Top Reasons Why Every Surgeon Needs Surgical Face Masks and ShieldsTop Reasons Why Every Surgeon Needs Surgical Face Masks and Shields
Surgical Masks Protect Against Airborne Pathogens
Surgical masks are a critical form of personal protective equipment (PPE) for surgeons and medical professionals. Wearing a proper surgical mask creates a physical barrier that prevents viral particles or infectious droplets from reaching the wearer’s mouth and nose. Especially during procedures like intubation or surgery, there is a high risk of exposure to airborne pathogens that can lead to dangerous respiratory infections.
High quality surgical masks are designed to filter out at least 95% of small particles. Most disposable masks consist of three layers – a water-resistant outer layer, a middle filter layer, and an inner moisture-absorbing layer. The middle layer is key for capturing tiny infectious particles. Surgical masks also feature flexible nose wires and elastic bands to ensure a tight seal around the face and prevent contaminated air from leaking in around the edges.
Viruses like influenza, coronavirus, and tuberculosis can linger in the air in droplet nuclei after an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These tiny residue particles float unseen in the air and can be inhaled. Proper surgical masks form an impenetrable barrier to block inhalation of these hazardous particles. Wearing a surgical mask is shown to reduce exposure risk by as much as 80% compared to not wearing a mask.
In the operating room where germs abound, surgical masks are the first line of defense for surgeons against airborne bugs. Masks prevent contaminated exhalations from reaching the sterile surgical field. They also protect patients from any germs exhaled by members of the surgical team. For lengthy procedures, masks prevent fatigue and throat irritation caused by long-term breathing of stale air. By trapping droplets and particles, surgical masks also help protect against splashes to the face from bodily fluids or irrigation liquids.
Any reputable surgeon knows that wearing proper PPE like surgical masks is non-negotiable. In the presence of infectious airborne pathogens during surgery, masks are absolutely crucial for avoiding transmission and safeguarding the wellbeing of both surgical staff and patients. Proper use of surgical masks is a fundamental element of safety protocols and risk reduction in the operating room. For surgeons, masking up is an essential precaution and professional responsibility.
Face Shields Provide Extra Protection for Eyes
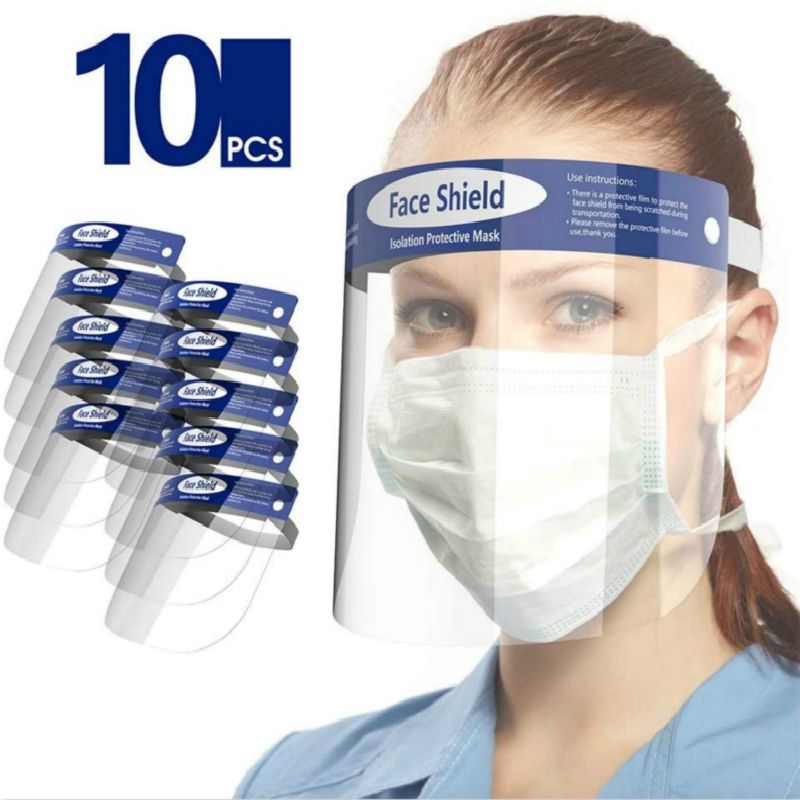
In addition to surgical masks, face shields are another vital form of personal protective equipment (PPE) for surgeons and OR staff. Face shields are clear plastic barriers that cover the entire face and wrap around the sides. While surgical masks protect the nose and mouth from airborne particles, face shields provide an additional layer of protection for the eyes.
