Is Ex-Lax safe for constipated children. How does Ex-Lax compare to Miralax. Can Ex-Lax replace enemas in treating bedwetting and accidents. What are the optimal dosages and timing for Ex-Lax in pediatric patients.
Understanding Ex-Lax: A Stimulant Laxative for Constipation Relief
Ex-Lax is a popular over-the-counter medication used to treat constipation in both adults and children. As a stimulant laxative derived from the senna plant, it works by prompting the intestinal muscles to contract, effectively pushing stool through the digestive tract. This mechanism of action differs from osmotic laxatives like Miralax, which draw water into the colon to soften stool.
Many parents consider using Ex-Lax for their constipated children, especially when other treatments have proven ineffective. However, it’s crucial to understand the proper usage, potential benefits, and any safety concerns associated with this medication.
Ex-Lax vs. Miralax: Key Differences in Laxative Types
To make an informed decision about which laxative to use for a child, it’s essential to understand the differences between Ex-Lax and Miralax:

- Ex-Lax (stimulant laxative): Stimulates intestinal muscle contractions
- Miralax (osmotic laxative): Draws water into the colon to soften stool
While both medications aim to relieve constipation, their mechanisms of action and potential side effects differ. Miralax is generally considered gentler and is often recommended for long-term use, while Ex-Lax is typically advised for short-term relief.
Are stimulant laxatives like Ex-Lax habit-forming?
Contrary to conventional wisdom, recent research suggests that stimulant laxatives like Ex-Lax may not be habit-forming in constipated children. A review article published in the Journal of Pediatric Surgery found no evidence of tolerance developing with senna-based laxatives. This challenges the long-held belief that stimulant laxatives should be used sparingly due to dependency concerns.
Ex-Lax in the Modified O’Regan Protocol (M.O.P.)
The Modified O’Regan Protocol (M.O.P.) is a treatment regimen designed to address bedwetting and accidents in children. While Ex-Lax is not a standard component of M.O.P., it can be a valuable adjunct in certain situations:

- When a child on M.O.P. struggles to achieve spontaneous bowel movements
- During the tapering phase of M.O.P. when transitioning from daily enemas
- As an additional tool to help clean out the rectum in conjunction with other M.O.P. treatments
Some parents report that adding Ex-Lax to their child’s M.O.P. regimen has been the key to achieving success in resolving bedwetting and accidents.
Safety and Efficacy of Ex-Lax for Pediatric Patients
When considering Ex-Lax for a constipated child, safety is paramount. The aforementioned review of eight studies on senna safety in constipated children found no evidence of harmful effects or dependency. However, it’s crucial to use Ex-Lax as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Can Ex-Lax replace enemas in treating bedwetting and accidents?
While Ex-Lax can be a helpful addition to treatment protocols, it is not recommended as a substitute for enemas in the M.O.P. regimen. Enemas are considered more effective at thoroughly cleaning out the rectum, which is crucial for resolving enuresis and encopresis.

Optimal Dosage and Timing of Ex-Lax for Children
Determining the right dosage of Ex-Lax for a child depends on various factors, including age, weight, and severity of constipation. It’s essential to consult with a pediatrician or gastroenterologist to establish the appropriate dose for your child.
How long does it take for Ex-Lax to work in children?
Ex-Lax typically takes 6 to 12 hours to produce a bowel movement in children. This timing can vary based on individual factors and the dosage administered. Parents should plan accordingly when giving Ex-Lax to their child, especially if timing is crucial (e.g., before school or bedtime).
Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Ex-Lax
While Ex-Lax is generally considered safe for short-term use in children, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects:
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Electrolyte imbalances (with prolonged use)
Parents should monitor their child’s response to Ex-Lax and discontinue use if severe side effects occur. It’s also crucial to ensure proper hydration when using any laxative.
Are there any contraindications for using Ex-Lax in children?
Ex-Lax should not be given to children with certain medical conditions, including:
- Intestinal obstruction
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Appendicitis
- Undiagnosed abdominal pain
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting Ex-Lax, especially if your child has any underlying health conditions.
Combining Ex-Lax with Other Constipation Treatments
Ex-Lax can be used in conjunction with other constipation treatments, but it’s essential to do so under medical supervision. Some potential combinations include:
- Ex-Lax with osmotic laxatives (e.g., Miralax)
- Ex-Lax as part of the M.O.P. regimen
- Ex-Lax with dietary changes and increased fluid intake
The effectiveness of these combinations can vary depending on the individual child’s needs and response to treatment.
How can Ex-Lax be incorporated into a comprehensive constipation management plan?
To effectively incorporate Ex-Lax into a child’s constipation management plan:

- Consult with a pediatric gastroenterologist to determine appropriate usage
- Start with the lowest effective dose and adjust as needed
- Monitor bowel movements and any side effects
- Use Ex-Lax in conjunction with dietary modifications and increased fluid intake
- Consider Ex-Lax as a short-term solution while addressing underlying causes of constipation
Long-term Considerations for Ex-Lax Use in Children
While Ex-Lax can be effective for short-term constipation relief, it’s important to consider the long-term implications of its use in children:
- Potential impact on natural bowel function
- Risk of electrolyte imbalances with prolonged use
- Importance of addressing underlying causes of chronic constipation
Parents and healthcare providers should work together to develop a comprehensive plan that addresses both immediate constipation relief and long-term gut health.
How can parents transition their child off Ex-Lax once constipation improves?
To safely transition a child off Ex-Lax:

- Gradually reduce the dosage under medical supervision
- Increase focus on dietary fiber and hydration
- Implement regular toileting habits and routines
- Consider natural alternatives like prune juice or fiber supplements
- Monitor bowel movements closely during the transition period
Alternative Treatments for Pediatric Constipation
While Ex-Lax can be effective, it’s not the only option for treating constipation in children. Other treatments to consider include:
- Dietary modifications (increased fiber and fluids)
- Regular exercise and physical activity
- Osmotic laxatives (e.g., Miralax, magnesium citrate)
- Probiotic supplements
- Behavioral interventions (e.g., scheduled toilet sits)
A comprehensive approach that combines multiple strategies often yields the best results in managing pediatric constipation.
What role do lifestyle changes play in managing childhood constipation?
Lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing and preventing constipation in children:
- Encouraging a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Ensuring adequate daily fluid intake
- Promoting regular physical activity
- Establishing consistent bathroom routines
- Addressing any underlying emotional or psychological factors
These changes, when implemented consistently, can significantly reduce the need for laxatives like Ex-Lax in the long term.

When to Seek Medical Attention for Childhood Constipation
While occasional constipation is common in children, certain signs warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody stools
- Persistent vomiting
- Significant weight loss
- Fever accompanying constipation
Parents should not hesitate to consult a healthcare provider if their child’s constipation persists despite home remedies or if there are concerns about underlying health issues.
How can parents differentiate between occasional and chronic constipation in children?
To distinguish between occasional and chronic constipation:
- Monitor frequency of bowel movements (less than three per week may indicate chronic constipation)
- Observe for signs of discomfort or pain during defecation
- Look for changes in appetite or energy levels
- Note any recurring episodes of constipation over several months
- Consider any patterns related to diet, stress, or lifestyle changes
If constipation becomes a recurring issue, it’s important to consult with a pediatrician to develop an appropriate long-term management plan.

The Role of Education in Managing Pediatric Constipation
Educating both parents and children about proper bowel health is crucial in managing and preventing constipation. This includes understanding:
- Normal bowel patterns and what constitutes constipation
- The importance of a balanced diet and hydration
- Proper toileting habits and positioning
- The potential consequences of chronic constipation
- When to seek medical help
By empowering families with knowledge, healthcare providers can improve outcomes and reduce the reliance on medications like Ex-Lax.
How can schools and caregivers support children with chronic constipation?
To support children with chronic constipation in school and other care settings:
- Educate staff about the child’s condition and management plan
- Ensure easy access to bathrooms and privacy
- Allow for scheduled bathroom breaks as needed
- Provide a supportive, non-judgmental environment
- Encourage healthy eating habits and adequate hydration
Collaboration between parents, healthcare providers, and caregivers is essential in managing constipation effectively across all aspects of a child’s life.

“Should I Give Ex-Lax to My Constipated Child?”
I get a lot of questions about Ex-Lax.
Parents want to know: What’s the difference between Ex-Lax and Miralax? Can Ex-Lax substitute for enemas? How much Ex-Lax can I safely give my child? How many hours does it take to kick in?
Ex-Lax is not a standard part of the Modified O’Regan Protocol (M.O.P.), the regimen I recommend for treating bedwetting and accidents. M.O.P. combines enemas and osmotic laxatives, a combination I have found resolves enuresis and encopresis better than any other treatment. However, Ex-Lax can be a helpful adjunct to M.O.P., and I have added it as an option on the M.O.P. Progression chart. For some children on M.O.P., Ex-Lax turns out to be the missing ingredient for success.
As one mom in our Facebook support group posted: “Even on M.O.P., our daughter wouldn’t ever completely empty on her own, but when we added Ex-Lax she did, and then she started having dry nights.”
For other families, Ex-Lax doesn’t help, but you won’t know until you try, and in certain circumstances, I think Ex-Lax is worth trying.
Below I answer questions I commonly get about Ex-Lax.
Q: What is the difference between Ex-Lax and Miralax?
A: Ex-Lax and products such as Senekot are stimulant laxatives. These products, derived from the senna plant, stimulate the intestinal muscles to contract and squeeze out idle poop.
By contrast, Miralax, a brand name for PEG 3350, is an osmotic laxative, a type of laxative that draws water into the colon to make poop mushier and help it slide through.
Other — and less controversial — osmotic laxatives include magnesium citrate (such as Natural Calm), lactulose (a prescription liquid), magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia and Pedia-Lax chewable tablets), and magnesium oxide (such as Mag-Go Kids).
Osmotic laxatives are not habit forming and are part of the daily M.O.P. regimen, second in importance to enemas.
According to the conventional wisdom, stimulant laxatives are habit forming and should be used sparingly; I, myself, have repeated this “wisdom,” having heard it from pediatric gastroenterologist colleagues.
However, I have not found any scientific evidence to support this notion, and neither did a recent review article conducted by a team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, in Columbus, Ohio, and published in the Journal of Pediatric Surgery. The article, which reviewed eight studies on senna safety in constipated children, found “no evidence of tolerance.”
And after much discussion with pediatric GI docs I trust, including one of the co-authors of the review article, I’ve come to believe that constipated children who use Ex-Lax do not actually become dependent on this medication to poop and that Ex-Lax is not habit-forming any more than enemas are — which is to say, not at all.
Certainly you would not want to give Ex-Lax (or enemas) to any person, adult or child, who is not constipated. But I believe that, as with enemas, Ex-Lax will only help clean out the child’s rectum and help the child overcome the withholding habit. At that point, the medication simply becomes unnecessary.
Q: If my doctor is opposed to enemas, can I use Ex-Lax as a substitute?
A: Not in my opinion. Though Ex-Lax does not seem to be habit forming, I believe enemas do a better job of cleaning out the rectum. I recommend Ex-Lax primarily as an extra tool for children who are on M.O.P. or who have completed protocol.
If your doctor believes enemas are risky or unsafe, I recommend handing him or her “The Physician’s Guide to M.O.P.” In this free download, I explain to colleagues why I consider enemas critical to resolving enuresis and encopresis.
Q: For children on M.O.P., how can Ex-Lax can be useful?
Parents of my Wake Forest clinic patients, as well as parents in our support group, have reported that Ex-Lax helps in these situations:
•When a child is on M.O.P. or M.O.P.+ — and even Double M.O.P. — but still has not achieved the all-important “spontaneous poop.”
One mom in our support group posted: “Ex-Lax is helping my son feel when he needs to poop. M.O.P. helped us eliminate poop accidents, but he never would self-initiate.”
M.O.P. helped us eliminate poop accidents, but he never would self-initiate.”
READ: “Has Your Child Achieved the Spontaneous Poop?”
Another mom posted: “Ex-Lax was the only change that brought my daughter to a clean X-ray.”
This girl took Ex-Lax in conjunction with Double M.O.P., a regimen that involves overnight oil-retention enemas followed by regular enemas in the morning. (Yes, that combination is safe, as olive oil and mineral oil enemas simply soften stool; they do not stimulate the colon.)
Her mom notes that the first time the girl took Ex-Lax, “it caused diarrhea, and she pooped four times.” But after that, Ex-Lax did not prompt her daughter to self-initiate pooping “and only produced poop on scheduled potty sits.”
•When a child is on Phase 2 or Phase 3 of M.O.P. — in other words, tapering from daily enemas — and goes a day without pooping.
A child who achieves dryness on M.O.P. but still has not achieved a daily spontaneous poop is a prime candidate for relapse. Some families who have learned this on the first go-around have been able to prevent relapse by adding Ex-Lax to the regimen on days when the child does not poop.
Some families who have learned this on the first go-around have been able to prevent relapse by adding Ex-Lax to the regimen on days when the child does not poop.
I recommend this only as a temporary situation. By the time children finish Phase 3 of M.O.P., they should be pooping on their own daily.
•When a child on M.O.P. goes on vacation, and enemas are too difficult to maintain.
It may not be realistic for a child to have enemas while on a trip, and that’s OK!
READ: 5 Ways to Manage Your Child’s Constipation and Bedwetting Treatment on Vacation
For a week or two, Ex-Lax may be the next best thing. During a vacation, it’s also important for the child to maintain the daily dose of osmotic laxative.
