How do remote temperature sensors work. What are the benefits of remote temperature monitoring. Which types of remote temperature sensors are available. How to choose the right remote sensor for your needs. What factors affect remote sensor accuracy and reliability. How are remote sensors used in homes and businesses. Why is remote temperature monitoring crucial for perishables.
Understanding Remote Temperature Monitoring
Remote temperature monitoring has revolutionized the way we track and manage temperatures across various environments. This technology enables users to monitor temperatures from a distance, providing real-time data and alerts without the need for constant manual checks.
Remote temperature sensors use thermocouple probes or thermistors to detect ambient temperature. These readings are then transmitted wirelessly to a receiver using radio frequencies. The receiver interfaces with software to track data and generate alerts when necessary.

How do remote temperature sensors operate?
Remote sensors are battery-powered devices that can be placed in various locations, including outdoors or in freezers. Their range depends on the strength of the base station or receiver, and extended networks can relay readings over long distances. This flexibility allows for comprehensive temperature monitoring in diverse settings.
Advantages of Remote Temperature Sensors
Remote temperature sensors offer numerous benefits over traditional thermometers and manual tracking methods:
- Real-time temperature access from anywhere
- Customizable alarm notifications for out-of-range conditions
- Hands-free monitoring and data logging
- Ability to monitor multiple locations from a single device or dashboard
- Early detection of issues to prevent losses
- Tracking and documentation for compliance purposes
These capabilities enable users to respond to temperature changes more quickly and optimize conditions for storage, comfort, efficiency, and various other applications.

Types of Remote Temperature Sensors
There are several types of remote temperature sensors available, each designed for specific applications:
- Indoor/Outdoor sensors: General-use, affordable options
- Food/Refrigerator sensors: NSF-rated for commercial kitchens
- Freezer sensors: Low-temperature rated, often with buffered probes
- High-temperature sensors: Rated for oven, furnace, and other high-heat applications
- Humidity and temperature sensors: Combine both readings in one device
- Pipe clamp sensors: Strap onto pipes for monitoring fluid temperatures
- Thermocouple sensors: Highly accurate probe tip sensors
Which remote temperature sensor is best for your needs?
When selecting a remote temperature sensor, consider factors such as the setup environment, accuracy requirements, and budget. Each type of sensor has its strengths and is designed for specific applications, so choosing the right one is crucial for effective temperature monitoring.
Selecting the Ideal Remote Sensor
Choosing the right remote temperature sensor involves considering several key factors:

- Measurement Range: Ensure it matches the expected temperature range
- Accuracy: Determine how precise the measurements need to be
- Resolution: Consider the smallest detectable temperature change
- Response Time: Evaluate how quickly it detects temperature shifts
- Transmission Range: Check the distance to the receiver
- Alarms: Look for customizable threshold options
- Display: Decide if a local LCD readout on the sensor is necessary
- Power Source: Consider battery type and life
- Approvals: Check for relevant certifications (UL, CE, NSF, etc.)
- Software: Evaluate data logging, analysis, and notification capabilities
By examining these specifications, you can find the right match for your specific situation and budget.
Accuracy and Reliability of Remote Sensors
Modern remote sensors offer impressive accuracy thanks to advanced calibration techniques and electronics. When evaluating sensor accuracy and reliability, consider the following:
How accurate are remote temperature sensors?
High-quality remote sensors can provide accuracy within ±0.5°F over a wide temperature range. Look for options with certifications from recognized testing agencies to ensure precision. Rapid sampling rates further improve consistency in readings.

What factors contribute to sensor reliability?
For optimal reliability, opt for reputable commercial-grade instruments with rigorous quality control and testing processes. Industrial sensors typically outlast cheaper consumer models, providing long-term performance and durability.
Remote Monitoring Applications in Homes and Businesses
Remote temperature sensors have opened up valuable monitoring options for both residential and commercial settings:
- Smart homes: Monitor room temperatures, incoming water temperature, basement conditions, etc.
- HVAC systems: Optimize for comfort and energy savings
- Data centers: Prevent hotspots and equipment failures
- Warehouses: Ensure proper storage conditions for various goods
- Manufacturing facilities: Meet process temperature specifications
- Restaurants: Monitor refrigeration and cooking temperatures
- Pharmacies: Maintain drugs at ideal temperatures
The applications for remote temperature monitoring are extensive, making it easier and more effective to manage temperatures across various industries and environments.
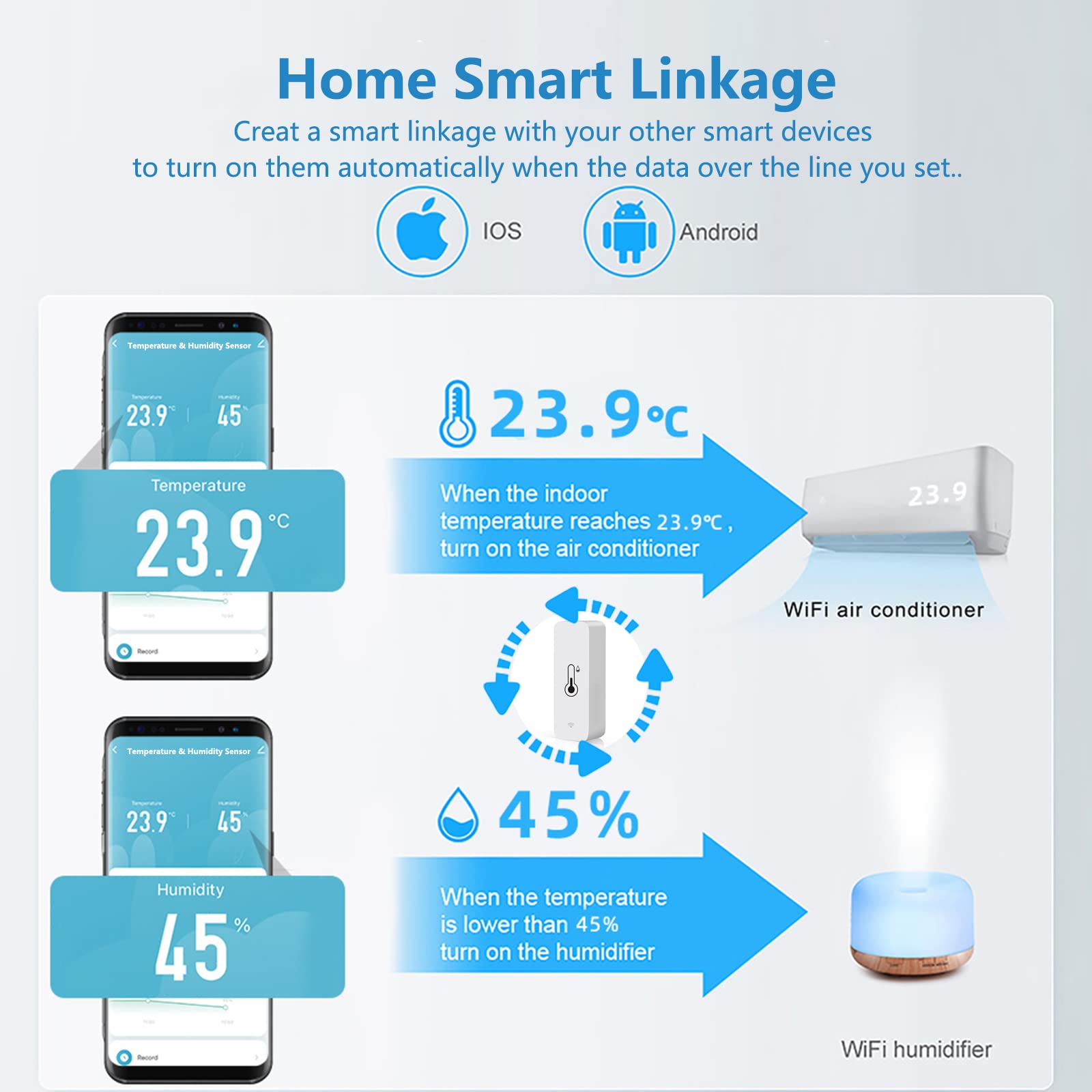
Temperature Monitoring for Perishable Goods
Remote sensors play a crucial role in monitoring perishable goods, ensuring proper cold chain compliance and preventing losses. Here’s how they benefit the perishables industry:
How do remote sensors help maintain perishable quality?
Users can define custom alarm thresholds matched to specific items. For example, fruits may require closer monitoring than frozen items. This customization allows for precise temperature control based on the needs of different perishables.
What advantages do remote sensors offer for compliance?
The data collected by remote sensors provides proof of compliance for audits. Additionally, immediate notifications allow users to address equipment failures or handling issues quickly, minimizing the risk of product spoilage or degradation.
Early Warning Temperature Alerts
Real-time remote monitoring enables a major benefit: early detection of temperature issues. This capability is crucial for preventing losses and maintaining optimal conditions.

How do early warning alerts work?
Remote sensors can be programmed with specific temperature thresholds. When these thresholds are exceeded, the system sends immediate alerts to designated personnel. This allows for rapid response to potential problems before they escalate.
What are the benefits of early warning temperature alerts?
Early warning alerts offer several advantages:
- Prevent product spoilage or damage
- Reduce energy costs by addressing HVAC issues promptly
- Minimize equipment downtime through proactive maintenance
- Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements
- Improve overall operational efficiency
By providing timely notifications, remote temperature sensors help businesses and homeowners maintain optimal conditions and avoid costly problems.
Integration with Smart Home and Building Systems
Remote temperature sensors can be integrated into smart home and building management systems, enhancing overall control and efficiency.
How do remote sensors work with smart home systems?
When integrated with smart home platforms, remote temperature sensors can:

- Trigger automated responses, such as adjusting thermostats or activating fans
- Provide data for energy optimization algorithms
- Contribute to overall home comfort and efficiency
What benefits do remote sensors offer in building management?
In commercial buildings, remote temperature sensors can:
- Optimize HVAC performance across multiple zones
- Contribute to energy-saving initiatives
- Enhance occupant comfort through precise temperature control
- Provide valuable data for predictive maintenance
By integrating remote sensors into smart systems, users can achieve greater control and efficiency in managing temperatures across various environments.
Remote Temperature Monitoring in Industrial Settings
Industrial environments often require precise temperature control for various processes and applications. Remote temperature sensors play a crucial role in these settings.
How are remote sensors used in industrial applications?
In industrial settings, remote temperature sensors can be used for:

- Monitoring equipment temperatures to prevent overheating
- Ensuring proper temperatures in chemical processes
- Maintaining ideal conditions in cleanrooms
- Monitoring temperatures in hazardous or hard-to-reach areas
- Tracking temperature-sensitive materials throughout production
What advantages do remote sensors offer in industrial environments?
Remote temperature monitoring in industrial settings provides several benefits:
- Improved safety by reducing the need for manual checks in dangerous areas
- Enhanced product quality through consistent temperature control
- Increased efficiency by optimizing processes based on temperature data
- Better compliance with industry regulations and standards
- Reduced downtime through predictive maintenance
By leveraging remote temperature sensors, industrial facilities can improve safety, efficiency, and product quality while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Remote Temperature Monitoring for Scientific Research
Scientific research often requires precise temperature control and monitoring. Remote temperature sensors provide valuable tools for researchers across various disciplines.

