How can proper site planning save money on excavation projects. What are the key local regulations to understand before digging. Which insider excavation tips do professionals use to reduce costs. How does choosing the right equipment impact project efficiency.
Understanding Local Excavation Regulations
Before embarking on any excavation project, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with local regulations. This knowledge can prevent costly delays and fines. Most municipalities require several key permits:
- Excavation/grading permit
- Underground utility location approval
- Traffic control plan (if applicable)
- Stormwater pollution prevention plan (for large projects)
Many areas also mandate bonding and insurance requirements for excavation contractors. This protects the municipality in case of infrastructure damage or incomplete work. Understanding right-of-way laws is equally important, as they dictate how close you can excavate to public property like streets and sidewalks.

Noise restrictions and work hour limitations may also apply in your area. To avoid potential issues, it’s advisable to over-communicate with local officials throughout the planning and permitting process.
Essential Excavation Best Practices
Professional excavators employ numerous techniques to ensure project efficiency and safety. Here are some key practices to adopt:
- Conduct a thorough site survey before digging
- Use hand digging for test pits to expose utilities
- Install trench shoring early to prevent collapses
- Utilize trench boxes for worker safety (OSHA requirement for depths over 5 feet)
- Implement proper sloping or benching for trenches deeper than 20 feet
- Maintain consistent dewatering to prevent erosion and wall collapse
- Use structural fill to replace unsuitable backfill material
These practices not only enhance safety but can also lead to significant cost savings by preventing accidents and project delays.
Soil Management and Environmental Considerations
Proper soil management is a critical aspect of professional excavation. How can you effectively manage excavated material? Consider these strategies:

- Protect stockpiles and excavations from runoff to prevent silt releases
- Adhere strictly to stormwater pollution plan requirements
- Phase excavation areas to minimize open trenches
- Use clean blankets to protect paved areas, speeding up cleanup
- Conduct frequent grade checks to avoid overdigging
- Reuse excavated material onsite when possible to reduce fill costs
By implementing these techniques, you can minimize environmental impact and potentially save on material costs.
Selecting the Appropriate Excavation Equipment
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for project success. What factors should you consider when selecting excavation machinery?
Material Composition
The type of material being excavated significantly influences equipment choice. Solid bedrock requires heavy-duty hydraulic breakers and excavators, while soft soil might only need a backhoe. Clay or caliche often necessitate specialized tools for efficient breaking.
Project Scale
The size and scope of your project dictate equipment needs. Large commercial sites typically require heavier machinery like excavators and loaders, while smaller residential projects might be manageable with a backhoe.

Site Constraints
Space limitations and access restrictions play a crucial role in equipment selection. Confined areas may necessitate compact machinery or even manual tools in extreme cases.
Maximizing Efficiency in Excavation Projects
Efficiency is key to keeping excavation costs under control. How can you optimize your excavation process?
- Implement a detailed project plan before breaking ground
- Ensure clear communication among all team members
- Utilize technology like GPS-guided equipment for precise digging
- Maintain equipment regularly to prevent breakdowns
- Train operators thoroughly on safety procedures and efficient techniques
By focusing on these areas, you can significantly improve project efficiency and reduce overall costs.
Safety Considerations in Excavation Work
Safety should always be the top priority in any excavation project. What are the key safety measures to implement?
Trench Safety
Trench collapses are among the most dangerous excavation hazards. To mitigate this risk:

- Always use proper shoring or trench boxes for depths over 5 feet
- Ensure proper sloping or benching for deeper trenches
- Provide safe entry and exit points at least every 25 feet
- Never allow workers in an unprotected trench
Underground Utility Protection
Hitting underground utilities can be costly and dangerous. How can you prevent utility strikes?
- Always call for utility location services before digging
- Use hand digging or vacuum excavation near marked utilities
- Train all workers on utility color codes and safe digging practices
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper PPE is crucial for worker safety. Ensure all workers wear:
- Hard hats
- Safety glasses
- Steel-toed boots
- High-visibility clothing
- Hearing protection when necessary
Cost-Saving Strategies in Excavation Projects
Reducing costs without compromising quality or safety is a key goal for any excavation project. What strategies can help achieve this balance?
Material Management
Efficient material management can lead to significant savings:

- Reuse excavated material on-site whenever possible
- Implement a soil management plan to minimize waste
- Consider on-site material processing to reduce transportation costs
Equipment Optimization
Proper equipment selection and use can greatly impact project costs:
- Choose equipment sized appropriately for the job
- Utilize multi-function equipment to reduce the number of machines needed
- Consider renting specialized equipment for short-term use
Labour Efficiency
Maximizing worker productivity is crucial for cost control:
- Provide thorough training on equipment and safety procedures
- Implement clear communication protocols
- Use technology like GPS guidance to improve accuracy and reduce rework
Environmental Considerations in Excavation
Modern excavation projects must prioritize environmental protection. How can you minimize environmental impact while maintaining project efficiency?
Erosion Control
Preventing soil erosion is crucial for environmental protection and project stability:
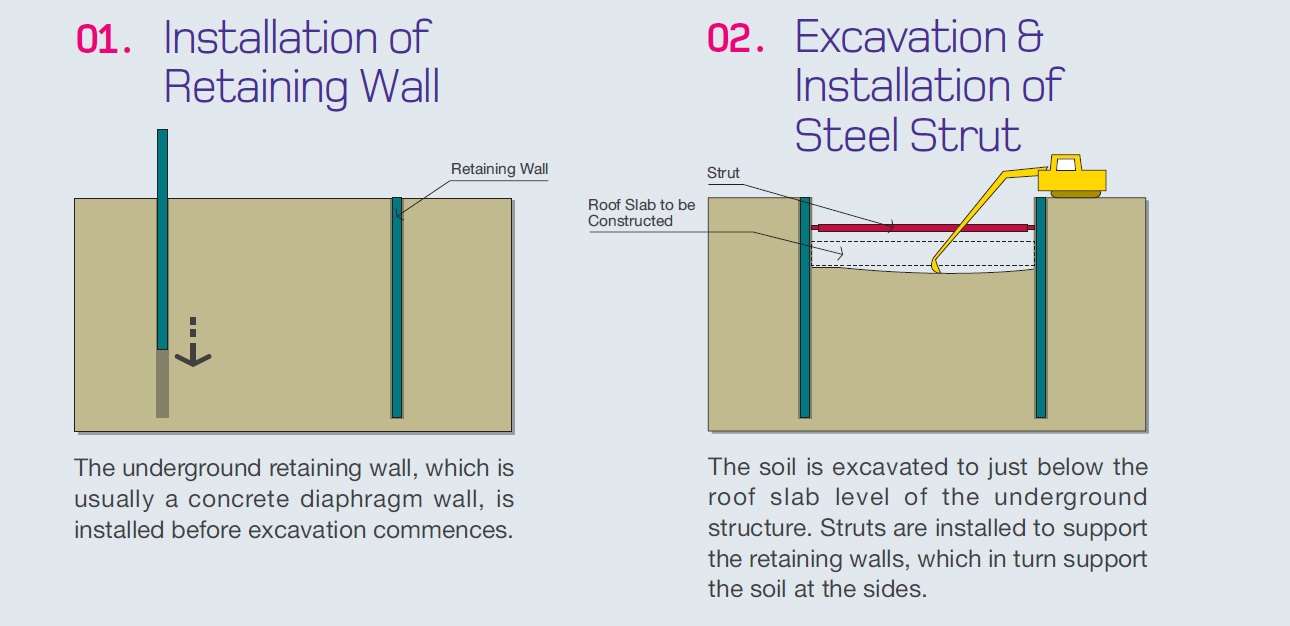
- Install silt fences or other barriers around the perimeter of the site
- Use erosion control blankets on slopes
- Implement a stormwater management plan
Dust Control
Dust from excavation can be a significant environmental and health concern. Mitigate this by:
- Using water sprays to dampen dusty areas
- Covering stockpiles and truck loads
- Limiting vehicle speeds on site
Waste Management
Proper handling of excavated materials is essential:
- Implement a waste sorting system to separate recyclable materials
- Dispose of contaminated soil according to local regulations
- Consider on-site remediation for contaminated soil when feasible
Technological Advancements in Excavation
The excavation industry is continually evolving with new technologies. How are these innovations improving efficiency and safety?
GPS and Machine Control Systems
GPS-guided excavation equipment offers numerous benefits:
- Increased accuracy, reducing over-excavation and rework
- Improved safety by reducing the need for workers near the excavation
- Enhanced productivity through optimized equipment movement
3D Modeling and BIM
3D modeling and Building Information Modeling (BIM) are revolutionizing project planning:

