Troubleshoot Your Rain Gauge. Fix Sensor Issues With These TipsTroubleshoot Your Rain Gauge. Fix Sensor Issues With These Tips
Having issues with your rain gauge not recording rainfall accurately? Don’t let a faulty sensor connection leave you high and dry without accurate precipitation data. Getting to the bottom of sensor problems can be frustrating, but this guide will walk through practical troubleshooting tips to get your gauge functioning properly again.
Check physical sensor connection
First things first – visually inspect the physical connection between the sensor and the main console. Make sure the sensor cable is fully plugged into the rain gauge base station. These connections can vibrate loose over time. Don’t just glance – actually unplug and reseat the connector firmly. While you’re there, check for any worn wires or corrosion on the terminals. Faulty cables are one of the most common issues with weather stations.
Try reconnecting sensor wire
If the physical connection looks fine, try unplugging and reconnecting the sensor wire anyway. The contacts may have a poor connection even if the cable appears securely fastened. Disconnecting and reconnecting can often resolve elusive connectivity issues. Don’t just unplug – actually disconnect the wire from the main body of the rain gauge as well. Examine the sensor connector for any dirt or debris that could impede a solid link.
Replace sensor battery

Make sure the onboard battery powering the sensor hasn’t died. Sensor batteries often last 1-2 years before needing replacement. If the battery has expired, the sensor won’t reliably transmit readings back to the base station. Check the battery voltage or simply replace the battery with a fresh one as a troubleshooting step. Your rain gauge documentation will show the type and model of battery needed.
Download updated app
If your rain gauge uses a wireless connection and mobile app, an outdated app can sometimes cause data connectivity problems. Check the app store to see if the manufacturer has released any updates. Download the latest app version and try re-syncing your gauge. Updated apps often contain bug fixes and performance improvements that may resolve your issues.
Reset rain gauge WiFi
For wireless rain gauges, resetting the WiFi connection can help. Unplug the base station from power for 10-15 minutes, then plug back in and go through the WiFi setup process again from scratch. Re-enter your wireless password when prompted. This forces the gauge to freshly associate with your router which may resolve flakey connection problems.
Adjust rain gauge placement

Make sure your gauge placement hasn’t changed. Nearby structures, landscape growth, or repositioning can all interfere with the gauge’s ability to accurately capture precipitation. Verify the unit has a clear 360 degree view from the sensor with no obstructions. Consult your installation guide for the manufacturer’s specific placement recommendations.
Clean debris from sensor
Inspect the rain collector funnel and sensor for any accumulated dirt, leaves, bird droppings, spider webs, etc. Clogged debris can impede the gauge’s measurements. Use a small brush and mild cleaner to gently remove any foreign material from the internal collector and sensor mechanism. Caution – don’t use anything abrasive as this can damage the precision surfaces.
Check WiFi signal strength
With wireless rain gauges, poor WiFi reception can mimic sensor problems. Use your phone or laptop to view WiFi signals near the base station. If the signal is low, try moving the router closer or installing a range extender. Low signal strength leads to intermittent connectivity and missed data.
Update gauge software/firmware
- Disconnect the sensor wire from both the base station and the rain gauge body
- Examine the connectors for dirt or debris
- Clean the connectors with a soft, dry cloth
- Reconnect the wire, ensuring a tight fit at both ends
Dead Sensor Battery
For rain gauges with battery-powered sensors, a dead battery can prevent accurate data transmission. To resolve this:
- Check the battery voltage using a multimeter
- Replace the battery with a fresh one of the correct type and model
- Consult your rain gauge documentation for specific battery requirements
Optimizing Rain Gauge Performance through Software and Connectivity
In addition to hardware issues, software and connectivity problems can also affect rain gauge performance. Addressing these factors can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of your rainfall measurements.
Updating Mobile Apps and Firmware
For rain gauges that utilize wireless connections and mobile apps, outdated software can lead to data connectivity issues. To ensure optimal performance:

- Check the app store for any available updates to your rain gauge’s mobile app
- Download and install the latest version of the app
- Re-sync your rain gauge with the updated app
- Visit the manufacturer’s website to check for firmware updates for your rain gauge
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to safely update your gauge’s firmware
Resetting WiFi Connections
Wireless rain gauges may experience connectivity issues that can be resolved by resetting the WiFi connection. To do this:
- Unplug the base station from its power source
- Wait for 10-15 minutes
- Plug the base station back in
- Go through the WiFi setup process from scratch
- Re-enter your wireless network password when prompted
This process forces the gauge to re-associate with your router, which can often resolve intermittent connection problems.
Improving WiFi Signal Strength
Poor WiFi reception can mimic sensor problems in wireless rain gauges. To address this:
- Use a smartphone or laptop to check WiFi signal strength near the base station
- If the signal is weak, consider moving your router closer to the rain gauge
- Install a WiFi range extender to boost signal coverage
- Ensure there are no large metal objects or electronic devices interfering with the signal
Proper Rain Gauge Placement and Maintenance for Accurate Readings
The location and condition of your rain gauge play crucial roles in its ability to provide accurate precipitation measurements. Let’s examine some key factors to consider for optimal rain gauge performance.