During surgical procedures like intubation, drilling, or extracting teeth, there is a high risk of splatter and spray from bodily fluids, irrigation liquids, or debris fragments. Mucous, saliva, or even minute drops of blood can contact unprotected eyes. Face shields create a see-through screen that prevents direct contact of hazardous splashes on the delicate mucous membranes of the eyes. The shields also protect the face, mouth, and mask from incidental splashes.
Another key benefit of face shields is they prevent bulk contaminants or large particles from accidentally falling into the eyes of the person wearing the shield. For example, loose hair or fibers from surgical drapes could drop into the eyes during certain procedures. The face shield blocks these types of particulates from making direct contact with the eyes.
Compared to goggles, face shields have the advantage of also protecting the mask and face. Full face shields extend from above the eyes down past the chin to block splashes from all angles. Face shields are more comfortable than goggles as well, avoiding issues like fogging up that can obscure vision during long surgeries.
Doctors performing invasive dental work, orthopedic surgery, or emergency trauma procedures should always supplement surgical masks with a face shield. For maximum safety, the CDC recommends the use of a face shield in combination with either a surgical mask or N95 respirator when performing aerosol-generating procedures.
Wearing proper eye protection gear demonstrates a surgeon’s commitment to safety. Face shields are indispensable for shielding surgeons’ eyes and masks from hazardous fluids, tissue, or debris during messy surgical procedures. No reputable surgeon should ever scrubs in for an invasive operation without protective eyewear like a face shield along with a surgical mask.
Disposable Masks Prevent Cross-Contamination

An essential advantage of disposable surgical masks is they help prevent cross-contamination in the operating room. Reusable gear can harbor infectious pathogens that get transferred from patient to patient. Single-use disposable masks mitigate this risk.
Cloth masks used repeatedly are difficult to properly disinfect between surgeries. The woven material can trap germs that linger even after washing. Disposable surgical masks made of non-woven meltblown fabric are designed to be worn one time then discarded. This eliminates the chance of residual contamination being passed between medical procedures.
Disposable masks also maintain their protective qualities better than reused cloth masks. The filtration effectiveness of cloth masks deteriorates substantially after being laundered. And repeated processing degrades the electrostatic charges in the material that capture small viral particles. Disposable surgical masks maintain their microbial barrier integrity when brand new.
Wearing a new disposable face mask for each surgery ensures maximum filtration efficiency. This creates an optimal barrier against airborne pathogens for both the surgical staff and the patient. A fresh new mask guarantees the filter layers haven’t been compromised by previous wear.
The FDA recommends medical masks be treated as single-use items. Hospitals and medical facilities have policies requiring staff change masks between patients to decrease infection transmission risks. Wearing a disposable surgical mask is standard procedure anytime a provider interacts with a new patient.
For surgeons, a new disposable mask for every operation is the safest practice. This prevents contaminated equipment from jeopardizing the sterile field. Discarding used masks after each procedure also eliminates inadvertent contact between surgical team members and patients’ bodily fluids or secretions left on a reused mask.
Responsible surgeons committed to safety always wear a new disposable face mask for each surgery. This ensures maximum protection against cross-contamination for both patients and medical staff in the OR.
Proper PPE Reduces Risk of Infection
- A water-resistant outer layer
- A middle filter layer (crucial for capturing tiny infectious particles)
- An inner moisture-absorbing layer
To ensure maximum protection, surgical masks are equipped with flexible nose wires and elastic bands. These features create a tight seal around the face, preventing contaminated air from seeping in through the edges.
Protection Against Airborne Viruses
Viruses such as influenza, coronavirus, and tuberculosis can persist in the air as droplet nuclei after an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or speaks. These microscopic particles float invisibly in the air, posing a significant inhalation risk. How do surgical masks combat this threat? By forming an impenetrable barrier, proper surgical masks effectively block the inhalation of these hazardous particles. Studies have shown that wearing a surgical mask can reduce exposure risk by as much as 80% compared to not wearing one.
The Operating Room: A Battleground Against Germs
In the operating room, where microorganisms proliferate, surgical masks act as the first line of defense for surgeons against airborne contaminants. These masks serve a dual purpose:
- Preventing contaminated exhalations from reaching the sterile surgical field
- Protecting patients from any germs exhaled by members of the surgical team
For extended procedures, masks also play a crucial role in preventing fatigue and throat irritation caused by prolonged breathing of stale air. Additionally, by trapping droplets and particles, surgical masks offer protection against splashes of bodily fluids or irrigation liquids to the face.
Face Shields: Enhancing Eye Protection for Surgeons
While surgical masks provide essential protection for the nose and mouth, face shields offer an additional layer of defense for the eyes. These clear plastic barriers cover the entire face and wrap around the sides, creating a comprehensive protective shield.