- Improved visualization of underground utilities and structures
- Better coordination between different trades
- More accurate quantity takeoffs and cost estimates
Drone Surveying
Drones are increasingly used in excavation projects for:
- Quick and accurate site surveys
- Progress monitoring and volume calculations
- Safety inspections of hard-to-reach areas
By leveraging these technologies, excavation professionals can significantly improve project outcomes while reducing costs and enhancing safety.
Dealing with Unexpected Challenges in Excavation
Even with thorough planning, excavation projects can encounter unforeseen issues. How can you effectively manage these challenges?
Unexpected Soil Conditions
Encountering unexpected soil types or conditions can significantly impact a project. To mitigate this:
- Conduct thorough geotechnical investigations before starting
- Have contingency plans for different soil types
- Be prepared to adjust equipment or techniques as needed
Underground Obstructions
Unmarked utilities or buried structures can cause delays and safety hazards. To handle these situations:

- Always call for utility location services before digging
- Use ground-penetrating radar for additional subsurface investigation
- Have protocols in place for safely handling unexpected discoveries
Weather-Related Challenges
Adverse weather can significantly impact excavation work. Prepare by:
- Including weather contingencies in your project timeline
- Having proper drainage and pumping equipment on hand
- Implementing erosion control measures that can withstand heavy rain
By anticipating and preparing for these challenges, you can minimize their impact on your project’s timeline and budget.
Proper Documentation and Record-Keeping in Excavation Projects
Maintaining accurate records is crucial for legal compliance and project management. What documentation should you prioritize?
Daily Reports
Comprehensive daily reports should include:
- Work completed and progress made
- Equipment used and hours operated
- Any safety incidents or near-misses
- Weather conditions and their impact on work
Soil Classification Records
Accurately documenting soil types encountered is important for:

- Ensuring proper shoring and excavation techniques are used
- Supporting any change orders due to unexpected conditions
- Compliance with local regulations and building codes
Survey and Measurement Records
Maintain detailed records of:
- Initial site surveys
- Regular progress measurements
- Final as-built surveys
These records can be invaluable for dispute resolution and final project approval.
Building Long-Term Relationships in the Excavation Industry
Success in the excavation industry often depends on building strong relationships. How can you foster these connections?
With Clients
To build lasting client relationships:
- Consistently deliver high-quality work
- Maintain open and honest communication throughout projects
- Be proactive in addressing issues and offering solutions
With Subcontractors and Suppliers
Strong relationships with subcontractors and suppliers can lead to better project outcomes:
- Pay promptly and fairly
- Provide clear expectations and feedback
- Foster a collaborative work environment
With Regulatory Bodies
Maintaining good relationships with local regulatory bodies can streamline future projects:

- Always comply with regulations and permit requirements
- Be transparent and cooperative during inspections
- Participate in industry associations and regulatory discussions
By focusing on relationship-building, you can create a network of trusted partners that can contribute to your long-term success in the excavation industry.
Proper Site Planning Before Excavation
Secret Excavation Tricks Used by Pros: 15 Insider Excavating Engineering Tips to Save You Money
When embarking on an excavation project, whether digging out a new swimming pool or installing underground utilities, it’s crucial to understand the local excavation regulations in your area. Following proper protocols and obtaining necessary permits can save you time, money, and significant headaches down the road. While requirements vary between municipalities, some best practices and insider tips apply across the board.
Understanding Local Excavation Regulations
Before breaking ground on any size excavation, the first step should always be contacting your local permitting office. They can provide excavation guidelines specific to your jurisdiction and property. Some common required permits include:
- Excavation/grading permit – Allows for earth removal and disturbance
- Underground utility location – Locates existing subsurface pipes/wires to avoid damage
- Traffic control plan – For excavations impacting sidewalks or roadways
- Stormwater pollution prevention – Mandatory on large projects disturbing over 1 acre
In addition to permits, many areas mandate bonding and insurance requirements on excavation contractors. This protects the municipality if your work crew damages infrastructure or doesn’t complete the project per regulations.
It’s also crucial to understand right-of-way laws for public property. Local laws dictate the distance you must keep excavations from the street, sidewalk, utility poles, etc. Excavating too close can result in fines or project shutdowns.
Noise and work hour restrictions may also apply. Avoid the headache by knowing the rules upfront. Remember, it never hurts to over-communicate with local officials throughout your planning and permitting process!
15 Insider Excavating Engineering Tips to Save You Money
Once you’ve secured proper permits, here are 15 excavation best practices used by seasoned construction pros:
- Survey the site yourself before digging – Look for clues about buried utilities or foundations.
- Hand dig test pits to expose utilities before trenching – Prevent accidental line slices.
- Shore trench walls early – Prevent collapses in unsound soils.
- Use trench boxes for worker safety – Required by OSHA after 5 feet depth.
- Slope or bench trenches deeper than 20 feet – Improves stability per OSHA requirements.
- Dewater constantly – Prevent erosion and sidewall collapse.
- Replace unsuitable backfill with structural fill – Eliminate trench settling.
- Compact backfill in lifts – Promote stability and reduce voids.
- Protect stockpiles and excavations from runoff – Prevent project delays from silt releases.
- Follow stormwater pollution plan requirements – Avoid fines andneighborhood complaints.
- Phase excavation areas – Minimize open trenches and improve site safety.
- Use clean blankets to protect paved areas – Speeds cleanup and closeout.
- Survey grade checks often – Avoid overdigging and excess material hauling.
- Reuse excavated material onsite when possible – Significant cost savings over imported fill.
- Communicate dig locations to entire crew – Prevent accidental utility hits.
By leveraging these insider techniques perfected by experienced excavation contractors, you can complete your project on time, on budget, and in compliance with local regulations. Remember to over-communicate with local officials and never cut corners on safety or permits. Here’s to a smooth, headache-free excavation project!
Choosing the Right Excavation Equipment
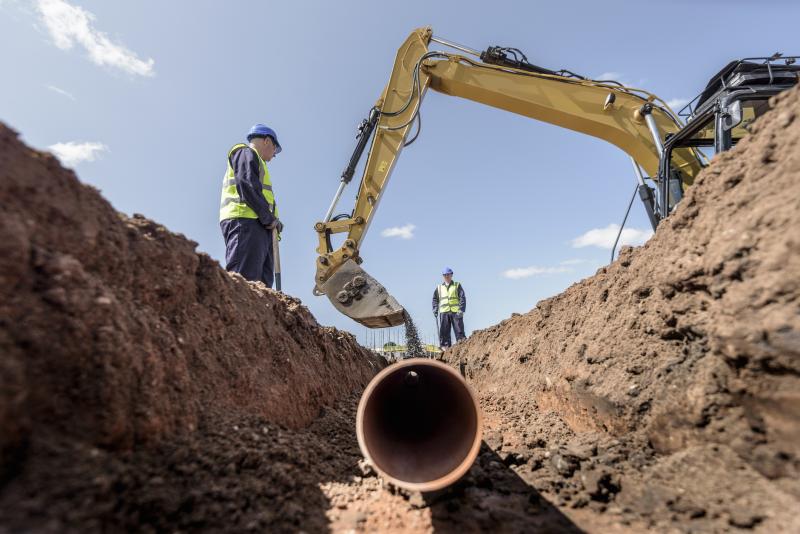

