What causes unexplained bruising on legs. How to identify if bruising is a sign of an underlying health condition. When should you see a doctor for unexplained bruises. What are the treatment options for various conditions causing bruising.
Understanding Bruising: Causes and Risk Factors
Bruising occurs when blood vessels beneath the skin are damaged, causing blood to leak and pool under the skin’s surface. While most bruises result from acute injuries, unexplained bruising on the legs can sometimes indicate an underlying health issue. Several factors can increase a person’s susceptibility to bruising:
- Age: Older adults are more prone to bruising and may experience slower healing times.
- Family history: Genetic factors can play a role in easy bruising.
- Inherited bleeding disorders: Conditions like von Willebrand’s disease can increase bruising susceptibility.
Common Health Conditions Associated with Unexplained Bruising
When bruises appear randomly on the legs without an apparent cause, it may be a sign of an underlying health condition. Some of these conditions include:
Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiencies in certain vitamins can lead to increased bruising:
- Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy): Can cause bleeding issues and bruising.
- Vitamin K deficiency: May result in inefficient blood clotting, leading to more frequent bruising.
Who is at risk for vitamin deficiencies? People experiencing malnutrition, older adults, and those who consume excessive alcohol are more likely to develop vitamin deficiencies that can lead to bruising.
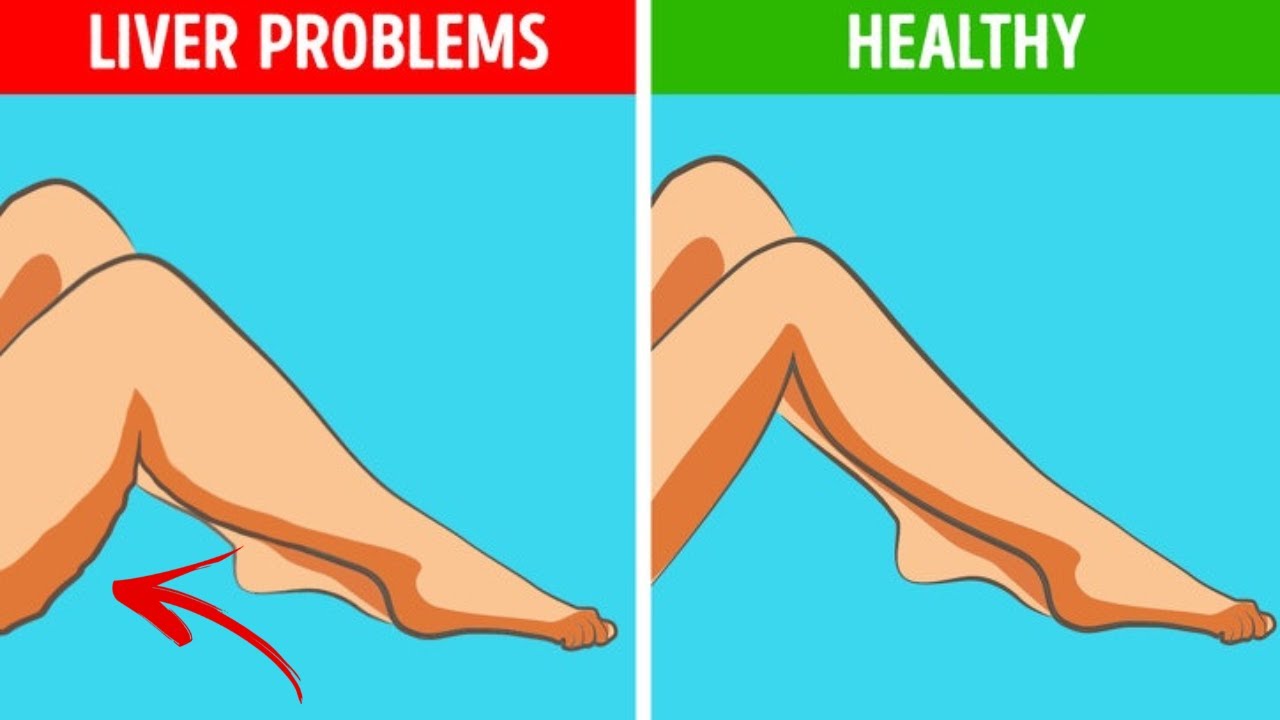
Liver Disease
Liver damage can impair the body’s ability to form blood clots and stop bleeding. Cirrhosis, a severe form of liver disease, can cause easy bruising along with other symptoms such as:
- Swelling of the legs and abdomen
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin)
- Severe itching
How is liver disease treated? Early diagnosis is crucial for liver healing. Treatment focuses on preventing further damage and protecting remaining healthy tissue. In cases where alcohol abuse is the cause, rehabilitation may be necessary to prevent additional liver damage.

Autoimmune Conditions
Certain autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, can cause unexplained bruising. Additionally, medications used to treat these conditions, particularly corticosteroids, may contribute to random bruising.
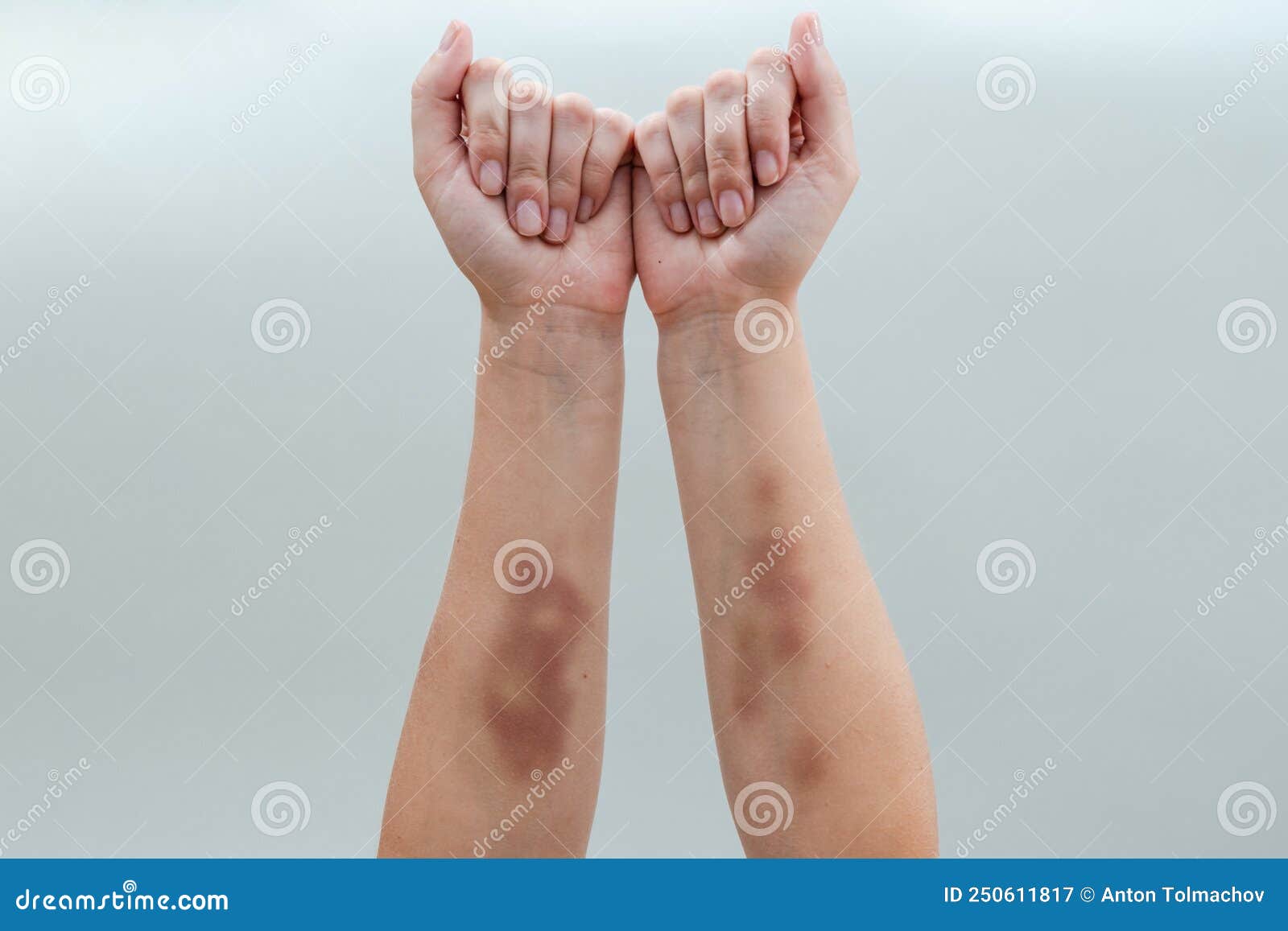
Thrombocytopenia: A Common Cause of Unexplained Bruising
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by low blood platelet counts, which can lead to improper blood clotting and increased risk of bleeding. This condition can arise from various factors, including:
- Pregnancy: Gestational thrombocytopenia affects 5-10% of pregnant or recently postpartum individuals.
- Cancer treatments: Chemotherapy can reduce platelet counts, increasing the risk of bleeding and bruising.
What are the symptoms of thrombocytopenia? In addition to easy bruising, symptoms may include:
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
- Nosebleeds
- Blood in urine or stool
- Fatigue
In severe cases, thrombocytopenia can lead to internal bleeding and brain hemorrhage.
