelming, especially for new players or parents. Follow these steps to make an informed decision:
- Determine your skill level (beginner, intermediate, or advanced)
- Consider your primary playing position
- Set a budget for your purchase
- Research different brands and models within your criteria
- Read reviews from other players or consult with coaches
- Visit a local sporting goods store to handle different sticks in person
- Consider trying out a teammate’s stick to get a feel for different options
- Make your purchase and allow time to break in your new stick
Why is it important to follow a systematic approach when choosing a lacrosse stick? By carefully considering your needs, skill level, and preferences, you’re more likely to select a stick that will help you perform your best and enjoy the game. Taking the time to research and try different options can lead to a more satisfying purchase and potentially save money in the long run by avoiding the need for frequent replacements.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Lacrosse Stick
Be wary of these common pitfalls when selecting your lacrosse stick:
- Choosing a stick based solely on appearance or brand name
- Opting for an advanced stick before mastering basic skills
- Neglecting to consider your primary playing position
- Failing to check regulations for your specific league or level of play
- Overlooking the importance of proper maintenance and care
By avoiding these mistakes, you’ll be more likely to choose a stick that enhances your performance and enjoyment of the game.
The Future of Lacrosse Stick Design
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in lacrosse stick design. Some potential developments on the horizon include:
- Smart sticks with integrated sensors for performance tracking
- Environmentally friendly materials for sustainable production
- Customizable 3D-printed heads for personalized performance
- Advanced shock-absorption technologies for improved comfort
How might these innovations impact the sport? Future advancements in lacrosse stick technology could lead to more precise skill development, enhanced player safety, and even greater customization options. As the sport continues to grow in popularity, we can expect manufacturers to invest in research and development to create equipment that pushes the boundaries of performance and player experience.
Balancing Innovation with Tradition
While technological advancements offer exciting possibilities, it’s important to consider how they align with the spirit and traditions of the sport. Governing bodies will need to carefully evaluate new technologies to ensure they maintain the integrity of the game while allowing for reasonable improvements in equipment design.
The Role of Proper Stick Selection in Player Development
Choosing the right lacrosse stick at each stage of a player’s development is crucial for fostering skill growth and enjoyment of the sport. Here’s how appropriate stick selection can impact player development:
- Beginner sticks build confidence and encourage proper technique
- Intermediate sticks challenge players to refine their skills
- Advanced sticks allow for maximum expression of talent and creativity
Why is progression through different stick types important? By using equipment that matches their skill level, players can focus on developing appropriate techniques and strategies without being hindered or overwhelmed by their equipment. This gradual progression helps maintain motivation and reduces the risk of developing bad habits due to using inappropriate gear.