Q: What are possible side-effects of Ex-Lax?
A: Stomachache, cramps, diarrhea, and nausea are among the most commonly reported symptoms. Often these symptoms subside when the dose is reduced, even by ¼ square.
A far more rare symptom is blistering in the perineum (around the anus). The team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital found that among its own patients prescribed senna, 2.2% developed blistering and “all blistering episodes were related to high dose, night-time accidents, or intense diarrhea with a long period of stool to skin contact.”
The team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital found that among its own patients prescribed senna, 2.2% developed blistering and “all blistering episodes were related to high dose, night-time accidents, or intense diarrhea with a long period of stool to skin contact.”
The children who experienced blistering took, on average, more than 60 mg of senna daily, equivalent to four squares of Ex-Lax.
Q: How many hours does it take Ex-Lax to kick in?
A: Often 8 to 10 hours, but that depends on the child. For some kids, it works more quickly.
One mom posted that her 6-year-old daughter would take Ex-Lx around 7 a.m., “and around 2:30 p.m. the feeling would hit her.”
Another mom posted that she gives her 4-year-old Ex-Lax in the evening, and her daughter poops after breakfast.
I suggest experimenting with Ex-Lax on the weekends rather than on a school day. See how long it takes to work on your child, and then time the medication so the child will be at home, rather than at school, when the urge to poop kicks in.
Q: How much Ex-Lax is safe for children to take?
A: I urge patients to start by following the instructions on the Ex-Lax label: 2 squares, either once or twice a day for children 12 and older (so, a maximum total of 4 squares), and 1 square once or twice a day for children (maximum 2 squares) for kids ages 6 to 11. The label says to consult your doctor if your child is under 6. For these kids, I generally advise starting with 1/2 or 1 square per day.
Keep in mind these are general ranges. You have to experiment with what works for your child. Many children on M.O.P. take ¾ square or 1 ½ squares once or twice a day or squares. Some kids take 6 squares a day, with good results and no side effects. I think this is OK for a few weeks or periodically.
As with dosing osmotic laxatives and enemas, Ex-Lax dosing requires trial and error.
Q: I’m afraid to give my son more than 1 square of Ex-Lax per day because I worry he’ll have a poop accident at school due to urgency. Is this a realistic concern?
Is this a realistic concern?
A: I suggest trying it on the weekend first, so you can get an idea of how long it takes for Ex-Lax to work on your son. If you’re worried, have him take it after school.
Bowel Cleanout
Your child is constipated and needs help to clean out the large amount of stool (poop) in the intestine.
What you need to know
- Start the clean-out on a weekend or some other time when your child will be home for two days (not at school).
- Plan to have your child stay close to a bathroom until the stool has passed.
- After taking the medicine, your child should pass a large amount of stool within 24 hours.
- There are no food restrictions during the clean-out.
- Your child should have almost clear, watery stools by the end of the next day.
- If the medicine does not work or you do not know if it worked, call your child’s doctor’s office.

- Your child may have stomach pain or cramping during the clean-out. This might mean he or she needs to go to the bathroom. Explain that the pain will go away when the stool is gone. A warm bath may also help.
What medicine my child needs to take
- Miralax® is a powder that is mixed into a drink. It helps soften the stool. It is sold over the counter at your local pharmacy. You can also buy it at stores like Walmart or Target, or your child’s doctor may give you a prescription.
- Ex-Lax® is a small chewable chocolate-flavored square. It is used to stimulate the bowels to help the stool move. It is sold over the counter at your local pharmacy and stores like Walmart or Target.
- If your child prefers to take pills INSTEAD of the Ex-lax chew, you may give your child Dulcolax®. It is also sold over the counter at your local pharmacy, Walmart, Target, etc.
How to give this medicine to your child
- Mix ___ capsful of Miralax into ___ ounces of warm water, juice or Gatorade.
 Chill in the refrigerator if desired to improve taste. *Do not mix with milk products.
Chill in the refrigerator if desired to improve taste. *Do not mix with milk products. - In the morning only and 30 minutes BEFORE drinking the Miralax mixture, give your child ___ squares of Ex-Lax OR ___ mg of Dulcolax. *Do not give your child both Ex-Lax and Dulcolax. Give one or the other.
- Drink half of the Miralax mixture in the morning and the other half in the afternoon.
- Repeat steps above for day 2 of clean-out.
How to begin a maintenance dosing of medicine after clean-out:
- After the clean-out is completed begin taking a lower dose of Miralax daily as instructed by your provider.
- Give ½ to 1 capful in 8 ounces of juice or water each day. Please tolerate loose apple-sauce-to-pudding consistency stools for 1 to 2 months to ensure full treatment. You may decrease or increase the dose if needed.
- Some children also need ex-lax chocolate flavored squares a few times a week in addition to Miralax.
 If so, start with ½ square in the afternoon after school so the child will have a good bowel movement before the next school day.
If so, start with ½ square in the afternoon after school so the child will have a good bowel movement before the next school day.
**The goal is for your child to have a soft bowel movement every day. This is important for bladder and bowel health**
Bowel Cleanout (PDF)
HH-II-238 1/19 | Copyright 2019, Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Are They Safe or Just A Quick Fix?
Children are constipated and it’s becoming a growing issue. Paediatric constipation makes up 25% of the referrals to gastroenterologists and most commonly, doctors are recommending over-the-counter laxatives for children to deal with what is largely a mechanical issue. This means that kids are being given a bandaid solution to something that most often has a very clear root cause. And so the question lingers: are laxatives safe for children? And if they’re not, what are the short and long term consequences?
‘Everyone poops!’ according to a popular children’s book. But do they? If we look at the adult population, we know that nearly 20% of the North American population is constipated and we spend a whopping 800 million dollars on laxatives per year. The question is, when did this start? Children are not immune to constipation – up to 8% of American children are constipated and up to 36% in developing countries. It’s in the top 10 complaints paediatricians see in their offices. Financially, the health services (doctors, emergency visits, specialists, etc.) to address children’s constipation is close to $4 billion every year.
But do they? If we look at the adult population, we know that nearly 20% of the North American population is constipated and we spend a whopping 800 million dollars on laxatives per year. The question is, when did this start? Children are not immune to constipation – up to 8% of American children are constipated and up to 36% in developing countries. It’s in the top 10 complaints paediatricians see in their offices. Financially, the health services (doctors, emergency visits, specialists, etc.) to address children’s constipation is close to $4 billion every year.
The biggest challenge of all? Very few of the treatments, laxatives included, are addressing the root cause.
Causes of Pediatric Constipation
There is definitely some overlap with adult causes, but children have their unique reasons for constipation. Note that 95% of childhood constipation is functional – that means it doesn’t have physiological cause, like a particular condition, disease or abnormality. Some of the reasons kids get constipated are:
Some of the reasons kids get constipated are:
- Food Intolerances or allergies. These can be a cause of pediatric constipation. This is a big one and too often ignored as it can be deemed challenging to test or adhere to. However, consider what you would do as a parent if your child had a nut allergy. Constipation may not be life threatening, but it absolutely impacts the quality of life of your child. Children with gluten-sensitivity can have similar symptoms as children with celiac disease (which is very difficult to fully diagnose in children) and includes constipation. Cow’s milk in particular can be especially constipating for kids.
- Sugar and Refined Foods: This one is related to both not taking in enough fiber and the impact sugar and refined foods have on the microbiome of kids (and adults alike). Foods high in sugar can disrupt the microbial balance in the gut and contribute directly to both constipation or intermittent constipation and diarrhea often associated with irritable bowel syndrome.

- Not enough fibre. Fibre is essential to good poops because it gives bulk to our stool. Our intestines are a muscle, and fibre gives them a workout. If children’s diets are erratic or if they are picky eaters, it can be tough to get them to eat enough fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds and other fibrous foods that will help them poop.
- Not enough water. Water helps us to soak up the fibre we’re eating and shuttles poop through our bowels and out the back door. Usually, if we’re dehydrated, we won’t poop properly or have hard, dry poops that are hard to pass.
- Not enough exercise. Children can spend a lot of time being sedentary, just like adults. Between sitting at school and spending time in front of screens, children may not get enough fresh air and exercise to pump the poop through the bowels.
- Holding it in. You’ve probably been around a child who is dancing around, clearly needing to pee, but refusing to go.
 Sometimes, children resist the urges to poop. It may be because they don’t want to stop the activity they are doing (playing a game, watching a show, etc.), or they have some kind of fear about going to the bathroom (see the next point).
Sometimes, children resist the urges to poop. It may be because they don’t want to stop the activity they are doing (playing a game, watching a show, etc.), or they have some kind of fear about going to the bathroom (see the next point). - Stress or fears about going to the bathroom. Bathroom fears may seem irrational to us as adults, but for children they are very real. Perhaps they always feel rushed when they have to go, maybe they experience cramps or pain when pooping and that’s scary to them, or maybe they don’t like public or school bathrooms. Children who had a harder time with toilet training are also more likely to be constipated.
- Stress and anxiety in general. There is a deep connection between the gut and the brain, called the enteric nervous system. When we are stressed out, our minds impact our bowels and vice versa. If a child is worried or anxious, they may have trouble going to the bathroom.
It is not easy to watch a child suffer and so many parents turn to paediatric laxatives to help bring their children symptomatic relief.
Common Laxative Options
Note: brand names may vary depending on where you live.
Stool Softeners or Osmotics
What They Do: These help attract water to the stool so it can pass more easily.
Short Term Side Effects: Includes nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea and dehydration.
Common Osmotic Laxatives
Polyethylene Glycol
Brand Names: MiraLAX, Dulcolax Balance, GoLytely, MiraLax, Glycolax, GoEvac, CoLav, CoLyte, GaviLyte-C, GaviLyte-G, GaviLyte-N, NuLYTELY, polyethylene glycol electrolyte soln, polyethylene glycol powder, TriLyte
Risk of Use: This product isn’t recommended for children under 2 years and older children cannot take it for more than 2 weeks. Long-term risks include ulcers, dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, and potential renal toxicity.
Magnesium Hydroxide
Brand Names: Milk of Magnesia, Fleet Pedia-Lax
Risk of Use: Safety has not been established for children under 2. Short term risks include cramping, diarrhea, electrolyte imbalance and muscle weakness.
Short term risks include cramping, diarrhea, electrolyte imbalance and muscle weakness.
Lactulose
Brand Names: Enulose, Kristalose, Constulose, Generlac
Risk of Use: Electrolyte imbalance, blood sugar imbalance
Magnesium Citrate
Brand names: Citroma
Risks of Use: Safety isn’t established in children under 2. Should only be used occasionally for constipation.
Sorbitol
Brand Names: Sorbitol
Risks of Use: Electrolyte imbalance and dehydration.
Lubricants
What They Do: These are often oils, like mineral oil, that help to ‘grease’ the stool so it can pass.
Short Term Effects: Cramps, nausea, vomiting, incontinence, poor absorption (especially of fat-soluble vitamins), rectal discharge.
Mineral Oil
Brand Name: Kondremul Plain
Risks of Use: Mineral oil is a byproduct of the petroleum industry and it can boost our cancer risk.
Stimulants
What They Do: These work quickly and target the intestinal muscles so they will immediately get the poop going.
Short Term Effects: These can be quite harsh in some cases, and can cause bloating, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, diaper rash and blisters.
Common Stimulant Laxatives
Senna
Brand Names: Senokot, ExLax Regular Strength, Lax Pills, Little Tummys Stimulant Laxative Drops, Senexon, SennaGen, Senna Smooth, ExLax Maximum Strength, SenokotXTRA
Risks of Use: Finger clubbing (when the shape of your fingers change). This one is not recommended for children under 2 and can be potentially toxic to children under six if they have up to 15mg.
Bisacodyl
Brand Names: Dulcolax, Correctol, BisacEvac, Bisacolax, Codulax, Alophen, Feen A Mint, Fleet Stimulant Laxative, Laxit, Modane
Risks of Use: Because this one must be taken as a tablet, it’s not recommended for children under six. Risks include rectal bleeding, bowel obstruction and laxative dependence.
Bulking Agents
What They Do: These are essentially fibre supplements to help provide bulk to stool.
Short Term Effects: Can include gas, bloating and constipation
Psyllium
Brand Names: Metamucil, Fiberall, Perdiem Fiber
Risks of Use: Psyllium in and of itself isn’t a dangerous ingredient. Unfortunately, it’s all of the additional unnecessary things like artificial colours, preservatives and loads of sugar that can be harmful. You can read up fully on the safety of Metamucil here.
The Non-Active Ingredients In Laxatives
“Non-active” or “non-medicinal” ingredients on labels are the components that don’t have the primary action, but are usually used to bind, colour, flavour or add shelf-life to a product. Laxatives for children can be in chewable tablets or liquid form, and laxative manufacturers end up adding artificial colours and flavours to make them taste better.
Some common “Non-Active” or Non-Medicinal Ingredients Include:
- Colloidal silicon dioxide: This is a suspected human carcinogen and may cause kidney stones.
- FD & C red #40 aluminum lake (or other artificial flavour): In addition to its carcinogenic properties and the risk of hypersensitivity reactions, Red 40 can also be contaminated with further carcinogens. Other animal studies have linked Red 40 to physical and developmental toxicity and DNA damage.
- Flavor: There isn’t much difference between natural and artificial flavours. Both typically start out as a real food and through many lab experiments and processes end up as a concentrated flavour agent. These flavor agents have been shown to adversely effect our body’s detoxification pathways and have been associated with an increased risk in brain tumour development.