Treatment Options for Thrombocytopenia
Several treatment approaches are available for managing thrombocytopenia:
- Corticosteroids
- Immunoglobulins
- Blood or platelet transfusions
- Splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen)
Rare Clotting Issues and Bleeding Disorders
Some individuals may experience frequent bruising due to rare clotting issues or bleeding disorders. These conditions can affect the body’s ability to form blood clots effectively, leading to increased bruising and bleeding risks.
Factor V Deficiency
Factor V deficiency is a rare genetic bleeding disorder that causes frequent nosebleeds, bleeding, and bruising. It affects approximately 1 in 1 million individuals and is more common in India and Iran.
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
People with Bernard-Soulier syndrome experience more frequent bruising, have a higher risk of nosebleeds, and may experience random bleeding episodes.
Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder that primarily affects males. Individuals with this condition lack essential proteins (factor VIII or IX) involved in the blood clotting process.
What are the common symptoms of bleeding disorders? People with these conditions may experience:
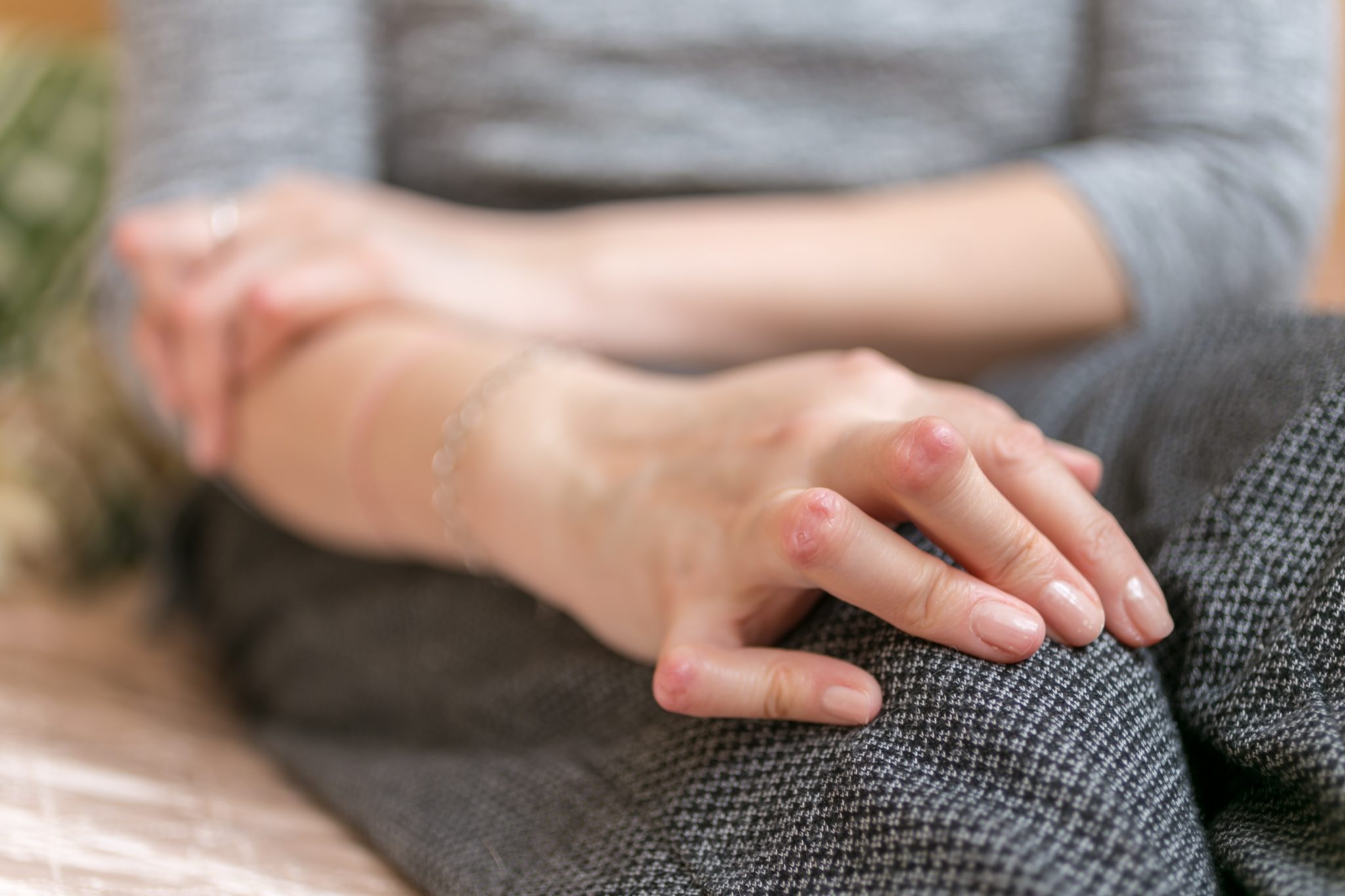

- Frequent nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums
- Blood in stool or urine
- Cuts that bleed for extended periods
- Heavy menstrual periods
When to Seek Medical Attention for Unexplained Bruising
While occasional bruising is usually not a cause for concern, there are instances when it’s important to consult a healthcare professional:
- Frequent, large bruises appearing without apparent cause
- Bruises that don’t heal within two weeks
- Bruising accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue, fever, or unexplained weight loss
- Family history of bleeding disorders
- Bruising while taking blood-thinning medications
How can a doctor diagnose the cause of unexplained bruising? A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, review medical history, and order blood tests to check platelet counts and assess clotting factors.
Preventing and Managing Unexplained Bruising
While some causes of unexplained bruising require medical intervention, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of bruising and manage existing bruises:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and K
- Stay hydrated to support healthy blood flow
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation
- Use protective gear during physical activities
- Apply cold compresses to fresh bruises to reduce swelling
- Elevate the affected area to minimize blood pooling
Are there any natural remedies for bruising? Some people find relief using arnica gel or bromelain supplements, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before trying any new treatments.
The Impact of Medications on Bruising
Certain medications can increase the likelihood of bruising or exacerbate existing bruising tendencies. These include:
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin, heparin)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Some antibiotics
- Certain antidepressants
Should you stop taking medications if you notice increased bruising? Never discontinue prescribed medications without consulting your healthcare provider. If you suspect a medication is causing excessive bruising, discuss your concerns with your doctor to explore alternative options or adjust dosages.

Interactions Between Medications and Supplements
Some dietary supplements and herbal remedies can interact with medications and affect blood clotting. Examples include:
- Ginkgo biloba
- Garlic supplements
- Fish oil
- Vitamin E supplements
How can you safely manage supplements and medications? Always inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you’re taking, especially if you’re prescribed blood-thinning medications or notice increased bruising.
Psychological Impact of Unexplained Bruising
Frequent, unexplained bruising can have psychological effects on individuals, particularly if the bruises are visible or extensive. Some potential psychological impacts include:
- Anxiety about underlying health conditions
- Self-consciousness about appearance
- Stress related to medical investigations
- Fear of engaging in physical activities
How can individuals cope with the psychological impact of unexplained bruising? Seeking support from healthcare providers, joining support groups, and practicing stress-reduction techniques can help manage the emotional aspects of dealing with frequent bruising.
Body Image and Self-Esteem
For some individuals, especially those with visible or extensive bruising, body image and self-esteem may be affected. Strategies to address these concerns include:
- Seeking counseling or therapy
- Learning makeup techniques to conceal bruises
- Wearing clothing that provides coverage, if desired
- Educating friends and family about the condition to increase understanding and support
Can addressing the psychological aspects of bruising improve overall well-being? Absolutely. Managing the emotional impact of unexplained bruising can lead to improved quality of life and better overall health outcomes.
Advances in Bruising Research and Treatment
Medical research continues to advance our understanding of bruising causes and potential treatments. Some areas of ongoing research include:
- Gene therapy for inherited bleeding disorders
- Novel platelet-stimulating medications
- Improved diagnostic techniques for identifying underlying causes of bruising
- Development of targeted therapies for specific bleeding disorders
What does the future hold for bruising treatment? As research progresses, we can expect more personalized and effective treatments for various conditions causing unexplained bruising, potentially improving outcomes for affected individuals.

Emerging Technologies in Bruise Assessment
New technologies are being developed to aid in the assessment and monitoring of bruises, including:
- Advanced imaging techniques for detecting subcutaneous bleeding
- Wearable devices that monitor clotting factors in real-time
- AI-powered algorithms for analyzing bruise patterns and predicting underlying causes
How might these technologies impact bruising diagnosis and treatment? These advancements could lead to earlier detection of underlying conditions, more accurate diagnoses, and improved treatment outcomes for individuals experiencing unexplained bruising.
What causes it? Is it treatable?
Usually, it is easy to pinpoint the cause of a bruise. Often, the culprit is an acute injury. Sometimes, however, bruising seems to occur for no apparent reason. If unexplained bruising appears a lot on the legs, it could be a symptom of an underlying health condition.
Bruising often occurs when blood vessels beneath the skin incur damage. Blood leaks out of the vessels and pools beneath the skin, which causes skin discoloration.
This article will look at the potential causes of unexplained bruising on the legs. It will also cover when to see a doctor.
Some people bruise more easily than others. The following sections will look at some of the factors that may increase a person’s likelihood of bruising.
Age
As a person ages, they become more susceptible to bruising. Bruises may also take longer to heal in older adults.