Ideal Rain Gauge Placement
Proper placement of your rain gauge is essential for collecting accurate rainfall data. Consider the following guidelines:
- Ensure the gauge has a clear 360-degree view from the sensor
- Avoid placing the gauge near buildings, trees, or other structures that could obstruct rainfall
- Position the gauge at least twice the height away from any nearby obstructions
- Mount the gauge on a level surface to prevent tipping or uneven collection
- Consult your rain gauge’s installation guide for specific placement recommendations
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Keeping your rain gauge clean and well-maintained is crucial for its accuracy and longevity. Follow these maintenance tips:
- Inspect the rain collector funnel and sensor regularly for debris
- Remove any accumulated dirt, leaves, bird droppings, or spider webs
- Use a small brush and mild cleaner to gently clean the internal collector and sensor mechanism
- Avoid using abrasive materials that could damage the precision surfaces
- Check for any signs of wear or damage on the gauge’s components
Verifying Rain Gauge Accuracy and Troubleshooting Persistent Issues
When you’ve addressed the common problems but still suspect your rain gauge isn’t functioning correctly, there are additional steps you can take to verify its accuracy and resolve persistent issues.

Comparing Readings with Other Sources
To confirm your rain gauge’s accuracy, consider these methods:
- Compare your gauge’s measurements with those of a neighboring weather station
- Place a manual rain bucket next to your gauge and compare readings after a rainfall event
- Check your measurements against official meteorological data for your area
- Use multiple measurement methods over time to establish a reliable baseline
Seeking Professional Assistance
If you’ve exhausted all troubleshooting options and your rain gauge still isn’t working correctly, it may be time to seek professional help:
- Contact the manufacturer’s technical support team
- Provide detailed information about the symptoms and troubleshooting steps you’ve taken
- Be prepared to provide your rain gauge’s model number and purchase date
- Follow any additional troubleshooting steps recommended by the support team
- Consider sending the unit for professional repair if it’s still under warranty
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for Rain Gauge Sensors
For those comfortable with more technical troubleshooting, there are advanced techniques you can employ to diagnose and potentially resolve complex rain gauge sensor issues.

Testing Sensor Continuity
Using a multimeter, you can test the continuity of your rain gauge’s sensor to identify any breaks in the circuit:
- Disconnect the sensor from the rain gauge
- Set your multimeter to the continuity or resistance setting
- Touch the multimeter probes to the sensor’s contacts
- Activate the sensor (e.g., by tipping the bucket mechanism)
- Listen for the multimeter’s beep or observe a change in resistance
If there’s no change in continuity when the sensor is activated, this could indicate a faulty sensor that needs replacement.
Calibrating Your Rain Gauge
Some rain gauges allow for calibration to ensure accuracy. Here’s a general process for calibration:
- Measure a precise amount of water (e.g., 1 inch or 25.4 mm)
- Slowly pour the water into the rain gauge’s collection funnel
- Compare the gauge’s reading to the known amount of water added
- If there’s a discrepancy, consult your gauge’s manual for calibration instructions
- Adjust the calibration factor as needed to match the known water amount
Remember that calibration procedures can vary between different rain gauge models, so always refer to your specific gauge’s documentation.

Understanding the Impact of Environmental Factors on Rain Gauge Accuracy
Environmental conditions can significantly affect the performance of your rain gauge. Being aware of these factors can help you interpret your data more accurately and make necessary adjustments.
Wind Effects on Rain Gauge Measurements
Wind can have a substantial impact on the accuracy of rain gauge readings:
- Strong winds can cause rain to fall at an angle, potentially missing the gauge’s opening
- Wind-induced turbulence around the gauge can affect the amount of rain collected
- Consider installing a wind shield around your rain gauge to minimize these effects
- Be aware that wind effects are more pronounced in exposed locations and during storms
Temperature and Humidity Considerations
Extreme temperatures and humidity levels can affect rain gauge performance:
- Very low temperatures can cause water to freeze in the gauge, leading to inaccurate readings
- High humidity can cause condensation inside the gauge, potentially triggering false readings
- Some gauges use heating elements to prevent freezing in cold climates
- Regular maintenance and cleaning are especially important in humid environments
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Rain Gauge Performance
As technology advances, new features and capabilities are being integrated into rain gauges to improve their accuracy and functionality. Understanding and utilizing these technologies can enhance your precipitation monitoring efforts.

Smart Rain Gauges and IoT Integration
Modern rain gauges are increasingly incorporating smart features and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity:
- WiFi-enabled gauges can transmit data directly to cloud-based storage systems
- Mobile apps allow for real-time monitoring and alerts on your smartphone
- Integration with smart home systems can automate tasks based on rainfall data
- Some gauges can connect to weather networks, contributing to larger data sets
Data Logging and Analysis Tools
Advanced rain gauges often come with sophisticated data logging and analysis capabilities:
- Built-in memory can store historical rainfall data for extended periods
- Software tools allow for graphing and trend analysis of precipitation patterns
- Some systems can export data in various formats for further analysis or reporting
- Integration with other weather sensors can provide a more comprehensive picture of local conditions
Best Practices for Long-Term Rain Gauge Reliability
To ensure your rain gauge continues to provide accurate measurements over time, it’s important to establish a routine of best practices for its operation and maintenance.