When starting an excavation project, one of the most important decisions is choosing the right equipment. The excavation tools and machinery selected can have a major impact on efficiency, costs, and safety. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting excavation equipment:
Type of Material Being Excavated
The composition of the ground or material being excavated should play a big role in equipment choice. Excavating solid bedrock requires heavy-duty hydraulic breakers and excavators. Digging in soft soil may only require a backhoe or similar single-bucket excavator. Other materials like clay or caliche require specific tools to break through efficiently.
Size and Scope of Project
The overall size of the excavation job is important too. A huge commercial site needs much heavier equipment than a small residential yard project. The depth of required digging and width of the excavation area also impact equipment needs. Larger sites usually need excavators and loaders rather than just a backhoe.
Space and Access Limitations
Pay close attention to space constraints and access limitations on the job site. Using excavators or large dozers won’t work in confined areas. In tight spots, a compact utility loader or mini-excavator is a better fit. Overhead obstacles, width restrictions, and low ground clearance may also restrict equipment options.
Safety and Environmental Factors
Safety should always be the top priority when excavating. Some sites have risks like underground utilities, contaminated soils, or groundwater issues. Specialized equipment with safety features helps mitigate these hazards. Things like hydraulic quick couplers, pressurized cabs, and gas monitors are important for dangerous excavation engineering situations.
Cost Efficiency and Productivity Needs
Project budgets and productivity requirements should guide equipment selection too. Bigger machines like large excavators or dozers maximize productivity but cost much more to purchase or rent. Smaller backhoes or skid steers offer greater cost efficiency for modest digging needs. Match the right machine size and features to the production rate required.
Operator Skill and Machine Complexity
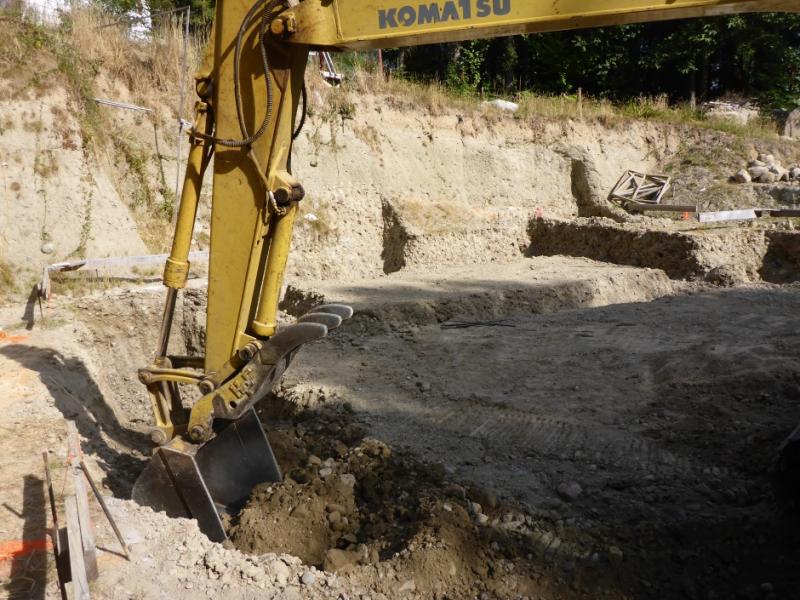

The training and skill level of equipment operators is crucial as well. Powerful but complex hydraulic excavators require experienced operators. A backhoe that is easier to use may be a better choice for basic excavation tasks or less skilled workers. Don’t choose a machine more complex than required for the job site’s operator expertise.
Maneuverability and Transportation
Consider how the excavation equipment will get to the job site and move around on it. Larger dozers or excavators require special trailers for transport. Tiny urban sites may need a compact mini-excavator that can fit through narrow access gates. Pick a machine that can easily maneuver around existing structures and obstacles on the excavation site.
Secret Excavation Tricks Used by Pros: 15 Insider Excavating Engineering Tips to Save You Money
Professional excavators rely on special tricks and techniques to get jobs done safely, efficiently, and under budget. Here are 15 insider tips from excavation pros to help your next digging project go smoothly:
- Go in with a plan – Map out dig areas, access points, and spoil pile locations to prevent extra work. Proper excavation engineering upfront prevents costly issues.
- Use technology – Use grade control systems and GPS on excavators to get precise cuts right the first time.
- Test soil stability – Check soil strength and composition before digging to anticipate safety needs and challenges.
- Shore properly – Use trench boxes, shoring, benching, or sloping to prevent dangerous collapses in unstable soils.
- Watch out for underground hazards – Call 811 and use private locating services to mark utilities, pipes, and cables before putting a bucket in the ground.
- Keep the site clean – Remove excess spoil promptly and organize tools/supplies to prevent injury and work delays.
- Use the right rig – Match excavator size and capability to the soil type and digging depth needed.
- Stage wisely – Position haul trucks, excavators, and other machines smartly to minimize double handling of material.
- Practice grade control – Use lasers, GPS, or an experienced spotter to guide cuts accurately.
- Dig a test hole first – Excavate a small trial hole to reveal hidden obstacles before full-scale digging.
- Watch the weather – Stop digging if excess water or storm damage are imminent to avoid cave-ins and other issues.
- Keep an eye on traffic – Use proper signage, barricades, and spotters to direct vehicles and prevent accidents around the excavation zone.
- Use pool excavation tricks – For deep digging, excavate the center first, then work outward to avoid cave-ins.
- Install dewatering pumps – Use pumps and proper drainage to keep excavations dry and stable.
- Get help – For complex or hazardous sites, hire excavation engineering experts to assess risks and recommend solutions.
Following these professional tips can significantly improve productivity, reduce costs, enhance safety, and prevent headaches on your excavation project. Remember – proper planning, the right equipment, and expert techniques are key to excavation success.
Implementing Erosion Control Measures
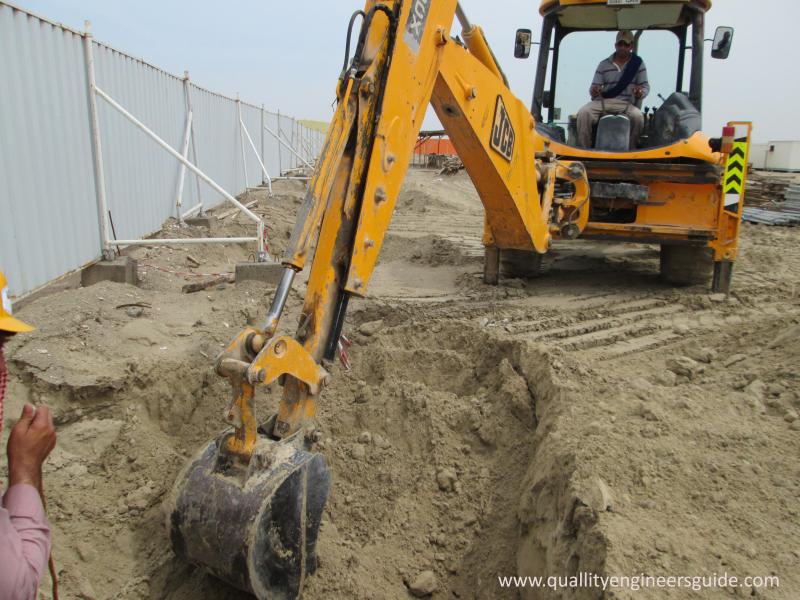