- Magnesium stearate: This may have the potential to cause allergic reactions. It can also be derived from palm oil, an oil that has led to habitat damage and environmental degredation.
- Maltodextrin: This ingredient is derived from wheat or corn and unless otherwise specified, the maltodextrin is likely coming from GMO corn with all the associated health risks. Several studies have linked maltodextrin consumption to the suppression of “good bacteria” in the digestive system increasing risk of gastro symptoms and intestinal inflammation.
- Mannitol: A sugar alcohol that can cause dizziness, headaches, nausea, vomiting, and fluid imbalances.
- Sorbitol: As mentioned earlier, this sugar alcohol can lead to electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, bloating, stomach cramps and diarrhea.
- Stearic acid: This is a fatty acid that is often derived from palm oil or cottonseed oil, which is a highly processed industrial oil that is usually riddled with pesticides (not to mention it’s also genetically modified.)
- Sucralose: This is an artificial sweetener with a host of risks like tumours, digestive issues (including altering the microbiome), diabetes, obesity, neurological symptoms, and many more.
Essentially what we’ve got here are artificial colours, flavours, additives and bunch of sweeteners. And do we really need to be giving our children more sugar?
The problem with children’s laxatives is when constipation becomes a chronic problem, they become dependent on them. So you’re constantly giving them these additional harmful ingredients on a daily basis, while also increasing their dependence on using laxatives to poop.
As well, with older children, like pre-teens and teens, laxative abuse can become a harmful weight loss method.
We want our children to have a lifetime of healthy pooping and there are a number of physical and emotional ways we can support them in this!
Boost whole, plant-based food intake
We know that plant-based foods like veggies, fruits, nuts, seeds, beans and legumes are rich sources of fibre, as well as vitamins and minerals that are essential to children’s health. Feed your kids both raw and cooked vegetables for variety, and get them involved as much as you can in the cooking process. Take them with you to the grocery store and let them pick out fruits and vegetables, and get them involved in the kitchen (using age-appropriate tools).
More tips and recipe inspiration here:
Eliminate common allergens
Evidence indicates that this can help with children’s constipation. I recommend eliminating gluten and dairy for sure as a starting point. You can then expand to try eliminating eggs, soy, nuts, peanuts and fish/shellfish. Experiment to see what works and what doesn’t.
Experiment with high-fibre FOODS
Vegetables are the top option. You can also add bulking foods like chia and flax, which also have mucilaginous properties that are beneficial to the digestive tract. Psyllium works best when taken on its own for constipation, while chia and flax can be adding to a number of delicious recipes like chia pudding or smoothies.
Boost fluid consumption
Aim to get your children drinking more liquids. Water is a top choice, or herbal teas if they are into them. You can also go for smoothies, green juice, vegetable broth or bone broth, nut milk or coconut milk. Remember that fruits and vegetables also have a high water intake so that counts too.
Give them time in the bathroom
Our lives are very scheduled, and often that extends to our children’s lives. It’s important to give children the time and space to go to the bathroom, which encourages them to fully relax and have a bowel movement. Younger kids might appreciate you being there, reading them a book or playing some music or singing songs.
Begin creating bowel habits by allowing your child 5-10 minutes in the bathroom, even if that means getting up a little earlier. If it seems impossible during the week, start off on the weekends and then transition to schooldays.
Decipher any bathrooms fears and address them
As I mentioned earlier, kids may be afraid of pooping for a particular reason. Suss out what that reason is and then determine the best solution. If necessary, recruit family members, teachers or medical professionals to help.
Try probiotics
Probiotics are important to digestion, immunity and brain health. They are beneficial to adult constipation, reducing transit time and improving stool consistency and frequency. In kids, probiotics can improve chronic constipation symptoms and can reduce abdominal pain. I recommend working with your favourite natural health care practitioner for the best dosages.
Alternatively, you can try adding fermented foods into your child’s diet for probiotic benefit.
Abdominal massage
Massaging the belly can help improve constipation and quality of life. You can do this for young children by massaging in circular motions, starting at the right hand side (where the colon begins) and then moving to the left, down, and to the right again. Older children may want to try this themselves.
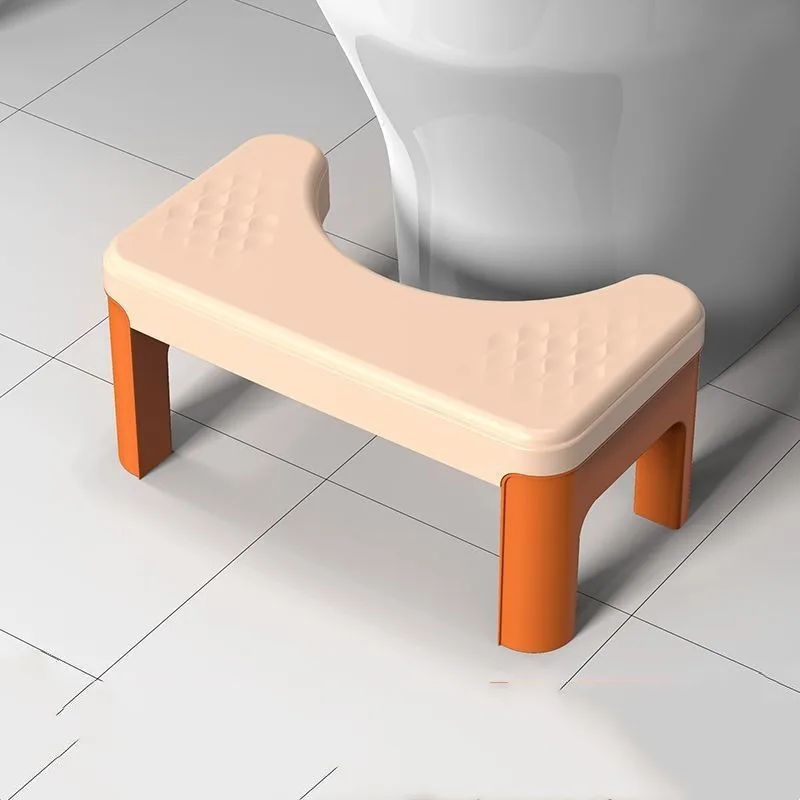
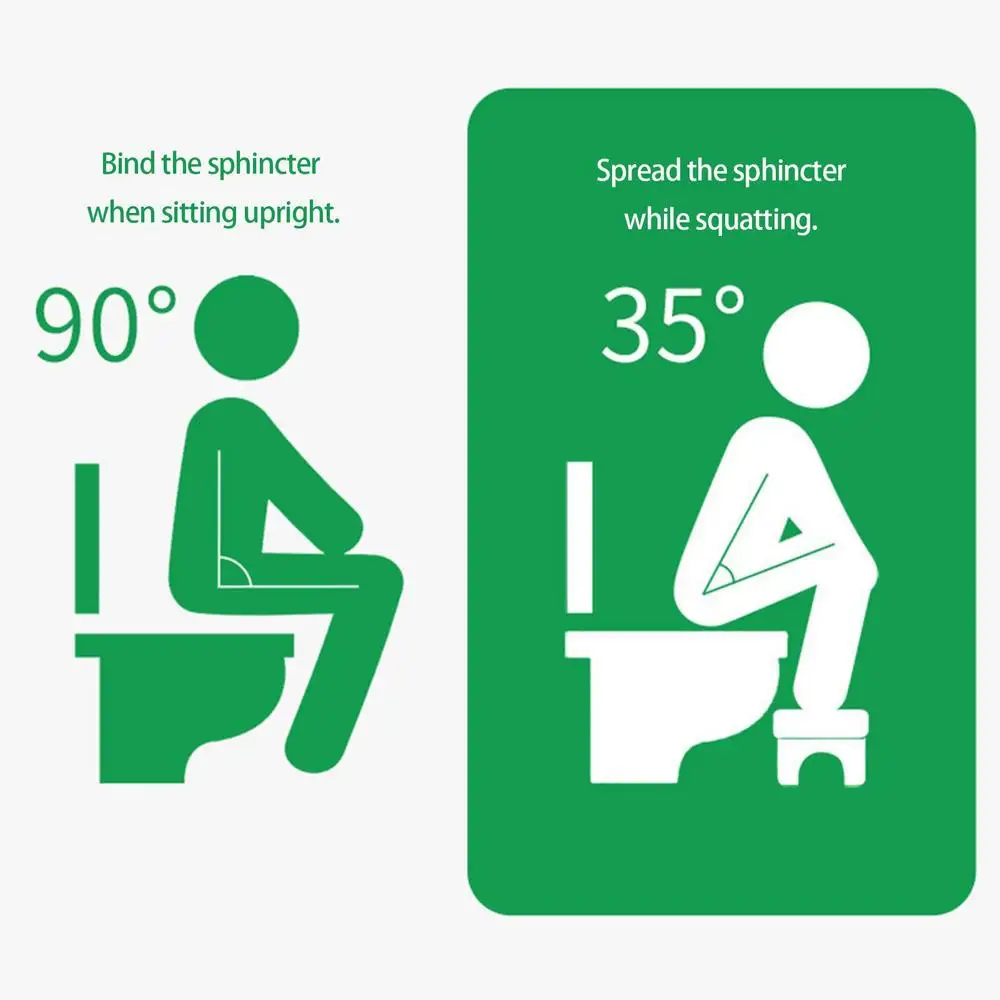
Get a squatty potty
The toilet is actually not the best invention when it comes to gut health. For thousands of years, we squatted – this helps to support our colon muscles and boost elimination. There are kid-sized squatty potties that will help them get into a good ‘pooping position.’
Talk about pooping openly
There is a lot of secrecy and shame about pooping in our society. If kids are scared to talk about it, they may also be intimidated about actually doing it. Try to avoid making negative comments about bowel movements, whether yours or your child’s. Talk about pooping – be open and proud!
It can be challenging to determine what the cause is for your child. Unfortunately, too often your paediatrician may not have the time to troubleshoot with you and can jump to recommending laxatives and then after a time, recommend a scope. This can have an even further detrimental effect, and contribute to an increase in stressful associations for your child. Given that the majority of constipation issues in children are functional, it may simply be a matter of trial and error to determine what the main contributing factors are. This is absolutely worth pursuing and managing as early as possible, to help ensure healthy, natural bathroom habits as your child grows.
If you have any tips that have worked for your kids, please share in the comments!
Fleet Pedia-Lax Saline Laxative, Kid-Friendly Watermelon Flavor, Chewable Tablets, 30 tablets
Fleet Pedia-Lax Saline Laxative, Kid-Friendly Watermelon Flavor, Chewable Tablets, 30 tablets | Rite Aid
The store will not work correctly in the case when cookies are disabled.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser.
For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
You have signed up successfully
{{#if error}}
{{/if}}
{{success}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{#genertatePrescriptionText pharmacyDetails.count}}
Your {{count}} {{prescriptions}} {{status}}
{{/genertatePrescriptionText}}
login
Please log in to your Pharmacy account
{{/in}}
Add Pharmacy Management
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
Allergy Relief Products. Shop Now
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
{{/in}}
From the Manufacturer
More Information
| Product Name | Fleet Pedia-Lax Saline Laxative Chewable Tablets, Watermelon – 30 ct |
|---|---|
| Sub Brand | Pedia-Lax |
| Package Count | 30 |
| Container Type | box |
| Form | Chewable Tablet |
| Country of Manufacture | United States |
| Best For | Digestive Health |
| Ingredient Preference | Made in the USA |
| Prop 65 | No |
Reviews 2
Customer Reviews
Great product
This product has been a lifesaver for my little guy who suffers from constipation. Typically within 6 hours there are results.
Review by
TunaPosted on
Made me extremely sick
I am regular size adult and used for only slight constipation, i took the max dose which is for kids of 6 tablets figuring i’d be fine as its a kids dose. I got severe painful waves of cramps, severe diarreah, a little dizziness, severe nausea . Terrible symptoms lasted about 2 hours or so and then got extreme chills for another 2 hours. I feel like i was hit by a semi truck and have been in bed for several hours now.
Review by
ajPosted on
PRODUCT DETAILS
Item No. 0350562
Poop should just happen. When it doesn’t, there’s Pedia-Lax. Formulated for kids ages 2-11, Pedia-Lax Laxative Chewable Tablets help to provide relief from occasional constipation in 30 minutes to 6 hours. The tasty watermelon flavored chewable tablets contain magnesium hydroxide, a saline laxative that offers gentle, stimulant-free relief. See package for full instructions and dosage information. Pedia-Lax is the Number One pediatrician-recommended children’s laxative brand (1). Unlike adult laxatives, Pedia-Lax Laxative Chewable Tablets are formulated for kids and are a safe solution for kids’ occasional constipation. Parents keep kids growing and Pedia-Lax helps keep kids going. (1) IQVIA, using the ProVoice Survey October 1, 2019 to October 31, 2019. Pedia-Lax products are FSA- and HSA-eligible in the U.S.
- Provides gentle relief from occasional constipation in 30 minutes to 6 hours.
- Formulated for kids ages 2-11
- Tasty, easy-to-take watermelon flavored chewable tablets.
- Contain magnesium hydroxide, a saline laxative that offers gentle relief.
- Pedia-Lax is the Number One pediatrician-recommended children’s laxative brand (1) (1) IQVIA, using the ProVoice Survey October 1, 2019 to October 31, 2019.
Over-the-counter digestive aids are now available for FSA and HSA reimbursement without a prescription. For any questions you may have regarding FSAs or HSAs, please browse our FAQ.