Regular Inspection and Cleaning Schedule
Implementing a consistent inspection and cleaning routine can prevent many common issues:
- Set a monthly reminder to visually inspect your rain gauge
- Clean the collection funnel and sensor mechanism at least every three months
- Check for signs of wear or damage during each inspection
- Keep a log of maintenance activities and any issues encountered
- Consider professional servicing annually for high-precision gauges
Seasonal Considerations for Rain Gauge Operation
Different seasons may require adjustments to your rain gauge setup:
- In winter, use antifreeze solutions in manual gauges to prevent freezing
- For electronic gauges, ensure heating elements are functioning before cold weather sets in
- In spring, check for any damage caused by winter conditions
- During summer, be vigilant about removing debris that may accumulate more frequently
- In autumn, prepare your gauge for the transition to colder weather
By following these best practices and staying attentive to your rain gauge’s needs, you can ensure reliable and accurate precipitation data for years to come. Remember that consistent maintenance and proper operation are key to maximizing the performance of your rain gauge, regardless of its type or sophistication level.

Having issues with your rain gauge not recording rainfall accurately? Don’t let a faulty sensor connection leave you high and dry without accurate precipitation data. Getting to the bottom of sensor problems can be frustrating, but this guide will walk through practical troubleshooting tips to get your gauge functioning properly again.
Check physical sensor connection
First things first – visually inspect the physical connection between the sensor and the main console. Make sure the sensor cable is fully plugged into the rain gauge base station. These connections can vibrate loose over time. Don’t just glance – actually unplug and reseat the connector firmly. While you’re there, check for any worn wires or corrosion on the terminals. Faulty cables are one of the most common issues with weather stations.
Try reconnecting sensor wire
If the physical connection looks fine, try unplugging and reconnecting the sensor wire anyway. The contacts may have a poor connection even if the cable appears securely fastened. Disconnecting and reconnecting can often resolve elusive connectivity issues. Don’t just unplug – actually disconnect the wire from the main body of the rain gauge as well. Examine the sensor connector for any dirt or debris that could impede a solid link.
Replace sensor battery

Make sure the onboard battery powering the sensor hasn’t died. Sensor batteries often last 1-2 years before needing replacement. If the battery has expired, the sensor won’t reliably transmit readings back to the base station. Check the battery voltage or simply replace the battery with a fresh one as a troubleshooting step. Your rain gauge documentation will show the type and model of battery needed.
Download updated app
If your rain gauge uses a wireless connection and mobile app, an outdated app can sometimes cause data connectivity problems. Check the app store to see if the manufacturer has released any updates. Download the latest app version and try re-syncing your gauge. Updated apps often contain bug fixes and performance improvements that may resolve your issues.
Reset rain gauge WiFi
For wireless rain gauges, resetting the WiFi connection can help. Unplug the base station from power for 10-15 minutes, then plug back in and go through the WiFi setup process again from scratch. Re-enter your wireless password when prompted. This forces the gauge to freshly associate with your router which may resolve flakey connection problems.
Adjust rain gauge placement

Make sure your gauge placement hasn’t changed. Nearby structures, landscape growth, or repositioning can all interfere with the gauge’s ability to accurately capture precipitation. Verify the unit has a clear 360 degree view from the sensor with no obstructions. Consult your installation guide for the manufacturer’s specific placement recommendations.
Clean debris from sensor
Inspect the rain collector funnel and sensor for any accumulated dirt, leaves, bird droppings, spider webs, etc. Clogged debris can impede the gauge’s measurements. Use a small brush and mild cleaner to gently remove any foreign material from the internal collector and sensor mechanism. Caution – don’t use anything abrasive as this can damage the precision surfaces.
Check WiFi signal strength
With wireless rain gauges, poor WiFi reception can mimic sensor problems. Use your phone or laptop to view WiFi signals near the base station. If the signal is low, try moving the router closer or installing a range extender. Low signal strength leads to intermittent connectivity and missed data.
Update gauge software/firmware
Check the manufacturer’s website to see if your rain gauge has any firmware or software updates available. Buggy firmware can definitely cause sensors to misbehave. Updating to the latest firmware rev often resolves problems with stability and data connectivity. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to safely update your gauge.
Contact manufacturer support
If you’ve tried all the basic troubleshooting steps and your rain gauge still isn’t working, reach out to the manufacturer’s tech support for assistance. Provide details on the symptoms you’re seeing along with steps attempted. Support reps can often diagnose obscure issues and provide useful advice for getting your gauge fully operational again.
Verify rain gauge model number
Double check to make sure you actually have the correct sensor model for your particular rain gauge station. Gauge makers often use sensors that look identical but have different programming inside. Using the wrong model sensor will lead to synchronization issues. Confirm the exact part number with the manufacturer if in doubt.
Compare readings to other gauges