Why are face shields particularly important during surgical procedures? Many invasive surgeries, such as intubation, drilling, or tooth extraction, carry a high risk of splatter and spray from bodily fluids, irrigation liquids, or debris fragments. Face shields create a transparent screen that prevents direct contact of hazardous splashes with the delicate mucous membranes of the eyes.
Advantages of Face Shields Over Goggles
Face shields offer several benefits compared to goggles:
- Protection for the entire face, mouth, and mask from incidental splashes
- Prevention of bulk contaminants or large particles from accidentally falling into the eyes
- Enhanced comfort, avoiding issues like fogging that can obscure vision during lengthy surgeries
For maximum safety, the CDC recommends using a face shield in combination with either a surgical mask or N95 respirator when performing aerosol-generating procedures.
The Importance of Disposable Masks in Preventing Cross-Contamination
Disposable surgical masks play a crucial role in preventing cross-contamination within the operating room. How do they achieve this? By being single-use items, disposable masks eliminate the risk of harboring infectious agents that could be present on reusable gear.
What are the potential risks of reusable masks? Reusable masks, if not properly sanitized between uses, can become breeding grounds for bacteria and viruses. This poses a significant risk of transferring pathogens between patients or from one surgical procedure to another.
Benefits of Disposable Masks
- Guaranteed sterility for each new procedure
- Elimination of the need for time-consuming and potentially unreliable sterilization processes
- Reduced risk of human error in cleaning and maintaining reusable masks
By using disposable masks, surgeons can ensure a fresh, sterile barrier for each patient, significantly reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
The Impact of Proper PPE on Surgical Outcomes
The use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including surgical masks and face shields, has a direct and significant impact on surgical outcomes. How does proper PPE affect patient safety?
Firstly, by reducing the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs). SSIs are a major concern in healthcare, leading to increased morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs. Proper use of surgical masks and face shields helps maintain a sterile field during surgery, minimizing the risk of contamination from the surgical team to the patient.
Secondly, PPE protects the surgical team from potential infections, ensuring they remain healthy and able to perform their duties effectively. This indirectly benefits patients by maintaining a fully staffed and healthy surgical team.
The Role of PPE in Building Patient Trust
Beyond the physical protection it provides, the visible use of proper PPE by surgeons and medical staff plays a crucial role in building patient trust. When patients see their healthcare providers taking all necessary precautions, it instills confidence in the quality of care they’re receiving.
Evolving PPE Standards in Response to Global Health Crises
Recent global health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, have led to significant changes in PPE standards and practices within the surgical field. How have these events impacted the use of surgical masks and face shields?
One notable change has been the increased emphasis on the use of N95 respirators in certain surgical settings. While traditional surgical masks remain essential, N95 respirators offer a higher level of filtration, particularly against airborne pathogens like the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Innovations in Surgical PPE
The heightened focus on infection control has also spurred innovations in surgical PPE. Some recent developments include:
- Antimicrobial coatings on face shields to further reduce the risk of contamination
- Improved designs for better breathability and comfort during long procedures
- Integration of smart technology for real-time monitoring of PPE effectiveness
These advancements aim to enhance protection while addressing common concerns such as comfort and communication difficulties associated with traditional PPE.
The Economic Implications of Surgical PPE Usage
While the primary focus of surgical PPE is on safety and infection control, it’s important to consider the economic implications of its usage. How does the consistent use of disposable masks and face shields impact healthcare costs?
On the surface, the continuous need for disposable PPE might seem to increase costs. However, when compared to the potential expenses associated with treating healthcare-acquired infections or managing outbreaks within a healthcare facility, the cost of PPE is relatively minimal.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Surgical PPE
A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of surgical PPE usage typically reveals significant long-term savings:
- Reduced incidence of surgical site infections leads to shorter hospital stays and fewer readmissions
- Decreased risk of healthcare worker infections results in less staff absenteeism and associated costs
- Improved patient outcomes and satisfaction can positively impact a hospital’s reputation and patient volume
Furthermore, the potential legal and financial repercussions of failing to provide adequate PPE can far outweigh the costs of consistent PPE usage.
Training and Compliance: Ensuring Proper Use of Surgical PPE
The effectiveness of surgical masks and face shields is heavily dependent on their proper use. How can healthcare institutions ensure that all surgical staff are using PPE correctly?
Comprehensive training programs are essential. These should cover not only the correct donning and doffing procedures but also the rationale behind PPE usage. Understanding the ‘why’ often leads to better compliance with the ‘how’.