HOW TO USE
Use dosage chart for proper dosing. Doses may be taken as a single daily dose or in divided doses. Drink a full glass (8 ounces) of liquid with each dose. Children 6 to under 12 years starting dose 3-6 tablets. Maximum dose per day (24 hours) 6 tablets. Children 2 to under 6 years starting dose 1-3 tablets. Maximum dose per day (24 hours) 3 tablets. Children under 2 years ask a doctor.
INGREDIENTS
Active Ingredients: In Each Tablet: Magnesium Hydroxide (400 Mg). Purpose: Saline Laxative. Inactive Ingredients: Colloidal Silicon Dioxide, Fd&C Red 40 Aluminum Lake, Flavor, Magnesium Stearate, Maltodextrin, Mannitol, Sorbitol, Stearic Acid, Sucralose.
SAFETY
Ask a doctor before using any laxative if you child has:
Kidney disease.
A magnesium-restricted diet.
Abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting.
A sudden change in bowel habits lasting more than 2 weeks.
Already used a laxative for more than 1 week.
Stop using this product and consult a doctor if your child:
Has rectal bleeding.
Does not have a bowel movement within 6 hours of taking this product.
These symptoms may be signs of a serious condition.
Keep out of reach of children.
In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center right away
Other Information:
The top of the bottle is sealed with foil for your safety. Do not use if foil imprinted “sealed for your protection” is broken or missing.
WARNING: This product can expose you to chemicals including ,
which is known to the State of California to cause . For more
information go to https://www.p65warnings.ca.gov.
Recommendations
Close
Just a moment while we apply your discounts.
=”evenodd”>!
Constipation
Constipation is defined as:
- Decreased frequency of bowel movements (generally every 3 or more days)
- Stool is harder, making it difficult or painful to pass
- Incomplete evacuation of bowel movement (BM) – Cannot pass all of the stool
Diagnosing Constipation
Using the Bristol stool chart will help you tell your doctor the kind of BMs your child is having. It is important for your doctor to know this so he or she can properly diagnose and treat your child.
A normal stool should be types 4 and 5. Type 6 may be normal for infants. Types 1-3 may suggest constipation and types 6 and 7 may suggest diarrhea.
It is also important to tell the doctor:
- About any prescription and over-the-counter medications and vitamins and supplements your child takes
- If your child’s abdomen (lower stomach) is swollen and/or hard (abdominal distension)
- If your child has lost weight or is not eating very much if at all
- If your child has a lot of rectal bleeding. It is not unusual to have an occasional small amount of rectal bleeding due to anal fissure.
Treating Constipation
Treating constipation is not an exact science. There are several treatment options to meet the unique needs of each child. Commonly used medications are available over the counter. Treatment typically includes diet changes and medications and has two phases – a three-day, aggressive, cleanout phase and a maintenance phase. Depending on your child’s age, the doctor may recommend one of the following plans.
Age 0-2 Years
Initial approach may include:
- prune/apple juice 2-3 oz. daily
- glycerin suppository
- rectal stimulation using Q tip or rectal thermometer
- consider limiting dairy intake
If the above approaches do not work by themselves, consider adding one of the following medications. Before you do, talk to your child’s doctor. It is important to include your child’s doctor in medical decision-making.
- ¼ capful polyethylene glycol (PEG) (also known as MiraLax, ClearLax, GlycoLax, etc.) daily, with or without glycerin suppository
- ½ capful PEG daily, with or without glycerin suppository
Continue the dose of PEG that works; give glycerin suppository if no BM in 3 days
Toddlers and Pre-Pubertal Children
Initial Phase
- Limit dairy intake
- High fiber diet (age + 5 grams daily) – use soluble fibers such as ‘psyllium husk’
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid withholding behavior
- Scheduled toilet times – before school, after every meal
- Encourage using bathrooms in school
If the above approaches do not work by themselves, consider adding one of the following medications. Before you do, talk to your child’s doctor. It is important to include your child’s doctor in medical decision-making.
- Start polyethylene glycol (PEG) (also known as MiraLax, ClearLax, GlycoLax, etc.) ½ capful daily
- If no help, double PEG dose (max 6 capfuls daily) until stools are soft.
If no success add a stimulant medication (twice a week)
- age 2-3 years: ½ Ex-Lax, or 1 glycerin or dulcolax suppository
- age 3-6 years: ½ to 1 Ex-Lax or ½ pediatric Fleet enema
- age 6 and above: 1-2 Ex-Lax or 1 pediatric Fleet enema
Maintenance Phase
- PEG – use the dose that worked before (every day)
- Stimulant medication – that worked before (twice a week)
Patients with purposeful withholding behavior due to control issues – referral to psychologist or behavioral therapist.
Teenagers
Initial Phase
- Limit dairy intake
- High fiber diet (age+5 grams daily) – use soluble fibers such as ‘psyllium husk’
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid withholding behavior – encourage using bathrooms in school
- Scheduled toilet times – after every meal
If the above approaches do not work by themselves, consider adding one of the following medications. Before you do, talk to your child’s doctor. It is important to include your child’s doctor in medical decision-making.
- Start polyethylene glycol (PEG) (also known as MiraLax, ClearLax, GlycoLax, etc.) 1 capful daily
- If no success, double PEG dose (max 6 capfuls daily) until stools are soft
- If no success add a stimulant medication (twice a week): 1-2 Ex-Lax or 1 pediatric fleet enema
Maintenance Phase
- PEG – dose that worked before (every day)
- Stimulant medication – that has worked before (twice a week)
Patients with purposeful withholding behavior due to control issues – referral to psychologist or behavioral therapist.
It may take a few days for the treatment to work. Contact your child’s doctor if you have questions or you do not feel the treatment is working after several days.
Printable Patient Information
Constipation
Management of Functional Constipation
Constipation Cleanout Instructions
Make an Appointment
If you or someone you care for is experiencing worrisome symptoms, we encourage you to make an appointment with one of our pediatric gastroenterologists, adult gastroenterologists or colorectal surgeons.
Lounge Life: Inside the AA Admirals Club Kids Lounge at LAX
Playgrounds at airports are few and far but Trips + Giggles will be making note of them where we see them. Know of a cool airport playground? Let us know!
It’s good to be an American…Airlines Admirals Club member. That’s because the airline’s lounge at Los Angeles International Airport has a pretty sweet children’s play area.
The bright and happy space features a couple of kid-sized tables where smaller children can work on puzzles, drawings or play with their toys. A leather banquette with tiny drink tables is a perfect place for parents to sit and watch the kids while sipping on their gin and tonic coffee. On the opposite end of the room is a media center for older children with two PCs. (The lounge has free WiFi too.) There’s plenty of toys found throughout the room in boxes, so the discovery of these should keep the kid occupied for a while.
This lounge is set to undego a makeover later this year but we’re pretty sure they will keep the kids’ area because why not? Already, the Admirals Lounge at LAX has been making small upgrades here and there, most notably by bringing on an executive chef, Chris Hsieh, who is cooking up fresh, and healthy dishes made with local ingredients. These offerings, available at self-serve stations and on a lounge menu, are mindful of many dietary restrictions including gluten-free, vegetarian and perhaps, most importantly for when you’re about to get on an airplane, low sodium. In short, this is airline lounge food you would actually eat and want to feed to your children.
Access to this lounge is guaranteed to first and business class passengers of American Airlines and other elite program members. You can see all those options here. But a day pass can be purchased for $50 and that gets three children up to the age of 18 in for free.
If you’re not feeling the day pass, there aren’t any other playground options in Terminal 4, other than letting the kids run wild through the gates. We really wish all airports and terminals had what LAX’s Tom Bradley International Terminal has–a great open playground for kids called The Beach. Someday…..
OTHER STORIES YOU MIGHT LIKE:
Welcome to The Beach at Los Angeles International Airport
Another Airport Playground: This Time at the AA Admirals Club at JFK
No Comments Yet
Login or Sign Up to comment
Why Traveling Families Should Avoid Flights Connecting in LAX
LAX may look nice, but don’t be deceived when traveling with kids…
I avoid Los Angeles’s main airport – LAX – like the plague. I’m lucky that I’m able to do so because I live in the San Francisco Bay Area, which is an excellent international and domestic gateway in its own right. Only very rarely does LAX have substantially better options for my travel needs.
My family traveled from SFO to Montreal on Air Canada last month. In order to redeem our United miles for business class tickets (at the saver rate, of course!), we had to accept a flight with a connection on the way back: YUL to LAX on Air Canada in business then LAX to SFO on United in coach. I knew that Air Canada and United were in different LAX terminals, and I knew that I would have to leave the secure area and go through a TSA checkpoint again in the United terminal.
But I’m a seasoned traveler. My daughter is old enough to carry her own carry-on bag and walk by herself. Our baby is portable and easy. My husband and I were traveling together, so we had two sets of adult hands to make the logistics work. We also knew we would pre-clear immigration and customs in Montreal, so our arrival at LAX would be equivalent to arriving on a US domestic flight. And our bags would be checked through to our final destination in SFO.
Seriously, how bad could connecting in LAX be?
It was bad.
After deplaning, we looked around for signs to direct us to the terminal where United is located. Nothing. We also looked at the departures boards to see if our United flight and gate would be listed there. Nothing. As far as we could tell, the only way to find out what terminal you need to change to is to (1) do the research before your trip, (2) pull up LAX info on your smartphone when you arrive or (3) ask an airline employee — if you can find one. There is simply no signage when you arrive in the Air Canada terminal that tells you where your United connection is located. This is crazy! I can only imagine that this is a connection that hundreds of people make daily since the airlines are in Star Alliance together.
We finally found an airline employee and learned that we needed to make our way from Terminal 2 to Terminal 7. I’m always willing to walk, but it was simply too long of a distance with a 5 year old and a stroller. We went out to the curb and looked for the free shuttle bus between terminals.
Again, no signage. Instead, we saw lots of folks wandering aimlessly until we all found an airport employee to direct us to the shuttle stop in the center island and tell us what letter shuttle to take (Shuttle A, in case you are wondering.). And then we waited. And waited. And waited. The number of people waiting increased until we reached the point where we doubted whether everyone would fit on a single shuttle when it finally did arrive.
Right at 25 minutes later, a shuttle finally came. We hurriedly folded up our stroller, grabbed our carry on bags, and elbowed through a bunch of pushy people all trying to make tight connections and desperately hoping to get on this one lonely shuttle. We made it. I even snagged a seat with the baby in my lap, although other families with kids were not so lucky.
We then inched our way, terminal-by-terminal from Terminal 2 to Terminal 7. That’s four intermediate stops if you are keeping score. At each stop, we spotted dozens and dozens of people hoping to snag a spot on this solitary shuttle. Lots of pushing and shoving and general unpleasantness. Each stop took about 5 minutes to off-load and load a new group of passengers. But we finally made it to our terminal.
I’d estimate it took well over an hour to make it from our Air Canada gate to the door of Terminal 7. And then, of course, we had another TSA security checkpoint to clear. Something is wrong when dealing with the TSA is the easiest part of your travel day!
Although it was nice to travel on the cr0ss-country portion of our trip in business class, I’m not sure I’d do it again if it means a terminal change in LAX. Too much hassle.
My final words of advice for those of you considering making a connection in LAX that involves a terminal change with kids: don’t do it. (And really don’t do it if you are a parent traveling solo. And especially don’t do it if you have to clear customs with kids. And also don’t do it if you are an air travel novice.)
LAX is truly an embarrassment. And logistically no fun for anyone, particularly families with kids.
Have you had an LAX connection horror story, either with or without kids? Share your experiences in the comments!
Share this!:
90,000 Child immunity. How to increase the immunity of a child? ›Clinic” Forpost “
Before thinking about how to increase the immunity of a child, make sure that this is not a congenital disorder!
In children, before trying to increase immunity, it is necessary to identify whether this is a congenital disorder. It is in childhood that such a disease as congenital immunodeficiency manifests itself. Parents often noticing any problems with the baby’s health (frequent colds in the child, heals for a long time, weak, etc.)assuming that the culprit of all this is weak immunity, they are trying with all their might to increase it. And if you stimulate the immune system against the background of some kind of congenital pathology, then this can lead to unforeseen consequences. And not only will it not strengthen the immune system, but also harm. Stimulating and whipping up the weakened and depleted immunity of the child will only lead to even greater exhaustion and failure in his work.
Indications for visiting an immunologist:
- the child suffers from ARVI more than 6 times a year;
- complications arise after colds;
- the baby suffers from allergies;
- the child has a herpes rash on the lips;
- more than once the child suffered from purulent otitis media or pneumonia, etc.
If constant violations are repeated for more than six months or a year, then it is important for the child to have an immunogram. It is advisable to conduct an immunogram for a child after 3 years, then it already better reflects the state of the child’s immunity and becomes informative.
How to raise the immunity of a child with acquired immunodeficiency
So, the first thing to do in childhood is to determine the congenital or acquired functional deficiency of the child’s immune system.In the case of not congenital, but acquired disorders, more emphasis should be placed on increasing the nonspecific factors of strengthening the child’s immunity. There is no need to give any strong immunostimulants, immune drugs to children, as adults. Children should be approached more subtly, because children have more physiological immunodeficiency. So nature itself came up with that the child’s body should get acquainted with all infections and it is easier to transfer them in childhood. Everyone knows that it is better to get sick with chickenpox just in childhood.After all, children tolerate high temperatures much easier than adults.