Erosion can cause major problems on excavation and construction sites. Implementing proper erosion control measures is crucial to prevent environmental damage, safety issues, and project delays. Here are some key tips for effectively controlling erosion:
Install Perimeter Controls
Start by protecting the outer edges of the site. Install silt fencing, sediment traps, and stabilized entrances to keep sediment from leaving the site. Maintain a perimeter buffer zone of vegetation if possible. Protect slopes and channels with barriers too.
Use Site Stabilization Techniques
Stabilize disturbed soil areas as soon as possible. Apply erosion control blankets, hydromulch, tackifiers, or straw over bare ground. Temporary seeding and mulching help stabilize until vegetation establishes. Schedule excavation in phases to limit exposed soil.
Control Water Flow
Manage stormwater runoff carefully. Use berms, swales, check dams and diversion ditches to direct flow away from bare soil. Consider terraces, contour trenching, and soil roughening to slow downhill water velocity and prevent gully erosion. Install sediment traps at drainage outlets.
Watch the Weather
Plan around forecasts to avoid exposing soil right before heavy rains. Stage erosion controls like silt fencing before storm events. Halt excavation during extreme weather until the site can be stabilized again. Inspect controls after storms for damage.
Maintain BMPs
Proper maintenance is essential. Inspect erosion control barriers regularly, especially after storms. Repair or replace damaged silt fences, sediment traps, inlet protection, and other BMPs promptly. Remove accumulated sediment to prevent breaches or overflow.
Manage Stockpiles
Cover or seed soil and aggregate stockpiles. Encircle them with silt fencing or berms. Position stockpiles away from slopes, channels, roads, and other drainage pathways. Stabilize access points where vehicles enter and exit.
Minimize Soil Disturbance
Schedule excavation in smaller phases to limit exposure. Designate equipment travel paths and material storage areas away from drainage channels. Allow as much existing vegetation to remain undisturbed as possible. Protect trees and shrubs at the perimeter.
Use Advanced Erosion Control Products
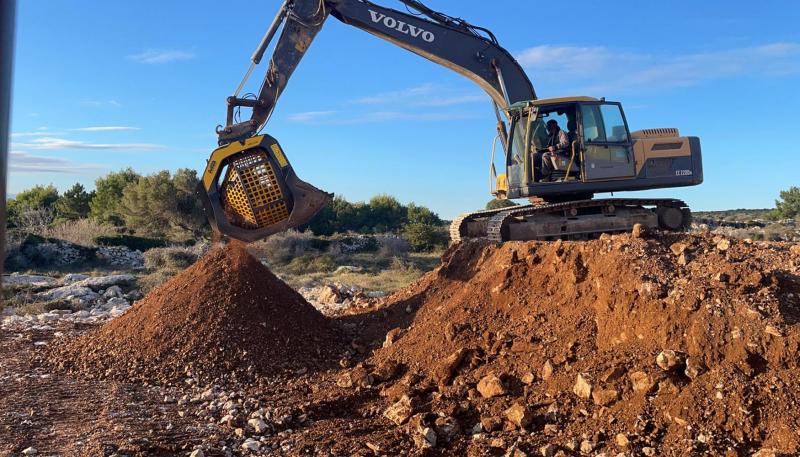

Consider new erosion control technologies to enhance performance. Bonded fiber matrix hydraulically applied products combine mulch, tackifier and seed for rapid protection. Rolled erosion control products with active seeding create instant vegetation. Consider exciting new excavation engineering products like flexourethane for erosion control in channels.
Secret Excavation Tricks Used by Pros: 15 Insider Excavating Engineering Tips to Save You Money
Professional excavators rely on special tricks and techniques to get jobs done safely, efficiently, and under budget. Here are 15 insider tips from excavation pros to help your next digging project go smoothly:
- Go in with a plan – Map out dig areas, access points, and spoil pile locations to prevent extra work. Proper excavation engineering upfront prevents costly issues.
- Use technology – Use grade control systems and GPS on excavators to get precise cuts right the first time.
- Test soil stability – Check soil strength and composition before digging to anticipate safety needs and challenges.
- Shore properly – Use trench boxes, shoring, benching, or sloping to prevent dangerous collapses in unstable soils.
- Watch out for underground hazards – Call 811 and use private locating services to mark utilities, pipes, and cables before putting a bucket in the ground.
- Keep the site clean – Remove excess spoil promptly and organize tools/supplies to prevent injury and work delays.
- Use the right rig – Match excavator size and capability to the soil type and digging depth needed.
- Stage wisely – Position haul trucks, excavators, and other machines smartly to minimize double handling of material.
- Practice grade control – Use lasers, GPS, or an experienced spotter to guide cuts accurately.
- Dig a test hole first – Excavate a small trial hole to reveal hidden obstacles before full-scale digging.
- Watch the weather – Stop digging if excess water or storm damage are imminent to avoid cave-ins and other issues.
- Keep an eye on traffic – Use proper signage, barricades, and spotters to direct vehicles and prevent accidents around the excavation zone.
- Use pool excavation tricks – For deep digging, excavate the center first, then work outward to avoid cave-ins.
- Install dewatering pumps – Use pumps and proper drainage to keep excavations dry and stable.
- Get help – For complex or hazardous sites, hire excavation engineering experts to assess risks and recommend solutions.
Following these professional tips can significantly improve productivity, reduce costs, enhance safety, and prevent headaches on your excavation project. Remember – proper planning, the right equipment, and expert techniques are key to excavation success.
Utility Locating Before You Dig

Hitting underground utilities during excavation can be disastrous. Severing a gas line, water main, or fiber optic cable can be incredibly dangerous and costly. That’s why properly locating buried utilities before digging is so crucial.
Call 811
Calling 811 to request utility locating services should always be your first step. 811 will notify all local utility companies of your planned excavation area and time frame. Utilities like gas, electric, cable, telephone, and water will then send locators to mark their underground lines.
Allow Adequate Lead Time
Call 811 well in advance of excavation – most states require at least 2 to 3 business days notice. This gives utility owners sufficient time to accurately locate and mark their underground infrastructure. Rushing utility locates often leads to missed lines.
Define the Excavation Limits
Provide 811 and locators detailed information on the exact dig area. Use white marking paint or flags to outline the excavation perimeter above ground. The more precise your markings, the better locators can search for utilities only within the dig zone.
Meet With the Locators
Talk with utility locators on site when they arrive. Review the scope of work and excavation plans. Escort them around the defined dig area to point out access routes and answer questions. Good communication ensures accurate utility marking.
Confirm All Utilities Are Marked
Ensure all utilities known to be at the site are marked. Check formarkers from gas, electric, cable, fiber optics, water, sewer, and telephone. If any expected utility owner did not mark their lines, contact them directly to avoid unmarked hazards.
Document and Respect the Marks
Carefully record the marking symbols and colors used. Utility colors follow national standards for easy recognition. Always dig with care around markings and avoid heavy equipment over marked lines.
Follow Excavation Standards
Adhere to safe digging practices near utilities, such as “soft dig” exposed line procedures. Support uncovered lines properly. Report any nicks or damage made to utilities. Follow all regulatory and excavation engineering best practices.
Call Again If Needed

Request re-marks if dig plans change or marks get obscured. Drainage work and deep excavations often require progressive relocates as you descend. Have utilities re-marked as necessary until the job is done.
Secret Excavation Tricks Used by Pros: 15 Insider Excavating Engineering Tips to Save You Money
Professional excavators rely on special tricks and techniques to get jobs done safely, efficiently, and under budget. Here are 15 insider tips from excavation pros to help your next digging project go smoothly:
- Go in with a plan – Map out dig areas, access points, and spoil pile locations to prevent extra work. Proper excavation engineering upfront prevents costly issues.
- Use technology – Use grade control systems and GPS on excavators to get precise cuts right the first time.
- Test soil stability – Check soil strength and composition before digging to anticipate safety needs and challenges.
- Shore properly – Use trench boxes, shoring, benching, or sloping to prevent dangerous collapses in unstable soils.
- Watch out for underground hazards – Call 811 and use private locating services to mark utilities, pipes, and cables before putting a bucket in the ground.
- Keep the site clean – Remove excess spoil promptly and organize tools/supplies to prevent injury and work delays.
- Use the right rig – Match excavator size and capability to the soil type and digging depth needed.
- Stage wisely – Position haul trucks, excavators, and other machines smartly to minimize double handling of material.
- Practice grade control – Use lasers, GPS, or an experienced spotter to guide cuts accurately.
- Dig a test hole first – Excavate a small trial hole to reveal hidden obstacles before full-scale digging.
- Watch the weather – Stop digging if excess water or storm damage are imminent to avoid cave-ins and other issues.
- Keep an eye on traffic – Use proper signage, barricades, and spotters to direct vehicles and prevent accidents around the excavation zone.
- Use pool excavation tricks – For deep digging, excavate the center first, then work outward to avoid cave-ins.
- Install dewatering pumps – Use pumps and proper drainage to keep excavations dry and stable.
- Get help – For complex or hazardous sites, hire excavation engineering experts to assess risks and recommend solutions.
Following these professional tips can significantly improve productivity, reduce costs, enhance safety, and prevent headaches on your excavation project. Remember – proper planning, the right equipment, and expert techniques are key to excavation success.
Hiring a Licensed and Insured Excavator