The Coach’s Perspective on Stick Selection
Coaches play a vital role in guiding players towards the right equipment choices. Here are some ways coaches can assist in the stick selection process:
- Assess individual player skills and recommend appropriate stick types
- Educate players and parents about the importance of proper equipment
- Organize stick demos or trial sessions to help players test different options
- Provide guidance on stick maintenance and care
- Stay informed about the latest equipment regulations and innovations
By taking an active role in the equipment selection process, coaches can help ensure that their players have the tools they need to succeed and enjoy the sport to its fullest.
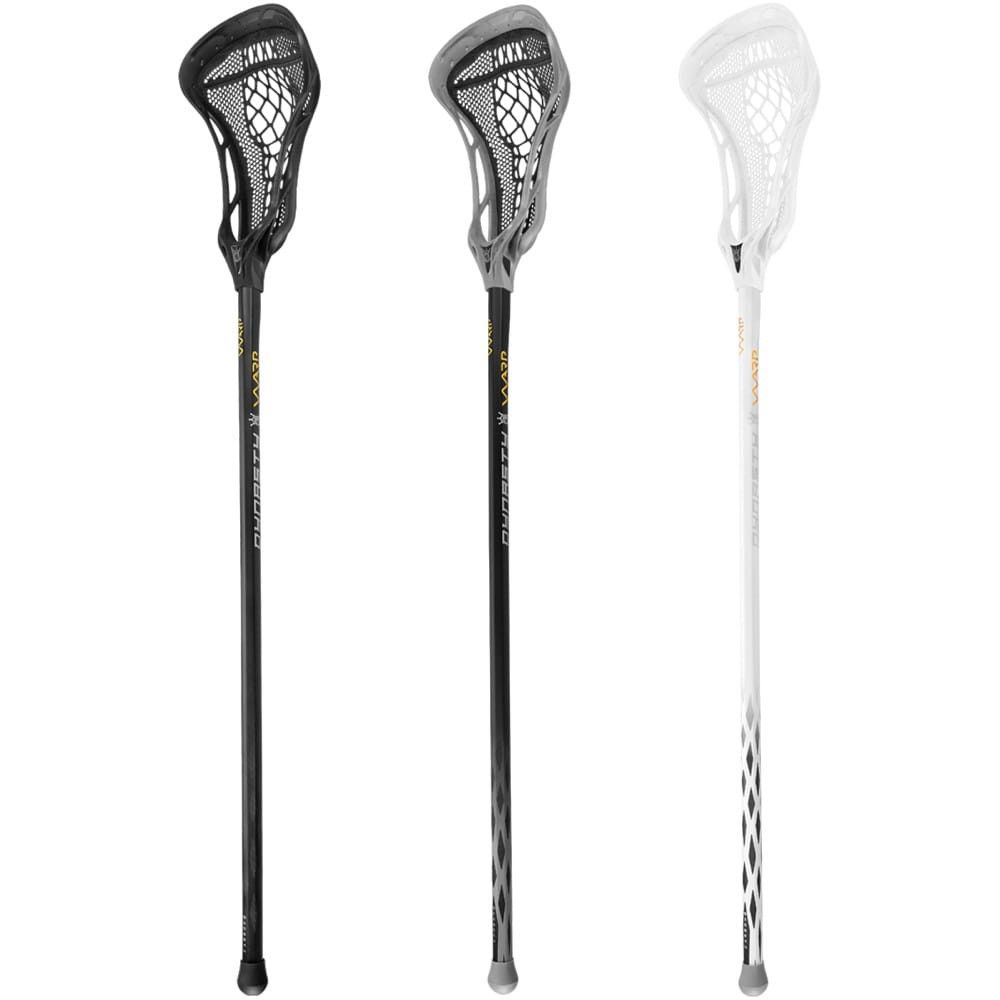
Different Levels Of Women’s Heads
Different Levels Of Women’s Heads | Universal Lacrosse Blog
Skip to content
Do you know the differences?
When looking at a wall of women’s lacrosse sticks, it can be very difficult to see the differences between each one and just say “they all look exactly alike!” I can assure you that during preseason, I get that from almost every beginner player and/or parent on a daily basis. Once I start to break things down for them, they start to understand why different levels of players (beginner, intermediate and expert) play with different shaped heads.
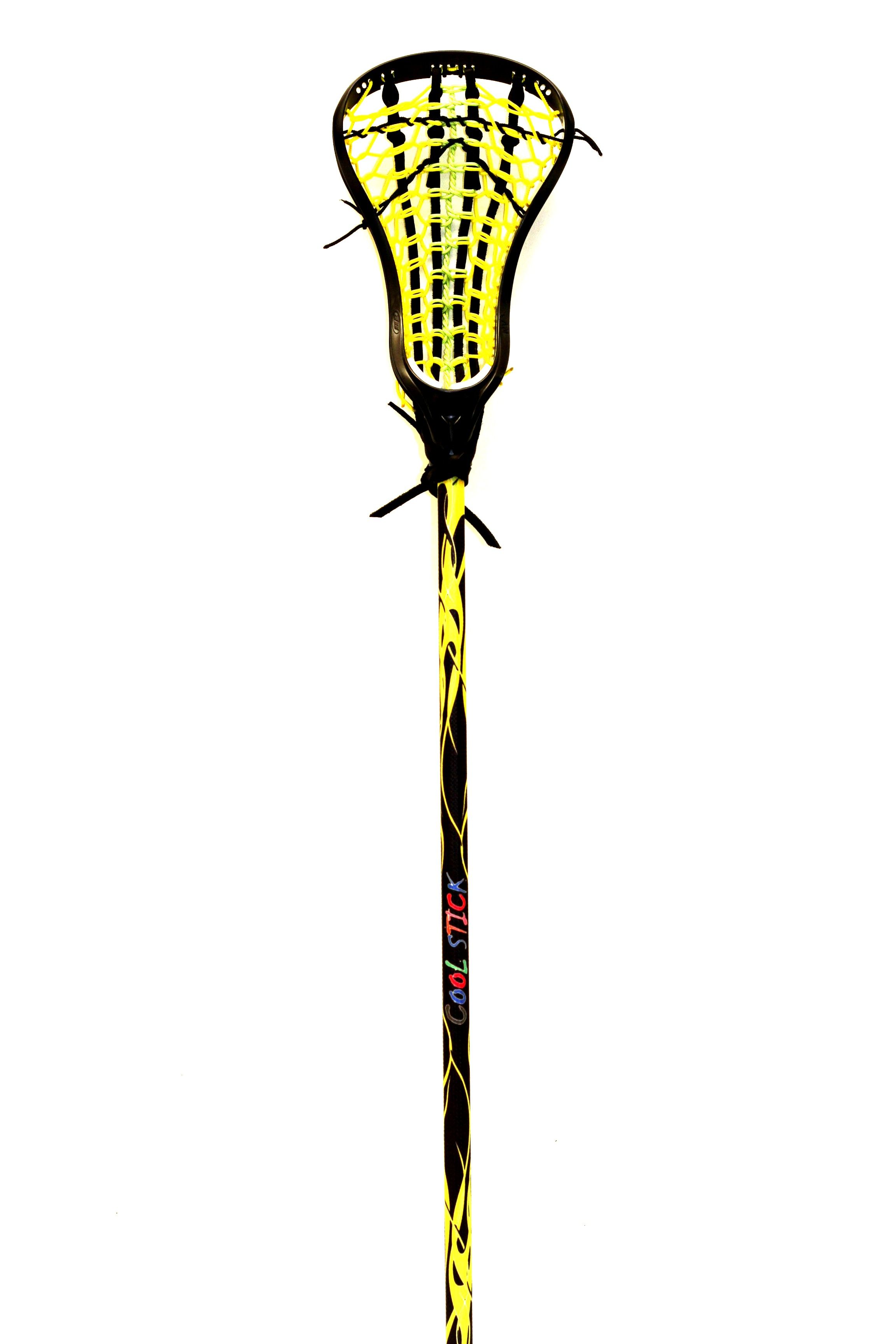
Beginner
Typically, beginners want to use a light weight stick and one that is very flat on the top scoop. I think we can all agree that learning to pick up ground balls can be frustrating in general, but as a beginner, you want to have a flat, pancake spatula looking scoop, which will make it much easier to get under the ball. All sticks, no matter what level, start off not broken in and can all give off the appearance of looking very flat. However once you pick up the stick and look at the scoop, you can usually tell if it is a beginner stick or not.
All sticks, no matter what level, start off not broken in and can all give off the appearance of looking very flat. However once you pick up the stick and look at the scoop, you can usually tell if it is a beginner stick or not.
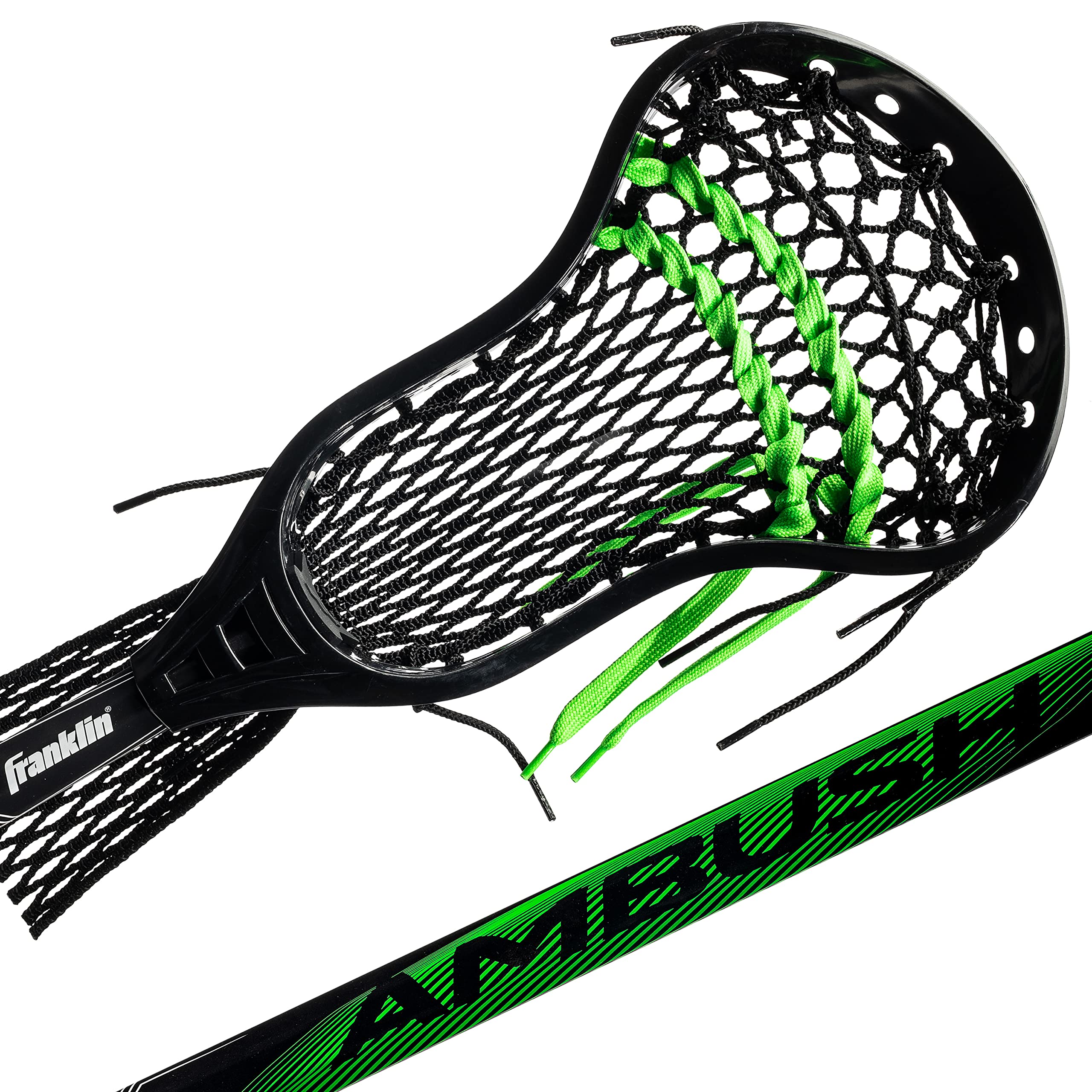
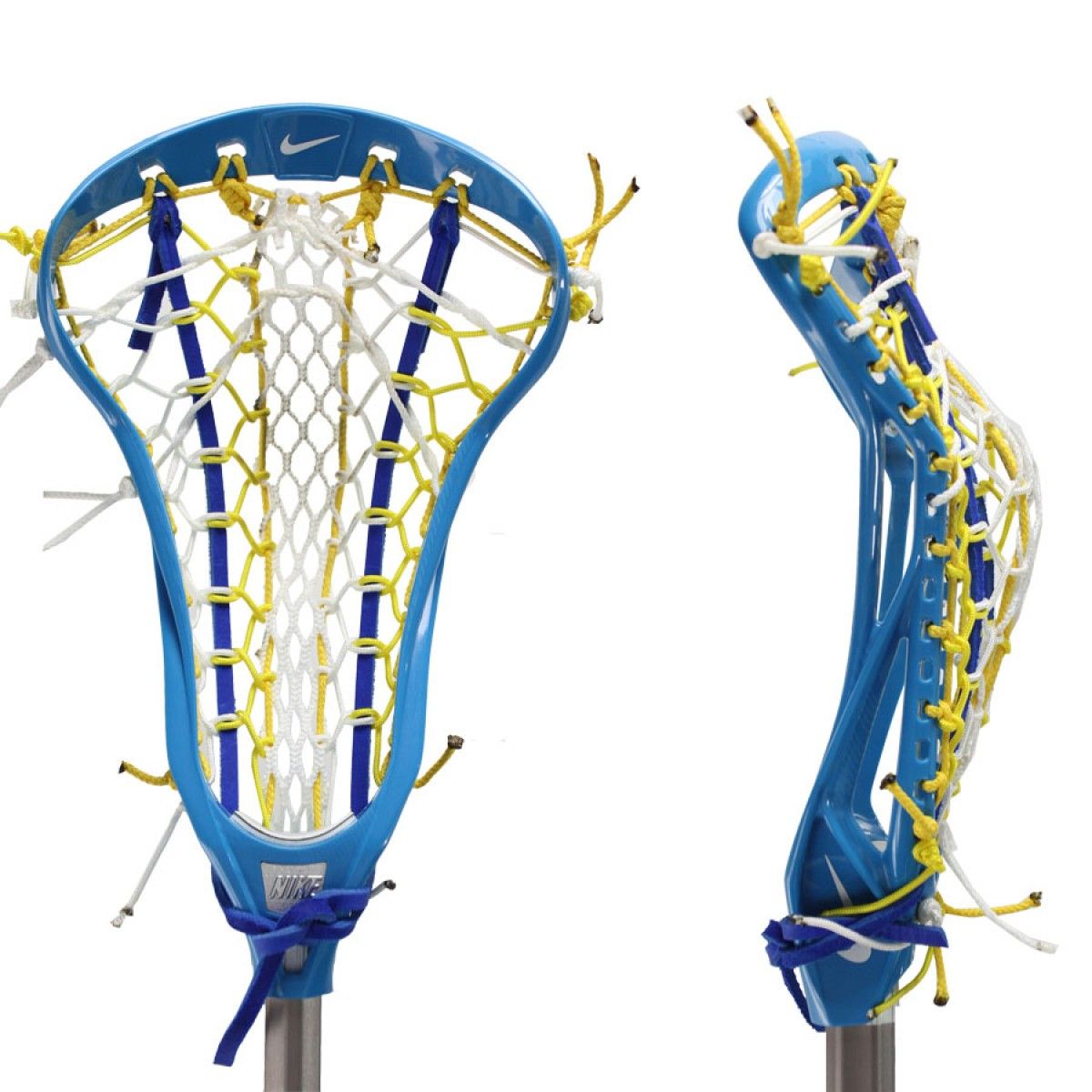
Intermediate
To me, intermediate players have played lacrosse for a year or two but only during the spring season. They have either grown and their stick is too short for them or they want a head that has a bit more shape to it so it stays in better while cradling. These players I usually ask what position they are mainly playing-attack, midfield or defense. I usually try to direct the midfielders and defense players towards sticks that still have a flatter scoop because they are still constantly picking up ground balls. Attack players can get away with a more narrow throat in their stick because it helps direct the ball to come out of the stick straight; allowing more accurate shots.
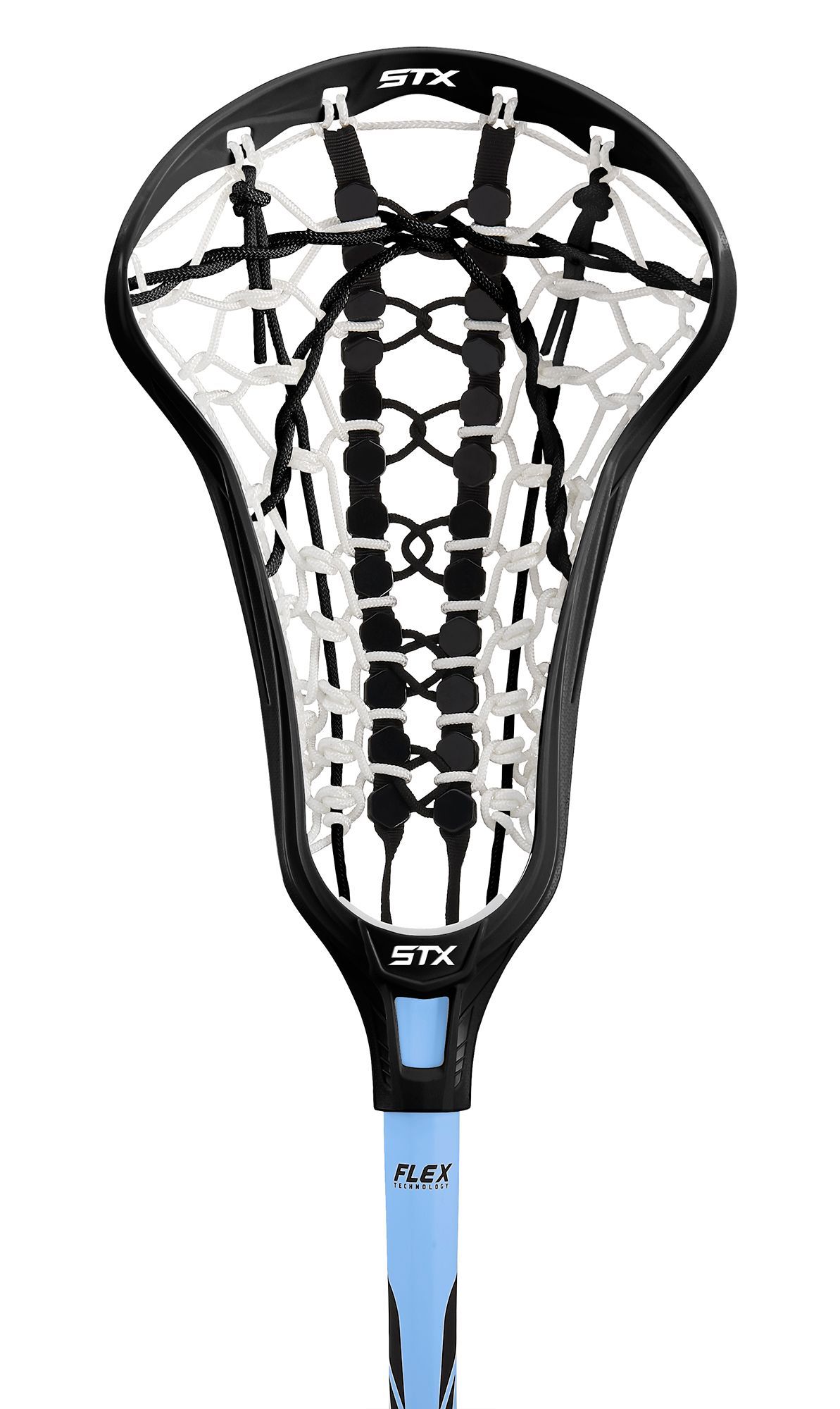
Advanced
These players have a stick in their hands year round and usually know exactly which stick they want because they have borrowed their friends sticks to play with. Sometimes advanced players will actually keep their current stick (because it’s lucky or extra special) and simply get it restrung with a different runway/pocket.
Sometimes advanced players will actually keep their current stick (because it’s lucky or extra special) and simply get it restrung with a different runway/pocket.
Even though to the untrained eye women’s lacrosse sticks can look very similar and just look different because they are different colors, they do vary quite a bit. Even though it’s always important to have a great looking stick, making sure you have one that meets your skill set is even more important.
Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
The Importance of End Caps
Sep 30, 2014
Different Types of Arm Protection
Oct 6, 2014
Youth Sports Team, Club & League Management App
Club, League, or Tournament Administrators
Learn more
Coaches, Players, and Fans
Learn more
Marketers, Sponsors, and Agencies
Learn more
Why TeamSnap?
25M
satisfied customers
19,000+
happy sport organizations
98%
customer satisfaction
12 years
serving teams and sports organizations
#1
mobile application
Everything you need to run your sports club.