Family history
According to one older study, people with close family members who bruise easily may also experience frequent bruising.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also note that some inherited bleeding disorders, such as von Willebrand’s disease, can make people more susceptible to bruising.
Most of the time, bruising occurs when a person bumps into things, falls, or injures themselves in another way. Bruises typically heal within a few weeks and are usually benign.
Sometimes, however, bruising is a symptom of a more significant health issue.
The following are a few of the possible conditions that may cause random bruising to appear on the legs.
Vitamin deficiencies
People who experience malnutrition could be deficient in vitamin C and may develop scurvy. Other people at risk of developing scurvy include older adults and people who drink a lot of alcohol.
Symptoms of scurvy include bleeding issues that may lead to bruising.
People deficient in vitamin K may also bruise more often. This is because their blood does not clot efficiently.
Although anyone can experience a vitamin K deficiency, it is more common in infants, as breast milk does not contain much of this nutrient.
Liver disease
A damaged liver affects the body’s ability to form clots and stop bleeding. According to the American Liver Foundation, people with cirrhosis may bleed or bruise more easily.
Other symptoms of cirrhosis include:
- swelling of the legs and abdomen
- yellowing of the skin, or jaundice
- severe itching
Treatment
If a person receives a diagnosis of liver disease early enough, the odds of the liver healing itself are higher.
The treatment pathways for liver disease — and cirrhosis, in particular — aim to prevent further liver damage and protect the remaining healthy tissue.
Because alcohol abuse disorder is a common cause of liver disease, some treatments may involve alcohol rehabilitation to help the person stop drinking and prevent further liver damage.
Autoimmune conditions
Some autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, may cause unexplained bruising.
Certain medications that help treat rheumatoid arthritis, including corticosteroids, may also contribute to random bruising.
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition that involves low blood platelet counts. When there are not enough platelets, the blood does not clot properly, which could increase the risk of a serious bleed.
Complications from the following may give rise to thrombocytopenia:
Approximately 5–10% of pregnant people and those who have recently given birth develop gestational thrombocytopenia.
Some cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, could increase a person’s risk of bleeding and bruising. This is because these therapies reduce the amount of platelets in the blood.
Some other symptoms of a low platelet count include:
In severe cases, thrombocytopenia may cause internal bleeding and brain hemorrhage.
Treatment
There are several treatment options for thrombocytopenia. These include:
- corticosteroids
- immunoglobulins
- blood or platelet transfusions
- splenectomy
Rare clotting issues and bleeding disorders
People with certain bleeding disorders may experience more frequent bruising. Some of these disorders include:
- Factor V deficiency: This rare genetic bleeding disorder causes frequent nosebleeds, bleeding, and bruising. It affects approximately 1 in 1 million individuals and is more common in India and Iran.
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome: People with this disorder bruise more frequently, have a higher risk of nosebleeds, and may experience random bleeding.
- Hemophilia: More males than females have hemophilia. People with this condition are missing factor VIII or IX. These factors are essential proteins involved in the blood clotting process.
Other symptoms that people with blood disorders may experience include:
- nosebleeds
- bleeding gums
- blood in the stool or urine
- cuts that bleed for a long time
- heavy periods
Treatment
Treatment options for bleeding disorders vary but may involve platelet transfusions, clotting factors, or medications to help with clotting.
Cancers
Several cancers that affect the blood cells can also cause random bruising. One of these cancers is multiple myeloma. The symptoms of this condition include thrombocytopenia, which lowers blood platelet counts and leads to bleeding and bruising.
Also, some of the initial symptoms of leukemia include bruising and bleeding, with bruises typically appearing on the back, legs, and hands.
Cancer is often treatable, especially when a person receives an early diagnosis. Treatment options vary depending on cancer type, but they may include medication, chemotherapy, and surgery.
Sepsis
Sepsis is a life threatening complication of an infection. It happens when the body overresponds to infection and releases a lot of inflammatory chemicals into the blood.
These chemicals can trigger the blood clotting process and reduce blood flow to the limbs and internal organs.
Sepsis is more common in infants and people with weakened immune systems.
The symptoms of sepsis include:
- pinprick or large purple bruising
- fever
- pale, clammy skin
- extreme fatigue
- chills and shivering
- rapid breathing
The following are some other possible causes of random bruising on the legs.
Dietary supplements
Although it is rare, some supplements may cause bleeding and bruising.
Supplements that may cause bruising include:
Medications
Some medications may affect the body’s clotting ability and cause unexplained bruising on the legs and other parts of the body.
These medications include:
Physical abuse
Sometimes, random bruising is the result of physical abuse.
Bruising as a result of physical abuse may:
- be random and not consistent with injury patterns
- occur in infants who cannot yet walk or crawl on their own
- cover a large area of the body
- be in the shape or pattern of a certain object
- may not match up with the reported injury
To diagnose unexplained bruising on the legs, a doctor will perform a physical examination and ask the person about whether or not they have a family history of bruising.
They will also ask about any other symptoms the person is experiencing and whether or not they are taking any medications or supplements.
The doctor may also perform other diagnostic tests, including blood tests, to rule out any serious underlying causes of bruising.
A person who experiences frequent unexplained bruising on the legs should make an appointment to see their doctor.
This is especially important if the bruising is:
- significant
- frequent
- long lasting
- very painful to the touch
- due to medication or supplement use
- in the same location every time
- serious despite being due to a small injury or bump
People who frequently experience unexplained bruising on their legs because of their age, sex, or family history should take care to prevent bumps and falls, if possible.
However, if the bruising is the result of taking specific medications or supplements, stopping them could eliminate further bruising. It is vital to speak to a doctor before stopping any medications.
Learn more about home remedies for treating bruises here.
Some people may bruise more easily than others, and unexplained bruising on the legs is likely a case of a minor injury that the person forgot about.
However, if bruising happens frequently, is severe, and takes a while to heal, it may be a symptom of an underlying condition that needs medical attention.
Leg Bruise – Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
A bruise, or ecchymosis, is a collection of blood in a confined area. It can form directly under the skin, within a muscle, in and around bone, or inside the body. Under the skin, a bruise may cause an area of discoloration that may change colors and spread before resolving. It typically starts with a pinkish red color, becomes bluish, and then turns a yellow-green color.
Pain is often present with bruising and is typically worse with bone bruises than with muscle or surface bruises. Swelling may occur, although muscle and bone bruises may not cause visible symptoms. Bruises can take anywhere from days to months to heal.
Leg bruises are due to an injury to your leg. Common causes of leg injury are automobile or other accidents, falls, sports injuries, bumping into objects, or violent acts. The risk of bruising is increased by medical conditions and medications that interfere with your blood’s ability to clot and by conditions that weaken blood vessels or thin your skin.
Bleeding into a bruise is often limited, but sometimes it can be rapid or ongoing. As a bruise continues to expand, it may form a collection of blood in the tissues known as a hematoma. In this case, the pressure it exerts on nearby structures increases. When this occurs in a superficial bruise, the blood supply to the overlying skin can be decreased. If it occurs in a muscle bruise, a condition called compartment syndrome can occur and can lead to death of muscle cells.
Leg bruises can occasionally have serious complications or may mask other serious injuries.
Seek immediate medical care (call 911) for leg bruises that are accompanied by severe pain, deformity, excessive swelling, high fever (higher than 101 degrees Fahrenheit), drainage from the bruise, red streaking around the bruise, or if symptoms of shock develop. Shock symptoms include pale or clammy skin, rapid heart rate, chest pain, decreased urine output, blue coloration of the lips and nails, confusion, dizziness, profuse sweating, and changes in level of consciousness.
If your leg bruise is persistent or causes you concern,
seek prompt medical care.
Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Remedies, Prevention
Bruises Overview
A bruise is a common skin injury that results in a discoloration of the skin. Blood from damaged blood cells deep beneath the skin collects near the surface of the skin, resulting in what we think of as a black and blue mark.
Causes of a Bruise
People typically get bruises when they bump into something or when something bumps into them.
- Bruises can occur in some people who exercise vigorously, such as athletes and weight lifters. These bruises result from microscopic tears in blood vessels under the skin.
- Unexplained bruises that occur easily or for no apparent reason may indicate a bleeding disorder, especially if the bruising is accompanied by frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums.
- Often, what are thought to be unexplained bruises on the shin or the thigh, for example, actually result from bumps into a bedpost or other object and failing to recall the injury.
- Bruises in elderly people frequently occur because their skin has become thinner with age. The tissues that support the underlying blood vessels have become more fragile.
- Bruises are also more common in those taking medicine to thin the blood.
Symptoms of a Bruise
- Initially, a fresh bruise may actually be reddish. It will then turn blue or dark purple within a few hours, then yellow or green after a few days as it heals.
- A bruise is commonly tender, and sometimes even painful for the first few days, but the pain usually goes away as the color fades.
- Because the skin is not broken in a bruise, there is no risk of infection.
When to Seek Medical Care
- Call the doctor if the bruise is accompanied by swelling and extreme pain, especially if you take a blood-thinning medication for a medical condition.
- Call the doctor if bruising occurs easily or for no apparent reason.
- Call the doctor if the bruise is painful and under a toenail or fingernail.
- Call the doctor if a bruise does not improve within two weeks or fails to completely clear after three or four weeks.
- Go to an emergency room if you think you have a broken bone along with the bruise.
- Some bruises, such as those on the head or the eye, can cause a lot of anxiety.