Corroborate your gauge’s measurements by comparing to a neighboring weather station or manual rain bucket. Place a bucket next to the gauge after clearing both and compare the readings after a rainstorm. Consistent variance points to an issue with your sensor’s calibration or measuring mechanism rather than connectivity.
Check for obstructions blocking sensor
Visually inspect around the rain gauge to make sure the sensor has an unobstructed view of the sky overhead. Nearby structures, landscape elements, or overhanging tree branches can physically block precipitation from reaching the gauge’s collector. Even thin obstructions can throw off readings.
Test rain gauge with water
Run a simple manual test by slowly pouring a measured amount of water directly into the gauge’s collection funnel. Confirm that the correct volume registers on the display or app. If measurements are off, the sensor itself likely has an issue versus a wireless connectivity problem.
Purchase replacement sensor
If your troubleshooting determines the sensor itself is faulty, purchase a replacement from the manufacturer. Sensors do degrade over time, especially if exposed to harsh weather. Swapping in a new OEM sensor should resolve any measurement abnormalities.
While rain gauge problems can be frustrating, methodically working through potential sensor issues and connectivity checks will typically identify the underlying problem. Pay close attention to physical connections and placement, update firmware, and leverage the manufacturer’s support resources. With concerted troubleshooting, your gauge will be back online providing reliable precipitation data again.
Frustrated by your rain gauge failing to register rainfall events? Before you chalk it up to a bad sensor, try reconnecting the sensor wire first. A loose wire is one of the most common culprits behind connectivity issues.
Try reconnecting sensor wire
Start by unplugging the sensor wire from the main body of the rain gauge. Examine the connector ends for any corrosion, damage, or bent pins. If the connector looks worn, you may need to replace the sensor cable. Use a cotton swab and some isopropyl alcohol to gently clean the male and female terminals, removing any dirt, debris or oxidation.
While disconnected, give the wires themselves a visual inspection. Look for any cracks, splits, or crimped sections that could indicate a broken internal wire. Wiggling the cable should not cause any fluctuations in connectivity. If the cable appears faulty, the simplest option is just replacing the sensor wire.
Before reconnecting, consider adding some dielectric grease to the terminals. This prevents moisture and corrosion from building up over time. Just use a thin, sparing amount before snapping the connectors back together. Grease helps maintain a positive connection and makes future disconnection easier.
Reseat the sensor wire firmly until you feel it click into place. Make sure the locking tab engages so the wire cannot vibrate loose. Some connectors have a threaded ring collar that needs tightened down for maximum integrity. Consult your rain gauge’s documentation for proper installation technique.
Listen closely as you jiggle the wire near the base station. Any crackling or changes in signal strength point to a flaky connection that needs addressed. The best connections should click into place with a satisfied “snap”, implying a solid mated joint.
With the sensor reconnected, observe your rain gauge during the next several rainstorms. If precipitation measurements suddenly improve, a faulty wire was likely the culprit. Sometime the simplest solutions do the trick!
Replace battery
While you have the sensor unplugged, consider replacing the battery as well. Low battery voltage can mimic connectivity issues. Your manual will specify the exact battery model and voltage needed. Have a fresh battery on hand for testing and troubleshooting purposes.
Inspect for corrosion
Examine the battery compartment and terminal contacts for any buildup of corrosion or oxidation. This can impede electrical flow causing intermittent operation. Clean any grime using a cotton swab and rubbing alcohol. A corroded battery compartment can affect even brand new batteries.
Check voltage
Use a voltmeter to test the battery’s output if possible. Compare against the manufacturer’s specifications for minimum voltage. Any reading below the threshold indicates the battery should be replaced. Don’t trust the built-in low battery indicator – test the voltage directly.
Even brand new batteries can be defective, so verify performance with a voltage check. This also establishes a baseline for future troubleshooting if connectivity problems reappear.
Use weatherproof batteries

For optimal battery life, use lithium or alkaline batteries designed for outdoor weather conditions. The temperature extremes and moisture of rain gauge operation can prematurely drain batteries not intended for the elements. Investing in weatherproof batteries prevents frequent replacements.
Rechargeable batteries are not recommended. Their lower voltages and reduced tolerance for temperature extremes makes them a poor fit for weather station use. Stick with disposable lithium or alkaline batteries in your rain gauge’s sensor.
If you’ve diligently inspected the connectors, replaced the battery, and the sensor wire still seems flaky, it may be time to replace the wire. But surprisingly often a thorough wire reseating or fresh battery restores connectivity. Try these simple steps before condemning the sensor cable.
An unresponsive rain gauge failing to register precipitation is frustrating. Before calling the manufacturer, try replacing the sensor battery as an easy first troubleshooting step.
Replace sensor battery