Learn more
“Registration was really easy. I put it together myself. I had some pretty gnarly stuff to put in there, and it was easy.“Tom Fennell, President, Mother Lode Rugby Football Club
12,000,000+ health checks completed
Meet new health requirements with fewer apps
You and your members don’t need more apps to juggle. Easily administer and collect self-assessments directly in TeamSnap!
Learn more
New Organizations can now customize the screening questions. Learn more.
“This is a dream come true as an organizer. You guys at TeamSnap are wizards with programming.
Looks pretty perfect.“Mike, NY Bluebirds
The world’s best app for sports team management.
Learn more
“TeamSnap is the best app I have found that has everything you need all in one, user-friendly app: scheduling, attendance and communication.“Tyler Hudson, Head Coach, Fayetteville Soccer Club
Easy for everyone
Rated hands down the easiest sports management platform. You’ll minimize distractions and stress less with tools that are easy for all users, including parents and fans.
Get time back
Save hours of administrative work so you can focus on the game, not the logistics. Administrators report saving 15 hours every week. Coaches report saving 12 hours every month.
Administrators report saving 15 hours every week. Coaches report saving 12 hours every month.
Happy members
TeamSnap is consistently ranked the #1 sports management platform, based on over 50,000 reviews. Our customers report a 98% satisfaction rate.
Built for any budget
We offer a range of plans from free to paid based on your needs and budget. First-time users always receive a free trial to test drive the options.
Supports 100+ sports and activities
With TeamSnap, all sports and activities are created equal. You play it, we support it — from youth and adult teams to recreational, competitive and everything in between.
Trusted by your peers
More coaches and administrators trust TeamSnap to manage their team or organization than any other brand. More than 24 million people and 3 million teams, clubs, leagues and associations rely on TeamSnap.
A new way to connect with active families
We help brands connect with an engaged audience of parents, players, fans and coaches
Learn more
Get started with TeamSnap today
The easiest way to manage your team or sports organization
Help against constipation.
 Buy cheap
Buy cheap
Buy
Buy
Cat
close
46 item(s)
RecessionFor reviewsRatingFor popularity
Price for increase
Price for decline
For reviews
Rating
Popular
Popular
Filter
Show
12 24 30 60
on the side
46 item(s)
Sort by Price for growthPrice for declineFor reviewsRatingFor popularity
Price for growth
9 0002 Price for falling
For recommendations
Rating
For popularity
For popularity
Filter
Show
12 24 30 60
on the side
Updated: 07/12/2023
Checked
Normal etch – one naive leftover factors, like to inject into the correct work of the whole organism. The stasis of uncorrupted stool in the intestines can lead to various unhandedness, in the case of a worsened mood to pain symptoms. Constipation can be a sign of serious damage in the body, as well as provoke the accumulation of toxins in the body and take the development of more unsafe ailments – for example, hemorrhoids.
Causes of constipation
Causes of constipation can be:
How do you get carried and prevent constipation? Also, it is better to consult with a doctor as soon as possible, so that you can choose the best fit for yourself for your mood. Actual preparations can be practically relieved and allow to relieve acute constipation, acute, for example, stress or disruption, otherwise help relieve chronic constipation, gradually improving intestinal motility and chemical processes, who cares. They can be in absolutely different medicinal forms – tablets, prescriptions for enemas, suppositories.
There are such groups of preparations:
- Harch fibers (etulose, derived from lyon). Absorb the motherland from the intestines, making the stool softer by the same.
 Rarely call out side effects, the prote can change the way other drugs are used.
Rarely call out side effects, the prote can change the way other drugs are used. - Stimulate peristalsis (bisacodyl, sodium picosulfate, canopy preparation, buckthorn). To tease the receptors of the intestines, and at the same time to sip on the rhythmic speed of yoga melodies.
- Osmotic transport (magnesium oxide, lactulose, sodium sulfate). Utrimuyut water in the intestines, mechanically teasing the walls, call defecation for decades. Patients who are ill with diabetes, when taking these diseases, it is necessary to change the electrolytic balance
- Plasticizers, or softeners (rare paraffin, docusate sodium). To make the chair m’yakshe slacken, to reshuffle yoga znevodnennya. It is necessary to prescribe after operations and slopes, and also in other situations, if we are ill, we cannot bear. It is not possible to take it for a long time, as the electrical balance may be destroyed.
- Protective products (mineral, algae, vaseline oil). It helps to make the stool easier and more protruding through the intestines.