- If a bruise (sometimes called a “goose egg”) occurs on the head, but the person did not black out and is able to remember the accident, it is unlikely that a serious head injury has resulted. On the other hand, if the person cannot remember what happened and you suspect the person may have a concussion, they should be taken to the nearest emergency room.
- If a bruise occurs just above the eye, you can expect the bruise to travel to the area just under the eye, possibly causing a black eye, because of the effects of gravity. As long as you are able to move the affected eye in all directions and do not have changes in your vision, it is unlikely to be a serious injury that requires a visit to the hospital.
Exams and Tests
If an injury is obviously a bruise and the doctor does not suspect any broken bones, the doctor will probably not perform any tests.
- If there is swelling or severe pain, the doctor may want to get an X-ray of the area to make sure there are no broken bones.
- If bruising occurs frequently and for no apparent reason, the doctor may have your blood tested to look for a bleeding disorder.
- Certain bruises, a pattern of bruises over time and in various stages of healing may alert a doctor to the possibility of physical abuse.
Bruises Treatment — Home Remedies
The treatment for a bruise is most effective right after the injury, while the bruise is still reddish.
- A cold compress such as an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables should be applied to the affected area for 20-30 minutes in order to speed healing and reduce swelling. Do not apply ice directly to the skin. Wrap the ice pack in a towel.
- If the bruise takes up a large area of the leg or foot, the leg should be kept elevated as much as possible during the first 24 hours after the injury.
- Acetaminophen may be taken for pain as instructed on the bottle. Avoid aspirin or ibuprofen because they slow the blood from clotting and may, in fact, prolong the bleeding.
- After about 48 hours, heat in the form of a warm washcloth applied to the bruise for 10 minutes or so two to three times a day may increase blood flow to the bruised area, allowing the skin to reabsorb the blood more quickly. Ultimately, the bruise will fade in color.
Medical Treatment for a Bruise
Doctors have no special treatment for bruises other than the techniques described above: ice packs and later heat, over-the-counter medications for pain, and elevation of the bruised area, if possible.
A suspected victim of domestic abuse may be referred to a social worker.
Bruise Prevention
To prevent a bruise:
- Wear protective gear (like shin guards) while playing contact sports such as soccer.
- Place furniture away from doorways and common walking paths within your home.
- Keep phone and electrical cords away from open areas where you may trip and fall.
- Be sure floors are kept dry and that rugs are slip resistant.
- Keep floors free of clutter.
- Plug in a small night light or use a flashlight if you need to walk to the bathroom during the night.
- If your doctor has prescribed blood-thinning drugs, be sure to have regular monitoring and adjust medications as necessary.
Outlook
Bruises typically take about two weeks to disappear.
Bruises and Blood Spots Under the Skin
Do you have bruises or blood spots under the skin?
If a bruise is rapidly spreading, you need try to stop the bleeding under the skin. Wrap the area (not too tightly) with an elastic bandage, such as an Ace wrap, and keep it on until you see a doctor. You can also put direct pressure on the area for 15 minutes at a time.
Yes
Bruises or blood spots under skin
No
Bruises or blood spots under skin
How old are you?
Less than 3 years
Less than 3 years
3 years or older
3 years or older
Are you male or female?
Why do we ask this question?
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as “male” and once as “female”). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Has there been a decrease in how alert or aware you are or how well you can think and respond?
Yes
Decreased level of consciousness
No
Decreased level of consciousness
Are there red streaks leading away from the area or pus draining from it?
Do you have diabetes, a weakened immune system, peripheral arterial disease, or any surgical hardware in the area?
“Hardware” includes things like artificial joints, plates or screws, catheters, and medicine pumps.
Yes
Diabetes, immune problems, peripheral arterial disease, or surgical hardware in affected area
No
Diabetes, immune problems, peripheral arterial disease, or surgical hardware in affected area
Do you think you may have a fever?
Do you feel lightheaded or dizzy, like you are going to faint?
It’s normal for some people to feel a little lightheaded when they first stand up. But anything more than that may be serious.
Are you bleeding now?
Yes
Abnormal bleeding now present
No
Abnormal bleeding now present
Do you think that the bruising may have been caused by abuse?
Yes
Bruises may have been caused by abuse
No
Bruises may have been caused by abuse
Has the number or size of bruises or blood spots increased for no clear reason?
Yes
Unexplained increase in size or number of bruises or blood spots
No
Unexplained increase in size or number of bruises or blood spots
Was the increase in bruises or blood spots fast?
Yes
Rapid increase in the number or size of bruises or blood spots
No
Rapid increase in the number or size of bruises or blood spots
Do you take a medicine that affects the blood’s ability to clot?
This may include blood thinners and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen. These medicines can cause bleeding and can make it harder to control bleeding.
Yes
Medicine may be causing bruises
No
Medicine may be causing bruises
Were the bruises caused by an injury?
Yes
Bruises caused by injury
No
Bruises caused by injury
Did a large, painful, very swollen bruise develop within 30 minutes after the injury?
Yes
Bruising within 30 minutes of injury
No
Bruising within 30 minutes of injury
Have you had bruises or blood spots for more than 2 weeks?
Yes
Bruises or blood spots for more than 2 weeks
No
Bruises or blood spots for more than 2 weeks
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may quickly occur after a sudden illness or injury.
Adults and older children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Feeling very dizzy or lightheaded, like you may pass out.
- Feeling very weak or having trouble standing.
- Not feeling alert or able to think clearly. You may be confused, restless, fearful, or unable to respond to questions.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may occur quickly after a sudden illness or injury.
Babies and young children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Being very sleepy or hard to wake up.
- Not responding when being touched or talked to.
- Breathing much faster than usual.
- Acting confused. The child may not know where he or she is.
Abnormal bleeding means any heavy or frequent bleeding or any bleeding that is not normal for you. Examples of abnormal bleeding include:
- Nosebleeds.
- Vaginal bleeding that is different (heavier, more frequent, at a different time of month) than what you are used to.
- Rectal bleeding and bloody stools.
- Bloody or pink urine.
- Gums that bleed easily when you eat or gently brush your teeth.
When you have abnormal bleeding in one area of your body, it’s important to think about whether you have been bleeding anywhere else. This can be a symptom of a more serious health problem.
Many prescription and nonprescription medicines may reduce your blood’s ability to clot and cause bruising or bleeding under the skin. A few examples are:
- Aspirin and other medicines (called blood thinners) that prevent blood clots. Also, taking a nonprescription medicine with a blood thinner may increase your risk of bruising and bleeding.
- Medicines used to treat cancer.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen (for example, Advil or Motrin).
- Steroids, such as prednisone.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
Symptoms of serious illness may include:
- A severe headache.
- A stiff neck.
- Mental changes, such as feeling confused or much less alert.
- Extreme fatigue (to the point where it’s hard for you to function).
- Shaking chills.
Symptoms of serious illness in a baby may include the following:
- The baby is limp and floppy like a rag doll.
- The baby doesn’t respond at all to being held, touched, or talked to.
- The baby is hard to wake up.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system’s ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don’t want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren’t serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don’t have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don’t have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor. You may need care sooner.
Do You Bruise Easily? When to Get It Checked Out – Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic
You’re undressing or showering and discover a bruise on your leg or arm. Baffled, you wonder: “Where did that come from? I don’t remember bumping into anything.”
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may never pinpoint the source. The bruise eventually disappears, along with your concern. But bruising shouldn’t always be dismissed so easily, says hematologist Dana Angelini, MD.
“It’s common to bump into things, not remember, and see small bruises on your legs or arms,” she says. “However, unprovoked bruises on your torso, back or face are unusual. And that’s a reason to get them checked out.”
Here’s what you should know about bruising.
How bruises develop
You may get a bruise from a bump or injury to the skin or the tissues beneath the skin. Since the skin isn’t cut or broken, you won’t see external bleeding. But damage to blood vessels below the skin causes them to rupture and leak blood.
Blood pooling and clotting beneath the surface causes skin discoloration. At first, the skin is often red or purplish. As the bruise heals, it may turn brown, green or yellow. The area often is swollen, tender or painful.
Why do I bruise so easily?
Minor accidents — running into furniture, falling, dropping something on your leg, hand or foot — are the most common cause of bruising.
Some over-the-counter medicines such as aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen), Plavix® (clopidogrel) and blood thinners (like Coumadin®) can increase your tendency to bruise. So can prescription medicines, such as certain antidepressants.
“Even over-the-counter supplements such as garlic, ginkgo, ginseng and fish oil can inhibit normal platelet function and cause bruising,” Dr. Angelini says.
Age is another factor. Older adults may bruise more easily than younger people. Their thinning skin often has less fat underneath to cushion the blood vessels.
Other possible causes of bruising include:
When bruising is cause for concern
Bruises due to minor injuries or accidents usually disappear on their own after a week or two. During the healing process, the bruise will change color before fading away. But it’s a good idea to get a bruise checked out by your doctor if it:
- Shows no signs of improvement after a week.
- Is located on a part of your body where injury or accident is unlikely.
- Keeps occurring or comes back.
- Is unusually large and unprovoked.
During an office visit, your doctor will review your family and personal medical history. You’ll answer questions like:
- Do any family members have an inherited blood disorder?
- Have you been bleeding from your nose or oral cavity?
- Have any surgeries resulted in above-average bleeding?
- Which medications and supplements do you take; have you recently started new ones?
- If you’re a woman, has your menstrual flow been heavier?
- Have you had other blood loss, such as in the urine or stool?