Recommendations: how to strengthen the immunity of a child
After examination and laboratory tests, if you stimulate the immune system, then more by physiological methods. This applies to the daily routine, nutrition of the child, hardening, drugs that provide additional protein for the immune system.
In extreme cases, with more persistent disorders, immunomodulators are advisable, or immune drugs with a replacement purpose (viferon is a ready-made interferon for a certain period of time to support the child’s immune system, nucleinate is a protein donor, etc.) There are many immunomodulators that increase the activity of the immune system and strengthen the body’s ability to resist infections.
However, the main thing that parents should understand is that immunotherapy should not become a platform for experiments on their own child. Such drugs can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor and after the fact of immunodeficiency or any disorder in the immune system is established on the basis of examining the baby and studying the results of his laboratory tests.
Natural stimulants of the child’s immunity
These are hunger, cold and physical activity. Extremism is unacceptable in any of these three directions – there is no need to specifically starve a child, overload it with physical exercises, or make it freeze. But something else is more important: opposite actions (excess food and heat, restriction of physical activity) very quickly lead to suppression of immunity (frequent infectious diseases) or to perverse reactions of immunity, that is, it seems to react, but not as it should (allergic or infectious and allergic diseases).
The correct daily regimen will help increase the immunity of a child
It is important that the child is not exhausted and overworked.
Each child has a significantly accelerated metabolism compared to adults. Therefore, on the one hand, the child is depleted faster, and on the other hand, it recovers faster than an adult. The elimination organs work better, everything in the children’s body works faster, burns faster, but new things are born faster.
Adequate sleep helps to strengthen the child’s immunity
For strong immunity, a child needs to sleep twice a day: at night and during the day, while sleeping longer at night than adults.In a dream, children grow better, because the metabolism during sleep in children remains faster than in adults. Proper rest works on the cells of the immune system and helps to boost the child’s immunity.
Rational and proper nutrition will strengthen the child’s immunity
The child’s nutrition should be more frequent, because the enzymatic system is still immature, it cannot digest and assimilate a lot of food in one meal. Therefore, a child should not be overfed, he should be given food in small portions, but more often than an adult.And the diet should be more varied, contain more vitamins, due to the same accelerated metabolism. Therefore, to strengthen the child’s immunity, it is necessary that the body has enough vitamins, trace elements, proteins and other useful and necessary substances. Remember that the child is also growing and needs to gain weight.
Good functioning of the digestive system is directly related to a strong and healthy immune system. After all, about 60-70% of immune cells are located in the gastrointestinal tract! It becomes clear that proper nutrition in the formation of powerful immunity in a child plays an important role.
Hardening is an excellent means to increase the immunity of a child
Children, like adults, have a lot of receptors on the ears, palms and soles, which are associated with the entire body. If you irritate and create some kind of extreme conditions for these receptors, they will send a message or impulse to alertness to all organs and systems, including the immune system.
What is the essence of hardening while strengthening the child’s immunity
Most are convinced that hardening is accustoming to the cold.For example, walking in the snow in shorts, etc.
In fact, the essence of hardening is to train the mucous membranes to quickly respond to a sudden change in temperature. After such training, the mucous membranes become a serious obstacle to viral infection.
How to temper a child correctly in order to strengthen the immune system?
Simple training – alternate “treatment” with cold and hot water of the forearms – from the hand to the elbow, from the feet to the knee. Let’s decide on the temperature of the water: cold – +20 ° C, hot – +35 ° C.Both the one and the other cannot cause negative feelings in the child. And contrast plays a role in hardening. In this case, the same “tolerable” difference of 15 ° C. Pouring should be done daily – 5-7 minutes a day. Doesn’t matter, in the morning or in the evening. But for a very long time – from autumn to late spring.
During this alertness, stress hormones are released. These hormones tone the blood vessels and the entire body on alert. Constantly the immune system and the body cannot be in this state and produce stress hormones.But there are people who have a lack of these hormones, and it is also useful for people who sleep for a long time, move little and are emotionally sluggish.
The psychological state of a child is an important factor in healthy immunity
The psychological factor is very important, the mood greatly affects the state of the child’s immunity. Again, through stress hormones: positive emotion is also stress, negative emotion is also stress. When a child is not noticed, is not given food for development, this negatively affects his immune system.It is important to train the child’s resistance to stress, which will further affect the stability of the immune system. This is also a kind of immune stimulation.
Attitude to health will increase the child’s immunity
Raising the usual ARI to the rank of an emergency, you can involuntarily inspire a child that he must be sick. And this attitude gives a negative result. It is reasonable to explain that fever, cough, runny nose are a natural reaction to the virus, nothing terrible happens.You just need to help the body cope with a cold: drink infusions of herbs, potions, steam your legs, if necessary, lie down. In this case, you can say: “You are already recovering, another day or two – and everything will be fine.”
“It is a mistake to think that a ‘weak’ child will not let ‘strong’ children learn, that he will make them stupider.”
This spring, not all future first-graders entered the schools their parents dreamed of. Someone was turned off based on the results of training in preparatory courses, someone did not pass the test selection or interview.For one reason or another, the children did not fit the school.
Useful Mela newsletter twice a week: Tuesday and Friday
I’m talking about elementary school – about children who just came to study or moved from one school to another in elementary grades. For most parents, this situation seems, though offensive, but fair. In the end, good schools are not rubbery – they need to teach those children who will pull a strong program, who can learn a lot and with enthusiasm, and who will ultimately be the face of this school.The fact that it is customary in our country to judge a school by its face, and the face is understood as indicators of academic performance, is a separate conversation.
A story with endless contests, selections, reviews, scarcity, elitism (there is not enough good for everyone) – deep in the blood of our man
Announce a frenzied competition for an educational institution, and people will reach out to break through a closed door – a matter of honor. No room for everyone? Let’s open more good schools, let’s make all schools equally good.Don’t like the word “the same”?
Talking about progressive models of education, we still continue to select children for schools. And when a number of gymnasiums canceled testing for admission to the first grade and began to take all children by registration, this caused a serious flurry of discontent among a number of parents – horror, children come “from the street”, schools will lose their brand, what to do, where do they go now? Paradoxically, we perceived even this simple condition – place of residence – as a challenge. They began to trade in registrations, getting to school is another challenge.It is sad that behind all these selections, sophisticated psychological tests, the irrepressible ardor of educators and parents, the child himself is lost.
Some need a child to take away, others – to enter, to attach. The first is to withstand, to withstand the assault of the maternal masses and to make sure that the school does not get “goods” that are not conditioned, the second is to convince the first that their child is “the same”, of high quality. What the child himself needs is silent.
Schools, progressive and fashionable, are determined to take children with high emotional intelligence, developed voluntary regulation of their activities, developed abstract-logical thinking, good speech, able to work in a team, hear and listen, motivated and eager to learn.True, I have always naively believed that raising such children is precisely the task of an educational institution, otherwise why would it be?
Today, knowledge literally lies under the pads of the fingers, and the school – the same, updated, modern – is not at all about teaching talents for the sake of a line in the ranking. At what point did the school become so close to sports? Who needs “achievement” in education and is it necessary in principle? Think about it, parents looking to shove their child into a high performing Olympiad school.
In the modern world, education is rapidly moving towards individualization. In fact, from an institution that gives a certain amount of knowledge, turning into a breeding ground for the development of personality through interaction with different people, through cognition, study of oneself and one’s capabilities. If you like, I generally see the school of the future as a kind of center of modular education – a place where you can learn and try a lot, as well as prepare for the exams necessary to continue your professional education or scientific career.I’m talking about the center of opportunity, not the center of limitations. Stratification with such an approach into those who need serious study and those who are fully satisfied with practical skills in certain areas is inevitable. And this is great, because it will allow you to maximize the potential of everyone.
When a school declares that each child has its own talent hidden, its task is to reveal this talent. And to open it first of all for the child himself, and not for the external public. Does the school solve this problem? If not, it’s old school – a school that has to die.A school that is not needed.
Humanity has accumulated a sufficient layer of scientific research to recognize the value of individual differences between people
We also have everything necessary to convey this value to the child in order to introduce him to himself. This knowledge has long been in practice, the world lives on it. Nevertheless, the school continues to work with those who meet a certain standard. For example, for me as a neuropsychologist, this standard primarily concerns left-brain children.Of those who are rejected in the beginning, there are a lot of left-handers – children who need time to adapt to these very standards. However, not only children with a non-standard course of cognitive and mental processes are left out, but also many children who do not have a propensity for intellectual activity, but have a lot of other talents. It is difficult to teach such children – this requires from the teacher at least attention to a small personality, and as a maximum – a desire to expand his methodological arsenal.
For me, a pro, a mentor and a guru is someone who is interested in a child as he is. The one who is ready to teach anyone who came to him – who will find the right word for everyone. There is a lot of talk now about coaching in education. This is natural. If earlier the teacher worked more as a transmitting link, a bearer of knowledge, now he is more of a coach – someone who helps to follow the path of education, inspires, helps to find energy and foster motivation. There are few teachers with coaching competencies, there will not be enough for all schools.Therefore, while selection, while selection. I was lucky to meet such people, and my children learn from such teachers – alas, outside of school.
It is a mistake to think that a “weak” child will not let “strong” children learn, that in some mythical way he will make beautiful, strong children more stupid, spoil their motivation or somehow harm them.
Everyone will take what they can from a good teacher. It is normal and correct to choose a school, first of all, according to values, and not according to the program and rating
Until this setting changes, there is no need to wait for any reforms in education.I do not believe in modernizing the education system towards openness, humanism, flexibility and efficiency without openness to every child simply on the grounds that he is a child who has come to study. If we cannot teach different children in the classroom, we are bad professionals, we stick to old formats, we do not know how to work in small groups, there are no funds for assistants, we cannot deviate from the methodology of frontal work, and so on. You need to learn, you need to change yourself, not your children.
We want to build schools for the smart? This is old, in an age when anyone understands that there are different strategies for working with information, different types of intelligence, and classical academic achievements in classical academic disciplines cannot serve as an indicator of the success of learning and unlocking the potential of a child.Let’s build schools for different ones – it’s much more interesting! But … we don’t know how yet.
“They didn’t take it” – a bitter sentence to the parent. I didn’t finish my studies, I didn’t invest, I didn’t notice … a continuous “not”. What should the parent of such a child feel? Anxiety. Anxiety about the future of the child – where is he, who is he to? Anxiety is a feeling that parasitizes our entire education system. Anxious parents, anxious jerked children. Somewhere aside is education itself. It’s sad that really interesting, good schools don’t have the courage to open doors for children, and it’s a shame for teachers who want to teach only “motivated” ones.I am sure that only when the school has outlived selection (at least at the level of the elementary school, and, incidentally, the secondary one), something will start to move, creak, and turn towards the modernization of education.
Muscle tone in children – MedSwiss Medical Center
Probably the most difficult year of a child’s life for parents is the very first! The stress after childbirth has not yet passed, they have not yet fully realized that they have become parents. And we must already monitor feeding, growth, weight, development and … tone.If the first criteria are clear, then the last one is always surprising. So what is it, muscle tone, which neurologists are concerned about, and which podiatrists and pediatricians refer to every now and then?
There are several medical definitions, we will give one of them – this is the minimum involuntary muscle tension, which is regulated by the central nervous system and is supported by rare impulses entering the muscles from it, and also depends on the impulses that arise in the muscle itself, especially when it is stretched.Muscle tone provides posture, readiness for a motor act, and the formation of body temperature.
Difficult? Let’s figure it out.
Muscles, like any other organ of our body, are always in good shape, even when we are sleeping or relaxing. Their work and readiness to work are checked by the brain in the same way as MTS or Beeline checks our presence in the network – a short impulse to the muscle (phone) and back. If we began to move, then the muscle stretches or contracts, which it also informs the brain about by impulses.The minimum low tone is noted when we sleep, take a warm bath. This is, of course, a highly simplified explanation. Well, why go into details, let’s leave them for specialists.
How to determine the state of the muscle, i.e. her tone? In the first place, just touching it – flabby, tense, elastic. Secondly, by making passive movements for the person. Have you seen, of course, how during the examination a pediatrician or a neurologist, or an orthopedist does exercises for a child? These movements, together with the tactile sensation of the moving muscles themselves, give an idea of the child’s tone.Parents of children up to 6-7-12 months. can be guided by the effort that must be used to dress or undress a child. If the tone is normal, then the arms slide into the sleeves and the legs slide easily into the trousers. Children from 6 months age can already voluntarily tense their muscles and interfere with dressing / undressing processes, creating a feeling of increased tone. Sometimes, on examination, they also mislead doctors.
Muscle tone is satisfactory or, as doctors write, “age appropriate”, high, low and dystonic.From the phrase “age appropriate” many make the correct conclusion that the tone changes depending on the age of the child. Indeed, after birth, the child is in the “fetal position”, arms and legs are bent and brought to the body, which allows him to keep warm and save energy to maintain internal metabolic processes in this new unknown and frightening world. That is, immediately after birth, muscle tone is very high. Then it gradually decreases, arms and legs straighten. And by the age of three months, the baby can already freely raise his head, stretch his arm, leg, hold the toy, lean on his forearms in the prone position and raise his chest.At this time, muscle tone is satisfactory. Starting from three months, muscle tone should be satisfactory throughout a long and happy life, naturally, decreasing in sleep and in a warm bath and increasing when we move, are nervous and when we are cold.
Let’s dwell on the word “dystonic”. It means not normal. This term denotes a deviation from the norm, and high / low serve as an additional explanation for the deviation. Again, we’re simplifying a little.