Key Elements of Effective PPE Training
- Regular hands-on practice sessions for donning and doffing PPE
- Education on different types of PPE and their specific applications
- Protocols for PPE disposal and hand hygiene
- Strategies for effective communication while wearing PPE
- Updates on the latest PPE guidelines and best practices
Additionally, healthcare institutions should implement monitoring systems to ensure ongoing compliance with PPE protocols. This can include regular audits, peer observations, and feedback mechanisms.
Addressing Barriers to PPE Compliance
What are some common barriers to proper PPE usage, and how can they be addressed? Some frequent issues include:
- Discomfort during long procedures
- Communication difficulties
- Time constraints in emergency situations
Addressing these barriers may involve investing in more comfortable PPE designs, implementing clear communication protocols for use with PPE, and ensuring that PPE is readily accessible in all areas where it might be needed.
By prioritizing training, monitoring, and addressing barriers to compliance, healthcare institutions can maximize the protective benefits of surgical masks and face shields, ultimately improving patient and staff safety.
Surgical Masks Protect Against Airborne Pathogens
Surgical masks are a critical form of personal protective equipment (PPE) for surgeons and medical professionals. Wearing a proper surgical mask creates a physical barrier that prevents viral particles or infectious droplets from reaching the wearer’s mouth and nose. Especially during procedures like intubation or surgery, there is a high risk of exposure to airborne pathogens that can lead to dangerous respiratory infections.
High quality surgical masks are designed to filter out at least 95% of small particles. Most disposable masks consist of three layers – a water-resistant outer layer, a middle filter layer, and an inner moisture-absorbing layer. The middle layer is key for capturing tiny infectious particles. Surgical masks also feature flexible nose wires and elastic bands to ensure a tight seal around the face and prevent contaminated air from leaking in around the edges.
Viruses like influenza, coronavirus, and tuberculosis can linger in the air in droplet nuclei after an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These tiny residue particles float unseen in the air and can be inhaled. Proper surgical masks form an impenetrable barrier to block inhalation of these hazardous particles. Wearing a surgical mask is shown to reduce exposure risk by as much as 80% compared to not wearing a mask.
In the operating room where germs abound, surgical masks are the first line of defense for surgeons against airborne bugs. Masks prevent contaminated exhalations from reaching the sterile surgical field. They also protect patients from any germs exhaled by members of the surgical team. For lengthy procedures, masks prevent fatigue and throat irritation caused by long-term breathing of stale air. By trapping droplets and particles, surgical masks also help protect against splashes to the face from bodily fluids or irrigation liquids.
Any reputable surgeon knows that wearing proper PPE like surgical masks is non-negotiable. In the presence of infectious airborne pathogens during surgery, masks are absolutely crucial for avoiding transmission and safeguarding the wellbeing of both surgical staff and patients. Proper use of surgical masks is a fundamental element of safety protocols and risk reduction in the operating room. For surgeons, masking up is an essential precaution and professional responsibility.
Face Shields Provide Extra Protection for Eyes

In addition to surgical masks, face shields are another vital form of personal protective equipment (PPE) for surgeons and OR staff. Face shields are clear plastic barriers that cover the entire face and wrap around the sides. While surgical masks protect the nose and mouth from airborne particles, face shields provide an additional layer of protection for the eyes.
During surgical procedures like intubation, drilling, or extracting teeth, there is a high risk of splatter and spray from bodily fluids, irrigation liquids, or debris fragments. Mucous, saliva, or even minute drops of blood can contact unprotected eyes. Face shields create a see-through screen that prevents direct contact of hazardous splashes on the delicate mucous membranes of the eyes. The shields also protect the face, mouth, and mask from incidental splashes.
Another key benefit of face shields is they prevent bulk contaminants or large particles from accidentally falling into the eyes of the person wearing the shield. For example, loose hair or fibers from surgical drapes could drop into the eyes during certain procedures. The face shield blocks these types of particulates from making direct contact with the eyes.
Compared to goggles, face shields have the advantage of also protecting the mask and face. Full face shields extend from above the eyes down past the chin to block splashes from all angles. Face shields are more comfortable than goggles as well, avoiding issues like fogging up that can obscure vision during long surgeries.
Doctors performing invasive dental work, orthopedic surgery, or emergency trauma procedures should always supplement surgical masks with a face shield. For maximum safety, the CDC recommends the use of a face shield in combination with either a surgical mask or N95 respirator when performing aerosol-generating procedures.
Wearing proper eye protection gear demonstrates a surgeon’s commitment to safety. Face shields are indispensable for shielding surgeons’ eyes and masks from hazardous fluids, tissue, or debris during messy surgical procedures. No reputable surgeon should ever scrubs in for an invasive operation without protective eyewear like a face shield along with a surgical mask.