- Have you ever had bleeding in unusual locations, like the joints, muscles or brain?
If your doctor decides medication is probably causing your bruising, he or she will discuss other options. “We’ll do a risk-benefit analysis,” Dr. Angelini says. “If life is going well, we might opt to keep you on the drug if it’s helping you control another disease. If the bruising is severe or interfering with your daily life, we’ll talk to the prescriber about replacing it with another medication.”
When the cause of bruising is unclear, your doctor will likely order blood work to check for platelet problems or other blood clotting abnormalities.
But don’t hesitate to ask your doctor for help. “We do a lot of consultations for bruising. When a serious bleeding disorder is ruled out, we’re happy to provide reassurance,” she says.
Board Certified Vein and Vascular Specialists
We all get bruises when we bump into something or fall down. Often, we may not remember exactly where a bruise came from. If you suffer from bulging or discolored varicose veins, you may get bruises more easily in that area. That’s because bruising, sometimes called vein bruising, is part of the body’s healing process after injury or trauma. Individuals can also get bruises after both minor medical treatments and major surgery. Bruises should improve steadily and gradually fade. If they don’t, you may need to see your doctor.
Minor Bruises
Bruises you may get after minimally-invasive Cincinnati vein treatment are generally very minor. Because of advancements in vein procedures, issues like varicose veins, spider veins, and vascular disease can all be treated through quick, efficient medical techniques in our offices. As bruises fade, your legs look and feel better than ever, as you’ll notice in our Before & After photo gallery. Follow your aftercare instructions from our clinic, which may include resting your bruised leg, propping it above heart level, applying an ice pack (for only 10 minutes at a time) and wearing compression socks. Keep in mind that non-strenuous walking is also encouraged to re-establish proper circulation.
How to Recognize Serious Bruising
Bruises may be serious, and require medical care when bruising:
Has not improved at all, or has gotten much worse, after a week. There could be a larger accumulation of blood, called a hematoma, under the skin. In some cases, a hematoma will need medical care or may clear up on its own. Contact your doctor for instructions and s/he may request you to come to the office.
- Causes severe pain or swelling.
- Feels warm and tender to the touch, with a possible “pulling” sensation when you move your leg. This can be a sign of DVT or deep vein thrombosis, which is a blood clot, typically occurring deep within the leg. Call or go to your local emergency room for immediate, expert care.
- Is seen on a body area where you typically never bruise.
- Keeps re-appearing, after initial healing.
- Covers a large area with no probable cause. This could be a sign of a minor medical issue, or something more serious. Blood disorders such as hemophilia, other blood clotting disorders, anemia, or leukemia are possible causes, so schedule a visit to your doctor for an evaluation.
Advanced Vein Treatments in Kentucky
If you need varicose vein treatment, such as laser vein treatment, to banish your vascular problems or prevent future vein bruising, we’re ready to help. At our VIA vein center, we are always here for you if you notice vein symptoms, including bruising, that concern you after any procedure. For expert vein care that will improve circulation, health, and appearance, contact us at Vascular and Interventional Associates in Crestview Hills, KY, today.
Why do you bruise easily? This is when to see a doctor
Do you ever feel like the main character in Hans Christian Andersen’s fairy tale “The Princess and the Pea,” in which the delicate princess wakes up “black and blue all over” after sleeping on a single pea covered by a tower of mattresses?
Your skin can reveal many clues about your health, so a tendency to bruise easily might make you worry.
Although finding frequent bruises can sometimes signal health problems, doctors say most cases are nothing to worry about.
Dr. Monique Tello, a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, encounters patients with “easy bruising anxiety” quite frequently.
“Thus far, in my ten years as an attending (physician), no one in my primary care practice has had any serious underlying condition,” Tello told TODAY. “Usually, they didn’t remember some bump, or were taking aspirin. Rarely, bruising can be a clue that there is a medical issue.”
Most bruises happen when you suffer an injury that fails to break the skin, but crushes the small blood vessels underneath. Blood then leaks and becomes trapped under the surface, leaving the telltale mark.
If you work out a lot, you might notice bruising in fatty areas that are exposed, like your thighs, buttocks or legs, said Dr. Abigail Waldman, a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Here are other possible causes of easy bruising:
Blood thinners
Besides injury, blood thinners — medications or supplements that slow down or decrease your blood’s clotting ability — may be the number one cause for easy bruising, Waldman said. They’re very common, ranging from aspirin to drugs like Coumadin. If you’re on blood thinners, it may take longer for bleeding to stop, leading to bigger bruises.
You might not even realize you’re taking something that thins your blood: Fish oil supplements, ginkgo biloba, alcohol and garlic have similar effects.
Other drugs
Steroids can lead to thinner skin, so you may notice bruising with just slight trauma. Chemotherapy can lower the number of platelets — the cells that help your blood to clot — in your body, the National Cancer Institute notes. A low platelet count means a higher risk of bruising.
Vitamin deficiency
Easy bruising might suggest you lack enough vitamin K, found in leafy green vegetables, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. Most people get enough of this fat-soluble vitamin in their diets, so you don’t need to take a supplement, Waldman said. But if you are deficient, it’s a sign you may not absorbing vitamins correctly, she added. That may include people with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
A severe lack of vitamin C — or scurvy — could also be the culprit because the vitamin is involved in building the walls of blood vessels, Waldman said. Scurvy is rare in the U.S. — symptoms include bleeding around hair follicles and bleeding gums.
Aging
As you age, your blood vessels become more fragile. “You can think of it like a hose that holds the blood,” Waldman said. “As you get older, you sort of have some leaks in the hose. So very small injuries can cause that area to open up and leak blood out into the skin, causing a bruise.”
Older skin is more fragile, too, and there’s less fat underneath it, leaving you with less cushion if you bump into something. All of those factors can lead to senile purpura, or bruises that show up after very slight injury in elderly people. The marks typically appear in areas that have had significant sun exposure, like the arms and the hands, Waldman said
“Unfortunately, there’s not a lot you can do to prevent it, except to try to avoid any even minimal injury. But sometimes it’s nice for patients just to have a diagnosis,” she added.
Cancer
In rare cases, easy bruising can be a sign of blood, bone marrow or lymph node cancers, Waldman said. These marks often show up as petechiae — very small red dots from bleeding under the skin — but can look like large bruises as well.
The bruises can be one clue of many, so doctors will ask about any accompanying bleeding from the gums, fevers, chills, night sweats, bone pain, Tello said.
“In my years of training, I rotated through oncology and ICU units where patients had had easy bruising as one of many signs of their underlying leukemia or bleeding disorder diagnosis originally,” she noted.
Liver disease
The liver’s many functions include producing clotting factors. When the organ is damaged and slows or stops producing the proteins needed for blood clotting, you will bruise or bleed easily, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Genetic factors
The tendency to bruise easily can run in families. Genetic causes can lead to changes in your platelet count or the factors that are involved in clotting.
See a doctor if you have:
• Significant pain and swelling. That could represent a larger bleed under the skin, especially if you’ve had a significant fall or injury, Waldman said.
• A bruise that lasts longer than two weeks without changing. It may not be a bruise at all or be caused by an underlying problem.
• Small blood spots accompanied by fever, chills, weight loss or any other systemic symptoms that are new.
• Recurrent bruises without any clear causes.
There’s no one true definition of being an “easy bruiser,” but Waldman defines it as bruising with minimal or no injury. In most cases, bruises are not a cause for worry.
Putting ice on a bruise can help minimize swelling and some data suggests taking arnica orally can help prevent bruising, she noted. Your body will clear most bruises within a week.
Follow TODAY Health and Wellness on Facebook and subscribe to our newsletter “One Small Thing” to get easy tips to improve your life every weekday!
The bruise is not a trifle
Unsuccessfully rounded the corner of the table or fireplace? Too actively honing your hula hoop waist? And now he is a bruise – a hematoma. It’s unpleasant, of course, but we know for sure – it will pass. And that’s where the spontaneous bruises come from, which seem to form for no reason. They are not “hand made” by an opponent in the boxing ring and not the result of falling off rollers or snowboards. Then what’s the matter? It turns out that things can be much more serious than expected …
Ice Blue
“Let’s decide right away – there are no unreasonable bruises.However, the reason for their appearance is not always obvious. Meanwhile, any hematoma is a hemorrhage into the skin and subcutaneous tissue, when the thinnest and most vulnerable vessels – capillaries – are damaged. It happens that the integrity of the veins is impaired. And here it is obvious: the larger the vessel, the more the hemorrhage, – the head of the 2nd Department of Internal Diseases of the Belarusian State Medical University, Professor Nikolai Soroka, introduces .
– One of the most common causes of bruising is Shenlein-Henoch disease (the old name for hemorrhagic vasculitis).The disease leads to fragility of blood vessels, which is why bruises appear on the legs, abdomen, and back. For example, in children, this is caused by a past viral infection and taking medications. They caught a sore throat or ARVI, they take antipyretic and antibiotics, and after 1 – 2 days, small-point bruises are strewn over the body. It is difficult to say what was the root cause of their appearance, infection or the effect of drugs. ”
Violation of the blood coagulation system is another serious reason for spontaneous bruising.A classic example: hemophilia is an incurable hereditary disease. Minor blow or compression – hematoma bruises instantly appear on the skin. Even more worrisome is the threat of bleeding into internal organs.