When it comes time for an excavation project on your property, whether it’s installing a pool, building a foundation, or putting in utility lines, hiring a qualified, licensed, and insured excavation contractor is crucial. Not only can excavation be dangerous, but a poor job can lead to structural issues, pipe leaks, erosion, and more down the road. Follow these insider tips to ensure you find the right excavator for the job.
1. Verify Licensing and Insurance
The number one rule is to only hire an excavation contractor who possesses an active license for your state and has the proper insurance, including liability and workers’ compensation. Ask to see current documentation. Unlicensed contractors often cut corners, violating building codes and safety practices. Proper licensing and insurance protects you from liability.
2. Look for Experience and Specialization
Find an excavator with extensive experience specifically in the type of project you need completed. Excavating for a pool requires different skills and equipment than excavating for sewer lines. Look for contractors who specialize in your type of project.
3. Ask About Equipment and Techniques
The right excavation equipment and techniques can make a big difference in time, safety, and quality of work. Ask the contractor what types of equipment they use for your specific project, such as hydraulic excavators, backhoes, and trenchers. Make sure they have techniques for safety and preventing utility line damage.
4. Request References
Don’t hire an excavator without checking references from recent completed projects similar to yours. Call the references and ask specific questions about the excavator’s quality of work, timeliness, site safety, communication, and more.
5. Check Reviews and Ratings
Beyond references, look for online customer reviews as well as ratings with organizations like the Better Business Bureau. This provides further insight into an excavator’s quality, reliability, and service.
6. Ask About Site Safety Measures
Excavation sites are fraught with dangers, including gas leaks, cave-ins, electrical shock, falling debris, and more. Make sure the excavator explains the safety measures they use, such as shoring trenches, scanning for underground utilities, and proper drainage.
7. Look for Comprehensive Project Planning

An experienced excavator doesn’t just show up and start digging. They should evaluate your site and project, create a detailed plan, discuss logistics with you, coordinate subcontractors, obtain permits, and prepare the work site before breaking ground.
8. Consider Sustainability
Today more excavators are utilizing sustainable techniques, such as reusing excavated soil on-site instead of hauling it away. If environmental sustainability is important to you, look for excavators using green practices.
9. Discuss Logistics Thoroughly
Before hiring an excavator, discuss all project logistics including: timeline, phases, costs, crew size, equipment, materials, site prep and access, restoration, waste removal, permits, inspections, and any obstacles unique to your property.
10. Get a Detailed Written Proposal
Don’t hire an excavator who won’t provide a detailed written proposal outlining the project scope, specifications, timeline, costs, equipment, materials, and any guarantees. If details are vague, keep looking.
11. Ask About Handling Unexpected Problems

Even experienced excavators encounter unexpected problems like hidden utilities, hard rock, groundwater, or bad weather. Ask upfront how the contractor handles such issues should they arise during your project.
12. Request Daily Cleanup and Safety Checks
Negotiate tidy daily cleanup and safety checks into your contract. Excavated areas and trenches should be properly secured at the end of each workday. Safety walks should be conducted to spot any issues.
13. Seek Sufficient Insurance Coverage
An excavator should have liability insurance of at least $1 million. For larger jobs, $2 million is better. Make sure you are listed as an additional insured party to cover your assets.
14. Don’t Automatically Choose the Lowest Bid
An extremely low bid can signal inexperience or corner cutting that leads to problems. Choose a fair bid that fits your budget from an experienced excavator with a proven track record.
15. Get a Written Warranty
Reputable excavators stand behind their work. Make sure any guarantees for materials, craftsmanship defects, and structural damage are spelled out clearly in writing before work begins.
By following these insider tips and asking the right questions upfront, you can find an experienced and conscientious licensed and insured excavation contractor to complete your next project properly and safely. Don’t cut corners when it comes to excavation on your property.
Getting Excavation Permits and Bonds
Performing any kind of excavation work usually requires obtaining permits and bonds to comply with state and local regulations. Skipping this important step can result in hefty fines or work stoppages. Follow these insider tips to make sure you secure the proper permits and bonds for your next excavation project.
1. Verify Permit Requirements
Different locations have different permit rules for excavation work. Check with your city or county building department to find out exactly what permits you’ll need based on the scope and location of your project.
2. Apply Well in Advance

Don’t wait until the last minute to apply for permits. The process can take days or even weeks, especially if revisions are needed. Apply for permits as soon as you finalize excavation plans to avoid delays.
3. Provide Detailed Plans
Excavation permit applications usually require detailed project plans, specifications, location maps, and other documentation. Provide comprehensive information to facilitate quick permit approval.
4. Follow Proper Procedures
Learn and follow your jurisdiction’s proper protocols for excavation permit applications, which may entail inspections, public notices, hearings, insurance, fees, and other requirements.
5. Call Before You Dig
Once permits are secured but before excavation begins, call 811 or your local underground utility locator service to mark buried utility lines on your property.
6. Post Permits On-Site
Make copies of all permits secured for the project. Post them visibly on-site so inspectors can quickly verify you have obtained proper permitting.
7. Consider a Bond

Depending on the scope, you may need to take out a permit bond to cover any potential damages or issues during excavation work.
8. Verify Insurance Requirements
Excavation permits often stipulate that you must have sufficient general liability insurance naming the jurisdiction as an additional insured.
9. Follow Safety Regulations
Permits usually come with safety rules for excavation, like shoring trenches over 5 feet deep. Follow all such safety mandates.
10. Allow Utility Inspections
Permits will specify points where underground utilities must be inspected before backfilling. Arrange for timely inspections.
11. Expect Site Inspections
Inspectors will routinely check the worksite to verify permits are posted and work complies with local codes.
12. Keep Documents On-Site
In addition to posted permits, keep copies of bonds and insurance paperwork available on-site for easy access by inspectors.
13. Coordinate Subcontractors
If using subcontractors, make sure they have all required permits and insurance documents before allowing work.
14. Allow Engineer Inspections
Engineered excavation plans will require inspection by the responsible engineer at defined milestones.
15. Close Out Permits
At project completion, follow proper protocols to close out open permits, which may require final inspections or paperwork.
Securing the right permits and bonds in advance is a crucial first step for any excavation project. Allow plenty of lead time and maintain an orderly on-site file for quick access to all necessary documentation. With careful attention to permitting, your excavation can proceed smoothly and safely while remaining in compliance.
Installing Proper Excavation Signage and Barriers
Excavation sites require adequate signage and barriers to ensure safety and comply with regulations. Improper or insufficient warnings and protections can lead to injuries, citations, or even lawsuits. Follow these key tips for installing the right excavation signage and barriers.
1. Check Local Signage Requirements