How do remote sensors benefit scientific research?
Remote temperature sensors offer several advantages in scientific settings:
- Continuous data collection without human intervention
- Ability to monitor temperatures in remote or inaccessible locations
- High precision and accuracy for sensitive experiments
- Real-time alerts for unexpected temperature fluctuations
- Easy integration with data analysis software
What types of research utilize remote temperature monitoring?
Remote temperature sensors are used in various scientific fields, including:
- Environmental research: Monitoring ecosystem temperatures
- Medical research: Maintaining precise conditions for samples and experiments
- Agricultural studies: Tracking soil and crop temperatures
- Oceanography: Measuring water temperatures at various depths
- Materials science: Monitoring temperature-dependent processes
By providing accurate, continuous temperature data, remote sensors enable researchers to conduct more precise experiments and gather valuable insights across a wide range of scientific disciplines.

Future Trends in Remote Temperature Monitoring
As technology continues to advance, remote temperature monitoring systems are likely to evolve and improve. Several trends are shaping the future of this technology.
What advancements can we expect in remote temperature sensors?
Future developments in remote temperature monitoring may include:
- Increased miniaturization of sensors for less intrusive monitoring
- Improved battery life and energy harvesting capabilities
- Enhanced wireless communication ranges and reliability
- Integration with artificial intelligence for predictive analytics
- Advanced materials for improved sensor accuracy and durability
How will these advancements impact temperature monitoring?
These developments are likely to result in:
- More comprehensive and granular temperature monitoring capabilities
- Increased adoption across various industries and applications
- Improved energy efficiency and sustainability in temperature control
- Enhanced decision-making through AI-powered insights
- Greater integration with other IoT devices and systems
As remote temperature monitoring technology continues to evolve, it will provide even more powerful tools for managing temperatures across a wide range of environments and applications.

Cost Considerations for Remote Temperature Monitoring
When implementing a remote temperature monitoring system, it’s important to consider the associated costs and potential return on investment.
What factors influence the cost of remote temperature monitoring?
The cost of a remote temperature monitoring system can vary based on several factors:
- Number and type of sensors required
- Accuracy and range of the sensors
- Complexity of the monitoring software
- Installation and setup requirements
- Ongoing maintenance and calibration needs
- Data storage and analysis capabilities
How can businesses justify the investment in remote temperature monitoring?
While there are upfront costs associated with implementing a remote temperature monitoring system, the potential benefits can often justify the investment:
- Reduced product loss due to temperature-related issues
- Improved energy efficiency and lower utility costs
- Decreased labor costs for manual temperature checks
- Enhanced compliance with regulatory requirements
- Improved customer satisfaction through consistent product quality
- Potential insurance premium reductions due to improved risk management
By carefully evaluating the costs and potential benefits, businesses can make informed decisions about implementing remote temperature monitoring systems and maximize their return on investment.

Best Practices for Implementing Remote Temperature Monitoring
To ensure the success of a remote temperature monitoring system, it’s important to follow best practices during implementation and ongoing use.
What steps should be taken when implementing a remote temperature monitoring system?
Consider the following best practices when setting up a remote temperature monitoring system:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of monitoring needs and objectives
- Choose sensors and software that meet specific requirements
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan
- Properly calibrate and install sensors in optimal locations
- Train staff on system use and maintenance
- Establish clear protocols for responding to alerts
- Regularly review and analyze collected data
- Perform routine maintenance and recalibration as needed
How can users maximize the benefits of remote temperature monitoring?
To get the most out of a remote temperature monitoring system:
- Regularly review and adjust temperature thresholds as needed
- Use data analytics to identify trends and optimize processes
- Integrate temperature data with other relevant metrics for comprehensive insights
- Continuously educate staff on the importance of temperature monitoring
- Stay informed about technological advancements and upgrade when beneficial
By following these best practices, users can ensure their remote temperature monitoring systems provide maximum value and effectively address their temperature-related challenges.

Monitoring temperature from a distance has become an essential need in today’s tech-driven world. With the ability to track temps remotely, we can stay informed and address issues quickly, without constant manual monitoring. Intrigued? Read on as we explore the ins and outs of remote temperature sensing.
Introduction to Remote Temperature Monitoring
Remote temperature monitoring involves using sensors to detect and record temps from afar. This allows you to keep tabs on conditions in multiple locations or hard-to-access areas from the convenience of your smartphone or computer.
Gone are the days of manual readings and data logging. Now your remote sensors can provide 24/7 monitoring and real-time alerts when thresholds are exceeded. Whether you’re concerned about perishables, HVAC performance, or virtually any temperature-sensitive application, remote sensing has got you covered.
Benefits of Remote Temperature Sensors
Remote sensors offer many advantages over traditional thermometers and manual tracking:
- Access temps in real time from anywhere
- Custom alarm notifications for out-of-range conditions
- Hands-free monitoring and datalogging
- Monitor multiple locations from one device/dashboard
- Early detection of issues to prevent losses
- Tracking and documentation for compliance
These capabilities allow you to respond to temp changes faster and optimize conditions for storage, comfort, efficiency, and more.
How Remote Temperature Sensors Work

Remote sensors contain thermocouple probes or thermistors to detect ambient temperature. Readings are transmitted wirelessly to a receiver using radio frequencies. The receiver then interfaces with software to track data and alerts.
Sensors run on battery power, so there’s no wiring required. Place them anywhere – even outside or in freezers. Their range depends on the strength of the base station/receiver. Extended networks can relay readings over very long distances.
Types of Remote Temperature Sensors
Many styles are available to suit your needs:
- Indoor/Outdoor – General use, affordable option
- Food/Refrigerator – NSF rated for commercial kitchens
- Freezer – Low temp rated, often with buffered probes
- High Temp – Rated for oven, furnace, etc. applications
- Humidity & Temp – Combines both readings in one
- Pipe Clamp – Straps onto pipes for monitoring fluids
- Thermocouple – Highly accurate probe tip sensors
Consider setup, environment, accuracy needs, and budget when selecting the right remote sensor.
Choosing the Right Remote Sensor

Key factors in choosing a remote temperature sensor:
- Measurement Range – Matches expected temps.
- Accuracy – How precise do you need it?
- Resolution – Smallest detectable change.
- Response Time – How quickly it detects temp shifts.
- Transmission Range – Distance to receiver.
- Alarms – Customizable to your thresholds.
- Display – Local LCD readout on sensor (optional).
- Power Source – Battery type and life.
- Approvals – UL, CE, NSF, etc.
- Software – Data logging, analysis, notifications.
Examine these specs to find the right match for your situation and spending plan.
Remote Sensor Accuracy and Reliability
Today’s remote sensors offer impressive accuracy thanks to advanced calibration and electronics. Look for options with certifications from recognized testing agencies.
Tight specifications like ±0.5°F over a wide range give you assurance the readings are precise. Rapid sampling further improves consistency.
For reliability, seek out reputable commercial-grade instruments with rigorous quality control and testing. Industrial sensors far outlast cheap consumer models.
Remote Monitoring for Homes and Businesses
Remote sensors have opened up invaluable monitoring options for homes and workplaces:
- Smart homes – Monitor rooms, incoming water, basement, etc.
- HVAC efficiency – Optimize for comfort and savings.
- Data centers – Prevent hotspots and failures.
- Warehouses – Ensure proper storage conditions.
- Manufacturing – Meet process temperature specs.
- Restaurants – Monitor refrigeration and cooking.
- Pharmacies – Maintain drugs at ideal temps.
The applications are nearly endless. Remote monitoring makes managing temps easier and more effective.
Temperature Monitoring for Perishables
Remote sensors are a lifesaver for monitoring perishable goods. They ensure proper cold chain compliance and prevent losses.
Users can define custom alarm thresholds matched to the item. For example, fruits need closer monitoring than frozen items.
The data provides proof of compliance for audits. And immediate notifications let you address equipment failures or handling issues quickly.
Early Warning Temperature Alerts
Real-time remote monitoring enables another major benefit – early detection of temperature excursions. Pre-defined alarm thresholds trigger notifications the moment a sensor reading veers out of the acceptable zone.
For example, if a walk-in cooler rises above 40°F, you’ll get an immediate alert. This allows you to correct the issue before products are ruined.
Such early warning capabilities are revolutionizing temperature control and loss prevention in many industries.
Remote Sensor Connectivity and Data Storage
Today’s sensors utilize wireless and cloud technology for seamless data access:
- Wireless sensors transmit to local receivers or gateways.
- Receivers connect via WiFi, cellular, or Ethernet.
- Cloud software stores unlimited data in the cloud.
- Access real-time readings and history from any web browser or mobile device.
Data is available instantly from anywhere without manual downloading. Web and apps provide powerful analytics and notifications too.
Installing and Mounting the Sensor