This is what the doctor ordered
Large spilled bruises can occur in people who are prescribed anticoagulants – drugs that thin the blood. Including the well-known warfarin and even aspirin. “It has long been recommended to prevent the development of thrombosis, heart attacks and strokes.However, today doctors refuse the widespread use of this drug as a method of primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases, – says Nikolai Fedorovich. – In Europe, studies were conducted with the participation of 10 thousand patients. As a result, it was confirmed: if a person has not suffered a vascular accident, while taking aspirin for prevention, this does not affect the risk of stroke or heart attack. However, it increases the chance of bleeding. After all, the drug changes the function of platelets, which provokes hemorrhages. “
Because today doctors are much stricter about such appointments. More often using aspirin as a secondary prevention. This means it is effective for people who have had myocardial infarction who already have angina pectoris or heart rhythm disturbances. In short, just in case, drinking aspirin is risky and unjustified. By the way, not only this drug can cause sudden hemorrhages, but also other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that are taken to get rid of headaches, tangible discomfort in the joints, spine.
Blood interest
The function of the blood corpuscles – platelets – is extremely important. During a wound – domestic or military – these assistants help the formation of a microthrombus, which prevents the body from losing a lot of blood. When there are not enough platelets (their norm is 150 – 350 thousand per microliter of blood; the indicator is considered to be less than 100; when it is even lower – less than 70, this is regarded as a clear threat to health), there is a danger of vascular damage and hemorrhage.This condition is called thrombocytopenia.
It happens that with a quantitative norm, platelets “in bad faith” fulfill their obligations. This happens, as already noted, with unjustified intake of aspirin. Hence the microcirculatory bruising. They look like multiple small hemorrhages up to 1 – 3 mm. Usually appear in front of the lower leg, on the flexion surfaces of the knee and elbow joints, sometimes on the buttocks.
Nikolay Soroka
Alarm
The appearance of small punctate bruises on the skin is associated with a malfunction of the liver, where factors of the blood coagulation system are formed.With cirrhosis and hepatitis, this function is impaired. This is the root of all evil – the true cause of bruising even with pressure and touch on the skin. Moreover, such hematomas do not disappear for a long time. A blood test for liver enzymes helps to clarify the situation.
When in elderly people, small-point bruises suddenly sprinkle on the skin of the legs, doctors prescribe an examination for cancer. After all, this is often one of the first symptoms of lung cancer.
There is a reason
The diagnosis of varicose veins is already a considerable likelihood of hemorrhage.After all, the blood pressure in the veins increases! Hence hematomas without injuries and bruises. Varicose veins should not be taken lightly. In consultation with a phlebologist, you can decide on a treatment plan from professionally selected compression hosiery to surgery.
Finally, a banal lack of vitamins C and P in the body again gives rise to bruising. Since the deficiency of ascorbic acid inhibits the synthesis of collagen in the connective tissue, which prevents the vessels from remaining elastic and not being injured.When the deficiency of vitamins is replenished, blood vessels are strengthened, their permeability decreases. This means that the risks of hemorrhage are minimal. Therefore, doctors often prescribe the well-known ascorutin. This drug is a combination of ascorbic acid and rutin, which has a targeted effect on the thickening of the vascular wall.
In short, the causes of sudden bruising can be very different – from vascular inflammation to a malignant tumor. The diagnostics prescribed by the doctor will help to dot the “i’s” in this complex issue.
Flowering time
Over time, the bruise changes noticeably outwardly, it seems to bloom. This happens under the influence of enzymes that destroy hemoglobin. At first it has a reddish tint, then blue and purple. Later, it turns noticeably green, turns brownish and finally turns yellow. Usually, it takes 10-14 days from hemorrhage to resorption of the hematoma.
Action Plan
Small hematoma from physical trauma can be easily managed at home using ice, heparin ointment, or troxevasin gel.If it is extensive, it must be removed surgically. Otherwise, a large amount of blood – sometimes up to 200 ml stagnates, which can cause suppuration and abscess. This happens with – hemophilia or an overdose of anticoagulants. For example, warfarin, a drug that is often prescribed after aortic or mitral valve replacement.
Author: Alla MARTINKEVICH
Soviet Belarus No. 128, July 9, 2015
90,000 Why do bruises and spots appear on the legs with varicose veins?
Are the bruises dangerous?
“No” – everyone will answer, because such spots on the body at least once in a lifetime appear in everyone.Under normal circumstances, they are right. However, there are exceptions.
In some, bruises are formed due to varicose veins. These cosmetic defects are not dangerous in themselves, but indicate a serious medical condition. So it’s important to show them to your doctor.
Before talking about bruises and spots with varicose veins, we will briefly describe the main signs and risks of this pathology.
Let’s start with the basics.
Varicose veins usually occur when the valve system malfunctions.This is the name for the membranes in large vessels, which reduce the risk of blood accumulation and reduce the load on the venous walls. Valves are like doors. They open and allow blood to flow to the heart, and then close and stop the flowing blood.
Valves stop working normally due to the following factors:
- Heredity
Some are born with weakened valves. According to statistics, if a mother and father suffer from varicose veins, then with a 90% probability their children will also acquire altered veins.
The valve system gradually wears out. In young people, these membranes withstand blood pressure better, but older valves often let it through. So people over 60 are more likely to suffer from varicose veins.
- Sedentary lifestyle
Blood circulation in the legs depends not only on the condition of the valves, but also on the contraction of muscles that compress the veins and push blood to the heart. In motionless legs, this mechanism does not work.If a person sits or stands in one place for several hours in a row, then the blood circulation in his vessels worsens, and the pressure on the walls of the veins increases.
- Hormonal imbalance
The level of hormones affects the elasticity of blood vessels. Therefore, with the use of contraceptives, the risk of changes in veins increases.
- Overweight
Blood volume depends on weight. Each extra kilogram increases the load on the vessel walls and the valve system.
The venous system of expectant mothers is in constant stress, as it is influenced by several dangerous factors. First of all, hormonal imbalances and weight gain.
The fetus is also dangerous for blood vessels. In the last trimester, the child grows so much that sometimes it puts pressure on the neighboring veins. Their lumen decreases, and the pressure on the vessel walls increases.
As you can see, even people without a genetic predisposition will sooner or later be at risk for varicose veins.
However, the disease itself does not kill.
It only worsens the quality of life and causes cosmetic discomfort.
Much worse is its complications:
- Trophic ulcers
- Pulmonary embolism
- Bleeding
On rare occasions, they even kill patients. For example, with external bleeding from diseased blood vessels, people can lose too much blood without timely medical attention.
Pulmonary embolism is no less dangerous.Blood clots often form inside the altered veins, which sometimes enter the bloodstream and get stuck in the vessels of the lungs. This causes respiratory arrest.
Fortunately, complications of varicose veins occur in only a few percent of patients. Others often live with the disease all their lives. However, all this time they are constantly at risk.
Therefore, doctors recommend treating altered veins immediately after the first symptoms appear:
- Heaviness in the legs
- Spider veins
- Edema
- Fatigue
- Burning and itching
- Feeling of fullness in the veins
- Night cramps
- Pain
Also, many have spots on the legs with varicose veins .They can be red or dark.
Causes of the appearance of spots on the legs with varicose veins
Usually, the skin turns pale or darkened when the tissues do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. With changed veins, this problem occurs often.
White or dark spots on the legs with varicose veins indicate the accumulation of venous blood in adjacent tissues. So the arterial blood doesn’t get to them. As a result, the skin dies slowly.First, it darkens, and then a white spot appears in the center – here in the future a trophic ulcer may appear.
That is, darkening is formed due to insufficient tissue nutrition.
red spots on the legs with varicose veins have a slightly different nature. Redness indicates inflammation. Therefore, most often such spots are found in people who have developed thrombophlebitis in altered vessels. With this pathology, blood clots form, and the venous wall becomes inflamed.Redness spreads along the vessel.
A change in the color of the skin in these cases indicates a malfunction of the veins. So with this symptom you need to see a doctor. He will make an accurate diagnosis. If external signs are caused by altered vessels, then in order to completely eliminate them, it is necessary to defeat the disease itself.
Why do bruises appear on the legs with varicose veins?
These blue spots under the skin are caused by trauma to the veins. Sometimes due to blows.In other cases, due to excessive pressure in the vessels. Blood accumulates in the tissues, which is why ugly bruises are visible.
How common are they?
Bruises on the legs with varicose veins do not occur in everyone, although the changed veins are more vulnerable to stress and are often injured.
It is therefore important to diagnose these spots.
How to distinguish bruises on the skin of varicose origin from household bruises?
Bruises with varicose veins have characteristic features:
- Hematomas appear for no apparent reason
- Dilated vessels appear near the bruise
- Blood accumulations disappear slowly or do not go away at all
So wait a few weeks.On average, ordinary bruises heal in about this time. If they have not disappeared, then you need to be examined by a doctor.
Fortunately, varicose veins develop slowly.
So that patients can consult a doctor at a convenient time for them. For example, after a planned vacation.
On the other hand, bruises on the legs with varicose veins are sometimes difficult to eliminate, because they are fed by damaged dilated vessels.
How dangerous are the symptoms of bruising and spots on the legs?
By themselves, they are not dangerous.
Yes, for some such skin changes can cause severe cosmetic discomfort.
Much more important, as indicated by hematomas and darkening of the skin. They usually warn a person about the development of varicose veins, vascular injuries and the death of the skin.