Disposable Masks Prevent Cross-Contamination

An essential advantage of disposable surgical masks is they help prevent cross-contamination in the operating room. Reusable gear can harbor infectious pathogens that get transferred from patient to patient. Single-use disposable masks mitigate this risk.
Cloth masks used repeatedly are difficult to properly disinfect between surgeries. The woven material can trap germs that linger even after washing. Disposable surgical masks made of non-woven meltblown fabric are designed to be worn one time then discarded. This eliminates the chance of residual contamination being passed between medical procedures.
Disposable masks also maintain their protective qualities better than reused cloth masks. The filtration effectiveness of cloth masks deteriorates substantially after being laundered. And repeated processing degrades the electrostatic charges in the material that capture small viral particles. Disposable surgical masks maintain their microbial barrier integrity when brand new.
Wearing a new disposable face mask for each surgery ensures maximum filtration efficiency. This creates an optimal barrier against airborne pathogens for both the surgical staff and the patient. A fresh new mask guarantees the filter layers haven’t been compromised by previous wear.
The FDA recommends medical masks be treated as single-use items. Hospitals and medical facilities have policies requiring staff change masks between patients to decrease infection transmission risks. Wearing a disposable surgical mask is standard procedure anytime a provider interacts with a new patient.
For surgeons, a new disposable mask for every operation is the safest practice. This prevents contaminated equipment from jeopardizing the sterile field. Discarding used masks after each procedure also eliminates inadvertent contact between surgical team members and patients’ bodily fluids or secretions left on a reused mask.
Responsible surgeons committed to safety always wear a new disposable face mask for each surgery. This ensures maximum protection against cross-contamination for both patients and medical staff in the OR.
Proper PPE Reduces Risk of Infection
Wearing the full recommended personal protective equipment (PPE) like masks and shields is proven to significantly reduce the risk of healthcare workers acquiring an infection during surgical procedures.
Various studies show wearing appropriate PPE gear substantially decreases chances of catching contagious illnesses from patients. A meta-analysis published in the British Medical Journal found consistent mask use reduced risk of SARS by around 70% for medical staff. Another study on influenza transmission in hospitals saw a 96% infection rate among unmasked healthcare workers versus only 11% for masked staff.
Proper use of PPE disrupts the spread of pathogens via contact, droplet, and airborne routes. Gowns, gloves, eyewear, masks, and head coverings combine to form a total barrier that blocks transmission through multiple modes. Following comprehensive PPE protocols minimizes exposure to infectious bodily fluids, aerosols, and surfaces.
In the OR where open tissues and blood create an ideal environment for bacteria growth, the protective effects of thorough PPE are magnified even more. Studies focused on surgical settings reinforce the critical role of PPE in preventing post-op infections among surgical teams.
However, PPE must be worn consistently and correctly to be effective. Doffing gear improperly can lead to self-contamination. And masks lose effectiveness if they become loose or saturated with moisture from breathing. Proper donning and doffing techniques are key for achieving full protective benefits.
Surgeons have ethical obligations to avoid spreading illnesses and protect their patients during surgery. Wearing the full recommended PPE ensemble is a proven way to reduce infection transmission risks in the OR for both staff and patients. But training on proper use and disposal of protective gear is also essential to realize the full risk reduction benefits.
Responsible surgeons always wear the right protective equipment and use it correctly to shield themselves and their patients from dangerous pathogens during invasive procedures. Proper PPE is a central pillar of surgical safety.
Masks and Shields Keep Patients Safe

Wearing surgical masks and face shields is critically important for keeping patients safe during operations and other procedures.
Patients undergoing surgery or invasive treatments are in an extremely vulnerable position. Anesthesia and procedural equipment like endotracheal tubes or intravenous lines breach their natural defenses. Surgical incisions open pathways for pathogens to enter normally sterile spaces in the body. Patients need maximum protection from any potential infectious exposures in the operating room environment.
By containing coughs and breath exhalations behind a barrier, surgical masks prevent airborne germs from reaching the patient’s mucous membranes. This protects intubated patients or those undergoing facial procedures where the mouth and airway are exposed. Face shields add another layer of protection against splashes of bodily fluids directly contacting patients’ eyes or open tissues.
In addition, patients often have compromised immunity during and after medical procedures due to sedation, medications, or stress. Their weakened state leaves them especially prone to infection from any pathogens introduced into the body. Diligent use of PPE helps avoid transmitting infectious particles or fluids from medical staff into unhealed wounds or invasive lines.
There have been several documented cases where sloppy PPE use by providers caused surgical site infections. In one case, a surgeon infected 14 cardiac surgery patients with a rare bacteria due to inconsistent mask use. Such scenarios demonstrate how vital provider PPE is for patient safety.