- Salt carrying (sodium sulfate, magnesium sulfate). Moisten the motherland into the intestines, making it easier for the stool to pass. Call to prescribe for usunennia hospitable fastening, vyklikanih otruennyam, with the presence of obstruction of the intestine.
- Chloride channel activator (lubiprostone). To improve intestinal motility, to increase the comfort of sitting in a new, comfortable, light and easy-to-pass stool.
How to combine drugs for constipation and diarrheal diseases and for the slug or intestines and normalize the microflora. It is also important to look at the way of life – polypshiti yakіst їzhi, start peristalsis of the intestines for the help of physical rights, as far as possible to overcome stress.
How to take care of constipation and diarrhea in Good Day Pharmacy
To buy the necessary medicines, you need to select them on the front page of the site or search by search row. After choosing the necessary parameters – the dosage form, the number of packages, dosing. Then a manager will contact you to discuss all the details and name the residual price. Our preparations will always cost you the most inexpensive way to the pharmacy’s retail approach to the choice of post-employees. You can change faces from any place in Ukraine – Vinnitsa, Chernihiv, Kiev.
After choosing the necessary parameters – the dosage form, the number of packages, dosing. Then a manager will contact you to discuss all the details and name the residual price. Our preparations will always cost you the most inexpensive way to the pharmacy’s retail approach to the choice of post-employees. You can change faces from any place in Ukraine – Vinnitsa, Chernihiv, Kiev.
Call respect
The site add.ua does not carry any negative feedback that may be blamed on the results of the shortcomings of the information posted on the site.
Filter
Filter
Virobnik
- ABC Farmaceutici (Italy)
- Ananta Medicare (India)
- Beaufour Ipsen Pharma (France)
- Cipla (India)
- Delpharm Orleans (France)
- Dr. Falk (Nimechchina)
- Guna (Italy)
- Instituto de Angeli (Italy)
- Krewel Meuselbach (Nimechchina)
- Kusum Healthcare (India)
- Molteni (Italy)
- Norgine Pharma (France)
- SCHONEN (VAT), Switzerland
- Solvay Pharmaceuticals (Netherlands)
- Arterium
- Borshchagivsky KhPZ ZAT NVC (Ukraine, Kiev)
9007 0
- Viola FF ZAT (Ukraine, Zaporizhzhya)
- Darnitsa PRAT (Ukraine, Kiev)
- Zhytomyrska FF TOV (Ukraine, Zhytomyr)
- Zdorovya TOV (Ukraine, Kharkiv)
- Ilan Pharm (Ukraine) 9 0003
- InterHim SP VAT (Ukraine, Odessa)
- Istok-Plus TOV (Ukraine, Zaporizhzhya)
- Lubnipharm VAT (U kraina, Lubny)
- Stada Nizhpharm
- Stoma AT (Ukraine, Kharkiv)
- TOV “DKP” Pharmaceutical factory “
- Farmak VAT (Ukraine, Kiev)
- Farmina (Poland) 900 03
- Yuriya-Pharm TOV (Ukraine, Kiev)
- Janssen Sіlag (France)
- Capsules
- Enema
- Drops
- Oliya 90 003
- Powder
- Retail
- Syrup
- 9No 002 Brand
- Kuchikoo
- Bisacodyl
- Guna-Bovel
- Guttalax 9000 3
- Duphalac
- Enterolax
- Legolax
- Magnesium sulfate
- Microlax
- Picolax
- Pikosen
For trans
Not found 9 Granules
Not found
Designated
- Laxative
Pack quantity
- 1
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 10
- 12
- 20
- 30
900 69 500
Not known
Head drug
- Bisacodyl
- Vaseline
- Guttalax
- Duphalac
- Enterolax
- Laktuvit
90 070
- Legolax
- Magnesium sulfate
- Normolact
- Picolax
- Pikosen
- Regulax
- Senadexin
- Farmina
N/A
Volume
- 5 ml
- 15 ml 004 20 ml
- 30 ml
- 50 ml
- 100 ml
- 120 ml
- 133 ml
- 180 ml
- 200 ml 500 ml
Not found
Applicant
- Johnson and Johnson Ukraine Carrying and preventing constipation is the most popular?
What are the cheapest products in the category Carrying and preventing constipation?
Most popular products in the category Carrying and taking care of constipation?
What is the price for carrying and taking care of constipation?
Variety of all products in the category Carriage and constipation vary from 12.
 00 ₴ to 546.00 ₴.
00 ₴ to 546.00 ₴.Alerts
Facebook messenger Telegram Call of the door
Unscramble the recipe
Online chat
How would you like to contact us?
Skasuwati
Button zv’yazyk
How to deal with constipation in a child?
8/15/17
A Parent’s Guide to a Very Common Problem in Children with Autism
0002
Symptoms of chronic constipation in a child include:
– Very hard and hard stools.
– Pain and difficulty in emptying the bowels.
– The child has a bowel movement three times a week or less.
Talk to your child’s doctor to determine if the child is constipated.
What causes constipation in children with autism?
1. Holding a stool
Some children try to hold a stool and ignore the urge to have a bowel movement. This can happen for various reasons, for example:
– Fear of the toilet.
– Reluctance to use the toilet outside the home.