Signage and barrier guidelines differ between jurisdictions. Check your local regulations for specifics like size, placement, wording, and reflectivity.
2. Place Visible Warning Signs
Position warning signs clearly visible from all approach directions. Use stands or posts for stability and proper sight lines. Illuminate for night visibility.
3. Mark All Underground Hazards
Use hazard markers, flashers, and painted lines on pavement to delineate the locations of any buried electric, gas, water, sewer or other underground utility lines.
4. Use Highly Reflective Materials
Signs, cones, drums, and barricades should all be made from reflectorized material for maximum visibility in low light conditions or at night.
5. Keep Signs Clear of Obstructions
Ensure excavation signs are not blocked from view by vehicles, equipment, stockpiles, or other objects on the site.
6. Place Signs At Key Locations
Position warning signs at entrances and exits from excavation areas as well as along perimeter fencing or barricades.
7. Secure Signs Against Displacement
Use sturdy sign stands and posts or cement barriers into the ground to prevent signs from shifting or falling over.
8. Check Signs Periodically
Inspect signs regularly and replace any that are damaged, defaced, or missing. Knocked over signs must be reinstalled properly.
9. Use Highly Visible Barrier Fencing
Surround excavations with orange plastic mesh fencing securely anchored to posts. This sends a clear visual warning.
10. Protect Large Excavations
For excavations wider than 2 feet, install protective barricades such as guardrails or cement barriers at least 6 feet from the edge.
11. Cover Excavations When Unattended
Use heavy steel plates or secured plywood to cover open trenches and holes when the site is vacant overnight or for longer periods.
12. Rope Off Less Hazardous Areas
For low depth excavations or small stripping/grading areas, use yellow caution ropes to mark boundaries.
13. Put Up Informational Signs
Help the public understand what’s happening by installing signs explaining the project and who to contact for questions or issues.
14. Use Flashing Beacons
Install portable sequential flashing beacons on barricades to grab attention during night work or on roadways.
15. Hire Flag Workers If Needed
For excavations requiring road or lane closures, hire properly trained flaggers in safety vests to direct traffic.
Adequate highly visible signage, barriers, and warnings prevent accidents and create a safe excavation site. Regular inspection and maintenance of signs, fences, and other protections are also essential. Follow these tips to properly install required excavation signage and barriers.
Conducting Pre-Excavation Site Inspections
Before any excavation project begins, it is crucial to perform a thorough site inspection. This allows excavation professionals to identify potential hazards, assess underground utilities, and develop an optimal excavation plan. While site inspections require an investment of time upfront, they end up saving contractors significant money and headaches down the road.
Here are 15 insider tips and tricks for conducting effective pre-excavation site inspections:
1. Walk the Entire Site

Don’t just view the site from your vehicle. Get out and walk the entire area that will be excavated. This allows you to observe the terrain and look for any indicators of underground utilities or other hazards. Mentally note any changes in elevation, soil conditions, standing water, and other factors that could impact equipment access or stability.
2. Look Up and Look Down
Scope out what’s above and below the site. Look for tree branches, power lines, bridges, or other overhead obstacles. Check the ground for manhole covers, meters, valves, or other clues about buried utilities. Avoid getting tunnel vision on the excavation itself – hazards can come from any direction.
3. Talk to the Property Owner
The property owner can provide useful insights about the site history and any known utilities. Were there previous structures on the site? Have there been any excavations or underground construction? The owner may share knowledge that isn’t available through utility locates or public records.
4. Review Utility Maps Thoroughly

Don’t rely solely on utility locates – the maps themselves contain valuable data. Check for the number and location of utilities, their depth, age, size, and contents. Note any abandoned lines. Review the maps for accuracy by comparing with visual indicators on-site.
5. Allow Adequate Time for Utility Locating
Call 811 well in advance so utilities have time to mark their underground lines. Depending on your area, this may take 72 hours or more. Trying to rush this process increases the odds of something being missed.
6. Verify Utility Locates Onsite
Don’t assume locates are 100% accurate, as there is room for human error. Verify the type and location of utilities by looking for corresponding meters, manhole covers, valves, junction boxes, or other equipment. Discrepancies should be reported to the utility owner before excavating.
7. Account for Unmarked Private Lines
Some private utility lines won’t be marked by public locators. Scrutinize the site for any evidence of unmarked lines, especially on commercial properties or large residential lots. An experienced eye can spot subtle clues. When in doubt, proceed with caution.
8. Confirm Utility Depths
Identify the approximate depth of buried utilities whenever possible. Shallow lines may need extra protection. Also check that utility depths match plans – incorrect installation height amplifies risk of strikes.
9. Document Pre-Excavation Conditions
Take dated photographs and video of the site from multiple angles before you break ground. This provides proof of pre-existing site conditions should any disputes arise. Pay special attention to capturing adjacent structures, pavements, and landscaping.
10. Watch for Signs of Previous Excavations
Look for patches in the pavement, changes in soil density, and other signs of prior digging. Previous excavations are magnets for subsurface hazards as utilities or structures may have been rebuilt. Exercise additional caution in these areas.
11. Identify Surface and Subsurface Hazards
Make note of any surface obstacles along with underground hazards identified through locates. Develop a plan to remove or avoid them. Don’t forget to look for hazards on neighboring properties that could impact your work area.
12. Check for Restricted Equipment Access

Ensure your excavation equipment can safely access the site. Check for tight spaces, steep slopes, weight limits on surrounding surfaces, overhead clearances, and obstacles to maneuvering on the property.
13. Assess Soil Conditions
Determine the soil composition through visual and physical examination. Consider how factors like soil stability, drainage, and corrosiveness will impact equipment performance and safety precautions.
14. Have a Safety Plan
Every site has hazards, so it’s critical to develop a safety plan upfront. Identify risks, determine protective actions, and establish emergency response procedures. Preplanning prevents having to make hasty, dangerous decisions later.
15. Document and Communicate Findings
Record all inspection findings in writing and photographs. Hold a pre-construction meeting to review the site assessment with all parties involved. This keeps everyone literally and figuratively on the same page before excavation begins.
In summary, comprehensive pre-excavation site inspections require diligence and attention to detail, but they return huge dividends in safety, efficiency, and cost-savings. Following these insider tips will help excavation pros conduct rigorous inspections that uncover potential problems upfront – before they have costly consequences down the line.
Digging Precise Trenches and Foundations

Excavating trenches and foundations with laser-like accuracy takes skill and know-how. Sloppy digging leads to infrastructure failures, construction delays, and inflated costs. By mastering precision excavation techniques, operators can deliver projects faster, safer, and more profitably.
Follow these 15 insider tips to carve flawless trenches and foundations every time:
1. Survey and Stake the Area
Work with surveyors to stake out the precise position and depth of the trench or foundation. Check measurements regularly as you dig to track your progress and make adjustments.
2. Use Grade Checking Devices
Laser, GPS, and optical grade checking tools quantify exactly where your bucket sits relative to target elevation. This enables making fine adjustments to maintain grade.
3. Choose the Right Equipment Size
Oversized excavators limit visibility and precision. Compact machines with narrow buckets provide tighter maneuverability for detail work. Attachments like tilting buckets also enhance accuracy.
4. Take Smaller Bites
Removing large chunks of dirt increases margin of error. Take smaller bucket loads for a more controlled, incremental approach. Let the machine do the work rather than forcing progress.
5. Approach From the Side
Digging straight down from above lacks finesse. Enter the trench or foundation from the side at a 45 degree angle. You can see better and use the bucket’s curl to pare away material.
6. Use Slope Buckets Cautiously
Tilted buckets are great for accuracy, but don’t create overly steep slopes. Collapsing trench walls put workers at risk. Maintain safe entry and exit points.
7. Shim Under Machinery
Placing timber, mats, or crushed stone beneath excavators provides a solid base. This prevents equipment sinking and inadvertent drift from target grade.
8. Check Grade Frequently
Confirm precise depth and slope every few bucket loads – not just at the end. Catch any deviations early before they grow. Consistent measurement augments consistency of the dig.
9. Communicate With Laborers