Doctors, nurses, and other providers have an ethical obligation to “first, do no harm” to their patients. Wearing masks and face shields during surgery or invasive procedures is a key way providers can uphold this duty. Proper use of PPE demonstrates a provider’s dedication to patient wellbeing above all else.
Responsible healthcare professionals committed to patient safety will always don masks and shields to protect their vulnerable charges. PPE keeps patients safe during their most defenseless moments.
Using PPE Shows You Care About Safety

In addition to physical protection, the responsible use of surgical masks, face shields, and other PPE gear signals a provider’s concern for safety precautions.
Patients in vulnerable medical situations need to be able to trust their caregivers. Wearing proper protective equipment helps reassure patients that their doctors and nurses are taking every possible measure to guard their wellbeing.
Seeing staff consistently adhere to PPE protocols shows patients the facility has good infection control practices in place. This perception of safety and attention to detail can help patients feel more comfortable and confident undergoing invasive procedures.
From hand hygiene to equipment sterilization, patients notice when providers cut corners on safety steps. But diligent use of PPE demonstrates a provider’s commitment to protocols and protecting patients from harm. This fosters a sense of trust in the care team.
In addition to preventing real hazards, PPE use has symbolic importance for patients. Gear like masks unconsciously reminds them the provider is treating every patient as potentially infectious. This prudence and discretion helps patients feel the staff has their best interests in mind.
Of course PPE only works when used consistently and correctly. But visibly masking up before interacting with each new patient shows respect for protocol and consideration of a patient’s vulnerability. This cultivates confidence in the provider’s competence and concern for safety.
Doctors and nurses wear PPE first and foremost to prevent infections. But the visual signal of seeing one’s caregivers suited up also offers reassurance. It conveys their attention to safety principles and commitment to protecting every patient from harm.
Masks Filter Out Germs and Microbes
The primary function of surgical masks is to filter out infectious particles suspended in the air to prevent transmission of diseases.
Microorganisms like bacteria and viruses can be spread via exhalations in close proximity. Surgical masks contain multiple layers of specialized non-woven fabric designed to capture microscopic pathogens. The electrostatic charges in the polypropylene fibers trap even tiny droplets and particles carrying viruses and germs.
Masks block the spread of pathogens associated with the flu, common cold, tuberculosis, COVID-19, and other respiratory illnesses. Studies show wearing masks reduced coronavirus transmission by up to 75% by filtering infected droplets. High quality surgical masks filter out a minimum of 95% of particulates 0.1 microns in size.
The filtration layers in surgical masks also absorb larger particles and splashes from coughs or sneezes. The mask’s water-resistant exterior prevents infectious fluids from permeating to the inner layers while allowing air to pass through for comfortable breathing.
Proper surgical masks maintain their shape and filtration efficiency even when saturated with moisture from breathing. This consistent particle capture prevents infecting others or the environment. Masks trap pathogens rather than allowing them to disperse freely through the air.
Wearing a mask doesn’t mean you can neglect other preventive measures like hand hygiene or distancing. But surgical masks are proven to meaningfully reduce transmission of airborne illnesses. The physical filtering barrier makes them foundational PPE for medical settings.
By filtering pathogenic particles, surgical masks create safer conditions for patients, providers, and medical staff alike. Their ability to capture microbes is key to reducing communicable disease transmission.
Shields Create Barrier Against Bodily Fluids

Face shields provide an essential physical barrier to protect medical staff from splashes of potentially infectious bodily fluids.
During invasive procedures like surgery, dental work, or intubation, there is risk of blood, saliva, mucous, or other fluids unexpectedly spraying or spattering. Face shields made of clear plastic provide a literal shield to block direct contact of these hazardous secretions with eyes or mucous membranes.
The full face coverage of shields prevents fluids from reaching the nose, mouth, and open respiratory tract – all prime entry points for infection. Studies show face shields lowered exposure to blood splashes by 96% compared to no face protection. Shields also reduce side exposure compared to goggles.
Many infectious diseases can be transmitted by contact with contaminated bodily fluids. A virus like hepatitis B can enter the body via mucous membranes exposed to infected blood splatter. Shields provide a seamless guard against this mode of transmission.
Face shields are more comfortable, effective, and convenient than safety goggles. The seamless protection from forehead to chin and ear to ear provides optimal splash protection without obstructing vision. The barrier remains clear rather than fogging up like goggles might.
For added safety, CDC guidelines recommend using a face shield together with a mask or respirator. The shield protects the mask surface from contamination. This multilayered approach provides the most secure protection during messy procedures.