– Unwillingness to interrupt the game.
– Fear of pain during bowel movements.
2. Toilet training
Children may resist and hold stool when toilet training is attempted. This can become a habit that is difficult to break later on.
3. Nutrition problems
– Lack of fiber found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
– Dairy products, if the child is allergic to cow’s milk or consumes too much dairy products.
– Insufficient intake of water and other beverages, especially when ill.
– Changes in appetite or diet due to illness of the child.
4. Stress and changes in daily routine.
Travel, weather changes, and stress can affect bowel function.
5. Medicines
Some medications, such as antacids, antidepressants, and some attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder medications, can cause stools that are too hard.
6.
 Associated medical problems.
Associated medical problems. Constipation is common in children who have movement problems, including decreased muscle tone and cerebral palsy. Also, constipation is possible in case of hypersensitivity to gluten or casein.
Acute constipation and encopresis
Acute constipation
Some (but not all) children with chronic constipation may have this problem. Acute constipation can be caused by too much hard stool in the colon. As a result, the child cannot have a bowel movement for several days. Acute constipation is diagnosed by a doctor by palpation of the abdomen or by X-ray. Acute constipation is often accompanied by loss of appetite and lethargy. After a bowel movement, the child feels better and the symptoms decrease.
Encoprese
This problem occurs in some (but not all) constipated children. Encopresis means that during constipation, the child has loose stools. This is a common problem.