Talk to ground personnel as you work. They can see trench floor and walls from all angles and provide guidance. Good communication enhances accuracy.
10. Avoid Over-Digging
It’s tempting to excavate slightly deeper as insurance against filling back in. But overdoing depth makes attaining precise finish grade tougher. Only dig to necessary spec.
11. Correct Mistakes Immediately
Don’t let small errors accumulate. If you undercut, backfill right away. If you overcut, fix before proceeding. Nipping issues quickly maintains integrity.
12. Use String Lines as Depth Guides
Running string lines at finish grade provides a visual target to work toward. Use multiple strings to check fairness across the surface.
13. Pour Mud Slab for Finish Work
For the final few inches, pouring a shallow mud slab establishes an absolute grade reference for precision trim. Scrape down in thin layers until contacting slab.
14. Take Your Time

Rushing leads to careless mistakes. Work methodically and double check as you go. Precision excavation takes patience and meticulousness.
15. Leave a Clean Finish
Avoid leaving jagged, uneven surfaces. Make the last bucket passes while moving backward to peel away roughness. Backfill selectively to patch any defects.
With practice and vigilance, excavation experts can sculpt flawless trenches and foundations every time. Remember to stake, measure twice, and correct promptly. By mastering these insider precision techniques, operators gain reputation and competitive advantage for quality work.
In summary, precision excavation separates the pros from the rookies. Paying attention to detail, using the right approach, and fixing mistakes immediately results in trenches and foundations that pass muster. Consistently delivering such high-caliber results is how excavators build their brand and bottom line.
Managing Excavated Soils and Materials
Handling the huge volumes of soil, rock, and other materials generated by excavation projects is a science unto itself. Experienced contractors have insider techniques for efficiently managing these outputs while saving money and avoiding violations.
Follow these 15 professional tips for mastering excavated material management:
1. Estimate Volumes Accurately
Anticipating soil volumes needing disposal or reuse helps plan transportation, storage, and processing. Perform thorough pre-excavation surveys to project quantities precisely.
2. Characterize Waste Types
Test materials to identify any contaminated or hazardous wastes requiring special handling. This prevents toxicity issues and violations for improper disposal of regulated substances.
3. Design Traffic Flows
Designate safe routes for hauling material on- and off-site. Make them efficient while avoiding impacts to operations and public roads. Traffic planning prevents delays.
4. Choose Optimal Equipment
Match excavators, loaders, and trucks to material types and haul distances. Smaller machines often work better for tight sites. Right-sizing equipment balances productivity and costs.
5. Stage Materials Properly
Design organized stockpiling areas close to work zones without obstructing access or traffic. This lets materials be reused efficiently with minimal handling.
6. Install Drainage Controls

Slope and berm stockpiles to divert runoff away from waterways and storm drains. Installing silt fences prevents sediment pollution during rains.
7. Limit Stockpile Heights
Excessively tall material piles can collapse or overload underlying soil. Adhere to geotechnical recommendations for safe maximum heights to prevent failures.
8. Cover Stockpiles and Trucks
Use tarps or hydroseeding to protect material from wind and rain erosion during transport and storage. This reduces waste and containment costs.
9. Recycle Onsite Whenever Possible
Reusing native soils, crushed materials, woody debris, and excess concrete onsite eliminates hauling fees and purchase of backfill. Just ensure specifications align.
10. Monitor Load Out Trucks
Inspect haul trucks for proper loading, tarping, and spill controls before leaving the site. This guards against materials escaping and violations occurring off-site.
11. Verify Disposal Destination

Confirm disposal or processing facilities are legally permitted to accept the material types and volumes being hauled. Mistakes lead to citations and project shutdowns.
12. Keep Detailed Records
Log each truckload’s contents, origin, time dispatched, destination, and other details. Comprehensive records protect against claims of improper disposal.
13. Rinse Truck Wheels
Use designated wash areas to rinse mud and debris off truck wheels before exiting the site. This prevents materials being tracked onto roads.
14. Repair Haul Routes
Inspect and maintain site roads during and after completion of hauling activities. Promptly fix any damage, potholes, ruts or dust issues.
15. Stabilize Vacated Areas
When material stockpiles are removed, stabilize the underlying ground to prevent erosion. Quickly revegetate or cover exposed soils.
By putting these soil and waste management practices to work, excavation pros demonstrate responsibility while avoiding costly fines. Protecting the surrounding environment and community is an essential part of a successful project.
In summary, smart planning and oversight of material handling keeps excavation jobs running smoothly while minimizing liability. Experienced contractors treat soil and waste management as an integrated component of site operations rather than an afterthought. Using these insider techniques enables executing projects in a prompt, compliant, and cost-effective manner.
Preventing Underground Utility Damage
Nothing wreaks havoc on an excavation project like striking and rupturing buried utilities. Beyond repair costs, mistakes lead to injuries, work stoppages, and furious clients. But they don’t have to.
Follow these insider tips to dodge underground hazards:
1. Research All Available Maps
Consult utility maps, as-builts, site plans, and public GIS records to understand what’s lurking below. Compile a comprehensive picture from all sources.
2. Perform Detailed Site Walks
Inspect the site thoroughly before excavating. Look for visual clues like meters, manhole covers, and changes in vegetation signaling underground lines.
3. Locate Early and Be Present During
Call 811 to have utilities marked several days prior to excavating. Also have a crew member on-site during locating to answer questions.
4. Double Check Locate Accuracy
Spot check marks against maps and indicators on the ground. Ensure types, depths, and alignments jibe. Flag any uncertainties for further verification.
5. Contact Non-Member Utilities

Some private utility owners don’t participate in 811, so reach out to them directly. Leave no lines unaccounted for prior to digging.
6. Assume Marks are Approximate
Treat locates as the general area, not precise location, of utilities. Hand dig within the tolerance zone to determine actual positions.
7. Excavate Around Mark-Outs Initially
Open up work areas by carefully digging outside the marked utility corridors first. This defines known “safe” zones for equipment before exposing lines.
8. Respect Clearance Distances
Maintain required separation between excavation activities and marked utilities per local regulations. Give them a wide berth.
9> Use Hand Tools Around Marks
Shift to hand shovels, trowels, or vacuum excavators within the final few feet of marked utilities. Gentle exposure prevents nicks or scrapes.
10. Support Exposed Utilities
Brace, shore up, or suspend exposed lines to protect them from settling, sagging, or accidental impact from equipment or materials.
11. Document Existing Conditions