Proper placement is key to accurate remote monitoring. Consider these guidelines:
- Central area with typical temperature.
- Good air circulation around probe.
- Avoid direct radiation from sun or appliances.
- Allow sufficient distance between sensors.
- Use brackets for pipe/wall mounting.
Most sensors can simply sit on a shelf or attach with tape/screws. Take time to position them correctly.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Tips
A few basic practices will keep your remote sensors running smoothly:
- Replace batteries annually.
- Check for damage, debris, corrosion.
- Ensure unobstructed line-of-sight to receiver.
- Watch for interference from other wireless devices.
- Confirm software and firmware are current.
- Recalibrate periodically for maximum accuracy.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for any routine maintenance and cleaning.
Top Remote Temperature Monitoring Brands
Look for proven brands when selecting remote monitoring equipment. Top names known for quality include:
- Cooper-Atkins
- Fluke
- Lascar Electronics
- LogTag
- Omega Engineering
- Sensaphone
- Dickson
- Amprobe
These manufacturers offer extensive selections with the latest features, technology, and competitive pricing.
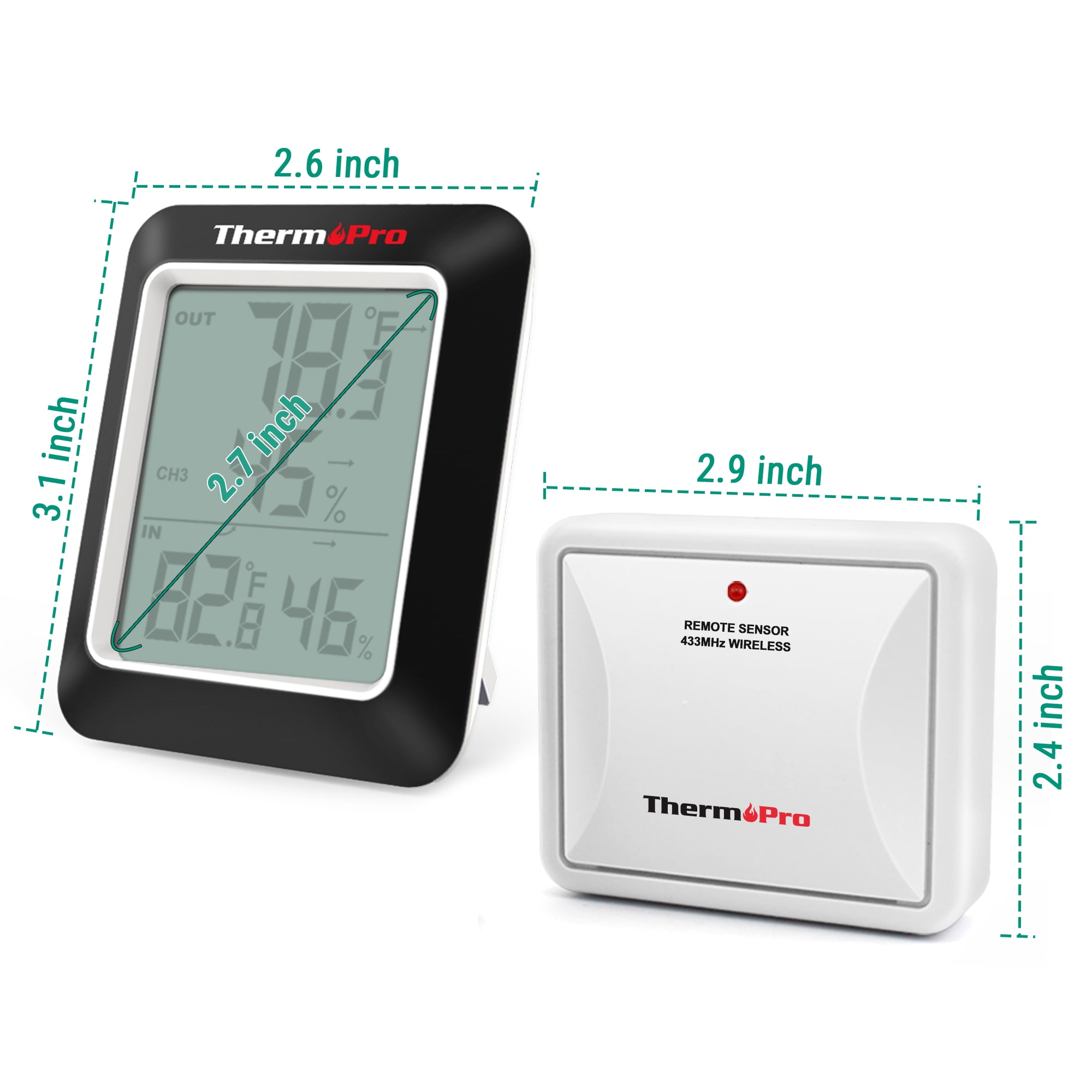
La Crosse Technology Remote Sensor Overview
La Crosse Technology offers a popular line of wireless temperature and humidity monitoring solutions. Their sensors pair with console displays as well as smart home hubs.
Highlights include LCD readouts on the sensors themselves, long 500ft+ transmission range, and flexible alarms. There are models optimized for indoor, outdoor, fridge, and freezer use.
La Crosse is based in Wisconsin and focuses on innovative weather stations, atomic clocks, and temperature monitors. Their products deliver professional-grade performance at affordable prices.
If you’re considering a La Crosse remote sensor, take time to identify the right model and placement for your application. Proper setup and care will provide years of reliable monitoring.
Start Monitoring Temperature Remotely

Remote temperature monitoring delivers game-changing visibility and control. As the technology continues advancing, its capabilities and applications will keep expanding.
Hopefully this overview has showcased the potential benefits for your environment. It’s now easier than ever to leverage remote sensors for optimized temperature management.
Implementing a system tailored to your facility and needs can provide huge dividends. So don’t delay – start reaping the rewards of remote monitoring!
Remote temperature sensors provide invaluable visibility and control for monitoring environments near and far. As this technology continues advancing, the benefits keep multiplying. Let’s explore some of the key advantages driving adoption of remote temperature sensing.
Benefits of Remote Temperature Sensors
Traditional thermometers require constant hands-on checks and manual data logging. Remote sensors change the game with automated monitoring and real-time data access. No wonder they’re becoming indispensable for homes and businesses alike.
Here are some of the top reasons to embrace remote temperature sensors:
- Real-Time Tracking – Get current readings anywhere instantly via apps and websites. No waiting for someone to physically check and record temps.
- Custom Alarms – Define your own thresholds for out-of-range alerts. Know right away when action is needed.
- Prevent Losses – Early detection of issues lets you correct problems before inventory or processes are impacted.
- Graph Trends – Visualize patterns over time to optimize temps and head off failures.
- Identify Inefficiencies – Pinpoint areas that are too hot or cold for adjustment.
- Track Compliance – Maintain digital proof of proper conditions when audited.
- Flexible Deployment – Monitor multiple points with a single system. Ideal for dispersed equipment.
- Automated Datlogging – Eliminate clipboards and Excel sheets with automatic cloud archiving.
- Smart Analysis – Reporting highlights insights for better decision making.
- Troubleshoot Remotely – Engineers can securely access readings to diagnose issues.
These capabilities are game-changers for controlling environments and processes, safeguarding inventory, and ensuring standards are met. The more you rely on stable temperatures, the more a remote monitoring system pays dividends.
For example, a restaurant using remote sensors in fridges, freezers, and walk-ins can prevent thousands in spoiled food costs over time. The system quickly detects cooling failures or door left ajar so staff can respond promptly.
An industrial plant that monitors parts or liquid temperatures at different process stages can identify inefficiencies. They may discover certain equipment runs hotter than needed, allowing adjustments for increased output or energy savings.
A climate-controlled archive for historical documents installs redundant remote monitoring with alarms. This provides an extra layer of protection to preserve irreplaceable records in the event of an HVAC failure.
And a pharmacy uses sensors in drug storage coolers, with alarms tied to key staff’s phones. Out-of-range conditions trigger immediate notifications so the issue can be addressed ASAP.
As you can see, the applications and benefits are nearly endless. Bottom line – if your operations rely on maintaining ideal temperature ranges, remote monitoring delivers immense value.
Other advantages include less labor for checking temps manually, flexibility to add sensors anywhere, and avoiding disruptions from constant monitoring. It’s a classic case where technology eliminates hassles while improving performance.
With today’s affordable pricing, quick and easy installation, and intuitive cloud-based interfaces, remote temperature monitoring makes sense for all types of organizations. Be sure to take advantage of the available incentives and rebates too.
There’s simply no better way to get complete temperature visibility and control across dispersed equipment and spaces. So embrace remote sensor technology to take your temp management to the next level!
Remote temperature monitoring is powered by innovative sensor technology that allows around-the-clock tracking from anywhere. The sensors detect ambient conditions and transmit data wirelessly to receivers and cloud platforms. Let’s examine how these versatile devices do their magic.
How Remote Temperature Sensors Work

While we take them for granted, remote sensors are remarkable feats of engineering. Here’s an inside look at the technology that enables them to remotely monitor temps:
Sensing Element
The core component that measures temperature is called the sensing element. Most remote sensors use either a thermocouple or thermistor.
Thermocouples contain two dissimilar metal wires joined at a probe tip. The voltage between them varies based on temperature. Thermistors change resistance as temps fluctuate.
These sensing elements offer high accuracy across wide temperature ranges. Their performance is digitized and calibrated for precision monitoring.
Transmitter
The sensor’s transmitter packages the temperature data into a radio signal that can be wirelessly communicated. Common transmission protocols used include:
- Bluetooth
- Zigbee
- Proprietary RF frequencies
- LoRaWAN
- WiFi
Factors like transmission range, power needs, network capacity, and security determine the best protocol for an application.
Power Supply
Remote sensors are powered by long-life batteries to avoid the need for wiring. Battery options include:
- AA or AAA cells
- Coin cell
- Lithium
- Rechargeable
Advanced designs allow 5+ years of operation on just batter power. Some sensors even harvest solar or kinetic energy to prolong battery life.
Receiver
A receiver gathers the incoming data transmissions from the sensors and decodes them back into temperature readings.
Receivers can be simple dedicated units with a display, or multi-sensor gateways with cloud connectivity. Advanced analytics and alerts are handled in the cloud.
Cloud Platform
Web and mobile apps provide seamless access to real-time readings and historical data without needing to touch the sensors or receiver. Cloud software enables:
- Remote monitoring and alerts
- Graphing and analytics
- Data storage and back-up
- API integration with other systems
The cloud allows users to check temps anywhere via their devices. It’s a smart hub for the sensor network.
By combining specialized sensing elements, wireless transmission, efficient power, intelligent receivers, and cloud integration, today’s remote temperature monitors deliver powerful capabilities without complexity. The hardware and software work seamlessly together for optimum performance.
Understanding the sensor fundamentals helps you select the right options and get the most from your network. So leverage these incredible technologies to gain temperature visibility like never before!
With the wide range of remote temperature monitoring applications, sensor technology has evolved to offer tailored solutions. There are now specialized sensor types to suit needs from the operating room to the top of a smokestack.
Types of Remote Temperature Sensors