Face shields are simple but powerful tools that physically interpose an impenetrable barrier against hazardous splashes. When dealing with potentially infectious fluids, this protection can prevent inadvertent exposures or unsafe contaminations.
Surgical Grade PPE Meets Strict Standards
Surgical masks, shields, and other personal protective equipment designed specifically for the operating room are manufactured to meet stringent regulatory standards for quality and performance.
Medical grade PPE used in surgery is regulated as a Class II medical device by the FDA. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices and quality system requirements to achieve FDA clearance to market their products.
Surgical masks must undergo testing to verify their bacterial filtration efficiency, particulate filtration efficiency, fluid resistance, breathability, and flammability. Only masks that meet minimum performance thresholds for capturing pathogens and resisting fluids receive FDA approval.
Quality standards also dictate design elements like mask layers and attachments. Surgical masks feature multi-layer construction with a synthetic hydrophobic outer layer, filtering middle layer, and moisture-absorbing inner layer. Fixed nose pieces prevent air leakage around the bridges of the nose.
Similarly, medical grade face shields are subject to testing for light transmission, distortion, cleanability, flammability, and coverage area. Shields must maintain optical clarity and provide full face protection to receive regulatory clearance.
Compliance with FDA standards ensures surgical PPE performs its protective functions reliably. Doctors can trust medical grade gear to provide a consistent barrier against biohazards when used properly. No shortcuts are taken in manufacturing to jeopardize product integrity.
The high benchmarks required for FDA approval give surgeons confidence in the quality of PPE products designed specifically for the operating room. Medical grade surgical masks and shields offer dependable protection clinicians can trust.
Don’t Skimp on Quality When Lives Are at Stake
In surgery and other invasive procedures, patients’ lives and health are on the line. This is no place to cut corners on safety gear like surgical masks and shields.
Subpar protective equipment puts both patients and providers at risk. Masks made with inferior materials may not filter pathogens reliably. Poorly fitted shields with gaps can still expose eyes to splashes. Flimsy disposable gear may deform when saturated, jeopardizing its protective abilities.
Bargain PPE also tends to be less comfortable and durable. Disposable masks may irritate skin, cause fogging, or rip easily. Uncomfortable gear discourages proper compliance and frequent changing.
Using surgical tools designed for reuse rather than single-use also skimps on safety. Reused instruments risk carrying over contaminants if cleaning is inadequate between procedures.
In the operating room setting, the highest quality PPE and instruments should be the standard. When life hangs in the balance, clinicians must use the most reliable equipment available.
Money saved by purchasing inferior products is not worth risking patient outcomes or provider safety. Low quality gear exposes patients to preventable harm and undermines their trust. For conscientious surgeons, safeguarding lives is more important than budgets.
Elective shortcuts may be tolerable elsewhere, but not in the OR. Surgery necessitates the best protective products backed by rigorous quality assurances. Patients deserve the greatest safety margins when undergoing dangerous procedures.
Investing in Safety Protects Your Practice

While high quality surgical masks, face shields, and other PPE may cost more upfront, the investment protects your medical practice in the long run.
Lawsuits from patients who acquire preventable infections can damage a provider’s reputation, not to mention financial and emotional tolls. One landmark case saw a surgeon pay $5.2 million for failing to mask up while treating a patient who developed HIV.
Hospitals also face regulatory penalties and reporting requirements when patients contract infections from lapses in protocol. CMS can reduce Medicare payments for excessive readmissions or hospital-acquired infections.
Staff illnesses acquired on the job from incomplete PPE create burdens like lost productivity, worker’s compensation claims, and days away from patients.
By comparison, providing comprehensive protective equipment is relatively inexpensive. High quality gear used consistently within protocols helps avoid far greater costs down the line.
The true cost of safety lapses goes beyond any particular patient or lawsuit. Infection control issues erode patient trust and referral networks that practices depend on.
While masks and shields carry upfront costs, they pale in comparison to the infinite value of patient and staff health. For conscientious practices, proper PPE is an investment in long-term viability.