Having defined what “muscle tone” is and how to evaluate it, you need to answer the frequent questions of parents: “where does it come from” and “how does it affect the development of the child.”
Why are there abnormalities in the condition of the muscles? First of all, as a consequence of the transferred hypoxia (lack of oxygen) during childbirth or during pregnancy. Hypoxia in childbirth is a separate difficult topic of conversation. Let’s leave her for another time. What is important? It is important that in the process of oxygen starvation, the cells of any organ deplete their reserves and stop working (they do not have nutrients and strength to perform their functions) or die.As a result, the child develops various disorders. The most sensitive organ to oxygen deficiency is the central nervous system, in other words, the brain. The governing body of all others. Therefore, as a result of the above, complete and precise control of muscle work is impaired. As a result, the tone can be spastic, high, slightly increased, slightly decreased, low, hypotonic, asymmetric. Violation of tone can be in all muscle groups or in one specific group, for example, in the flexors of the arms, extensors of the legs.
Muscle tone almost always determines the dynamics of motor development. And any deviations from the norm can interfere with the natural process of movement development. Well, for example, a high or low tone in the hand does not give the child the opportunity to roll over on his back or to take and hold the toy in his hand, violation of the tone in the legs does not make it possible to get on all fours, crawl or sit down.
It should be noted that not all changes in muscle tone are pathological.First, there is an individual characteristic. This is when increased or decreased tone does not prevent the child from developing in accordance with age. Secondly, there is a delay in the rate of maturation of the nervous system and the muscles themselves, then everything in a child’s life happens a little later than in peers. Thirdly, the change in tone against the background of the rapid growth of the child, when the muscles do not keep pace with the growth of the bones of the skeleton. When an organ grows, many processes take place in it, incl. germination by vessels, and this does not allow it to perform its functions well.And this means that at some moments the tone can become higher, lower, again normal, again higher or lower. Was higher in the arms, lower in the legs, etc. Each stage of acquiring new movements also changes the tone. The child began to crawl, he likes it, and he crawls from dawn to dusk. Muscles are overstrained, tired, and the tone rises. The child got up on his feet, began to take the first steps – the muscles are overstrained, the tone rises.
To correct the violation of tone, massage and drugs are used that improve blood flow to the central parts of the nervous system.Massage improves blood flow to the muscles, which means it improves their nutrition, and by the type of feedback (remember, the brain constantly checks the condition of the muscles, and they themselves report what they are doing at that moment) stimulates the work of those parts of the nervous system that are behind them answer. Drugs (nootropics, vascular) increase blood flow to those cells that have suffered (depleted their reserves), gives them the strength to do their job in full.
Now let’s consider in what cases you need to see a doctor? Undoubtedly, if your child lies constantly very relaxed and does not tend to move.If, on the contrary, it is very tight: arms and legs, or only arms, or only legs, or one limb is bent and almost always pressed to the body. If the child is lagging behind in motor development. Now on the Internet, you can easily find a table of the correct development of a child. If children over 18 months old get up from the floor with difficulty and only at the support, they do not climb stairs well, do not step over the sills. Well, and of course, if the child lost the skill, he sat down or got up and suddenly stopped.
I always want the parents to understand what is happening with the child, do not refuse treatment and methodically follow all the doctor’s instructions.It happens that parents think, go to many doctors, collect different opinions and … lose precious time! A cell of the nervous system spends all available reserves to fight the lack of oxygen, and when they run out, it dies. And she’s not alone! And if help comes in time, she will live and work! Perhaps not at full strength, but this means there will not be a complete loss of the ability to walk or grab toys. For example, there will be simply muscle weakness. And with this you can live and build up strength, not strength, so dexterity.I devote a lot of time to this, because the doctor is always bitter and insulting if he can help, he strives with all his might, but does not find support from his parents. Tell me, could not you convince and prove? But in our time of the Internet – everyone is his own specialist and doctor, and most believe that they know exactly what and how to treat. I wish you all good luck and health!
Pediatric neurologist of the MedSwiss network
Solovieva M.E.
Other articles
How to strengthen the immune system of a child
A seasonal rise in the incidence of influenza will begin very soon.Children are the most vulnerable to this disease – after all, their immunity is actively formed and is forced to resist not only infections, but also the stress that lies in wait for the growing organism in all periods of its social adaptation. Especially during periods of active growth or when adapting in a children’s team.
Usually, when treating acute respiratory infections or flu, parents relieve the symptoms of the disease, and if these symptoms recur regularly, they sigh and wait for the baby to “outgrow” childhood illnesses.But the solution is simple – you need to strengthen the child’s defense system, that is, children’s immunity. Only about 10% of people have strong immunity from birth; in the rest, it depends on conditions and lifestyle.
So, what is needed to form a strong immunity?
Positive psychological microclimate in the family. Don’t yell at the child. It has been scientifically proven that any raising of the voice is extremely stressful for babies. And under stress, the body’s ability to fight viruses is weakened.Viruses often hide inside the cell and wait for the slightest weakening of the body in order to cause illness.
Mode of the day. Human nature loves rhythms – a certain alternation of sleep and wakefulness, food and walks. If all this is done at the same time, the body can be compared to a machine operating in an economical mode – wears out less and lasts longer. And all the rhythms are laid at a very early age and remain for life. Therefore, it is important to teach the child from early childhood to the regime and strictly observe it both on weekdays and on holidays.Compliance with the daily regimen with obligatory daytime sleep up to 7 years is a guarantee of health. The child should not lie in bed for a long time in the morning, he must get up no later than 9 am, and in the evening the lights should not be later than 22 hours.
Proper nutrition. To increase the child’s resistance to respiratory diseases, it is necessary to give him foods rich in vitamin A (carotene). Children should definitely eat raw carrot salad with sour cream and pumpkin puree with butter, liver pancakes and eggs.
Vitamins of group B normalize the general metabolism, have a beneficial effect on the processes of hematopoiesis, which ultimately helps to strengthen the health of the child. They are rich in dairy and meat products, cereals, leafy and leguminous vegetables, seafood.
But vitamin C is especially good for strengthening the immune system. First of all, foods containing vitamin C are fresh vegetables and fruits. A child needs to cook vegetables and fruits with minimal heat treatment so as not to destroy the very unstable vitamin C.And if you grind them fresh, then do it immediately before use. You need to feed your child with vegetables and fruits little by little, but regularly.
Not only what the child eats is of great importance, but also how many times a day he does it. The standard “adult” breakfast-lunch-dinner scheme is absolutely not suitable for children. To these – obligatory – meals should be added lunch, or second breakfast and afternoon tea. Even if in kindergarten or at school the child is provided with four meals a day, this is not a reason to let him leave the house without “his” dry ration (in the end, the baby may not like the food from the public catering and he will remain hungry).Put him with you an apple, banana, cereal, yogurt, a piece of chocolate, a few nuts, and a bottle of water or juice (preferably not too sweet).
Give your baby a rosehip decoction once a day instead of water. Rosehip broth is drunk in courses of two weeks, followed by a break for a month. You can give it to children from the age of four months.
And even here there is a nuance: this storehouse of vitamin C removes potassium from the body. So, for maximum benefit, it is advisable to use dried apricots, raisins, bananas – everything that contains potassium and that allows the age of the child, along with the rosehip.
Fresh air at least two hours a day. There are both air baths and sun baths, saturating the body with such necessary vitamin D. Even in cloudy weather, you can take sun baths – ultraviolet rays freely pass through the clouds. It is important to be able to dress the child for the weather – mothers and grandmothers worry that the baby will freeze and dress him like a cabbage, while the child overheats, sweats and, naturally, gets sick. Light freezing will stimulate the child to be active and keep him warm.But overheating will lead to a sharp decrease in immunity. We dress the child “as ourselves”, that is, the same number of layers of clothing.
Hardening. Water hardening is a separate large topic, consisting of several procedures – wiping, dousing, foot baths, contrast showers, and later a sauna or Russian bath. But you need to start with rubdowns – this is suitable even for the smallest.
Personal and collective hygiene. Every day in the house it is necessary to carry out wet cleaning, since in the dry room the dust is in a suspended state – in the access zone to the respiratory tract.If you even once examine a little dust under a microscope, you will simply be horrified – mold spores, particles of human skin, insect remains, live micro mites. From an early age it is necessary to to develop the child’s skill to wash their hands before eating and after using the toilet. Cleanliness and hygiene of the nose and throat is important for the child, teach your child to rinse his mouth with cool water from childhood, rinse and clean the nose. In addition, it is important to create the necessary microclimate in the house, cool (20-22 degrees) and humid (50-60% humidity) air help to normalize breathing and prevent colds.
The basis for strengthening the immune system is non-drug means, they are usually very lazy to perform, but they are the most effective. In addition, all these methods, with rare exceptions, have no contraindications.
Another effective method of influenza prevention is vaccination. A flu vaccination campaign is currently underway. Specialists of the Rospotrebnadzor Administration for the Altai Republic and the FBUZ “Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Altai Republic”, headed by the chief sanitary doctor of the Altai Republic L.V. Shchuchinov urge all residents of the region to be vaccinated against influenza.
Prevention of colds is a multi-component and long-term process that is much easier and more effective for people who take care of their health all the time, and not only during seasonal flu epidemics. A rational diet, a healthy lifestyle, hardening and active sports will increase the body’s resistance to colds and prevent the occurrence of many other health problems.Take care of your health!
Dysarthria in children – causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of dysarthria in a child in Moscow in the children’s clinic “SM-Doctor”
GET
CONSULTATION
Contents:
Description of the disease
Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatment
Dysarthria is a severe speech disorder in which it becomes slurred and slurred.
About the disease
Dysarthria is a violation of speech skills due to damage to the speech motor apparatus. The localization of the pathological process leading to the problem can develop at different levels of the nervous system responsible for the formation of sounds, the logical harmony of the story:
- nuclei of the cranial nerves responsible for the nervous control of the tongue, lips, soft palate, etc .;
- pathways between the cortex and the cerebral nuclei;
- cerebellum and pathways, pathways from it and to it;
- cerebral cortex.
90,011 subcortical centers;
Diagnostics is carried out simultaneously by a neurologist (finds out the level of the topical lesion of the nervous system and the nature of the pathological process) and a speech therapist (determines the degree of speech disorders in order to make a prediction of correction).
Treatment is aimed at eliminating or stabilizing the background pathology that led to speech disorders, as well as articulatory correction.
Symptoms of dysarthria
The pathogenetic mechanisms of dysarthria are multifaceted and are associated with defective innervation of the organs involved in the formation of speech.These are the respiratory muscles, muscles of the lips, tongue and soft palate, larynx and vocal folds. As a result, speech becomes slurred and indistinct.
Violation of muscle contraction can be of two types – spastic and hypotonic variant. Therefore, the data of an objective examination are different:
- Muscle spasm. Tension of lips, tongue, face and neck. The lips are tightly closed. Restriction of movement when pronouncing sounds.
- Muscle hypotonia. The tongue is flaccid, almost motionless at the bottom of the mouth.The mouth is half-open, because lips do not close. Increased salivation is noted. Due to the immobility of the soft palate, the voice acquires a nasal tone (becomes nasal).
With dysarthria, the pronunciation of almost all sounds is impaired – both consonants and vowels. The child softens hard consonants. When pronouncing hissing and sibilant sounds, the tongue is pushed not forward, but to the side, the interdental spaces are involved.
Due to a complex violation of innervation, the characteristics of the voice also change.He becomes quiet, weak, deaf, gets nasal, etc. An imbalance in the control of the respiratory act leads to the fact that the exhalation is shortened, and during the pronunciation of speech, breathing becomes more frequent and becomes intermittent.
Due to inarticulate speech, the child cannot clearly differentiate sounds by ear. This leads to an unformed vocabulary and the inability to construct a sentence grammatically correctly. Therefore, it is so important not to waste time and start correcting speech disorders as early as possible.
Causes of dysarthria
- toxicosis;
- antenatal hypoxia;
- immune conflict by the ABO system and the Rh factor;
- chronic pathologies in a mother carrying a child;
- complicated course of childbirth;
- birth trauma;
- asphyxiation.
90,011 deliveries before 37 weeks;
All these factors can lead to organic brain damage, incl.including centers responsible for the development of speech. At the same time, infantile cerebral palsy is often formed, and its severity correlates with the severity of speech disorders.
In addition, dysarthria can develop in early childhood in the original healthy child. In this case, the reasons lie in severe neuroinfections and intoxications, for example, carbon monoxide, alcohol poisoning, etc., as well as tumors and brain injuries.
Diagnosis of dysarthria
A child with speech impairment is examined simultaneously by a neurologist and a speech therapist.
A neurologist conducts an objective examination, assesses the severity of reflexes and prescribes additional diagnostic methods. As a rule, neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the brain, which makes it possible to identify focal lesions. Rheoencephalography and encephalography can also be performed.
Speech therapy testing is aimed at assessing speech and non-speech disorders. Non-speech parameters:
- development of mimic and speech muscles;
- range of motion in the temporomandibular joint;
- breathing pattern, etc.
Speech parameters of the assessment:
- speech;
- synchronicity of the work of the organs involved in the formation of speech;
- Correct pronunciation of sounds, construction of sentences, etc.
On the basis of a comprehensive examination, the severity of dysarthria is determined. There are 4 degrees of speech impairments:
- First degree (erased form) – speech disorders are invisible to others, detected only during speech therapy examination.
- Second degree – speech is understandable, but there are defects in the pronunciation of sounds.