Photograph and video exposed utilities from all angles to capture pre-excavation state. This protects against false damage claims.
12. Keep Utilities Visible
Avoid inadvertent burial by covering or backfilling. Safety depends on maintaining visibility. Use markers if necessary.
13. Assign a Spotter
Dedicate an individual to guide equipment operators and warn them away from underground hazards within their blind spots.
14. Stay Alert for Unmarked Lines
Watch for unknown utilities that become apparent during excavation. Even seasoned pros encounter surprises from time to time.
15. Communicate Changes
Alert supervisors and utility owners immediately if lines are damaged or new ones are discovered. Situation awareness protects all parties.
Technology assists with identifying underground infrastructure, but attentive operators are the last line of defense for averting utility hits. By putting these safeguards into daily practice, excavators maintain productivity while protecting public safety and pocketbooks.
In summary, damages and work disruptions from striking buried utilities are entirely preventable with proper planning and care. Diligently pursuing available information, excavating cautiously, and communicating changes are the insider techniques that separate pros from amateurs on complex underground jobs.
Ensuring Worksite and Worker Safety
Excavation jobs present a range of hazards that require diligent safety management. Cave-ins, falls, struck-bys, and other threats endanger workers daily. Applying insider knowledge helps contractors maintain secure worksites.
Use these professional safety tips on every project:
1. Inspect and Shore Excavations
Assess soil stability and install protective systems per OSHA requirements to prevent collapse. This safeguards employees inside trenches and holes.
2. Control Water Accumulation
Continuously pump out accumulating stormwater, groundwater or process water. No excavation stays secure for long if it turns swampy.
3. Store Spoils Properly
Pile excavated dirt and materials at least 2 feet back from the edge of trenches and slopes. Proper spoil storage prevents falling debris hazards.
4. Provide Adequate Access
Use ladders, ramps or stairs to permit safe entry and exit of excavations deeper than 4 feet. This allows escape in emergencies.
5. Monitor Air Quality
Test for adequate oxygen, hazardous fumes and dust. Ventilate confined spaces as needed to ensure adequate respiration.
6. Isolate Energized Lines
Disable overhead power in the work zone. Bury or shield any unavoidable underground energy sources. Prevent contact and arcs.
7. Establish Traffic Controls
Use signs, barriers, flaggers and detours to reroute vehicles away from the excavation. Protect workers from traffic threats.
8. Eliminate Drop-Offs
Backfill or cover any dredging or trenches left overnight. Open holes pose a deadly fall risk in the dark to trespassers.
9. Wear High Visibility Vests
Class 2 or 3 reflective vests make workers stand out. This prevents struck-bys when operating around heavy machinery.
10. Use Spotters
Dedicate spotters to guide equipment and warn workers of reverse movements. Workers within swing radii are vulnerable.
11. Conduct Toolbox Talks
Hold daily safety briefings detailing hazards and protective actions. This reinforces vigilance and safe behavior.
12. Train Competently
Verify all operators and laborers are formally trained on excavation hazards and OSHA requirements. Knowledge drives safety.
13. Inspect Rigging Gear
Check slings, shackles, hooks and hoists regularly for wear or damage. Don’t risk failure of lifting components.
14. Secure Utilities
Support or disable overhead and underground utilities within work zones. Prevent inadvertent contact or breakage.
15. Maintain Order
Keep sites clean and clutter-free. Tools, materials, and spoils in the wrong place become trip and fall hazards.
Staying attentive to safety helps contractors complete quality work without loss. By institutionalizing these practices, excavation companies cultivate stellar safety cultures.
In summary, managing excavation safety demands broad awareness and responsibility beyond just following rules. It requires supervisors and workers actively hunting risks, applying proven tactics, and working together to prevent harm. This insider outlook is the key to everyone going home uninjured at day’s end.
Backfilling and Compacting Correctly
Backfilling and compacting determines the long-term stability and safety of excavated areas. The pros know proper techniques make the difference between success and settling trenches, buckling walls, and cracked pavement. Follow these insider tips to backfill like an expert:
1. Inspect Before Backfilling
Look for druminess, mud lenses and voids left by the excavation process. Address any subgrade issues before applying backfill materials to avoid problems later.
2. Select Suitable Fill Materials
Use site-specific backfill of controlled gradation that won’t settle excessively or retain water. Consult geotech testing and specifications.
3. Follow Compaction Sequence
Backfill in thin 8- to 10-inch lifts. Compact each sequentially from side to side before adding more. This prevents bridging and compaction voids.
4. Use Proper Compaction Equipment
Match plate compactors, rammers or rollers to soil type for optimal densification. Lighter equipment is appropriate for granular soils only.
5. Test Fill Moisture Content
Sample backfill moisture regularly. Add water into genuinely dry soils. Let overly wet soils dry before compacting to achieve proper moisture level.
6. Don’t Over-Compact
Excessive compaction causes particle breakdown and settlement issues over time. Stick to the specified degree of compaction – no more.
7. Perform Quality Control Testing
Conduct in-place density and compaction testing at sufficient intervals as backfilling progresses. Verify uniform compaction meets specifications.
8. Protect Adjacent Foundations
Install drain board and guard against over-compaction next to existing footings or walls. Prevent damaging adjacent structures.
9. Backfill Around Utilities Cautiously
Use hand compaction to avoid damaging underground utilities and conduits. Leave protective slack and don’t compact directly over.
10. Seal Around Penetrations
Caulk or grout around penetrations such as manholes before backfilling. This key step prevents differential settlement.
11. Break Up Spoil Chunks
Pulverize oversized excavated chunks before backfilling. Large particles and clods leave voids failing to compact fully.
12. Minimize Lift Thickness
Thinner compacted lifts result in denser, stronger fills less prone to settling. Maximum 10-inch lifts is ideal for granular soils.
13. Use Low Permeability Backfill on Slopes
Cohesive fills with limited drainage on slopes prevent infiltration and sloughing. Granular fills erode more easily.
14. Seal the Surface
Apply asphalt, concrete, or impermeable clay cap to surface of backfilled area. This fortifies fills and prevents erosion.
15. Let Backfills Settle
Allow sufficient time for settlement before rebuilding structures or pavement over the backfill zone. Rushing leads to failures.
Backfilling isn’t glamorous work, but it’s vital for site function and safety. By sticking to best practices, pros deliver strong, long-lasting trench and excavation infill that stands the test of time.
In summary, proper backfilling and compaction involves as much finesse as the initial dig. Careful lift placement, equipment selection, moisture control, and testing ensures the stability of the finished product. There are no shortcuts – just insider techniques that separate sloppy work from trench longevity.
Final Grading and Surface Restoration
Excavation pros know the importance of proper grading and restoration to bring sites full-circle. Without diligent surface reconditioning, trenching scars remain visible and erosion takes its toll. Use these insider tips for seamless surfaces post-dig:
1. Plan Restoration Details Upfront
Identify restoration requirements, materials, sequencing, etc. in your project plans. Discuss specifics with owners and permitting agencies early.
2. Protect Existing Vegetation
Fence off trees, shrubs, and sod outside work areas for preservation. This minimizes vegetation damage and replacement requirements.
3. Strip and Stockpile Topsoil
Scrape away topsoil before excavating and store it separately from other spoils. Topsoil will be needed later for seeding and landscaping.
4. Create Smooth Final Grading
Make final backfill lifts thin and hand grade to achieve gentle, uniform finished elevations. Eliminate dips, bumps and ponding areas.
5. Cut Clean Perimeter Edges

Trim excavation edges perpendicular to surroundings before restoration. Feathered or uneven edges appear sloppy.
6. Decompact Subgrades
Rip or plow subsoils to depth needed for vegetation. This loosens overly dense trench backfill for proper drainage and root growth.
7. Replace Damaged Improvements
Repair or replace damaged pavement, curb, sidewalk, fencing, etc. Match new sections to existing for consistent appearance.
8. Reinstall Salvaged Hardscape
Carefully relay bricks, pavers, tiles and other undamaged hardscape removed during excavation. This retains original site character.
9. Apply Topsoil Evenly
Spread stockpiled topsoil uniformly across restored areas 6 to 8 inches deep. Topsoil fuels healthy revegetation.
10. Choose Durable Vegetation
Select hardy grasses, plants and shrubs adapted to the site’s sun, drainage and soil. Robust varieties resist decline over time.
11. Vegetate Before Rains Arrive

Reseed and mulch as soon as finishing grading allows. Established vegetation prevents erosion during the first rains.
12. Water New Vegetation
Nurture grass and plants with consistent watering their first few weeks until fully rooted. Temporary irrigation prevents washouts.
13. Inspect After Rainfall
Check restored surfaces following storms or irrigation for washouts, soil slips and areas needing reseeding. Make repairs immediately.
14. Remedy Settlement
If trenches settle post-construction, fill depressions and regrade while under warranty. Don’t leave ruts for the owner.
15. Clean Up Completely
Remove all construction debris, unused materials and trash from the site. Pick up every stray bit. Clean sites impress owners.
Carefully restoring disturbed ground to its original undisturbed condition takes skill and persistence. By following these best practices, excavators guarantee surface quality that makes clients and permitting agencies happy.
In summary, lasting surface restoration relies on recreating pre-construction appearances. Meticulous grading, improvements replacement, and protective landscaping hide scars and prevent erosion. This degree of care exemplifies professional workmanship.