Here are some of the common categories and use cases:
General Purpose
General remote sensors cover a wide temp range with basic accuracy. They work for applications like indoor and outdoor monitoring, HVAC systems, and storage rooms.
Ultra-Low Freezer
Rated down to -100°C, these detect temps inside medical freezers, cryogenic tanks, and extreme cold transport.
Food Safety and Storage
NSF rated models are made for commercial kitchens and fridge/freezers. Some contain buffered probes to avoid conduction errors.
High Temperature
With extended ranges up to 300°C, these sensors work in ovens, furnaces, kilns, and heating/drying processes.
Pipe Clamp
Strap-on pipe sensors monitor fluid temps in plumbing systems, manufacturing, etc. Many are armored for protection.
Infrared/Thermal Imaging
Infrared scanners map surface temps from a distance. Great for spotting heat loss and electrical/mechanical issues.
Humidity & Temperature

Combination sensors record both RH and temp in one unit. Ideal for environmental monitoring.
Alarm & Detection
Pre-wired sensors connect to alarm panels to trigger alerts for out-of-range temps in critical applications.
Thermocouple Probes
Thermocouple sensors offer fast response and very high accuracy for specialized uses.
Wireless Thermistor
Digital precision thermistors transmit readings via Bluetooth/RF for lab use and tight-tolerance processes.
Additional varieties include tiny bead-style mini sensors, industrial RTD probes, and flexible thin-film versions. Sensors continue advancing to conquer new challenges.
Key considerations when selecting a sensor type include measuring range, accuracy, speed of response, sensor design, and approvals needed. Match these to your environment and tolerance requirements.
With such diversity available today, you’re sure to find just the right remote temperature monitoring sensor for your unique application needs.
With the dizzying selection of remote temperature sensors available, it can be tricky choosing the right model. Carefully considering your needs and requirements will ensure you get a sensor that delivers maximum benefit.
Choosing the Right Remote Sensor
Walk through these key factors to identify the ideal temperature sensor for your application:
Monitoring Range
Match the sensor’s rated temperature span to your expected range. For example, ultra-low freezers need -80°C+ capacity. Avoid exceeding the minimum/maximum of the sensor.
Accuracy and Resolution
How precise do the measurements need to be? Tighter accuracy like ±0.5°C may be critical, versus ±2°C for casual monitoring. Similarly, resolution indicates the smallest detectable change.
Measurement Type
Consider the sensing element technology – thermocouple, thermistor, RTD, infrared, etc. This impacts factors like speed, accuracy, and probe design.
Probe Design
Is a flexible, armored, or buffered probe required? Does it need to be waterproof, long, or slim? Specialized probes suit certain uses.
Sensor Size and Housing
A large outdoor model may not fit small spaces. Tough polycarbonate or stainless housings withstand harsh environments.
Outputs and Connectivity

Digital options allow networked monitoring versus analog sensors that may need hardwiring. Wireless models require less labor.
Remote Access
Verify the sensor works with remote receiver and software for your needs, like cloud-based apps and alerts.
Approvals and Certifications
Select an option with required ratings for commercial facilities, like UL, CE, or NSF compliance.
Display and Interface
An integrated local display allows checking readings without software. Keypads or buttons may be useful as well.
By carefully weighing factors such as these against budgets, you’ll find the ideal remote temperature monitoring solution.
Remote Sensor Accuracy and Reliability
When it comes to using remote sensors to monitor temperature, accuracy and reliability are crucial. No one wants to rely on data that isn’t correct or sensors that fail when you need them most. So how can you ensure your remote temperature sensors are as precise and dependable as possible?
Here are 15 tips to maximize remote sensor accuracy and uptime:
1. Choose reputable brands and models

Not all remote sensors are created equal. Stick with reputable manufacturers like La Crosse Technology that have a proven track record for accuracy and durability. Check reviews and specs carefully before buying.
2. Look for sensors with NIST traceable calibration
Many top remote sensor models are calibrated against NIST standards during manufacturing. This rigorous calibration ensures accuracy within very tight tolerances, often to within +/- 1 degree.
3. Consider “smart” app-connected sensors
Newer app-enabled sensors allow you to monitor calibration status remotely and receive alerts if readings seem off. This makes it easier to identify and correct any accuracy issues proactively.
4. Get sensors with weatherproof, robust housing
Look for industrial-grade housing that can withstand dust, moisture, UV rays and other environmental factors that could degrade accuracy over time. La Crosse Technology’s commercial sensors meet IPX3 water resistance ratings for example.
5. Ensure proper placement and setup
Carefully follow manufacturer guidelines for installing remote sensors in optimal locations away from heat sources, direct sun or wind tunnels. Proper setup is key for reliable data collection.
6. Maintain an unobstructed signal path
Make sure the signal path between your remote sensors and hub remains clear. Trees growing, new construction and other changes can disrupt communication and introduce errors.
7. Change batteries regularly
Replace batteries at least once per year, more often in challenging environments. Use fresh, high-quality lithium batteries only. Weak batteries are a common cause of remote sensor failures.
8. Protect against electrical interference
Avoid mounting sensors too close to motors, generators, transmitters or strong EMI/RFI sources which may degrade signal reception and accuracy.
9. Watch for bio-fouling and physical damage
Inspect sensors periodically for algae growth, bent/broken antennas, cracked housing or other visible damage that could introduce errors. Repair or replace as needed.
10. Consider redundancy/back-up sensors

For critical monitoring applications, deploy redundant sensors for the same parameter to provide back-up data in case a sensor fails. Statistical analysis can reveal anomalies or disagreements.
11. Take advantage of data logging features
Many sensors allow recording trends and history internally or in the cloud. Analyzing historical data can reveal calibration drift or drop-outs.
12. Verify with secondary standards periodically
Spot check remote sensor accuracy at least annually using NIST-traceable reference standards. This can identify calibration drift not apparent otherwise.
13. Monitor power supply integrity
For AC-powered remote sensors, use power conditioning and UPS systems to prevent electrical spikes/surges from damaging sensitive electronics.
14. Consider wireless repeating/meshing solutions
In challenging reception environments, wireless signal repeaters and mesh networks can strengthen communication integrity between sensors and base stations.
15. Watch for firmware/software updates
Some sensors support firmware or software updates to fix bugs and improve performance. Keep systems updated for optimal stability.
By following best practices like these, you can feel confident your remote temperature monitoring system will deliver accurate, reliable data around the clock. Precision remote sensors like those from trusted manufacturers such as La Crosse Technology combined with a robust data monitoring regime give you the peace of mind your critical measurement data is always correct.
Remote Monitoring for Homes and Businesses
Keeping tabs on temperature from afar has never been more important. With remote work on the rise, business owners need to monitor conditions in empty offices. For homeowners, checking on freezing pipes or AC issues while on vacation can prevent thousands in damages. Fortunately, remote sensor technology has come a long way in recent years.
Will a remote temperature sensor solve all your problems? Maybe not all of them, but these gadgets can definitely provide peace of mind. Let’s explore the 15 best ways you can monitor temperature from anywhere.
1. Get Notifications for Extreme Temps
The #1 reason homeowners and businesses use remote sensors is to get notifications when temperatures reach concerning levels. Most models allow you to set a minimum and maximum temperature threshold. If the mercury dips too low or spikes too high, you’ll get an alert.
This feature alone can save you from disaster. Frozen pipes, dead plants, spoiled food…extreme temperatures can wreak havoc if no one’s around to notice. With a remote sensor, you don’t have to worry.
2. Check the Forecast
High-end temperature monitors can also tell you the weather forecast. You’ll know if a cold front is moving in or a heat wave is around the corner. For homes and businesses in extreme climates, this data is invaluable.
It allows you to be proactive. Crank up the heat before pipes freeze. Fire up the AC before sweltering temps arrive. For critical equipment or valuables, it pays to know what’s coming.
3. Monitor Multiple Locations
Some remote sensors are stationary, but others are portable and battery-powered. With these models, you can monitor temperature in multiple zones or rooms. Place one outside, one in the basement, one near heat-sensitive gear, etc.
This gives you a more complete picture of conditions on your property. You’ll know the temperature by the hot water heater, the wine cellar, the attic — wherever you need to keep tabs.
4. Get Visual Timelines

Modern temperature sensors record data round-the-clock. With the right app or dashboard, you can view the temperature timeline in clear graphs and charts. Most models archive the data so you can look back.
Visual timelines make trends easy to spot. You’ll see if there’s recurring overheating in the server room, for example, or if outdoor temps regularly spike in the afternoon.
5. Monitor Humidity Too
Temperature and humidity go hand in hand. Many remote sensors track both metrics, allowing you to monitor comfort and mold risk. You’ll get alerts when humidity is too high or too low.
For businesses monitoring unoccupied offices, this data is crucial. Certain levels of humidity can damage furniture, electronics and documents over time.
6. Automate Temperature Control
Advanced sensors do more than just monitor temperature — they can also control your HVAC system. Automated temperature regulation helps optimize energy efficiency.
For example, remote sensors could detect when a space is unoccupied and tell your AC or furnace to minimize runtime. Smart thermostats achieve a similar result, often by syncing with motion detectors.
7. Monitor Indoor Air Quality