- Third degree – speech becomes indistinct, only people from close environment understand it.
- The fourth degree (anarthria) – speech is completely indistinct, even people who are constantly with the child do not understand it.
Treatment of dysarthria
- Neurological vector. The neurologist is treating the underlying disease that led to speech impairment.For this, vascular drugs, nootropics, vitamins and others can be prescribed. In the presence of a brain tumor compressing the speech center, removal is indicated (at this stage, a neurosurgeon joins).
- Speech therapy vector. Formation of skills of correct pronunciation of sounds, construction of sentences, etc. This is a very painstaking work that must be continued on a daily basis.
In achieving the desired results, it is very important to start therapy as early as possible, the diligence of the parents and the patient himself.Specialists of “SM-Doctor” build a program for working with a child in such a way that the motivation to achieve the goal does not disappear at any stage, but only increases. This and the high professionalism of speech therapists, neurologists and other participating doctors allow you to achieve high results and restore intelligibility.
As soon as the first signs of dysarthria in a child began to be noticed, do not delay the visit to a specialist. Only a comprehensive specialized examination will identify or exclude the problem.In “SM-Doctor” you will be met by competent doctors and speech therapists who will help you establish an objective diagnosis and correct the identified violations. Sign up for a consultation with professionals at a convenient time! We find an approach to every child, even the most difficult one.
Doctors:
To make an appointment
We guarantee non-disclosure of personal data and the absence of advertising mailings by
the phone you specified.Your data is necessary to provide feedback and
arranging an appointment with a clinic specialist.
Orthopedic traumatologist answers frequently asked questions
Young parents always have many questions about their child’s development. We asked the most frequently asked questions to the traumatologist-orthopedist of EuroMed Clinic Dmitry Olegovich Sagdeev.
– A small child is recommended to see an orthopedist quite often: a month, at three months, at six months, a year… What is the reason for this, what exactly does the orthopedist evaluate?
– The orthopedist looks at how the child’s musculoskeletal system develops during periods of its active development in order to notice possible deviations in its development in time and correct them. At an early stage – a month – we do ultrasound of the hip joints so as not to miss any congenital pathology. At three to four months, we repeat the ultrasound scan for control in order to see the dynamics of joint development.
Based on the results of an ultrasound examination, the doctor may suspect violations of the formation and dynamics of the development of the hip joint.
The doctor of ultrasound diagnostics assesses the formation of the joint on a special scale (Graf’s scale), and then the orthopedist determines whether correction is required by therapeutic exercises, whether any physiotherapy is needed, etc.
The sooner deviations in the development of the child are identified, the more effective the treatment will be.
At about six months, the child begins to sit down, then he will get up, walk, and it is important to know how his hip joint is formed and, if there are violations, to have time to correct them before that moment.
Dysplasia of the hip joint is a violation of the formation of the hip joint, which in severe forms leads to the formation of subluxation or dislocation of the head of the femur.
– When dysplasia of the hip joint is detected, the wearing of orthopedic structures is usually prescribed: Frejk’s pillows, Vilensky’s splints, etc. They look quite frightening, and the parents are afraid that the child will be uncomfortable in them.
– The child will not experience discomfort.He does not yet have a stable understanding of what position his lower limbs should be in, so the construction will not interfere with him.
At the same time, thanks to the effect of these structures, the child’s legs are located at a certain angle, and in this position the head of the femur is centered in the cavity, it is in the correct position, any deforming load is removed from it, which allows the joint to develop correctly. If this is not done, then a constant deforming load will be exerted on the head of the femur, which ultimately will entail subluxation and dislocation of the hip.This will already be a severe degree of hip dysplasia.
– In addition to dysplasia, ultrasound always looks at the formation of ossification nuclei in the hip joint. Why is their correct development so important to us?
– The femoral head consists of cartilage tissue. The core of ossification is located inside the femoral head and, gradually increasing, it reinforces it from the inside and gives the structure stability under axial load. In the absence of an ossification nucleus, any axial load on the thigh leads to its deformation, as a result of which subluxation may develop and further – dislocation of the thigh.Accordingly, if the core of ossification does not develop or develops with a delay, any axial loads are strictly prohibited: you cannot stand, and even more so, you cannot walk.
– Can I sit?
– Sitting is not prohibited with a slowed rate of ossification (ossification, bone formation), provided that the roof of the acetabulum is normally formed, the head of the femur is centered. This is determined by ultrasound.
– What influences the formation of ossification nuclei, how can their development be stimulated?
– First of all, activity.Therefore, we recommend that you engage in therapeutic exercises with your child right from birth. Mom needs to do gymnastics with her child every day. Moreover, it is important that this should be a normal load, the so-called static one – when the child lies and the mother spreads his arms and legs. I categorically do not recommend “dynamic gymnastics”, which is gaining popularity now – a set of exercises in which the child is twisted, twisted, swayed, rotated by the arms and legs, etc. Such exercises contribute to overstrain of the developing musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the child, and create a high risk of injury: from stretching before dislocation with rupture of the ligaments of the joint.
From 2.5 months, a child can and even needs to visit the pool. Individual lessons with a trainer in water are very useful for the development of the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems, muscle training, and strengthening of immunity.
Massage is useful as an auxiliary procedure.
Vitamin D is also needed, it stimulates the development of bone tissue. Vitamin D is recommended to be given to almost all children under two years of age, and some even later.This issue is solved jointly by a pediatrician and an orthopedist, doctors select the dosage of the drug and the duration of its administration. In our region, there is little sunlight, which provokes vitamin D deficiency in almost all children, which leads to rickets. In Siberia, most children who do not take vitamin D have rickets to one degree or another.
If indicated, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapy: magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, applications with polymineral mud wipes.These are time-tested effective techniques.
– Doctors say that a child should not be seated before he sits himself, put, stimulate to an early standing, walking. What is the reason for this?
– This is due to the fact that in a small child the musculoskeletal system is still immature, and she and the central nervous system are not ready for active axial loads. If we begin to actively verticalize the child, to stimulate him to sit, stand, this can lead to deformation of the spine, disruption of the formation of joints.At the start, they should develop without axial loads, as nature has laid down. Systems, and, first of all, the central nervous system, must mature so that the signal from the brain from, so to speak, the “central computer” reaches the periphery without distortion and the response, from the periphery to the center, is also adequate. There is no need to rush. When these structures are ready, the child will sit down and crawl and get up by himself.
– What are the age norms when a child sits down, gets up?
– Indeed, there are certain norms, but one should not focus too much on them.Each child develops according to his own individual program, there is no need to adjust everyone to the same standard. To assess its development, you need to take into account many different circumstances, ranging from the characteristics of the course of pregnancy and childbirth. Timing and norms are needed, I think, more for doctors to adequately assess whether the child is developing correctly or not, and if there is a delay, to see it in time and help the baby.
Children begin to sit down at about six months, crawl at 7-8 months.Classical development: the child first sat down, then crawled, then begins to get up, move with support. Then, when he felt that he was ready, he detached himself from the support and took the first independent steps. This happens when the musculoskeletal system has matured, the central nervous system and the vestibular apparatus have adapted. And all these systems have learned to work together correctly.
Some children begin to crawl before they sit down, some will get up before they crawl.It happens that the child does not crawl at all, but immediately got up and went. All these are features of individual development.
– What is wrong with such devices as a walker, allowing the child to “go” much earlier, entertaining him?
– Walkers knock down the “program” of the correct interaction between the central nervous system, the vestibular apparatus and the musculoskeletal system. In the walker, the child takes an unnatural position, he does not take a full step in them, but simply hangs, pushes off with his toes and moves in space.His brain and muscles remember this incorrect program of vertical position and movement, and subsequently, when the child tries to start walking without a walker, these incorrect settings are triggered, the wrong muscle groups that should keep him upright are turned on, and the child falls down. After the walker, it is very difficult for a child to maintain balance on his own, later it is quite difficult to correct this.
– Another problem associated with the fact that the child began to be placed before he was ready is flat feet.Right?
– Flat feet are congenital and functional (acquired).
If a child is positioned too early, he may develop incorrect positioning of the foot. And often as a result, doctors diagnose planovalgus deformity of the feet. This flat-valgus placement of the feet is usually not pathological. On examination, the doctor determines whether the foot is mobile or rigid (inactive), and if the foot is mobile, it is easily brought into the correction position, then we are not talking about deformation, this is just an incorrect setting, which is corrected by therapeutic exercises, the correct distribution of loads.
All these attitudes that mothers complain about: raking in socks, seeming curvature of the limbs, is a consequence of the child’s transition from a horizontal position to a vertical one and his adaptation to upright posture. During the prenatal period of development, the fetus is tightly “packed” inside the uterus: the arms are pressed to the body, and the legs are folded in a rather unnatural way for a person – the feet are turned inward, the bones of the lower leg and thighs are also twisted inward, and the hips in the hip joints, on the contrary, turn outward as much as possible …When the baby is just learning to stand, the wrong position of the feet is imperceptible, since the turn of his legs in the hip joints and the twisting of the bones of the thighs and shins happened in opposite directions – that is, they compensated each other, and the feet stand as if straight. Then the ratio in the hip joint begins to change – the head of the femur is centered, and this happens a little faster than the change in the rotation of the shin bones. And during this period, parents notice clubfoot and begin to worry.But in fact, in most cases, this is an absolutely normal stage of development, and there is no need to panic that the child is somehow walking unevenly, putting his foot in the wrong way. Nature is smart, she has provided for the entire mechanism of development of the lower extremities, and you should not interfere with this process. Of course, if this bothers you, then it makes sense to consult a doctor to determine whether these changes are physiological or pathological. If pathology – we treat, if physiology – there is no need to treat.
For the prevention of improper installation of the foot, passive therapeutic exercises, the choice of the correct orthopedic regimen are necessary.
A small child cannot yet actively fulfill the direct wishes of his parents and do gymnastics himself, therefore at this stage a passive influence is recommended: walking barefoot on uneven surfaces, on grass, on sand, on pebbles (of course, we make sure that the child is not injured so that the surfaces are safe). As the child grows up (after about three years), we move on to active physical therapy in a playful way. For example, we run on our heels to wash, eat breakfast on our toes, go to the bedroom like a penguin, watch cartoons like a bear.Try to make it interesting for the child to do this, and then he will get used to it and will be happy to do the exercises himself.
Important for the correct fit of the foot and the selection of shoes. Shoes should be lightweight, with an elastic sole, an instep support – a lined arch. If the arch is laid out on the sole, no additional insoles are needed (unless prescribed by the doctor). The height of the shoe is up to the ankle (you don’t need to buy high ankle boots), so that the ankle works freely, and the short muscles of the lower leg can develop correctly – the very ones that hold the transverse and longitudinal arch of the foot.
For a child starting to walk, it is optimal to have a closed heel and toe in the shoe – this is how the toes are protected from possible injuries if the child hesitates.
– Real flat feet are treated differently?
– Yes, “real” flat feet cannot be cured by gymnastics. If this is congenital flat feet, then it is treated quite difficult and in many stages. There are many surgical techniques that the doctor selects depending on the severity of the case and its characteristics.Treatment begins with staged plaster casts. There are minimally invasive surgical aids on the tendon-ligamentous apparatus with the subsequent use of special devices – braces. There are also various surgical aids related to the intervention on the joints of the foot, aimed at correcting the ratio of the bones of the foot and eliminating planovalgus deformity.
– Why should flat feet and clubfoot be treated?
– Because these violations lead to the deformation of the entire skeleton.From the bottom up, like a snowball, there are violations. Improper support leads to improper placement of the hip, changes in the position of the pelvis, knee joints suffer, receiving altered load. To even out the load on the knee joint, the hip begins to rotate, trying to bring out some kind of support position. The thigh unfolded, began to dislocate from the hip joint. To prevent him from dislocating, the pelvis tilted. The pelvis tilted – the angle of inclination of the spine changed. Accordingly, the spine bent to keep the head straight.As a result: gross violations of the gait and the entire musculoskeletal system, scoliotic deformities from the spine. These conditions do not pose a threat to life, but the quality of life of a person with orthopedic problems suffers greatly.
– Another very common diagnosis that newborn babies are diagnosed with is torticollis. How serious is this pathology?
– Many children are diagnosed with neurogenic functional torticollis, often with subluxation of the first cervical vertebra (C1).Most often, this is a functional disorder that goes away on its own with our minimal intervention, and it does not pose any threat to the health of the child.
Children with functional torticollis are observed jointly by a neurologist and an orthopedist, usually corrective styling, an orthopedic pillow and a soft fixing collar are enough for this situation to be resolved without any complications.
It is important to separate functional torticollis from congenital muscle torticollis.If the latter is suspected, an ultrasound of the sternocleidomastoid muscles of the neck is performed at two months, which allows us to make the correct diagnosis with a high dose of probability. If an ultrasound examination reveals any changes in the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then we begin to carry out complex treatment aimed at eliminating torticollis and restoring the functional ability of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The treatment includes fixing the head with an orthopedic collar, physiotherapy courses are prescribed, aimed at improving muscle nutrition and restoring their structure.With unsuccessful conservative treatment, if the deformity grows, then after a year, surgical treatment of congenital muscle torticollis is performed.
If you have any doubts, questions, worries, do not be afraid to consult a doctor. Children’s orthopedist, neurologist, pediatrician – these are specialists who are always ready to answer your questions and help your baby grow up healthy.