Rain gauge sensors are powered by small onboard batteries that provide current to measure rainfall and transmit data. Like any battery, their capacity degrades over time leading to low voltage issues. Replacing an expired battery often restores full functionality.
Consult your owner’s manual to identify the correct battery type and voltage for your particular rain gauge model. Sensors typically use common coin cell or AA batteries available at any retailer. Note any required specialty batteries to have on hand.
Slide off the battery compartment cover to access the battery. Batteries are usually secured in a clip or soldered holder. Gently remove the old battery from its connections. Thoroughly clean any corrosion from the battery terminals using a cotton swab and rubbing alcohol.
Compare the new battery visually against the old to ensure you purchased the correct size. Also verify the voltage matches the product specifications. Carefully insert the new battery, observing proper polarity. Secure the battery in its holder and reinstall the cover.
With fresh power connected, try re-syncing the rain gauge per the manufacturer instructions. If the sensor immediately responds and connectivity improves, low battery voltage was likely the issue.
Check voltage first
For a definitive diagnosis, use a voltmeter to check battery voltage before swapping the battery. Compare against the product manual for minimum voltage threshold. This quantifies when replacement is truly needed.
Insert correctly
When installing the new battery, pay close attention to proper polarity. Inserting the battery backwards can damage the sensor electronics or cause malfunctions.
Watch expiration dates
When purchasing replacement batteries, inspect manufacturing dates on packaging. Avoid old stock that may have been sitting on shelves awhile. Starting with fresh batteries maximizes operational life.
Dispose properly
Don’t just toss dead batteries in the trash. Many municipalities offer recycling programs or hazardous waste days to properly dispose of used batteries. This keeps toxic compounds out of landfills.
Consider rechargeable
For frequently replaced batteries, investing in rechargeable NiMH cells can save money long-term. Compare voltage specs carefully and follow the charging guidelines. Rechargeables may need replacement more often though.
While checking connectors and wires is wise, don’t overlook the critical role of the sensor battery. A simple battery swap often gets balky rain gauges transmitting reliably again. Schedule periodic battery changes to avoid extended downtime and data gaps.
With a fresh power source, your rain gauge sensor should spring back to life. Just be sure to use the correct battery type and install with proper polarity. Don’t discard dead batteries – recycle them responsibly. Keep spare batteries on hand for promptly troubleshooting connection loss.
Having connectivity problems with your WiFi rain gauge? Before calling the manufacturer, check your mobile app store for any available software updates. An outdated app version can prevent your gauge from syncing properly.
Download updated app

Rain gauge manufacturers frequently release enhanced versions of their companion mobile apps to squash bugs and improve performance. However, the app update process relies on users proactively checking for and installing these upgrades.
Open your phone’s app store (Google Play or Apple App Store) and search for your rain gauge’s app. On the app page, check the current version installed on your device and compare it to the latest available version for download.
If your version is behind, proceed to update the app to the newest release. Take note of any version-specific compatibility requirements. You may need to also update your phone’s operating system to support the latest app release.
Once downloaded, open the rain gauge app and attempt to re-sync with your station per the manufacturer’s instructions. With any luck, the firmware improvements in the updated app will resolve your connectivity difficulties.
Check change log
When updating apps, always review the publisher’s change log detailing bug fixes, patches, and enhancements with each new version. Look for any modifications specific to improving connectivity and stability.
Write down settings

Note your app settings before updating in case they get reset. Easily forgetting WiFi passwords or gauge configurations will only slow the reconnection process.
Update operating system
Don’t neglect to also update your phone’s OS to match the app’s minimum requirements. Using the latest OS improves security and stability.
Delete and reinstall
If issues persist after updating, try deleting and freshly reinstalling the rain gauge app. This wipes out any corrupted cached data.
Don’t let an outdated companion app stop you from getting the most out of your new WiFi-enabled rain gauge. Schedule periodic checks for app updates to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. Keeping core firmware up-to-date is just as important as replacing batteries and cleaning sensors.
A quick app upgrade could restore lost connectivity and have your rain gauge’s data flowing to your mobile device once again. Rely on app developers to continuously enhance and refine your weather station’s operation.
Is your WiFi-enabled rain gauge constantly dropping its wireless connection? Before getting frustrated, try resetting your gauge’s WiFi settings and forcing it to freshly re-pair with your network.
Reset rain gauge WiFi
Like any gadget, rain gauges can sometimes get “confused” and have trouble maintaining a consistent wireless link, even when your network signal is strong. Resetting the WiFi connection essentially gives the gauge a fresh start.
Begin by powering down the rain gauge base station completely – unplug from electrical outlet if it uses an AC adapter. Leave it disconnected for 10-15 minutes to discharge any residual power in the system.
Next, reconnect the power cord and turn the base station back on. Access the gauge’s WiFi setup menu just like when you initially configured it. Step through the process to reconnect it to your wireless network, re-entering your SSID and WiFi password when prompted.
If you’ve forgotten your WiFi network credentials, take a quick moment to look them up before starting. Having this info handy prevents frustration during the reset process.
Once the reset is complete, load up the companion mobile app and try re-syncing with your rain gauge per the normal connection routine. Often this forced reboot strengthens the flaky wireless link.
Check signal strength