Some next-gen sensors track air quality metrics like particulate matter, CO2, and VOCs (volatile organic compounds). This allows you to monitor indoor pollutants that can impact health and comfort.
If pollutants exceed healthy thresholds, you can be notified. Then, you can address issues before occupants experience problems. This is especially useful for offices, schools, elderly care centers, etc.
8. Get Mold Risk Alerts
By monitoring both temperature and humidity over time, sophisticated sensors can assess mold risk. Data can reveal if conditions are favorable for microbial growth.
In damp basements or bathrooms, early alerts allow you to lower humidity before mold takes hold. This prevents costly clean-up projects down the road.
9. Monitor Noise Levels
Some models track decibel levels along with temperature. This gives you visibility into both comfort factors. You’ll know if sound from road traffic, machinery, barking dogs etc. exceeds desired limits.
For vacant properties, noise alerts may signal trespassers or a break-in. For occupied spaces, they allow you to address noise pollution issues.
10. Detect Water Leaks
Specialized sensors can also detect water leaks, giving you immediate notification. They accomplish this by monitoring subtle changes in humidity at floor level when pipes burst or appliances overflow.
For unoccupied homes and businesses, leak detection alerts allow you to dispatch help immediately to minimize damage. Leaky roofs and appliances leaking on floors are often caught right away too.
11. Monitor Power Outages
By tracking when battery power kicks in, remote sensors can reveal power failures. Again, this allows you to take swift action when properties are unoccupied.
Frequent outages may indicate wiring problems need addressed. Knowing outages occurred also provides useful context for other alerts you receive during that timeframe.
12. Ensure Habitable Temperatures
For landlords monitoring rental properties, temperature tracking helps ensure tenants are provided habitable living conditions. Being able to prove suitable heating and cooling is provided can prevent disputes.
In commercial spaces, OSHA and other regulations often require temperature monitoring records for worker health and safety. Remote sensors provide helpful documentation.
13. Optimize Stockrooms & Storage Areas
Warehouses, pharmaceutical stockrooms, art storage facilities and more can benefit from remote monitoring. Ensuring temperatures remain stable protects inventory against damage.
If cooling fails in a server room, for example, system administrators will know immediately before equipment overheats. Timely alerts prevent losses.
14. Protect Valuables from Heat & UV Rays
For museums, archives, collections and galleries, sensors help protect irreplaceable artifacts. Temperature and UV monitoring ensures light and heat remain within safe parameters.
Direct sunlight, extreme heat, and drastic temperature swings speed deterioration. Tight monitoring allows curators to modify conditions to maximize preservation.
15. Verify Food Safety
Commercial kitchens, refrigerators and transport vehicles use remote sensors to verify food safety. Proper temperature control inhibits bacterial growth and spoilage.
Most food safety regulations require monitoring and reporting. Digital records also provide traceability if any product quality issues arise.
The applications for remote temperature monitoring are nearly endless. The right sensors provide peace of mind for homeowners and optimize safety for unoccupied spaces. They prevent losses and enhance transparency. While no technology is a silver bullet, automated tracking brings us one step closer to predictive, proactive facility management.
Temperature Monitoring for Perishables
Keeping close tabs on temperature is crucial for companies shipping and storing perishable goods. Whether it’s fresh produce, meat, dairy, flowers or pharmaceuticals, precise temperature control is key to quality and safety. But how can you ensure optimal conditions when you’re not there? Remote temperature sensors are the answer.
Technology has enabled robust real-time monitoring of perishables in transport and storage. Proactive tracking minimizes losses and provides documentation to verify compliance. Let’s review the top ways remote sensors are improving oversight for goods requiring strict climate control.
1. Verify Conditions During Transport
Monitoring temperature, humidity and light in transit ensures perishables remain saleable upon arrival. Sensors placed with produce shipments for example, can identify if refrigeration fails or gets too cold.
Alerts notify the driver to adjust truck temp as needed. Delays from rejected loads are avoided and thermostat problems can be proactively repaired.
2. Prevent & Detect Shipment Diversion
Valuable cargo like pharmaceuticals can be targeted by thieves. GPS-enabled sensors allow monitoring of the shipment’s route in real time so diversions can be rapidly identified and addressed.
Door sensors also provide alerts to indicate potential theft. Driver notification and coordination with law enforcement can often recover stolen goods.
3. Optimize Cold Chain Compliance
Stringent regulations govern temperature control for foods, drugs and chemicals. Remote sensors provide round-the-clock data to document compliance with storage and transport requirements.
Electronic records are far easier to retrieve than paper logs. And real-time tracking enables proactive adjustments before excessive temperature swings occur.
4. Prevent Rejection & Rework
No company wants to pay to ship product only to have it rejected upon arrival. Remote monitoring helps identify if temperature, humidity or other conditions fell outside acceptable limits in transit so contingencies can be made.
This might mean quickly finding an alternate buyer for still-usable product. Or separating damaged portions that require rework to salvage some value.
5. Troubleshoot Problem Shipments
Data logged by sensors can provide invaluable clues if perishable products arrive out of spec. Reviewing the temperature profile throughout the journey helps pinpoint where and when problems arose.
Was there a delay at customs where the container got too hot? Did refrigeration fail mid-route? Detailed timelines aid investigation so improvements can be made.
6. Select Optimal Routing
Because sensors record environmental data, companies can analyze which routes and modes of transport better maintain target conditions. Routing decisions can then be optimized.
For example, sensors may reveal that adding an extra day by ship is preferable for delicate flowers vs. a shorter truck route with extreme daytime temperatures.
7. Verify Warehouse Conditions
Monitoring cold storage units, clean rooms and controlled atmospheres ensures conditions remain optimized 24/7. Alerts provide opportunity to correct issues promptly, before inventory is impacted.
Data logs also verify protocol compliance and can aid root cause investigation of any product defects that do arise.
8. Ensure First In/First Out Rotation

Sensors enable cloud-based monitoring to confirm proper first in/first out rotation of perishable stock. Data validates the oldest products get shipped out first, preventing losses from expiration.
Rotation exceptions appear if a newer pallet gets pulled instead of the one with the shortest remaining shelf life. Corrective action can be taken.
9. Adjust Environmental Controls Remotely
Remote temperature and humidity adjustment enables suppliers to tweak warehouse conditions as needed to protect goods. If they know a hot day is coming, cooling can be dialed down preemptively.
Worker safety is enhanced too – no one has to enter extreme environments to manually adjust thermostats.
10. Enhance Shipment Integrity
Monitoring seals, door openings and other sensor data helps detect tampering or diversion. For high-value cargo, this improves security and transparency.
Tracked metrics like light and moisture also provide insight on storage conditions that may compromise quality or packaging integrity during extended storage.
11. Optimize Energy Efficiency
Remote monitoring enables adjustling temperature precisely to product needs, avoiding overcooling. Doors left open can be quickly identified to prevent unnecessary refrigeration loss.
As sensors identify trends and inefficiencies, protocols can be enhanced to cut energy costs.
12. Prevent Theft & Diversion
Monitoring location, seals, door access and other metrics provides transparency to prevent theft and verify chain of custody. Detailed timelines enable rapid response if anomalies occur.
This is especially critical for cannabis, pharmaceuticals, currency shipments and high-value consumer products prone to black market diversion.
13. Support Insurance Claims
If losses do occur, recorded sensor data provides critical documentation for insurance claims and loss prevention improvements.
Having time-stamped proof of temperatures, humidity levels, delays, seal breaches and more substantiates claims of damage or theft.
14. Spot Equipment Failures

Temperature spikes and drops often indicate refrigeration issues that need repair. Spotting problems quickly limits losses. Extended high humidity reveals dehumidifier failures.
Data aids preventative and predictive maintenance. Issues can be addressed before catastrophe strikes.
15. Improve Packaging
Product design improvements such as enhanced insulation, cooling gel packs and moisture absorbents can extend perishable life. Sensor data pinpoints vulnerabilities and tests package iterations.
Over-packaging can be pared back as data is gathered on minimal effective packaging requirements for specific products.
Sensor technology delivers actionable intelligence to optimize perishable quality and safety. Remote monitoring enables proactive intervention, documentation and analysis. While up-front costs exist, prevented losses justify the investment. The data ultimately helps strengthen operational processes and reduces waste.
With enhanced visibility into cold chain specifics, perishable handling enters a new era – smarter, safer and more efficient. Meanwhile, consumers benefit from fresher, higher-quality foods, pharmaceuticals and other climate-sensitive goods.
Early Warning Temperature Alerts

Extreme temperatures can wreak havoc if no one is around to notice. Pipes burst, plants die, food spoils. By the time you return, the damage is done. Fortunately, remote temperature sensors provide an early warning system to prevent disasters.
Today’s sensor technology can notify you the moment concerning temperatures are reached. But how exactly can early alerts protect homes and businesses? Let’s explore the top benefits of proactive monitoring.
1. Prevent Frozen Pipe Bursts
In frigid climates, vacant homes are at risk when the mercury plunges. Pipes can freeze and rupture, unleashing catastrophic flooding upon return. Temperature alerts give advance notice to take preventative action.
Turn on heat, drip faucets, and schedule check-ins to confirm pipes remain intact. Early warnings let you dodge expensive repairs.
2. Protect Plants from Frost
Gardeners invest heavily in their plants each season. An overnight frost can undo all that careful cultivation. Cold alerts provide time to shield or bring plants indoors before disaster strikes.
With warnings in place, you can prevent cold snaps from killing your prize azaleas or early-blooming rhododendrons.
3. Prevent Hot Car Battery Death
In scorching climates, extreme heat can kill car batteries sitting unattended for weeks. Getting stranded is the last thing you want at the airport. Temperature alerts cue you to start the car periodically or set up shade.
A simple text allows you to prevent an untimely demise of your vehicle’s battery due to baking temperatures.
4. Rescue Overheating Pets
Even with adequate food and water, pets left home alone can succumb to heat stroke on sweltering days. Temperature warnings clue you in to get back quick or dispatch someone for animal welfare checks.
Your pets rely on you to ensure their safety. Remote monitoring helps look out for them when you can’t be there.
5. Prevent Spoilage of Freezer/Fridge Foods
Coming home to a fridge full of spoiled food is a nightmare. Power failures or freezer breakdowns rapidly accelerate food waste. But temperature alerts notify you of rising cold storage temps before it’s too late.
This allows you to mitigate losses by dealing with the issue promptly. Early warnings let you save the steak instead of tossing it.
6. Protect Wine Collections from Cook Swings