Optional
Subluxation in the elbow joint
A very common trauma in children is the subluxation of the radial head in the elbow joint.In the elbow joint, three bones are connected: the humerus, the ulnar and the radius. Ligaments exist to hold these bones together. In young children, the ligaments are very elastic, loose and can easily slip over the bone. With age, the ligaments become stronger, and sub-ligaments no longer happen so easily.
This injury happens when the child is abruptly pulled by the hand: the dad twisted it, just sharply lifted the child by the wrists (the child must be lifted, supporting by the armpits), or it even happens that the parent leads the child by the hand, the baby slipped, hung on the arm – and a subluxation occurs …
At the moment of injury, you can hear the click of the joint. Usually, with an injury, the child experiences short-term sharp pain, which goes away almost immediately. The main sign of injury is that the child stops bending the arm at the elbow – children keep the injured arm fully extended.
As soon as possible after an injury, the child should be shown to a traumatologist who will correct the subluxation and return the ligament to its place.
When should I see a traumatologist?
Children often fall, hit, and get injured in one way or another.How to determine when you can get by with a patch and iodine, and when you need to go to the emergency room?
- Any cut, puncture wound should be shown to the doctor. Do not fill the wound with brilliant green or iodine! This will add chemical burns to the cut. There is no need to apply cotton wool to an open wound – its fibers are then extremely difficult to remove from the wound. If the injury site is heavily contaminated, rinse with clean water. Then cover the wound with a clean cloth (sterile bandage, handkerchief, etc.), apply a pressure bandage and, as soon as possible, go to the emergency room.The doctor will conduct the initial surgical treatment of the wound, thoroughly clean it (you are unlikely to be able to do it so well on your own), restore the integrity of all structures and apply a bandage.
- If noticeable swelling appears at the injury site. This may indicate that this is not just a bruise, but also a fracture, dislocation or rupture of the ligaments.
- If the child has lost consciousness, even for a short time. This may indicate a traumatic brain injury, which can have serious consequences.
- If a child has vomited after an injury. Vomiting, nausea, and pallor also indicate the possibility of traumatic brain injury.
- If the child hits his head. The consequences of a head blow may not be immediately noticeable, and at the same time have very serious consequences.
- If the child has hit the belly. When struck by the stomach, damage to internal organs and internal bleeding is possible.
- If the child has fallen from a height (from a chair, table, etc.), fell off a bicycle, etc.It happens that outwardly it does not manifest itself in any way, but the internal organs are damaged.
- If the child is worried, he behaves in an unusual way.
In general, in case of any doubt, it is better to play it safe and see a doctor. Traumas in children – this is such a question when it is better, as they say, to overdo it than to miss it. Do not be ashamed, afraid that you distract emergency doctors or emergency room doctors over trifles. Your child’s health is the most important thing!
Caution: trampoline!
Trampoline is a very popular entertainment among modern children.Unfortunately, this fun can lead to serious problems. The most common injury that children and adolescents receive on trampolines is a compression fracture of the spine. Recently, there have been a lot of cases of compression fractures of the spines, including those who are professionally involved in trampoline sports.
There is no safe way to be on trampolines. A child, even without falling, can break the spine, since during jumping, the spine receives very large axial loads.Especially, of course, this is dangerous for children with a weak muscle corset.
Food poisoning in a child – the rules of prevention and treatment
Many are accustomed to treating mild forms of food poisoning as a kind of inevitability that will sooner or later overtake everyone. There are frequent cases when, even when treating children, parents do not resort to the help of doctors, but get by with a “standard” set of funds from grandmother’s recipes or TV advertisements. Gastric lavage with potassium permanganate, intake of activated charcoal or some other absorbent, this is the usual set in the hands of an “experienced” parent.However, not everyone clearly understands the essence of intoxication of the body, not everyone can correctly determine its nature and predict the consequences. Not everyone knows that in some cases, poisoning can be caused by deadly bacteria, for example, botulism, and sometimes it happens that under the symptoms of intoxication of the body is hidden a completely different disease, for example, heatstroke. And while the parents are trying to overcome the false poisoning of the child, they lose precious time, which can lead to a sharp deterioration in the condition and serious consequences.
Considering all of the above, it should be noted that parents should not self-medicate, even if it seems to them that it is food poisoning in a child and that they themselves will quickly cope. We recommend that you always seek medical attention, although, if possible, take some steps to alleviate the condition of the child. We will describe how to prevent food intoxication and what to do if it occurs.
We also recommend reading the material “Protecting Children from the Sun”, in which you will learn about the dangers of the scorching summer sun, about common myths about this and about the correct methods of protection.If you are raising a teenager and have begun to notice oddities in his behavior, then we recommend that you read an important article on the common signs of drug addiction in adolescents.
A child will not get food poisoning if adults follow simple rules
Food poisoning of children – possible ways of intoxication and their symptoms
Remember that infants and children of preschool and primary school age are especially susceptible to food poisoning, since they still do not have a strong immune system.Food poisoning in children, as well as in adults, most often occurs when eating food that is contaminated with microbes. Manifestations are divided in two forms – toxicoinfection, as well as intoxication.
Usually toxicoinfection is caused by microbes belonging to the Salmonella group, as well as para-intestinal and Escherichia coli. Note that Salmonella is very common and often infects the intestines of birds and animals. And when the animal’s body weakens and, accordingly, its protective functions too, Salmonella infect all internal organs.Such meat, having got on the table to people after weak heat treatment, causes poisoning. Eggs, pates, milk, cheese, fish and cottage cheese can also become infected with salmonella. Symptoms of poisoning usually occur several hours later or later, depending on the dose, organism and nature of the poisoning. The child begins to feel nausea, vomiting, headache, stools are frequent and thin, and the body temperature rises. The disease lasts from two days to a week and in the overwhelming majority of cases ends with recovery.
Food intoxication of the child’s body occurs due to the ingestion of food that contains poisons in the form of microbial waste products. They are called toxins. Most often, such poisoning is caused by staphylococcus. He, as a rule, gets into ready-made dishes from those who have pustular skin diseases. Poisoning is common through cakes, ice cream, pastries, sausage, ham, sausages, and so on. Even when incorporated into raw foods, this toxin is not easy to destroy.At boiling point, it does not break down for several hours. Symptoms of poisoning usually appear in time in the same way as with a toxic infection. The clinical picture and course of the disease are similar.
Botulism causes a very dangerous poisoning of the body, which, without urgent medical intervention, can result in the death of a child. Botulism bacteria multiply actively in an anoxic environment and release a strong toxin. It collapses after 20 minutes of boiling, but in order to destroy the spores themselves, it is necessary to maintain a temperature of 120 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes.The most common source of poisoning is various kinds of canned food, namely meat, fish, vegetables. But there were cases of intoxication through the ground, which was contaminated with the feces of sick animals. The onset of the disease occurs after a couple of hours, although an incubation period of several days is sometimes possible. The child feels dry mouth, dizziness, general weakness and shortness of breath, the pulse quickens, paralysis of the eye and facial muscles occurs, as well as the muscles of the soft palate and tongue.Because of this, a disorder of speech, vision and swallowing occurs – the child chokes and begins to poorly distinguish between nearby objects and text. The toxin affects the nervous apparatus of the heart and the central nervous system. The disease lasts 4-8 days, is difficult and without medical intervention can lead to death due to paralysis of the respiratory center.
Note that botulism spores may contain canned honey, even commercially produced honey.Therefore, in no case give such honey to children under one year old, they may develop infant botulism. And for adults, it is usually harmless.
In infants, botulism, as a rule, begins with constipation, then the baby begins to suck poorly and swallows with difficulty, his eyelids begin to weaken, he makes weak sounds or words, and general impotence develops.
Non-bacterial poisoning usually occurs due to the consumption of poisonous mushrooms, fish or potatoes that have turned green from light, which accumulate poisonous solanine under their skin.Many mushrooms are poisonous in nature, and there are many false mushrooms, remember that it is not recommended for children to eat mushrooms under 12 at all. They are especially often poisoned with mushrooms – lines that are very similar to edible morels. Poisonous gelwellic acid, a very potent poison that is resistant to heat, develops only in lines under dry weather conditions. Pay attention to the photos and avoid buying and picking such mushrooms.
Poisonous – line. Edible morel.
Poisoning of some fish toxins may be due to improper handling or transportation. For example, mackerel produces poisons if it is untimely frozen. Also keep in mind that children should not be given Japanese sushi with fish or shrimp, which can also serve as a source of dangerous poisoning.
Food poisoning of children – prevention of diseases
Here are the basic rules for the prevention of food poisoning in children:
- The first and main rule adults should remember from school: “wash your hands before eating”, and this is not just a general slogan, but a vital necessity.Washing hands before eating reduces the risk of poisoning by several times.
- Next, the second rule is to thoroughly wash the foods you eat raw – vegetables and fruits. Do not give raw milk and eggs to children. It is also recommended to boil pasteurized milk from the store.
- Do not allow children to eat “grown-up” foods such as Japanese sushi, smoked fish, mushrooms, and so on.
- Meat of poultry, animals, must undergo a thorough heat treatment, use the rule: “you cannot digest the meat.”The same goes for fish, seafood and eggs.
- When canning at home, strictly adhere to the technology and temperature regime for the destruction of botulism spores. Do not use homemade or manufactured products with bloated bags, cans, or lids (also known as bombing). Do not eat foods with a suspicious odor or consistency.
- Store perishable food in the refrigerator only during its expiration date and in a container with a closed lid. Remember that cakes, cream cakes, salads with mayonnaise, open bags of food and drinks that do not contain preservatives, such as natural juices, go bad very quickly.Remember the approximate storage time of popular products in cold weather up to 8 degrees (without cold it is much shorter, and sometimes products cannot be stored without cold at all). Of course, modern preservatives can prolong the life of some products, but do you need to risk the health of your children in vain?
- Curd mass, curd cream or cheese curds – in the cold up to 24 hours (it is impossible to store without cold).
- Fried pies with meat or fish – in the cold up to 24 hours, in a cool place up to 12 hours.
- Pastry with butter cream – in the cold up to 6 C ° storage time up to 36 hours, in a cool place up to 12 hours.
- Pastry with custard – in the cold up to 6 hours, it is impossible to store without cold.
- Serve hot fish or meat dishes shortly after cooking, do not store perishable food outside the refrigerator.
- When buying and before using, always check the expiration date of the products.
- Do not buy very early fruits and vegetables (for example, tomatoes, watermelons, melons or strawberries), they usually contain a lot of chemical growth stimulants that can cause acute poisoning.
- Do not buy food in questionable places from hands or trays. Especially in the hot season, especially on the beach, especially meat products (pasties, belyashi, etc.) especially for children! Remember that meat in the sun can turn into poison after 20-30 minutes.
Actions of parents if the child has food poisoning
Provision of medical care in case of poisoning
In case of food poisoning of a child, the most important thing is to promptly provide the child with medical care.If you are on vacation, then contact the administration of the hotel or recreation center so that they take urgent measures. If you are at home, call a doctor, emergency room, or ambulance, depending on the situation. In the event of a sharp deterioration in the condition, immediately call an ambulance (even if you have called a doctor at home before that), dangerous syndromes include: vomiting or diarrhea with blood, delirium, hallucinations, loss of consciousness, asphyxia (the child is choking), weakening of the pulse, cyanosis skin (the child begins to turn blue).
Always remain calm, do not frighten, but rather calm the child. Describe the nature of the problem and symptoms clearly and in detail to the medical professional by phone, ask for general recommendations by phone, what you need to do before the ambulance or doctor arrives.
Please note that the symptoms of the disease can only look like poisoning, but in fact it can be a completely different disease, for example, sunstroke. Only a doctor can make a qualified diagnosis.
General actions in case of child poisoning
If you are sure that the child has food poisoning (preferably after consulting a doctor by phone), then first of all, ensure that the stomach is emptied of food, which is most likely the cause of the disease.To do this, give your child a lot of warm boiled water to drink, and then induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue. The procedure must be repeated until the vomit comes out clean, without pieces of food and mucus. We DO NOT RECOMMEND without the advice of a doctor to wash the stomach with potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). But if you are planning to make such a solution, then use either drops, or in the case of crystals, carefully pour the solution into another dish to avoid internal burns with small particles.Remember that the potassium permanganate solution should be slightly pink, and do not give potassium permanganate to children under 5 years old.
Use sorbents to remove absorbed harmful substances and toxins from the child’s intestines. These are substances that draw in toxins and then remove them from the body. Popular drugs are: activated carbon, Polyphepan, Carbolong. But remember that in some cases – with ulcerative and erosive lesions of the intestines and stomach, these drugs may be contraindicated.The drug Enterosgel is very popular, it does not irritate the mucous membranes and has excellent sorbing properties of toxins, and it also absorbs bilirubin.
In case of poisoning, which are accompanied by diarrhea and flatulence, you can use Bifylact extra or Extraalact, they also contain microbial components that restore normal intestinal flora.

 Chill in the refrigerator if desired to improve taste. *Do not mix with milk products.
Chill in the refrigerator if desired to improve taste. *Do not mix with milk products. If so, start with ½ square in the afternoon after school so the child will have a good bowel movement before the next school day.
If so, start with ½ square in the afternoon after school so the child will have a good bowel movement before the next school day.
 Sometimes, children resist the urges to poop. It may be because they don’t want to stop the activity they are doing (playing a game, watching a show, etc.), or they have some kind of fear about going to the bathroom (see the next point).
Sometimes, children resist the urges to poop. It may be because they don’t want to stop the activity they are doing (playing a game, watching a show, etc.), or they have some kind of fear about going to the bathroom (see the next point).