Proper Gear Gives Peace of Mind in Surgery
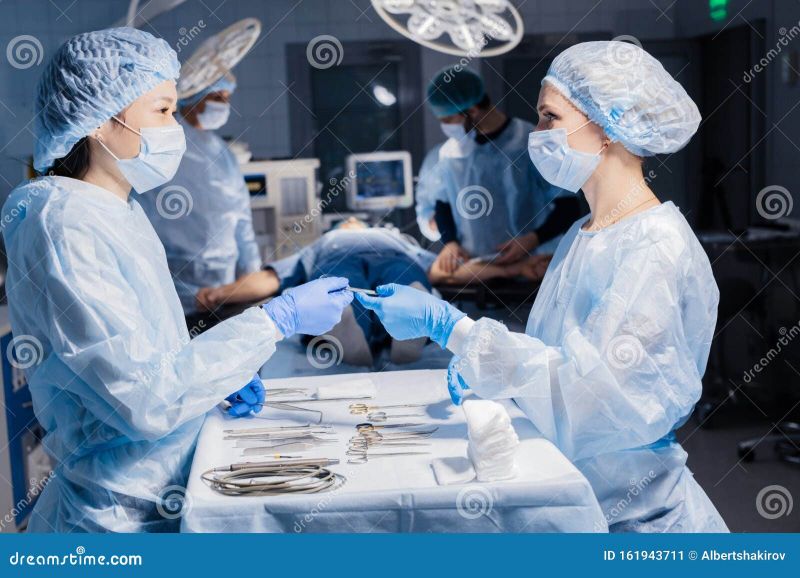
Having complete and reliable PPE provides reassurance and peace of mind for surgeons performing high-stakes operations.
Surgery is mentally and emotionally taxing work even under ideal conditions. Knowing you have only the best protective equipment frees your mind to focus on the intricate procedure rather than distractions over safety.
The highest quality surgical masks maintain their shape and filtration even when soaked with moisture, preventing worries about compromised barrier function. Top-tier face shields offer full splash protection without risk of fluids leaking around ill-fitting edges.
Proper medical grade PPE stands up to the rigors and extended duration of surgery. Providers can concentrate on patients rather than being distracted adjusting loose straps or foggy eyewear.
In an operating room emergency, no time can be lost to subpar equipment failure. Complete confidence in gear allows surgeons to respond decisively without reservations clouding their judgement.
Knowing sterile reusable tools won’t transmit pathogens also grants assurance. Comprehensive protections create a mental environment conducive to peak performance.
Surgeons carry immense responsibility for patients’ lives under their knives. Trustworthy PPE removes doubts so surgeons can devote their full mental energies to the delicate work at hand.
Reliable protective equipment provides confidence and clarity for focused execution. Surgeons perform best when safety systems they trust allow them to zero in on surgical tasks.
Staying Protected Lets You Focus on Patients
The right protective gear allows surgeons to keep their full attention where it matters most – on the patient.
In the operating room, patients’ lives are literally in surgeons’ hands. This critical work requires total mental engagement without distractions from discomfort or safety worries.
Quality surgical masks maintain their shape and filtration ability even when damp, preventing diversion to adjust ill-fitting masks. Face shields offer complete splash protection without risk of fluids leaking around poorly-designed edges.
Proper medical PPE holds up under lengthy procedures. Surgeons can stay focused on delicate tissues rather than being distracted by fogged eyewear or slipping mask straps.
Reliable sterile instruments also prevent disruptions to ensure pathogen transmission isn’t top of mind during surgery. Comprehensive protections enable an uninterrupted zone of concentration.
Surgeons succeed by keeping patients the singular focus. Quality PPE removes nagging distractions about subpar gear. Surgeons can devote their full mental energies to exercising their skills without diversion.
For the extended durations of complex surgery, protective equipment must function flawlessly. When safety protocols are meticulous, surgeons can invest full attention into their work’s purpose – saving the precious life before them.
The highest standard PPE allows surgeons to rise to the demands of their calling – serving each patient with skilled hands, clear eyes, and complete presence of mind.
Never Take Shortcuts with Surgical Safety

Surgery leaves patients at their most vulnerable. Surgeons must never compromise on safety by taking shortcuts with protective gear.
In too many hospitals, PPE protocols exist only on paper. In practice, staff reuse masks between patients or skip eye protection to save time. But in surgery, skipping steps gambles with patients’ lives.
Lapses like reusing contaminated surgical equipment or neglecting N95 respirators during airborne-prone procedures reflect dangerous disregard for safety principles. Yet hospitals often fail to enforce standards consistently.
Some surgeons boast of operating skill but ignore basics like hand hygiene that transmit pathogens. Certain old guard surgeons scoff at masks despite proven benefits. Their ego supersedes patients’ wellbeing.
But in surgery, half measures don’t cut it. Patients under the knife entrust their lives to the surgeon’s standards. Surgeons must not betray that covenant of trust by cutting corners.
Surgery leaves no margin for error. Patients deserve the fullest precautions to avoid preventable harm when under the knife. For surgeons, upholding rigorous safety protocols is a sacred duty.
The operating room is no place for hubris or defiance of sound protocols. Patients need providers who put safety first, no exceptions. When lives hang in the balance, surgical safety should never be compromised.