Ulcers are often formed in the center of dark spots. These non-healing wounds not only reduce the patient’s quality of life, but also increase the risk of tissue infection.
Therefore, spots with varicose veins are important to show to the doctor.So you will reduce the likelihood of trophic ulcers.
Which doctor should I contact if I have bruises and spots on my legs?
To a phlebologist.
Moreover, darkening or pallor of the skin must be checked with a doctor as soon as possible. Although ulcers do not develop overnight, it is best not to risk it.
What to do with a bruise with varicose veins ?
Confirm the diagnosis first. If the blue spot on the skin does not disappear in two weeks, then this is not an ordinary hematoma.It is most likely associated with altered vessels. So a phlebologist should check it.
First, he will examine the spots on the skin, get acquainted with the patient’s medical history, and then prescribe tests. For example, ultrasound. This test will show the condition of the veins and the doctor will then make a diagnosis.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, the doctor will choose one of the therapy options.
Modern painless methods of treating varicose veins
Previously, doctors removed altered vessels only by surgery, which left long scars on the skin.
New procedures are less traumatic.
After them, the diseased veins disappear, and the skin remains unharmed.
Microsclerotherapy
This operation removes only spider veins.
Microsclerotherapy removes arachnoid, tree-like and linear patterns from dilated skin vessels.
- Procedure
The doctor injects sclerosant into the center of the spider veins. The walls of the veins become inflamed and overgrown.
Up to 98% of manifestations disappear immediately after the injection, and the remnants of the dilated vessels disappear within four weeks. The therapy is painless and leaves no scars.
Unfortunately, this method is ineffective against large modified veins and therefore is not used for varicose veins.
Endovasal laser coagulation
This procedure helps to remove dilated vessels up to 10 mm in diameter.
With the help of laser coagulation, doctors treat varicose veins, as well as eliminate hemangiomas and angiomatosis.They also use this method to fight trophic ulcers.
- Procedure
The phlebologist makes a narrow puncture in the diseased vein, inserts a catheter with a laser into it and processes the vessel walls. Soon the vein becomes inflamed and overgrown.
The treatment lasts only 40 minutes. Patients do not feel pain due to local anesthesia.
In atherosclerosis and thrombophlebitis, laser coagulation is not prescribed, and doctors choose other methods of influencing the vessels.
Foam sclerotherapy
Using this procedure, doctors remove altered veins with a diameter of more than 10 mm.
Foam sclerotherapy is used for lesions of peripheral and great veins. It is prescribed for varicose veins.
- Procedure
The phlebologist injects a sclerosant into the diseased vessel, which mixes with air and turns into foam. The substance quickly fills the vein and destroys its walls.Further, the vessel grows overgrown.
Foam sclerotherapy effectively removes even large varicose veins in just 20 minutes.
In case of heart failure and exacerbations of chronic diseases, this procedure is not performed.
Miniflebectomy
This method allows you to remove altered vessels with a diameter of up to 18 mm.
Doctors usually remove the largest varicose veins with miniflebectomy. It is also carried out after thrombophlebitis and with swelling of the legs.
- Procedure
The doctor pierces a hole in the skin with a diameter of up to two millimeters, inserts special hooks inside and pulls the diseased vein out. Then he removes the vessel in parts.
Since the phlebologist removes the altered vein, the recurrence of varicose veins in it will never occur. The operation takes no more than an hour. After treatment, patients do not need hospitalization and they fully recover within 10 days.
Even the best therapies are not always effective when administered by inexperienced doctors. Therefore, it is important to treat the vessels in a reliable clinic.
We will help you get rid of varicose veins
In the center of phlebology “Institute of Veins” the best phlebologists of Kiev and Kharkov fight against vascular pathologies. Among our doctors there are specialists with experience of 20 years or more. They faced different forms of varicose veins. So during the diagnosis, we will not only determine the condition of the veins, but also choose the safest and simplest method of treatment.
Our doctors practice seamless removal of altered vessels. After them, scars do not appear. Therefore, the patients of the clinic can feel free to return to summer clothes and not hide their legs.
Come to the Vein Institute clinic and check for suspicious bruises and spots on the skin. If necessary, we will eliminate the cause of their occurrence. And often in one procedure.
Surgeon of the highest category, phlebologist
Experience: 21 years
Surgeon of the highest category, phlebologist
Work experience: 20 years
Phlebologist of the highest category
Work experience: 34 years
Dermatologist higher.cat., director
Work experience: 20 years
First category surgeon
Work experience: 15 years
Surgeon, phlebologist
Work experience: 17 years
Surgeon, phlebologist
Work experience: 5 years
First category surgeon
Work experience: 12 years
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Work experience: 10 years
Vascular surgeon, chief physician
Work experience: 11 years
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Work experience: 8 years
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Work experience: 5 years
Bruise for no reason – Archive
Eat more greens (especially celery and parsley), citrus fruits, apricots, cherries, seafood, fish, chicken eggs, seaweed and dairy products.It’s also a good idea to include vegetable oils such as olive oil or fish oil in your diet. Make sure that your diet is varied and you do not eat only pasta or potatoes five days a week. But if you have any chronic diseases or are taking a lot of medications, then you should consult with your doctor about nutrition, because, for example, some greens are contraindicated when taking blood thinners.
Women at risk
If a bruise has just appeared, then a cold compress will help, since cold tends to cause vasoconstriction, which means that the bruise will not be very large.You can use all kinds of medications, for example, heparin ointments. There are also many folk remedies. So, it is necessary to dilute the potato starch to the consistency of gruel and apply it to the bruises for 20-30 minutes. A tincture of calendula helps well in the fight against hematomas on the legs and arms – it is applied in the form of a mesh or a continuous layer to the area of the bruise, going beyond its borders by a centimeter.
The simplest and most affordable means is an iodine mesh or a vodka compress: cotton wool or gauze is moistened in vodka, applied to the bruise and covered with polyethylene on top.Keep the compress on the affected area for about 20 minutes. Salt compress also helps to get rid of the hematoma. For its preparation, use 10 grams of salt and 100 milliliters of water.
If we talk about the risk group, then, of course, most often bruises appear in people of age, while in women it is much more common than in men. Representatives of the fair sex turn to doctors with a similar problem after menopause, because they lack estrogen in their bodies and the walls of blood vessels become more brittle, as a result of which bruises appear, and men are aged sixty and older.But, of course, any disease can appear in people of any age, therefore, young people should not be frivolous about the periodic appearance of bruises that were not caused by external influences.
Of course, if a bruise develops, you should not immediately fall into hysterics and run to the emergency room. First, you need to remember if there was any external factor, for example, you could lift a heavy bag, touch the corner of the table, overdo it with the load in the gym, and so on.If hematomas periodically appear on your body for no reason at all, then you should contact your doctor and check, first of all, the condition of the blood, liver and the presence of rheumatological diseases.
Sources of vitamins, the lack of which can cause bruising:
Rosehip, sea buckthorn, black currant, parsley, pepper, Brussels sprouts, dill, wild garlic, hawthorn, broccoli, cauliflower and white cabbage, kiwi, kiwi, strawberries, lemon, tangerine, pineapple, sorrel, green onions, green peas, tomatoes, radish, potatoes, apples, garlic, cucumbers, beets, carrots.
In summer, it is better to eat vegetables and fruits immediately after purchase, and ideally freshly picked and raw, since vitamin C is destroyed by heat, light and air. For the same reasons, it is best to chop vegetables for salad as large as possible and immediately before serving.
Green leafy vegetables, spinach, cauliflower and white cabbage, broccoli, tomatoes, cucumbers, squash, pumpkin, asparagus, potatoes, oatmeal, rose hips, green tea, kiwi, bananas, avocado, olive and soybean oil.Also found in animal products: pork and beef liver, chicken eggs, fish oil, milk and dairy products.
Vitamins of group B
Main sources: liver, fish, eggs (especially hard-boiled), nuts, cereals and dairy products (cheese, cottage cheese, sour cream). Also, do not forget about vegetables, especially broccoli, and beans.
Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid)
Beef liver, broccoli, carrots, cheese, corn flour, dates, eggs, fish, milk, peanuts, pork, potatoes, tomatoes, wheat germ, whole grain products.
7 problems with the body, which can be reported by causeless bruises on the body
What if bruises on the skin appear for no reason, what is the nature of this phenomenon and is it worth worrying?
Bright Side collected the opinions of doctors about what exactly can happen in the body if bruises often appear on the skin. Pay attention and consult a specialist. A doctor who deals with such issues is called a hematologist.
If bruises appear, the capillaries are severely thinned.What influences them?
1. Taking medication
Taking medication that affects the blood can lead to mild or severe bruising. Most often these are antidepressants, analgesics, anti-inflammatory, iron-containing and anti-asthma drugs.
Some of the best known medicines that thin the blood and can lead to bruising are aspirin, cavinton and their analogues.
If you notice a connection between taking medications and changes in the skin, you should consult a doctor.You may need to temporarily interrupt the intake to eliminate the risk of internal bleeding.
2. Diseases of the blood
Diseases of the blood and blood vessels can be one of the possible causes of unexpected bruising. Varicose veins, von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenia or a formidable diagnosis of leukemia are always circulatory problems.
Do not postpone the visit to the doctor if you notice other alarming symptoms: pain and swelling of the legs, bleeding gums, small capillary points on the body, nosebleeds.
3. Lack of nutrients
Vitamins, vitamins! We make sure that children get enough of them, and we often forget about ourselves. With sudden bruises, the body shows us: it lacks important elements.