Encopresis can develop if a child holds a stool for so long that it becomes difficult for him to have a bowel movement. The stool becomes larger and drier. Due to the retention of large stools, the intestinal muscles get tired and relax. After the muscles relax, loose stools can seep into the underwear.The child does not feel that this is happening and cannot control loose stools. This usually happens several times a day, causing the underwear to become dirty. Sometimes encopresis is confused with diarrhea, but the child does not actually have diarrhea because most of the stool in the intestines remains solid.
Many children with encopresis experience loss of appetite and decreased interest in daily activities. After a bowel movement, the child feels better and these symptoms decrease.
Treatment of constipation
There are three main approaches to the treatment of constipation.
Talk to your child’s doctor about what type of treatment is best for you:
1.
 Dietary changes
Dietary changes – Increasing fiber in the diet will make bowel movements easier.
– Increasing fluid intake , especially water and juice, helps soften stools and reduces the chance of constipation.
2. Behavioral changes
– Regular exercise . Physical activity improves the functioning of the abdominal muscles, which facilitates bowel movements. Regular exercise, including walking, jumping rope, ball games, cycling and swimming, can help with constipation.
– Bowel training in the toilet . It is important that the child knows how to use the toilet at the first urge. The best way to teach this is through planned and extended “sit-downs” where the child is rewarded for simply sitting on the toilet for extended periods of time.
3. Medications
Children often need medication to have regular bowel movements. These can be:
– Preparations for daily use.

– Single-dose preparations that “cleanse” the intestines in case of severe difficulty with emptying.
Increasing fiber in the child’s diet
A diet high in fiber promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. Fiber is a substance that the body cannot digest. There are two types of fiber – soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber promotes the entry of water into the intestines. Insoluble fiber facilitates the passage of stool through the intestines. Both types of fiber are needed to prevent constipation.
Fiber is an important part of a healthy diet. A lot of fiber is found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. They also contain a lot of protein, vitamins and minerals. A diet high in these foods is the best way to get enough fiber.
Where to find fiber
When shopping for food, you can check the nutritional information of the product, including the fiber level. Good choices are foods that contain at least 2 grams of fiber per serving.

When shopping, check whether products contain whole grains, whole grain flour, and oatmeal. Perhaps there are options for your child’s favorite foods with whole grains, that is, higher fiber content. For example, whole grain cheese crackers, whole grain wheat flour bread, high fiber cereals may be suitable for you.
Recommended Fiber Intakes
– Ages 1 to 3: 19 grams per day (for boys and girls).
– Ages 4 to 8: 25 grams per day (for boys and girls).
– Ages 9 to 13: 31 grams per day for boys and 26 grams per day for girls.
Examples of high fiber foods
– White beans: 9.5 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Oatmeal: 8.8 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Red beans: 8.2 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Beans: 7.5 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Pear (with skin): 4.3 grams per small pear.
– Raspberries: 4.0 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Baked potatoes (with skin): 3.8 grams per piece.
– Almonds: 3.
 3 grams per 30 grams.
3 grams per 30 grams.– Apple (with skin): 3.3 grams per piece.
– Banana: 3.1 grams for one medium-sized piece.
– Orange: 3.1 grams per medium sized piece.
– Peanut butter: 3.0 grams per 2 tablespoons.
– Broccoli: 2.8 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Green peas: 2.5 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Avocado: 2.3 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Corn: 1.6 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Strawberries: 1.5 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Wild rice: 1.5 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Raisins: 1.4 grams per 1/2 cup.
– Popcorn: 1.2 grams per 1 cup.
Increasing fiber and fluid in the child’s diet
It is advisable to offer children foods rich in fiber from an early age so that their use becomes a lifelong habit.
If your child is currently constipated, it is important to increase fiber levels very gradually over 2-3 weeks. Too much fiber in the diet can worsen constipation or cause gas, abdominal pain and diarrhea.

Increasing fiber will only be effective if the child also starts drinking more fluids. Make sure your child not only starts eating more fiber, but also starts drinking more water and juice.
How to Increase Fiber Without Child Resistance
Children with autism often resist change, especially dietary changes. Parents need to be patient and try different approaches, for example:
– Switch to crackers and whole grain pasta.
– Try whole grain bread and pizza. Many types of whole-grain bread do not differ in appearance from ordinary white bread.
– Offer your child whole grain muesli or popcorn as a snack.
— Offer your child dried fruit as a sweet treat (prunes, dried apricots, raisins).
– Try to make cocktails from frozen fruits or berries based on juice or milk.
– Offer your child carrot, bell pepper, or celery sticks to dip in peanut butter, hummus, or salad dressing.
— Add shredded vegetables or vegetable puree to your child’s favorite meals, such as pasta or pizza.

– Make funny faces or figures out of slices of fruits and vegetables.
– Invite the child to dip fruit slices in nut butter or his favorite kind of yogurt.
– Bake cookies, muffins or pies with whole wheat flour.
Increasing fluid intake
Enough water is essential to keep the body healthy. It is found in both foods and drinks. As you increase the amount of fiber in your diet, you also need to increase your fluid intake.
How much liquid do you need?
– Follow your thirst. The amount of water a child needs varies depending on physical activity and what the child eats. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the signs of thirst in a child.
– When a child drinks enough water, his urine becomes clear, light yellow in color. Dark, tea-colored urine usually means your child needs to drink more.
Fluid types
1. Water: The best source of fluid.
2. 100% juice: good for health, but should be limited.