Wine enthusiasts invest thousands in cultivating fine reserves. But high heat and wide temperature swings degrade labels over time. Alerts provide peace of mind that storage conditions won’t damage your prized vintages.
For serious oenophiles, proactive monitoring is essential to safeguard their collections for proper aging.
7. Prevent Mold & Mildew Growth
Excessive moisture and humidity create a playground for mold, especially in unused cabins and vacation homes. But early humidity alerts allow you to adjust conditions before mold takes hold and creates a massive remediation project.
A little proactive vigilance goes a long way to prevent spore colonies from establishing themselves in your absence.
8. Save Sensitive Art & Instruments
Fluctuating humidity and temperature slowly degrade pianos, guitars, paintings and other prized possessions. Early notification of concerning conditions provides opportunity to modify the environment.
Closely monitoring storage spaces allows you to take preventative steps to preserve your expensive collections and instruments.
9. Avoid Losses in Unattended Retail Stores

After-hours moisture leaks or drastic temperature changes can ruin merchandise. Remote alerts help managers address issues immediately, before inventory is impacted.
Ensuring systems keep operating in unmanned stores prevents returns, losses and headaches down the road.
10. Prevent Heat-related Building Damage
In intense heat, unattended buildings are vulnerable. Excessive heat can damage roofing, warp siding and cause asphalt to bleed. Temperature alerts cue you to cool things down.
Putting a plan in place to actively manage vacant buildings protects your property until you return.
11. Safeguard Server Rooms
Modern businesses rely on servers operating optimally 24/7. Excess heat can cause system crashes and component failures. Cooling alerts prompt action before critical infrastructure gets fried.
With remote oversight, businesses can meet their duty to securely maintain digital assets and protect data centers.
12. Verify Safe Temperatures for Children & Elderly
Ensuring comfortable yet safe temperature limits gives peace of mind when leaving elderly relatives or kids home alone. You’ll be notified if conditions get dangerously hot or cold.
Proactive monitoring helps safeguard loved ones who are more vulnerable to extremes.
13. Prevent Fire Hazards
Electrical, HVAC and other equipment failures often show up first as temperature anomalies. An unvented furnace or electrical short can spark fires. Early alerts provide warning to address instabilities before disaster strikes.
Monitoring allows you to mitigate risks proactively when nobody is home to detect issues.
14. Optimize Energy Use
Extreme temperature alerts clue you in to problems with insulation, furnace runtimes, ineffective shades and other efficiency issues. This allows you to improve systems and practices to reduce energy costs.
Oversights are easier to identify with consistent temperature data to reveal trends.
15. Verify Regulatory Compliance

In pharmaceuticals, commercial kitchens and chemical plants, defined temperature limits must be maintained. Monitoring and documentation ensure standards are met at all times.
Data also aids incident investigation if regulatory questions arise. Having records is critical for compliance.
Remote temperature alerts enable issues to be addressed before they become catastrophes. A few key warnings can prevent untold damages.
Homeowners gain peace of mind that pets and pipes will remain safe. Businesses dodge inventory losses and data center disasters. For minimal investment, temperature notifications provide tremendous protection and oversight.
Remote Sensor Connectivity and Data Storage
Modern remote sensors do far more than just record temperature or humidity. Advanced connectivity and data handling enable powerful tracking, notification, analysis and control capabilities.
How do the latest sensors transmit data? What backend systems support today’s remote monitoring applications? Let’s explore key innovations in sensor connectivity and data usage.
1. Wireless Data Transmission

From stand-alone buildings to vehicles, vessels and in-transit containers, wireless connectivity allows remote sensors to transmit data from nearly anywhere. Most leverage cellular, WiFi or low-power networks like LoRaWAN.
Wireless transmission enables real-time tracking and notifications. Hardwiring sensors is not required.
2. Two-Way Communication
Advanced sensors don’t just transmit sensor data, they also receive control commands and configuration updates from the backend monitoring system. This two-way communication enables complete remote oversight.
Operators can tweak sensor behavior and thresholds in real time without touching the sensors physically.
3. Encrypted Data Transmission
Bank-level encryption protects sensor data transmission from interception or tampering. This ensures sensitive readings remain private and secure as they traverse networks.
Encrypted messaging provides peace of mind when monitoring valuable cargo, critical infrastructure or PHI (protected health information).
4. Always-On Connectivity
Utilizing multiple cellular networks ensures constant connectivity dead zones are avoided. If one carrier has an outage, the sensor automatically fails over to another.
Persistent connectivity prevents data gaps, enabling true 24/7 real-time monitoring and control.
5. Remote Diagnostics & Updates
Two-way communication allows remote diagnosis of sensor issues and over-the-air software/configuration updates. No hands-on maintenance required.
Continuous improvement and problem resolution can happen instantly across the entire sensor deployment.
6. Scalable Cloud Architecture
Sensor data is aggregated in the cloud for analysis, alarms, visualization, reporting and API connectivity. Cloud infrastructure scales seamlessly as sensors and users are added.
Capacity matches demand without limits. Onsite datacenter buildouts are avoided.
7. Data Redundancy & Failover
Cloud platforms utilize resilient server architecture with failover databases and backups. If any component fails, automated redundancy ensures uptime and data integrity.
Monitoring continues uninterrupted even if individual servers go down.
8. Intuitive Web & Mobile Interfaces

Alerts, charts and control functions are accessible via user-friendly web dashboards and mobile apps. Permissions, locations and data views can be customized for each user.
Usability maximizes benefits for non-technical users across field personnel, management and executives.
9. Custom Reporting & Exports
Flexible reporting generates PDFs or CSV file exports for compliance, analysis and recordkeeping. Reports can contain charts, maps, custom time periods and filtered sensor data.
User controls allow building reports containing any required dataset.
10. Third-Party System Integrations
Open APIs enable direct integration with existing inventory systems, facility management platforms, predictive maintenance tools and more. Sensor data can augment broader capabilities.
New efficiencies are gained when sensor monitoring is unified with other software systems.
11. Automation & Control Functions
Sensor alerts can trigger automated corrective actions like adjusting HVAC systems or generating service tickets. Email and SMS alert rules are customizable.
Autonomous issue resolution reduces downtime and human intervention.
12. Edge Data Processing

Performing initial data aggregation and pattern recognition right at the sensor edge reduces network traffic and cloud processing overhead.
Only meaningful event data gets transmitted upstream for additional analysis.
13. Tenants & Permission Controls
Monitoring platforms support role-based access and multiple customer tenants. Sensor networks can be logically separated and assigned to designated users.
Customers only see their own data partitions for privacy.
14. Location Tracking
GPS and geofencing abilities provide visibility into sensor positioning and proximity-based alerts. Location ensures readings correlate to the right asset.
Mappers visualize sensor movement in real time during transport.
15. Tamper Alerts
Sensors can report removal, motion, case opening or electromagnetic interference to reveal potential tampering or damage.
Security notifications trigger rapid response to protect valuables, critical cargo or PHI.
Sophisticated connectivity and data handling transform modern remote sensors from simple data-loggers into powerful IoT platforms. They deliver actionable intelligence for homes, supply chains, facilities and logistics.
With comprehensive backend functionality, organizations gain expanded visibility, control and analytical abilities to protect assets around the globe.
Installing and Mounting the Sensor
Once you’ve selected the right remote temperature sensor for your needs, proper installation is key to gathering accurate, reliable data. Thoughtful sensor placement and mounting also helps the devices work well over the long haul.
What are the best practices for installing remote sensors? Let’s explore proven tips for seamless deployment in homes and industrial settings alike.
1. Ensure Adequate Wireless Signal Strength
Before permanently installing sensors, test the wireless connectivity in the exact mounting locations you have in mind. This verifies transmission reliability.
Check for any dead zones where concrete, metal structures or distance may interfere. Relocate the sensor if needed until stable communication is confirmed.
2. Minimize Cable Lengths
If hardwired sensors are used, shorter cable lengths are preferable. Extended runs are prone to electromagnetic interference which can distort readings.
Limit cabling to the minimum workable length when wiring remote probes. This safeguards data integrity.
3. Select Representative Locations
Install temperature sensors in positions that experience similar conditions to the environments you aim to monitor. Place them centrally rather than along room perimeters, for example.
Careful placement captures conditions affecting the equipment or inventory you hope to protect.
4. Avoid Heat Sources & Direct Sunlight
Proximity to appliances, machinery or windows can skew temperature results. Position sensors well away from heaters, vents, ovens and direct sun exposure.
Ensuring an accurate ambient reading prevents false alarms triggered by temporary heat spikes.
5. Consider Air Circulation Effects
Locations with poor air mixing may experience temporary temperature layers that are not representative. Ceiling vents, server racks and shelving can create microclimates.
Factor in airflow patterns when selecting installation sites to obtain useful data.
6. Facilitate Access for Maintenance
While remote sensors require little care, occasional calibration and battery changes may be needed over time. Make sure they are placed conveniently within reach.
Avoid difficult-to-access installation sites that would require special equipment.
7. Utilize Included Mounting Hardware

Remote sensors include brackets, magnets, tape or other provisions to facilitate clean installation. Take advantage of these factory options before improvising your own methods.
Purpose-designed mounts keep the device secure while protecting wires and connections.
8. Consider Tamper Resistance
For monitoring refrigerated trucks, pharmaceutical shipments or equipment rooms, tamper-resistant fixtures or adhesives keep the sensor firmly in place.
Avoid loose mounting that could permit casual tampering or inadvertent repositioning.
9. Select Stable Mounting Surfaces
Vibration or frequent impacts can loosen remote sensors over time. Choose a solid, permanent surface unlikely to experience heavy movement or adjustments.
A firmly fastened mount prevents sensor drift or detachment.
10. Allow Space for Antenna Positioning
Leave ample clearance around the antenna housing to prevent obstructed wireless transmission. Cables, shelves, walls and containers placed too closely can degrade the signal.
Refer to product specs for specific antenna spacing needs and sight-line requirements.
11. Use Included Cable Shielding
Shielded cabling minimizes electromagnetic interference for sensor probes located remotely from the main recording unit.
Proper shielding prevents distorted readings caused by nearby motors, pumps, transformers or other equipment.
12. Label Sensor Locations
For networks containing multiple sensors, properly label each device and its installation location. This avoids confusion if troubleshooting is needed.
Naming conventions that identify building and room details provide helpful context.
13. Secure Exposed Wiring
Contain and fasten any loose cables between probe units and monitoring hardware. This prevents snags or cuts that could compromise data flow.
Proper wire management maintains system integrity and safety.
14. Confirm Readings Remotely
Verify remote sensor readings from the software interface prior to leaving the site. This validates proper installation and device functionality.
Catching issues immediately allows problems to be addressed on site rather than requiring a return service call.
15. Set Threshold Alerts