So, B12 is involved in hematopoiesis, vitamin K is responsible for clotting, and vitamin C plays one of the first violins in the formation of new tissues, without it, the vessels become fragile.
Another important vitamin – P. Without it, collagen is not produced and the walls of blood vessels become thinner, which means that in addition to bruises, the condition of the skin also worsens – not at all a joyful picture.
An element whose balance is simply necessary for the body is iron. Its excess, like its deficiency, affects the capillaries.
Do not rush to carry out artificial fortification, first check the diet and take tests for vitamin deficiency.
Source of vitamin P – fresh green tea, apples, pumpkin and garlic. Vitamin K in bananas, eggs, nuts, and oily fish. B12 – beef liver, fish, cheese, green salad.
4. Strength training, lifting weights
Lifting weights is a secondary cause of bruising.This means that the capillaries are already weak, and physical activity “completes the picture.” Nevertheless, too strong loads can provoke rupture of completely healthy capillaries. For example, strength training that you are not ready for.
Such bruises can appear even in children: overweight school backpacks are a reality of our time.
It is believed that bruises due to muscle strain are not dangerous, but they indicate that you are not taking the load.
5.Hormonal disruptions
Hormonal “swing” is one of the most common causes of bruising. They occur when there is not enough estrogen in the body.
This situation is possible with menopause, taking hormonal drugs, pregnancy. Lack of estrogen significantly weakens blood vessels, and capillary walls can be damaged with little or no effort.
6. Age-related changes
A sad but natural reason that doctors talk about is age-related changes in the body, the so-called wear of capillaries.The vascular system is weakened because tissue elasticity decreases with age.
It should be noted that such “age” bruises appear mainly on the legs. Still, they arise from minor blows to which young skin simply “would not pay attention.”
7. Diabetes mellitus
Sugar and blood are the first associations when this disease is mentioned. Diabetes has a negative effect on blood circulation, so bruising is very easy.Moreover, this process does not necessarily accompany an already developed disease, it may be one of the symptoms of a just beginning problem.
Other symptoms: atypical thirst, poor wound healing, rapid fatigue and occasional blurred vision, possible white spots of vitiligo on the skin.
Bruises appear on the body. Do I need to see a doctor
Bruises on the body from impact, injury or strong pressure are common in life.At the site of injury, the capillaries rupture, and blood seeps into the surrounding tissue layer, forming a bruise. But if bruises appear “on their own”, then their appearance is the first signal to think about your health. The cause of their occurrence can be either a minor or a rather serious disease.
Unreasonable, at first glance, bruises on the body may signal the possible presence of such diseases as hemorrhagic vasculitis, varicose veins, fragility of blood vessels, impaired blood circulation, decreased blood clotting and a lack of platelets.Bruises can appear due to hormonal disorders and with prolonged use of medications such as antidepressants, analgesics, anti-inflammatory and anti-asthma drugs. This is due to their ability to reduce blood clotting, which subsequently leads to bruising. In addition, bruises on the body can appear with diseases of the circulatory system, with hypertension, rheumatism, liver diseases, after recent infectious diseases.
It should also be noted that the occurrence of bruises on the body for no reason often indicates a lack of vitamins of groups C, K and P. in the human body.Due to their insufficient content, there is a violation of the process of production of collagen – a protein that protects the walls of capillaries from rupture and cracks. With a lack of collagen, the vessels become weak and fragile, and as a result, the appearance of bruises on the body.
This problem cannot be ignored. In no case should you resort to self-medication. To identify the cause of the appearance of “unreasonable bruises” on the body, you need to go to an appointment with a general practitioner. Only a doctor will be able to identify the cause of the bruises and prescribe the necessary examinations and treatment.
The most important thing in the life of every person is his health! After all, if the body signals about any disease in the form of bruises, one should not take it lightly. A timely diagnosis at the earliest stage of the disease is the key to successful treatment!
Material prepared by: Kashpar T.A.
90,000 How to get rid of a bruise when a hematoma becomes a cause for panic
There is no escape from bruises, and many of us are so used to them that they do not even react to the appearance of another “spot”.In fact, hematomas (the medical name for bruises) are not all that harmless. Interfax.by found out what is the nature of these painful spots, how to treat them, and when you need to sound the alarm.
What is hematoma
Hematomas are, roughly speaking, subcutaneous hemorrhages that occur as a result of a bruise. Any blow damages blood vessels, as a result of which “released” blood spreads and causes swelling – slight swelling of soft tissues
At risk are:
- Elderly people, as their vessels lose elasticity;
- Vacationers who do not follow the measures on the beaches, scalded skin is prone to bruising;
- Athletes;
- People who abuse antipyretics and pain relievers, they thin the blood.
In addition to blows, the cause of bruising is vitamin deficiency. If you notice that you regularly appear “marks”, most likely the matter is in the deficiency of vitamins C and K. But you do not need to immediately go to the pharmacy and start self-medication, get tested to avoid hypervitaminosis.
Why are hematomas dangerous?
At first glance, bruises are not dangerous, except that they spoil your appearance, but in fact, regular microtrauma leads to a weakening of the vascular network, which is fraught with varicose veins.
Also, you should not neglect medical help if you get a bruise after a serious injury. Especially if the hematoma is very painful and affects mobility.
Contact your doctor (traumatologist, surgeon, hematologist) immediately if you notice that the bruises do not go away for a long time or appear on their own. It is necessary to exclude thrombocytopenia – a blood clotting disorder in which platelet function is suppressed. Weakened cells of “quick response” cannot timely close the site of vascular damage and block bleeding.
A large postoperative hematoma should also become a reason for contacting doctors.
What to do with a bruise
So, if you have determined that your bruise is not the result of any serious disturbances in the body, then you can try to either hide it or speed up healing.
As a rule, bruises on the trunk disappear within two weeks, on the face – within a week – nine days. They stay on their feet as long as possible – for a month.
If you suddenly bump and feel that you are about to have a bruise, first try to prevent it: fill a bag or heating pad with ice and apply it to the damaged area for the first few hours. The main thing is not to overcool! You should be especially careful with the areas of the face, neck, armpits, groin. Cool the bruise for 15 minutes, then give the skin a break for 10-15 minutes – remove the ice. Remember to “cool down” until the bruise develops. As soon as the hemorrhage became noticeable on the skin, on the contrary, it should be warmed up.The heat will improve blood microcirculation and help the small hematoma to dissolve. If you don’t have time to sit with a heating pad, apply pepper plaster, which has good warming properties.
The injured limb is best positioned vertically to reduce swelling.
Watch your hematoma, it should change shades. If the bruise remains the same as on the first day, see your doctor. By the way, persistent redness and swelling is evidence of infection.
If you need to get rid of the bruise as quickly as possible, you can use the “grandmother’s” methods. But be careful here, not all methods are suitable for everyone:
- Make a compress from strong brewed tea;
- Wrap the bruised area with mashed cabbage leaves and tie tightly;
- Apply finely grated potato gruel to the injured area;
- buy dry bodyagu at the pharmacy, grind it in a mortar, add a spoonful of vegetable oil.Apply the resulting mass to the sore spot. Be careful – the crushed water stick gets nibbled. It can also provoke dermatitis;
- Rub the bruise with a piece of butter;
- Apply iodine mesh (not suitable for people with hyperthyroidism).
Do not overtighten the bruised area, this can slow down the recovery process for a long time.
Caution, bruise: how to get rid of a bruise
Slipping on an icy path, bumping your toe on a nightstand, bumping your forehead into a door opened by a careless work colleague – these are the simple everyday ways to get a bruise, which in a few days will turn into a bright “smart” bruise.In this article, we will show you safe ways to quickly get rid of the consequences of a bruise – bumps and bruises.
What is a contusion
A bruise is a soft tissue injury that does not affect the bone. In case of a bruise, the integrity of the skin is not violated, and the subcutaneous tissue and small blood vessels “suffer” first of all.
Determining that you “got” a bruise is quite simple. The bruised area heats up and feels mild pain. To the touch, the bruised area becomes denser, reddens and slightly swells.If you bruise a joint (such as a knee or elbow), swelling may appear on the affected leg or arm, and a bruise may develop after a couple of days.
Why does a bruise appear after a bruise? The blow to the body damages the blood vessels, and blood flows from them into the soft tissues. “Holes” in small vessels quickly tighten special cells. But it takes several days for the “cleaner” cells to remove blood from the soft tissues. The work of the “cleaning cells” can be observed with our own eyes – when a bruise from purple-red gradually turns dark blue, and then turns yellow and completely disappears.
If you are hurt, it is important to make sure that the impact does not damage the bone. If the swelling is large, and it is scary to even touch the bruised area, it is better to consult a traumatologist. The doctor will send you for an x-ray. If the bones are intact, you can heal yourself.
How to reduce bruised pain
If you have just hit, the best thing to do is to apply cold to the area of the injury. Cold slows down bleeding under the skin and cools pain-sensitive receptors, decreasing the strength of the pain signal that the receptors transmit to the brain.As a result, bruising and swelling will be less than they would be without cooling.
For cooling a bruise, a plastic bag with a stabbed person is well suited (ice “pieces” cannot be used – you can get a cold burn). If there is no ice, you can substitute the affected area under a stream of cold tap water for 1-5 minutes.
How to quickly get rid of a bruise
The most important thing to do when dealing with bruising is to reduce inflammation.