– 120-180 ml per day for children under 6 years old
– 240-360 ml per day for children over 6 years old
– Some juices (pear, apple, plum) contain sugars that act as a natural laxative and may help with constipation.
3. Milk:
– An important part of a child’s nutrition.
— Excessive consumption of milk can lead to constipation.
– Desirable rate for milk: 480-720 ml per day (2-3 cups).
4. Sports drinks and drinks with electrolytes:
– They often have added sugar.
– Not the best choice for children.
– Check with your doctor before giving these drinks to your child.
5. Fruit drinks, soft drinks:
– They usually have added sugar.
– Not the best choice for children.
– It is better to save them for special occasions, such as holidays, you should not give them to the child regularly.
Fluids and constipation
It is very important to increase fluid intake at the same time as increasing fiber.
 Fluid helps soften stools and make bowel movements easier.
Fluid helps soften stools and make bowel movements easier.– Some juices (pear, apple, plum) are natural laxatives.
— It is advisable to give the child a lot to drink between meals, this contributes to regular bowel movements.
– Drinks with a lot of sugar, caffeine or “fortified with vitamins” can increase constipation.
Tips for increasing fluid intake
— Encourage your child to drink water between meals, on a full stomach the child may drink too little.
– Offer your child fruits with a high water content, such as grapes, oranges, or watermelon, as snacks and treats.
— Keep a bottle or cup of water handy so your child can always have a drink. Add some citrus juice to your water to make it taste better. Or try adding some other drink to the water.
– Lead by example. Children are more likely to drink water when they see their parents or siblings drinking water.
Toilet training
In case of constipation, it is very important to teach the child to use the toilet as soon as he feels the first urge.
 The easiest way to teach this is with a daily period of time when the child sits on the toilet for a long time. When a child gets used to sitting on the toilet for a long time, it will be easier for him to relax the muscles that hold the stool. With daily toilet seating time, your child will become less likely to hold a stool. When the child stops holding the stool, the intestines return to normal size and become more sensitive.
The easiest way to teach this is with a daily period of time when the child sits on the toilet for a long time. When a child gets used to sitting on the toilet for a long time, it will be easier for him to relax the muscles that hold the stool. With daily toilet seating time, your child will become less likely to hold a stool. When the child stops holding the stool, the intestines return to normal size and become more sensitive.How to teach your child to sit on the toilet for a long time every day
1. Be patient with yourself and your child. Learning a new skill, especially this skill, is never easy.
2. Start by teaching your child to sit on the toilet, even if he does not defecate:
– Start with 1-2 minutes. Very slowly increase the time to 10-12 minutes.
– Use a visual timer to let your child know how long they need to sit.
– Offer the child some quiet activity while he sits on the toilet. For example, reading a book, drawing, playing a handheld computer game, listening to music or audio books.

– Try to save the child’s favorite pastime for sitting on the toilet and do not offer it at other times.
– Praise your child even for small progress.
– Never force a child to sit on the toilet and never force him to sit on it unless you are working with a behavior specialist to help you do it safely.
3. Choose a time for your child to use the toilet.
– Making toilet use a regular part of a child’s daily routine will help develop a normal bowel habit.
— Children with autism often like routine. Making toilet seating a part of the daily routine will reduce the risk of child resistance.
– Try using a visual timetable with pictures, one of the items being toilet time.
— If your child is most likely to have a bowel movement at some time of the day, try to schedule toilet seating for that time.
— Morning is the best time for most people, but it may not be suitable for a child who will be rushed to kindergarten or school in the morning.

– For some children, the best time is after coming home from school or kindergarten.
4. Make sure your child is comfortable.
– Choose the toilet seat or potty that is most comfortable for your child.
— Use a child seat for the toilet if the normal seat is too big for the child.
– Use the footrest if the child’s feet do not touch the floor.
How to teach a bowel movement in the toilet
1. Make sure your child sits on the toilet for extended periods 1-2 times each day.
2. Teach your child that “poop goes down the toilet” by emptying dirty diapers or underwear.
3. Try to time your child to sit on the toilet when you think your child is most likely to have a stool.
4. Try to stimulate the gastrocolic reflex before sitting on the toilet. This reflex occurs after eating or drinking and allows the bowel muscles to expel stool after eating. To stimulate this reflex, try to get your child to eat or snack, and drink a warm drink before sitting on the toilet.

5. Watch for possible signs in the child’s behavior. If you notice that he wants to use the toilet, then take him there. Signs may include:
– Changes in facial expressions.
– Attempts to go to a quiet part of the house.
– Muscular tension.
Positive reinforcement
– Start with rewards for your child just sitting on the toilet.
– When the child begins to empty his bowels on the toilet, start rewarding him for it.
– Small rewards that the child receives immediately after the desired behavior work best.
– Give rewards less frequently over time.
Try not to use food as a reward. Instead, you can reward your child with:
– Sing your favorite song with your child.
– Hugs, tickling, verbal praise.
– Favorite game with a child.
– Stickers that will allow the child to track their progress.
– Time for your favorite pastime.
– Tokens (in the form of stickers, stars or other items) that can then be exchanged for very large rewards, such as a trip to the cinema or to the park.

Many children with autism have special interests. They can be used when planning rewards. For example, if a child is interested in cars, then as a reward, he can look at car magazines. If a child loves trains, then he can receive stickers with trains as a reward.
Positive rewards lead to the desired changes in behavior much faster than any punishment or criticism.
If the child is dirty
– Say something like “I noticed that you are dirty” or “Please change.”
– Help the child to do this as needed.
— Do not scold the child or draw attention to what has happened.
If the child does not want to sit on the toilet
– Try to get the child as close to the toilet as possible when he begins to have a bowel movement. If the child does it in diapers while standing, then try to have him do it while standing in the toilet.
– When the child has defecated in the diaper, throw the contents of the diaper down the toilet in front of the child.

– Teach your child to sit on the toilet with their clothes down. Give your child a toy that can keep him busy for a while.
– Over time, move on to having the child sit on the toilet with the lid up but wearing a diaper.
– When the baby is comfortable sitting on the toilet with the lid up, cut a hole in the diaper and enlarge it over time. Try to have the child sit on the toilet in a diaper while having a bowel movement.
Specialist help
Very often it is difficult for a family to change what happens at home. Toilet training can be a very complex behavioral problem. Some families need additional specialist support. Signs that the family needs more help include:
– The child becomes very upset when taken to the toilet.
– Child holds stool longer and longer.
— Constipation progresses in the child.
— Everything connected with the toilet causes tantrums or aggression in the child.
Specialists may include child psychologist, behavioral analyst, pediatrician.
 Sometimes staff at the child care facility that the child attends can help find the right specialist.
Sometimes staff at the child care facility that the child attends can help find the right specialist.Daily preparations
— May be started immediately if the child does not have severe constipation.
– Taken orally.
– Most effective when taken daily.
Purpose of taking the drug:
– Soft stools and bowel movements every day.
– All stool comes out of the bowels.
Dosage of the drug:
– The initial dose of the drug must be prescribed by a doctor. Sometimes the dosage needs to be varied. Talk to your doctor about this, he will help you change the dosage.
When it is necessary to increase the dosage of the drug:
– Small and hard stools.
– The child does not have a bowel movement every day.
– The child has difficulty emptying the bowels or is in pain.
When to reduce the dosage of the drug:
– Loose stools.
— The child has abdominal pain or cramps.
Duration of drug treatment
— As a rule, the course of treatment lasts at least 6 months.