Configure temperature excursion alerts for the installed sensors before leaving. Confirm notifications are received on your phone, email or platform dashboard.
Proper configuration activation reduces the need to revisit sites later just to tweak alarm settings.
With mindful placement, mounting and verification, remote sensors can gather optimal data right from the start. Follow best practices during installation for maximum longevity and reliability.
Sensor networks with professional deployment deliver consistent, accurate tracking. They serve as trustworthy frontline sentries for facilities and shipments worldwide.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Tips
Remote temperature monitoring systems require minimal upkeep, but occasional maintenance is recommended to keep them running optimally. Knowing potential trouble spots also helps resolve any issues promptly.
What basic upkeep is required? And how can you diagnose and fix common problems? Here are key maintenance and troubleshooting tips for your remote sensors.
1. Monitor Battery Levels
Remote sensors have limited battery life, anywhere from 1-5 years usually. Monitoring voltage levels allows ample time to plan replacements.
Letting batteries fully drain can lead to gaps in temperature data until replacements are installed.
2. Keep Firmware Updated
Manufacturers periodically release sensor firmware updates with new features and bug fixes. Keeping devices current ensures maximum functionality.
Outdated firmware leaves sensors vulnerable to connectivity problems already addressed via updates.
3. Test Wireless Signal Strength
Periodically verify sensors maintain adequate wireless signal reach. New equipment or structures nearby could degrade connectivity over time.
Early warning allows antennas to be relocated or signal repeaters added to restore reliable data flows.
4. Calibrate Sensors Annually
Recalibration using a reference temperature source annually helps ensure readings stay accurate over years of service.
Drift can occur slowly. Regular calibration maintains precision and prevents false alarms.
5. Verify Key Notifications Work
Simulate temperature excursions to confirm configured alerts and alarm rules still function properly during maintenance windows.
Malfunctioning alerts defeat the purpose of 24/7 monitoring. Test them periodically.
6. Check for Physical Damage
Look for loose wires, cracked casings, water intrusion or similar physical degradation that could undermine sensor function.
Repair or replace damaged units before breaches develop that jeopardize data integrity.
7. Clean Sensor Lenses and Probes
Gently clean accumulated dust, oils and grime off optical lenses and temperature probes when doing site maintenance.
Soiled optics and contacts can inhibit accurate readings.
8. Verify Mounting Security
Ensure screws, magnets, adhesive pads and other mounting provisions remain firmly anchored. Tighten or augment as needed.
Loose sensors result in position shifts and possible reading inaccuracies.
9. Check Sensor Locations
Confirm temperature sensors remain in their intended locations and have not been inadvertently moved or repositioned.
Readings from misplaced sensors lose relevance. Return any shifted units to their designated spots.
10. Rule Out RF Interference
If wireless connectivity becomes intermittent, nearby radio frequency sources may be the culprit. Move the sensor away from suspect noise sources as a test.
Microwaves, motors, power lines and plasma cutters are common RF emitters to avoid.
11. Switch Batteries Before Failure
Don’t wait until batteries fully die before replacing them. Swap them out when 20-30% capacity remains to avoid data gaps.
Having fresh spares ready preserves monitoring continuity.
12. Verify API Data Flows
If remote sensors integrate with other systems via APIs, check that automated data flows remain intact during maintenance checks.
Loss of API functionality undermines dependent business processes relying on sensor data.
13. Confirm Time Sync Accuracy
Ensure device clocks maintain accurate time synchronization for data timestamp precision. Reset if significant drift is found.
Without time sync, data analytics, reports and graphs lose meaning.
14. Reboot Malfunctioning Units
Power cycle unresponsive sensors by removing and restoring battery power. Most issues resolve with a quick reboot.
Avoid factory resets which erase your configurations and require sensor reprogramming.
15. Seek Tech Support If Needed
For stubborn connectivity, calibration or data issues that evade troubleshooting, engage technical support for additional expertise.
Vendor assistance can quickly remedy problems before they disrupt monitoring objectives.
Basic preventative care optimizes remote sensor lifespan and performance. Staying vigilant for potential problems also ensures reliable continuity you can count on.
With proactive maintenance and troubleshooting, your temperature monitoring capabilities will provide many years of robust data collection and alerts.
Top Remote Temperature Monitoring Brands
Selecting the right temperature monitoring system starts with choosing a reputable brand. Established manufacturers offer time-tested reliability along with robust features and connectivity.
Which solution providers lead the pack? Here are 15 top remote temperature monitoring brands used by homes and businesses worldwide.
1. La Crosse Technology
Known for weather stations and sensors, La Crosse Technology provides a wide selection of remote thermometers. Models include alerts, graphs, and integration with smart home platforms.
Trusted by both homeowners and commercial users, La Crosse is a leader in accessible monitoring technology.
2. Ambient Weather
From weather enthusiasts to industrial clients, Ambient Weather meets temperature tracking needs with DIY and pro-grade options. Systems are rugged and accurate.
Ambient also manufactures monitoring stations for wind, rain, light and more to provide complete environmental insight.
3. AcuRite
AcuRite specializes in weather instrumentation for consumer and commercial markets. Temperature options range from basic indoor/outdoor displays to sophisticated sensors.
Intuitive AcuRite designs and accurate readings make environmental monitoring simple for any user.
4. Onset
Known for data loggers and meters, Onset provides research-grade sensors for agriculture, energy, facilities and more. Models meet rigorous scientific standards.
Users trust Onset for precision temperature tracking in mission-critical applications worldwide.
5. Monnit
Combining wireless sensors with cloud-based monitoring, Monnit solutions include temperature among dozens of measurement options. Integrations and automation capabilities provide a complete view of operations.
Enterprise-level remote monitoring is cost-effective and scalable with Monnit’s full-stack offerings.
6. Omega Engineering
From food processing to life sciences, Omega Engineering supplies top-tier data acquisition and control solutions. Its temperature probes and transmitters provide research-level performance.
Trusted by leading organizations, Omega sets the standard for industrial-grade environmental monitoring.
7. Cooper-Atkins
Cooper-Atkins sensors track temperature, humidity and more in facilities across food service, manufacturing, and warehousing. The company is an expert in monitoring automation and compliance.
Rugged hardware and intuitive software make Cooper-Atkins a mainstay for regulated industries.
8. Sensaphone
Providing automated 24/7 monitoring since 1973, Sensaphone offers all-in-one systems with sensors, alarm dialers and voice notifications. Models are available for both commercial and residential sites.
Sensaphone simplifies environmental oversight for non-technical users across the globe.
9. SensoScientific
Specializing in pharmaceutical and biomedical tracking, SensoScientific delivers compliant, validated monitoring solutions. Wireless sensors connect to a central FDA-compliant gateway.
High accuracy and rigorous sensor calibrations meet stringent industry regulations.
10. Emerson
A titan in process controls and automation, Emerson’s measurement technologies include precision temperature transmitters for demanding applications. Models integrate with control systems.
Emerson provides rock-solid stability for heavy industrial and high-value processes.
11. ThermoWorks
Known for premium thermometers and probes, ThermoWorks also provides data loggers and wireless monitoring systems tailored for food service and HVAC. Accuracy is independently verified.
When high precision is non-negotiable, ThermoWorks delivers reliable caliber remote monitoring.
12. Digi-Key
Electronics supplier Digi-Key stocks a huge selection of modular monitoring components for DIY sensor networks. Industrial-grade transmitters, data loggers and more are all available.
For custom-designed monitoring, Digi-Key provides trusted building blocks.
13. Rotronic
Swiss manufacturer Rotronic is a leader in relative humidity and temperature instruments. Models meet metrology standards for laboratories, museums, and healthcare.
Precise calibration and adjustment ensure data from Rotronic sensors is court-admissible.
14. ControlByWeb
With cloud automation systems for remote site management, ControlByWeb enables monitoring and HVAC control from anywhere. Robust data logging capabilities are included.
Intuitive dashboards and alerts simplify oversight of distributed properties and facilities.
15. Monnit Wireless Sensors
From standalone loggers to enterprise-grade sensor networks, Monnit provides complete temperature and environmental monitoring. Integrations allow leveraging data across the organization.
Scalable and cost-effective, Monnit solutions grow from small trials into global deployments.
Whether you need an affordable home sensor or industrial-scale solutions, these top brands deliver proven technology. Look for robust connectivity, data continuity protections, and user-friendly operation when evaluating monitoring options.
With the right temperature surveillance system, you gain 24/7 visibility over assets near and far. No location is too remote.
La Crosse Remote Sensor Overview

For over 30 years, La Crosse Technology has provided reliable weather stations and environmental monitors to consumers and businesses alike. Their remote sensor options offer flexible temperature and humidity tracking.
How do La Crosse sensors work and what capabilities do they offer users? Let’s explore the key features and technologies that make them a popular choice.
Accurate and Calibrated Readings
La Crosse sensors use precision thermometers and hygrometers to provide temperature and humidity readings accurate to ±1°F and 3-5% RH. Sensors are calibrated at the factory.
Quality components ensure the environmental data collected can be trusted for critical monitoring applications.
Wireless Transmission
Using 433MHz or 915MHz frequencies, La Crosse transmitters beam readings back to the display console up to 330 feet away. No wires to run.
Placement flexibility and mobility are enabled by wireless connectivity between the probe and the monitoring station.
Remote Probing