While resetting WiFi, inspect wireless signal strength at the gauge’s base station location. Consistently low signal can cause recurring drops.
Change wireless channel
If the gauge struggles to maintain a connection after resetting, try changing your router’s wireless channel/frequency to resolve conflicts.
Update router firmware
Buggy router firmware can also manifest as wireless connectivity problems. Check your router brand’s website for any available firmware updates.
Don’t immediately jump to replacing your rain gauge if wireless connectivity becomes intermittent. Nine times out of ten, a basic WiFi reset restores consistent linkage and data transmission. Think of it as giving your gauge a fresh start when acting glitchy.
A quick power cycle and running through onboard WiFi setup forces your gauge to re-optimize its wireless connection. Save yourself headaches before digging deeper into troubleshooting sensor issues.
Erratic rain gauge readings got you scratching your head? Before assuming the sensor is faulty, check if anything is obstructing rainfall from reaching the gauge properly. Proper placement is critical for accuracy.
Adjust rain gauge placement
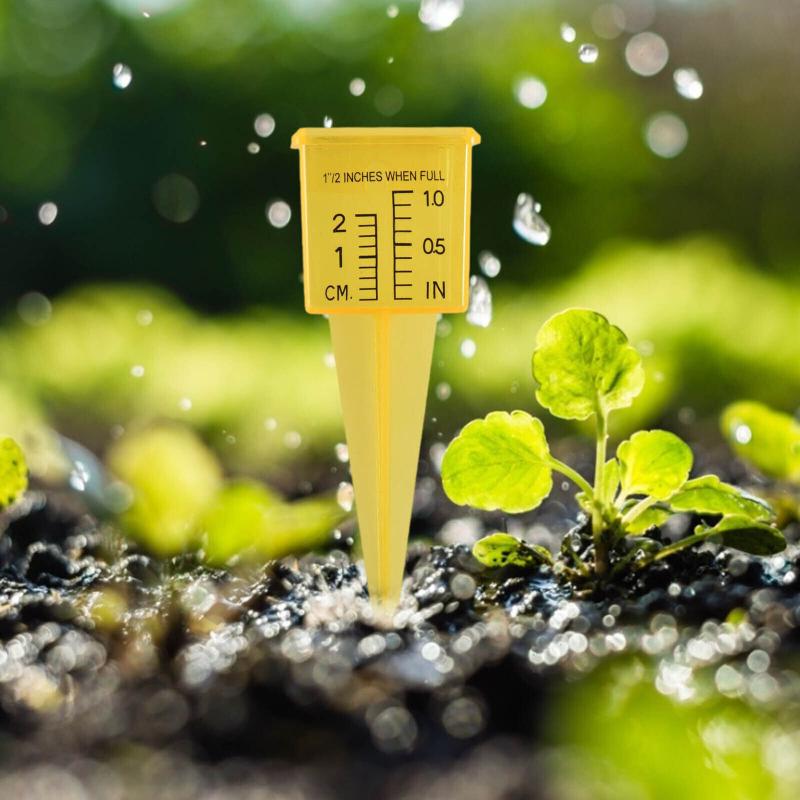

Rain gauges work best with a clear, unimpeded view of the sky. Nearby objects and structures can inadvertently block or redirect precipitation, resulting in underreported rainfall. Even thin obstructions impact accuracy.
Carefully inspect your gauge’s installation location from all angles. Look for any overhanging branches, power lines, walls, fences, etc. that may obstruct the unit’s collector funnel. You want full 360 degree clearance.
Check the product manual for your specific model’s recommended spacing from buildings and trees. In general, aim for at least 2-3 feet of clearance on all sides and 6 feet of overhead clearance if possible.
If any obstructions are visible, consider relocating the rain gauge to a better position. Failing that, try pruning back any encroaching branches or reorienting the gauge to mitigate interference.
Elevate gauge
For optimal accuracy, mount the rain gauge on a stationary platform 2-3 feet off the ground to avoid splashback and localized wind currents.
Check bubble level
Make sure the gauge base is completely level after installation. An angled collector funnel can skew accuracy. Double check with a spirit level.
Secure firmly
Anchor mounting pole or fasteners securely so the gauge doesn’t shift position over time as winds buffet it.
Consistent weird readings, especially when nearby gauges report normally, are often tracing back to improper siting or obstructions. Before swapping sensors, take another look at placement best practices first. With good visibility and secure mounting, your gauge can provide reliable data.
Careful rain gauge placement removes external accuracy variables from the equation. Don’t let poor installation jeopardize the quality of your rainfall measurements. Take the time to optimize positioning.
Rain gauge giving crazy readings that don’t match actual rainfall? Before replacing the sensor, give it a good cleaning to remove any debris blocking accurate measurements.
Clean debris from sensor