— After 6 months of daily bowel movements, the doctor may decide to gradually reduce the dosage of the drug.
– If you stop taking the drug before the intestines return to normal, then constipation will begin again.
— It is important to make sure that the child has soft stools every day.
How do drugs to treat constipation work?
There are three types of laxatives. They act differently.
1. Osmotic laxatives. They carry water into the stool to keep it soft. Safe and often given to children. Usually taken every day. Suitable for long term use.
Examples: polyethylene glycol without electrolytes, magnesium hydroxide, magnesium citrate, lactulose, sorbitol.
2. Stimulant laxatives. They promote contractions of the intestinal muscles and promote stool in the intestines. As a rule, they are prescribed for a single dose.
Examples: senna, bisacodyl.

3. Lubricating laxatives. Facilitates the passage of stool through the intestines with an oil base.
Examples: vaseline oil, glycerin suppositories.
Acute constipation medicines
Acute constipation occurs when large masses of hard stool block the intestines. If the doctor thinks that there is a blockage in the intestines, then as a first treatment option, he may prescribe a drug that will “cleanse” the intestines.
Your doctor will work with you to determine the best type of drug. Sometimes drugs that are taken by mouth are best. Sometimes drugs that are injected into the intestines are better suited. This “clearing” usually takes 2-3 days. It is best to spend it on the weekend or on vacation. The child will need to spend 2-3 days near the toilet and use it often.
These drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor. He will tell you how long and how often to take the drug.
Enema procedure
Most cases of constipation in children are treated with drugs taken by mouth.
 In some cases, children need a drug that is injected into the rectum. Talk to your doctor about what treatment is best for your child. Do not give your child an enema without talking to the doctor first. Below is information about giving an enema, if needed.
In some cases, children need a drug that is injected into the rectum. Talk to your doctor about what treatment is best for your child. Do not give your child an enema without talking to the doctor first. Below is information about giving an enema, if needed.How to prepare a child for an enema
– Explain the procedure to the child in a way that they can understand, perhaps with illustrations.
– Let the child look at and touch the enema bottle.
– Touch the tip of the enema to his hand so he knows what it’s like.
– Help your child practice beforehand how to lie down properly during an enema.
Enema Preparation
— Read the instructions for the enema very carefully. Check out the pictures and instructions in the instructions.
– Make sure the enema is at room temperature.
– Prepare everything you need: an enema bottle; towel on which the child will lie; pillows; music, a favorite toy, or other items to help your child stay calm; wet cleansing wipes.

Decide where you will give the enema. Sometimes it’s best to put the baby on a blanket or large towel on the bathroom floor next to the toilet.
– Place towels and/or pillows for your child to lie down comfortably.
– Have another person stand at eye level with the child during the procedure – read to him, sing, talk, play music or otherwise distract him and help him lie still.
How to give an enema
1. Wash your hands.
2. Remove the protective cap from the enema tip. The tip should have a lubricant that makes it easier to administer the enema.
3. Help the child lie on his left side with his knees pressed against his chest.
4. Have your helper talk or sing to your child in an effort to soothe and encourage.
5. Hold the enema in one hand. With your other hand, spread your buttocks until you see the anus.
5. Insert the end of the bottle very carefully into the anus. Don’t force it in.
6. Position the end of the enema towards the child’s back.

 Looks pretty perfect.“Mike, NY Bluebirds
Looks pretty perfect.“Mike, NY Bluebirds Rarely call out side effects, the prote can change the way other drugs are used.
Rarely call out side effects, the prote can change the way other drugs are used.
 00 ₴ to 546.00 ₴.
00 ₴ to 546.00 ₴.
 Associated medical problems.
Associated medical problems. 
 Dietary changes
Dietary changes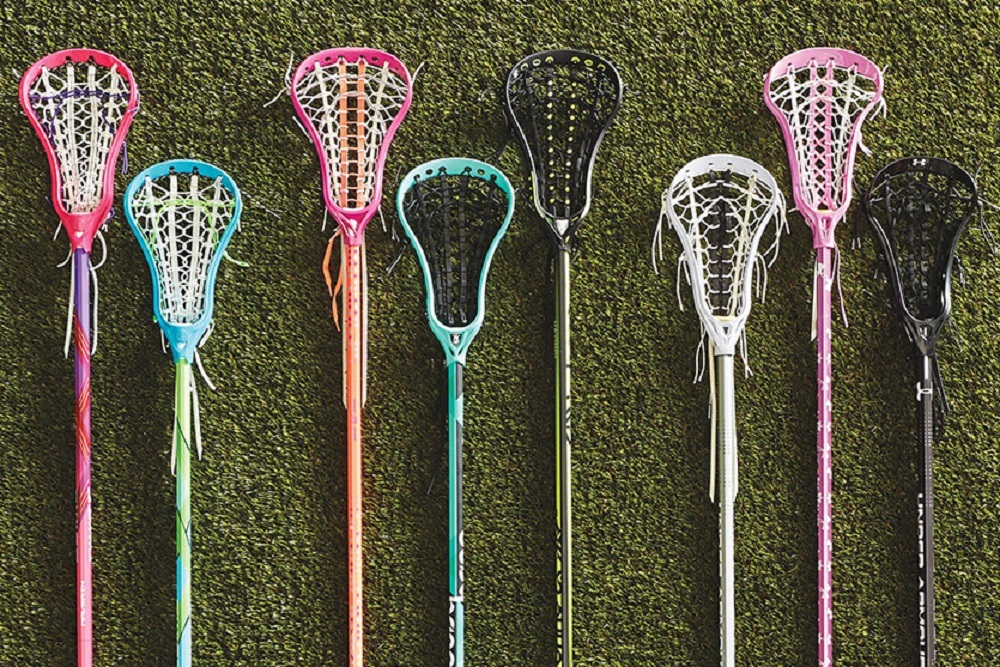 

 3 grams per 30 grams.
3 grams per 30 grams.


 Fluid helps soften stools and make bowel movements easier.
Fluid helps soften stools and make bowel movements easier. The easiest way to teach this is with a daily period of time when the child sits on the toilet for a long time. When a child gets used to sitting on the toilet for a long time, it will be easier for him to relax the muscles that hold the stool. With daily toilet seating time, your child will become less likely to hold a stool. When the child stops holding the stool, the intestines return to normal size and become more sensitive.
The easiest way to teach this is with a daily period of time when the child sits on the toilet for a long time. When a child gets used to sitting on the toilet for a long time, it will be easier for him to relax the muscles that hold the stool. With daily toilet seating time, your child will become less likely to hold a stool. When the child stops holding the stool, the intestines return to normal size and become more sensitive.




 Sometimes staff at the child care facility that the child attends can help find the right specialist.
Sometimes staff at the child care facility that the child attends can help find the right specialist.

 In some cases, children need a drug that is injected into the rectum. Talk to your doctor about what treatment is best for your child. Do not give your child an enema without talking to the doctor first. Below is information about giving an enema, if needed.
In some cases, children need a drug that is injected into the rectum. Talk to your doctor about what treatment is best for your child. Do not give your child an enema without talking to the doctor first. Below is information about giving an enema, if needed.