Separate probe modules allow placing sensors remotely from the indoor display. Probe and console are linked wirelessly.
Detached probing enables monitoring temperatures anywhere desired without requiring the console in the same location.
Multiple Sensor Capacity
La Crosse monitoring stations can receive data from up to 15 remote probes simultaneously. Each probe reports its ID for tracking.
A single console organizes data from across a property in one easy-to-access dashboard.
LCD Display Console
Readings display instantly on a backlit LCD console with clock and moon phase calendar. Touchscreen options are also available.
At-a-glance monitoring keeps users updated on current conditions without requiring a smartphone or computer.
Alarm Notifications
When temperatures go above or below defined thresholds, the monitoring station activates audio, visual, and radio alarms to advise users immediately.
Customizable alert settings notify users of dangerous extremes that require intervention.
Smart Home Integrations
Select La Crosse models integrate with Alexa, Google Assistant and IFTTT for voice-activated status updates and smart notifications.
Connecting to smart ecosystems optimizes automation and convenience.
Graphing & Trend Analysis
Using included software, recorded data from the sensors can be downloaded to a PC for graphing and trendspotting. Data is date/time stamped.
Graphical logs provide insights on usage patterns and system performance.
Mobile App Access
iOS and Android apps enable monitoring sensor readings and configuring the console from mobile devices inside or outside the home.
Mobile accessibility makes oversight convenient anywhere with cellular service.
Power Options
Monitoring stations can be powered by wall outlets, batteries, solar panels or USB, depending on model. Remote probes use batteries or solar.
Flexibility in power sources facilitates use in varied environments and locations.
Rugged and Weatherproof
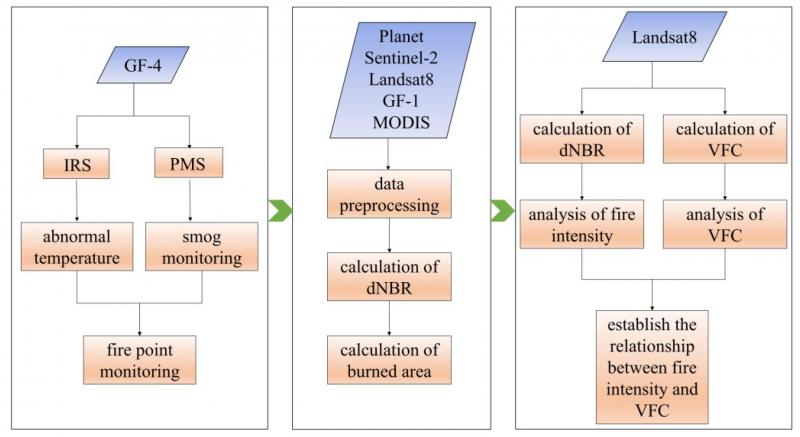
La Crosse sensors withstand use in dusty attics, humid basements, outside yards and more. Their composite housing protects components.
Designed for real-world home use, the sensors operate reliably in tough environments.
Affordable Cost
With models ranging from $20 to $300, La Crosse provides an economical entry point for temperature monitoring. Sensors are an accessible technology.
Budget-friendly pricing makes La Crosse stations popular for personal use around the home.
Trusted sensor accuracy combined with helpful alert options make La Crosse systems a wise choice. Their versatility supports many monitoring applications.
Reliable readings and intuitive operation empower users to take control of conditions. Enjoy peace of mind with La Crosse remote environmental vigilance.
Start Monitoring Temperature Remotely
In today’s connected world, being able to monitor temperature from afar has never been easier or more vital. Whether you’re a parent wanting to check on a baby, a business needing to maintain proper warehouse conditions, or even a gardener ensuring your greenhouse doesn’t get too hot, temperature sensors and monitors help provide peace of mind and prevent disasters.
With so many options on the market, how do you know which remote temperature monitoring system is right for you? Here we’ll explore the 15 best ways to keep an eye on temperature from a distance. From basic monitors to sophisticated sensors, we’ll help you find the perfect fit.
1. Smart Thermostats

A smart thermostat like the Nest or Ecobee lets you control your home’s temperature settings from your smartphone, even when you’re away. Most connect to WiFi and allow programming based on your schedule and presence. Not only does this allow remote monitoring, but it can also help save energy and money while keeping your home at just the right temperature.
2. Wireless Indoor/Outdoor Thermometers
Simple and affordable, an indoor/outdoor thermometer displays the temperature both inside and outside your home. Models like the La Crosse Technology C85845 allow you to place the outdoor sensor up to 100 feet away while monitoring the indoor temperature from a base station. Monitor freezing conditions, keep your home comfortable, and get weather updates without leaving the couch.
3. Smart Garage Monitor
For those with attached garages, a smart garage monitor lets you check temperature and humidity levels from inside the home. This helps prevent pipes from freezing in cold climates. It also allows monitoring of summer heat to keep stored items from becoming damaged. Options like the MyQ Smart Garage Hub provide app notifications if the garage gets too hot, too cold, or the door is left open.
4. Smart Microwave Oven
Smart microwaves like the GE Smart Countertop Oven allow remote monitoring via an app. This lets you check on cooking progress and receive alerts when food is ready. While not exclusively for temperature sensing, this feature gives peace of mind for tasks like melting chocolate or proofing dough. Get the perfect bake every time without babysitting your microwave.
5. Grill/Smoker Smart Monitor
For aspiring backyard pitmasters, smart grill monitors are a game changer for BBQ. Probes continuously monitor meat temperature so you can keep the perfect cooking conditions from anywhere. Receive alerts when food is prepped to perfection. Options like the Fireboard 2 Drive allow monitoring from an app, while also automatically adjusting your smoker or pellet grill to maintain the desired heat. Never overcook a brisket again.
6. Smart Coffee Maker
For the coffee obsessed, smart coffee makers like the Behmor Connected let you start brewing from your phone. Customize temperature, presoak time, and brew strength to fit your morning routine. Use an app to monitor brew progress and know when your coffee is ready. Some models even allow temperature adjustments mid-brew. Say goodbye to burnt coffee when you get distracted.
7. Fridge/Freezer Smart Monitor
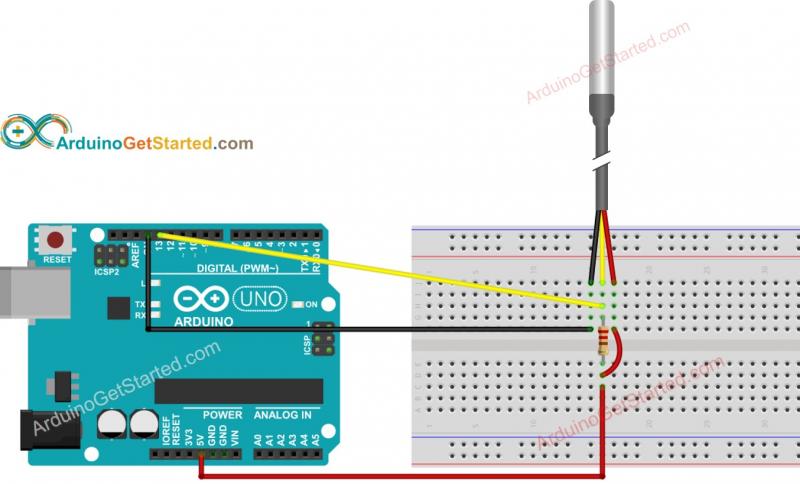
Smart fridge monitors allow you to keep an eye on interior appliance temperatures, even when away from home. This helps prevent food spoilage if the door is left open or the unit loses power. Options like the Samsung Family Hub feature built-in cameras to peek inside. Receive mobile alerts if temperatures veer out of specified ranges. Some even integrate with voice assistants for 24/7 monitoring.
8. Pet Treat Dispenser/Camera
Let technology help care for your pets while you’re away with a smart treat dispenser. The Petcube Bites 2 connects with WiFi and allows you to view, talk to and toss treats to your furry friend from your smartphone. It also features a 160-degree webcam and sensors to monitor room temperature so you know your home is comfortable for pets while you’re out.
9. Smart Nursery Monitor
High-tech baby monitors like the Nanit Plus track everything from temperature to breathing motion. Room sensor monitors cool and overheated nursery conditions. Get notifications if your baby is too hot or cold. Track room temperature and humidity over time and see trends. Receive alerts for unsafe conditions so you can adjust remotely or head home.
10. Wireless Temperature/Humidity Data Logger
For more sophisticated remote monitoring, a compact data logger allows in-depth tracking over time. Models like the La Crosse Alerts capture temperature, humidity, water leaks and more. Easily configure alerts when readings exceed set limits. Data logs wirelessly transmit to your devices for clear data visualization and analysis through an app or web portal. Ideal for facilities, warehouses, HVAC efficiency and more.
11. Bluetooth Meat Thermometer
Ditch the guesswork and enjoy perfectly cooked proteins with a Bluetooth meat thermometer. Options like the ThermoWorks Smoke connect wirelessly to your smart device up to 300 feet away. Get alerts when your food reaches the target temp, so there’s no need to hover over a grill or smoker. Save ideal time and temp graphs forRepe future reference. Some models even allow monitoring of multiple proteins at once.
12. Smart Weather Station
Get hyperlocal weather data from your own backyard with an app-connected personal weather station. Devices like the Ambient Weather WS-2902C provide remote insight into temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, wind and more. Customizable alerts warn of severe conditions. See forecast trends from the comfort of home. Many options integrate with voice assistants and smart home systems for expanded control.
13. Remote PoE Temperature Sensor
When wiring over distances for industrial applications, a remote PoE temperature sensor allows ethernet connectivity. Options like the NVT PhyTemp PT-1T-POE feature a probe on a long cable and Power over Ethernet for simple installation. Readings transmit digitally to minimize interference. Receive alerts when pre-set limits are exceeded. Configure triggers to protect equipment and prevent downtime in remote facilities.
14. Smart Water Leak/Freeze Detector
Protect your home and prevent catastrophic water damage with a smart leak detector. Options like the Honeywell Home Water Leak and Freeze Alarm connect to WiFi for alerts to your devices. Temperature sensors notify you if pipes are in danger of freezing. Moisture triggers issue mobile alerts before major flooding occurs. Receive push notifications immediately to prevent extensive repairs.
15. Connected Tank Propane Monitor
Get alerts and handle propane tank ordering from afar with a smart tank monitor. The Tank Utility propane monitor provides wireless monitoring of fuel level, battery backup alerts and leak detection. Stay notified of tank levels and get ahead of shortages. Integration with providers like AmeriGas even enables direct delivery scheduling and cloud monitoring.
With all of these great options for monitoring temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions from afar, you can pick the solution that provides the right functionality and experience for your needs and budget. So go ahead and give yourself some peace of mind by implementing one of these fantastic remote monitoring systems.