Over time, dirt, dust, spider webs, bird droppings, and other gunk can accumulate in your rain gauge’s collector funnel and sensor mechanism. This debris can impede the sensor’s measurements, resulting in lower or sporadic readings.
Gently remove the collector funnel to access the rain sensor housed underneath. Use a soft brush and mild soap and water to carefully clean the internal funnel surfaces as well as the sensor itself. Avoid abrasive cleaners or scrubbing.
Pay particular attention to the tipping bucket that captures rainfall. A single spider web strand across the bucket opening can affect results. Check that water can freely flow into the bucket from all directions.
Rinse away any soap residue thoroughly when finished cleaning to prevent contamination. Allow all components to fully dry before reassembling. Perform a quick test by pouring measured water through the funnel.
Check monthly
Schedule periodic monthly cleanings to prevent excessive buildup, especially if sited under trees. Seasonal debris will vary.
Avoid harsh chemicals
Stick to mild cleaners like dilute vinegar or soapy water. Harsh chemicals can damage sensor components and leach into collectors.
Inspect o-rings
When disassembled, check any rubber gaskets or o-rings for wear or cracks. Replace aging seals to prevent leaks.
With a freshly cleaned sensor mechanism, your rain gauge should resume accurately logging precipitation data. Don’t let seemingly minor buildup throw off your readings.
Regular cleaning removes one more variable while troubleshooting rain gauge performance. Invest a few minutes in maintenance for confidence in your rainfall measurements.
Does your WiFi rain gauge constantly drop connection or show “out of range”? Weak wireless signal could be the culprit behind connectivity problems.
Check WiFi signal strength
Like any WiFi-enabled device, rain gauges need sufficient wireless signal strength for consistent data transmission. Low signal causes intermittent drops and syncing issues.
Use your smartphone to download a wireless analysis app like WiFi SweetSpots. Walk the perimeter of your property reading signal levels near the rain gauge base station.
Compare the gauge’s signal reading against the app’s recommendation for good connectivity. If significantly lower than optimal, take steps to boost signal such as moving the WiFi router closer or installing a range extender.
Switch wireless bands
If possible, change your wireless router’s broadcast band from 2.4Ghz to 5Ghz for a stronger signal to the rain gauge. But first confirm the gauge supports 5Ghz.
Change WiFi channel
If the gauge’s signal seems weak, try manually switching your router’s wireless channel/frequency to a less congested option.
Replace router antenna
Consider upgrading router antennas if the internal ones don’t provide enough range. High-gain directional antennas focus signal strength.
Add wireless extender
strategic wireless extender can strengthen WiFi coverage to the gauge’s location. Check extender reviews and placement guidance for optimal reach.
Flaky rain gauge connectivity usually comes down to poor wireless signal at the sensor location. Analyze signal strength as part of routine troubleshooting when issues arise.
Don’t let WiFi “dead zones” result in missing precipitation data. Take steps to amplify and stabilize wireless coverage across your property.
Experiencing glitches or odd behavior from your rain gauge? Outdated firmware could be the culprit. Take a few minutes to check for and install any available software updates.
Update gauge software/firmware
Like any electronics, rain gauges rely on onboard firmware to control functionality. Manufacturers periodically release enhanced versions that squash bugs and optimize performance.
On your gauge’s support webpage, check for a Software or Firmware link listing available updates. Compare the latest version against what’s currently installed to see if you’re behind.
Back up your rain gauge’s settings and data before installing updates. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to download and flash the new firmware onto your gauge safely.
After updating, allow time to monitor gauge operation before assuming issues are fixed. Major firmware revisions can take days to re-stabilize.
Reset to defaults
If firmware updates don’t resolve problems, reset the gauge to factory defaults and reconfigure from scratch. This wipes any corrupted settings.
Update app too
Don’t forget to also check for any companion mobile app updates which may be required for optimal functionality.
Check release notes

Read firmware release notes looking for bug fixes related to your specific issues before deciding to upgrade.
Periodically updating your rain gauge’s operating system is just as important as replacing worn parts. Outdated firmware can manifest as intermittent glitches.
Stay current on available upgrades to enjoy the latest performance enhancements and keep issues at bay.
After trying all the DIY troubleshooting tips with no luck, it may be time to leverage the rain gauge manufacturer’s support resources for additional help.
Contact manufacturer support
Reputable rain gauge makers provide technical support options to assist customers experiencing issues. Before replacing the entire unit, consider tapping into their product expertise.
Check your owner’s manual or the company website for support contact information. Many offer email-based support systems to submit detailed questions. Phone support or online chat may also be available.
When contacting support, explain the troubleshooting steps already attempted and exactly how the gauge is malfunctioning. Include photos or video illustrating the problem if possible.
Research online first
Before reaching out to support, search online user forums for similar issues. You may find existing advice and solutions.
Ask about firmware
Inquire if updated firmware is available that could potentially address your problem.
Request an RMA
If support determines hardware failure, ask about return/exchange process for further diagnosis or part replacement.
Tap into the deep knowledge base of the manufacturer when stumped on a stubborn rain gauge problem. Support reps encounter every issue imaginable and can usually recommend additional troubleshooting tips.
Explain your situation clearly and work collaboratively with support to resuscitate your ailing rain gauge. With their assistance, you’ll likely be back up and running smoothly.
Having no luck getting your rain gauge sensor to sync up? Before getting too far into troubleshooting, verify you have the correct sensor model for your base station.
Verify rain gauge model number

It’s easy to mistakenly purchase the wrong replacement sensor that looks identical but isn’t programmed for your particular gauge base.
Examine any model number markings on the existing sensor board and on the inside of the rain collector. Cross-reference these against the gauge manufacturer’s documentation to validate you have the proper sensor.
Closely check connectors to make sure the replacement sensor’s plug matches the base station jack. Similar but incompatible connectors can fit loosely.
Buy directly from manufacturer
When purchasing replacement rain gauge sensors, order directly from the manufacturer if possible. This guarantees model compatibility.
Beware generic sensors
Avoid buying generic aftermarket or used sensors that claim broad compatibility. You likely need an OEM model-specific part.
Register new sensor
Some brands require registering a new sensor’s serial number through software to sync with the base. Check manuals for details.
It seems like a small detail, but sensor-to-base incompatibility due to mismatched models results in all kinds of connectivity and data issues. Eliminate any guesswork or assumptions.
Matching the exact replacement sensor designed for your base station will have you gathering consistent precipitation data again quickly.
Noticing your rain gauge readings don’t match other nearby gauges? Cross-checking multiple sources helps validate accuracy issues.
Compare readings to other gauges
If your gauge is reporting unusually high or low rainfall versus other stations, sensor malfunction could be the cause. But first confirm with comparison readings.
Place a basic plastic rain collector next to your gauge after clearing both. Record each gauge’s daily results after a rainstorm. Repeat for several events.
Consult your local weather station or neighbors’ gauges during the same period. Compare statistics to get a wider data set.
If your gauge consistently measures significantly different amounts, take notes on variance percentage and direction. This points to an issue with your unit rather than natural location variability.
Average results
For the most accurate picture, average comparisons from multiple gauges over an extended time period.
Calibrate annually
Check your gauge’s manual on recalibrating annually before the rainy season to ensure accuracy.
Consider issues
If variant, research possible causes like obstruction, mounting, leveling, or contamination.
Cross-validating your rain gauge against other sources identifies if readings are naturally inconsistent or likely inaccurate. Then you can focus troubleshooting efforts appropriately.
Through sharp observation and pattern recognition, gauge comparability provides insight on your sensor’s performance. But use an average from multiple instruments rather than relying on any one.
Inconsistent rain gauge readings got you scratching your head? Nearby obstructions blocking the sensor could be throwing things off.
Check for obstructions blocking sensor
For maximum accuracy, a rain gauge sensor needs an unimpeded 360 degree view of the sky to catch precipitation. Even thin obstructions can interrupt rainfall reaching the sensor.
Carefully inspect around and above your gauge. Look for new structures, vegetation growth, trees, power lines, fences or anything encroaching the sensor’s field of view.
Check the base is still properly leveled. Tilting could move obstructions into the path of rainfall. Review manufacturer spacing guidelines.
Gently rotate the sensor bucket assembly by hand, observing for any resistance or rubbing. Spinning should move smoothly without friction.
Consider relocating
If obstructions are causing interference, consider moving the entire rain gauge base to a clearer location.
Prune vegetation
Tree branches and bushes encroaching the gauge may simply need trimmed back to restore clear visibility.
Add spacer
A taller mounting pole can raise the gauge sensor above nearby obstructions if repositioning isn’t possible.
Don’t let nearby objects and encroachments block accurate rainfall measurements. Periodically scan for developing obstructions and take corrective action to maintain visibility.
Unimpeded rain gauge exposure preserves data integrity and ensures you’re tracking true precipitation patterns.
Still not sure if rain gauge inaccuracies are from sensor malfunction or external factors? Try manually testing with measured water to isolate the sensor.
Test rain gauge with water

Pouring a known amount of water into your gauge isolates whether the sensor and electronics are actually functioning properly.
Carefully add exactly 1 inch of water directly into the rain collector using a measuring cup. Funnel the water in different spots to test from all directions.
Observe if the gauge display or app registers 1 inch, or very close to it, from the manual input. Repeat several times with varying amounts.
If the gauge consistently under or over reports the manually measured water, it points to a sensor malfunction versus external environmental factors impacting accuracy.
Use distilled water
For cleanliness, use distilled or demineralized water to prevent mineral buildup during testing.
Adjust amount
Tailor starting water amounts to the gauge’s resolution. Add in small increments working up.
Note discrepancies
Document exactly how much reported measurements diverge from actual water added.
Manual testing isolates rain gauge hardware issues from placement, obstruction and other external variables. Consistent variance confirms sensor problems versus application factors.
This simple water testing provides empirical data on your gauge’s accuracy and need for sensor repair or replacement.
If all troubleshooting points to a defective rain gauge sensor, it may be time to purchase a replacement part to get your station functioning accurately again.
Purchase replacement sensor
Like any part, rain gauge sensors gradually degrade with age and exposure to the elements. When malfunction becomes obvious, swapping in a new OEM sensor typically resolves any issues.
Confirm your exact rain gauge make and model before ordering. Sensors are often model-specific. Purchase from the manufacturer if possible for guaranteed compatibility.
Carefully remove the old sensor per instructions, disconnecting any wires and fasteners. Install the new part following the provided directions. Consult support if needed.
Reset calibrations
After installing the replacement, reset any sensor calibrations or configurations per the manual. This synchronizes the new part.
Return old sensor
If replacing under warranty, follow proper return procedures for the defective sensor. This provides diagnostics for the manufacturer.
Re-test accuracy
After swapping the sensor, repeat manual accuracy testing to validate readings are now normal.
While cleaning and minor repairs can stretch sensor life, eventually replacement becomes necessary. Factor in the cost of new parts as rain gauges age.
With an OEM spec sensor properly installed, your weather station will resume providing reliable precipitation data.

