Why should you upgrade to a 5 GHz WiFi router. How does the 5 GHz band offer faster speeds than 2.4 GHz. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a 5 GHz router. How can you set up and configure a new 5 GHz router for optimal performance.
Understanding 5 GHz WiFi Routers: The Gateway to Faster Internet
In the ever-evolving world of wireless technology, 5 GHz WiFi routers have emerged as a game-changer for home and office networks. These advanced devices operate on the 5 GHz frequency band, offering significant advantages over their 2.4 GHz counterparts. But what exactly makes 5 GHz routers so special?
5 GHz routers provide faster data transfer speeds, reduced interference, and improved overall performance for bandwidth-intensive activities. This makes them ideal for households with multiple connected devices, gamers, and streaming enthusiasts. As we delve deeper into the world of 5 GHz routers, we’ll explore their benefits, features, and how to choose the best one for your needs.

The Speed Advantage: How 5 GHz Outpaces 2.4 GHz
One of the primary reasons to invest in a 5 GHz router is the significant speed boost it offers. But how does it achieve these faster speeds?
- Greater bandwidth: The 5 GHz band provides more available bandwidth, allowing for higher data transfer rates.
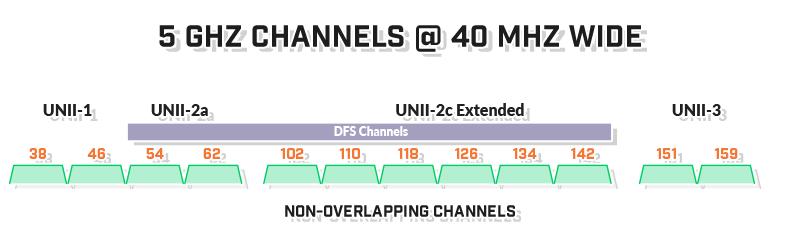
- More channels: With 24 non-overlapping channels compared to just 3 in the 2.4 GHz band, 5 GHz routers can better distribute network traffic.
- Less congestion: Fewer devices currently use the 5 GHz spectrum, resulting in less interference and more reliable connections.
While 2.4 GHz routers typically max out around 300 Mbps, 5 GHz routers can support speeds up to 1 Gbps with modern WiFi standards. This dramatic increase in speed can make a noticeable difference in your online experience, especially when streaming 4K content, gaming online, or conducting video calls.
Is the speed difference noticeable in real-world scenarios?
In most cases, yes. Users often report smoother streaming, faster file transfers, and reduced lag in online gaming when using a 5 GHz connection. However, the actual speed improvement depends on various factors, including your internet service plan, the number of connected devices, and physical obstacles in your home or office.
![]()
Combating Interference: The 5 GHz Advantage in Crowded Areas
In densely populated areas or apartment buildings, WiFi interference can be a significant issue. 5 GHz routers offer a solution to this problem in several ways:
- Less crowded spectrum: Fewer devices currently use the 5 GHz band, reducing the chance of interference from neighboring networks.
- Shorter range: The shorter wavelengths of 5 GHz signals don’t travel as far, which helps minimize interference between nearby networks.
- More channels: With more available channels, 5 GHz routers can find clearer frequencies for data transmission.
These factors combine to create a more stable and reliable connection, especially in areas with many competing WiFi networks. This can lead to fewer dropped connections, less buffering during streaming, and more consistent performance overall.
Are there any drawbacks to the shorter range of 5 GHz signals?
While the shorter range can be beneficial for reducing interference, it also means that 5 GHz signals have more difficulty penetrating walls and solid objects. As a result, 5 GHz routers may not provide as much coverage in larger homes or offices with many walls. In these cases, a dual-band router or a mesh WiFi system might be the best solution, offering both the speed of 5 GHz and the range of 2.4 GHz.

Embracing the Latest WiFi Standards: 802.11ac and Beyond
One of the key advantages of 5 GHz routers is their compatibility with newer WiFi standards. The 802.11ac standard, also known as WiFi 5, was designed to operate exclusively on the 5 GHz band. This standard offers several improvements over its predecessors:
- Faster theoretical speeds: Up to 3.5 Gbps in some configurations
- Improved MIMO technology: Better handling of multiple simultaneous connections
- Beamforming: More focused and efficient signal transmission
Even newer standards like WiFi 6 (802.11ax) build upon these improvements, offering even faster speeds and better performance in crowded environments. By investing in a 5 GHz router, you’re future-proofing your network and ensuring compatibility with the latest WiFi technologies.
Should you wait for WiFi 6E routers before upgrading?
WiFi 6E, which adds support for the 6 GHz band, is an exciting development in wireless technology. However, for most users, a current 5 GHz router with WiFi 5 or WiFi 6 support will provide excellent performance for years to come. Unless you have specific needs that require the absolute latest technology, there’s no need to wait for WiFi 6E to become widely available before upgrading your router.

Selecting the Perfect 5 GHz Router: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right 5 GHz router can be overwhelming with the multitude of options available. Here are some crucial factors to consider when making your decision:
- WiFi standards support: Look for routers that support 802.11ac (WiFi 5) or 802.11ax (WiFi 6) for the best performance.
- MU-MIMO and beamforming: These technologies improve performance when multiple devices are connected simultaneously.
- Processor speed and memory: A faster processor and more RAM can handle more connected devices and complex network tasks.
- Antenna design: External antennas often provide better range and can be adjusted for optimal coverage.
- QoS features: Quality of Service settings allow you to prioritize certain types of traffic or devices on your network.
- Number of Ethernet ports: Consider how many wired connections you need for devices like smart TVs or gaming consoles.
- Security features: Look for WPA3 support and other advanced security protocols to protect your network.
When evaluating these factors, consider your specific needs and usage patterns. A household with multiple 4K streaming devices and online gamers will have different requirements than a small apartment with just a few connected devices.

Are gaming-specific routers worth the extra cost?
For serious gamers, routers marketed specifically for gaming can offer valuable features like prioritized gaming traffic, lower latency, and specialized software for monitoring and optimizing network performance. However, these routers often come with a premium price tag. For casual gamers or those on a budget, a high-quality general-purpose 5 GHz router can still provide excellent gaming performance.
Single Band vs. Dual Band: Choosing the Right Configuration
When shopping for a 5 GHz router, you’ll encounter both single-band and dual-band options. Understanding the differences can help you make the right choice:
- Single-band 5 GHz routers: These operate exclusively on the 5 GHz band, offering maximum performance but potentially limited compatibility with older devices.
- Dual-band routers: These provide both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, offering flexibility and backward compatibility.
Dual-band routers are generally the more versatile choice, allowing you to connect older devices that only support 2.4 GHz while still taking advantage of 5 GHz speeds for newer devices. Some dual-band routers even allow you to create separate networks for each band, giving you more control over your home network.

Can you use a single-band 5 GHz router if you have older devices?
While it’s possible to use a single-band 5 GHz router with older devices, you may need to purchase a separate WiFi extender or adapter to connect devices that only support 2.4 GHz. For most users, a dual-band router provides the best balance of performance and compatibility without the need for additional hardware.
Setting Up Your New 5 GHz Router: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen your new 5 GHz router, proper setup is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Follow these steps to get your new router up and running:
- Position the router: Place it in a central location, preferably elevated and away from obstructions.
- Connect to your modem: Use an Ethernet cable to link your router to your modem.
- Power on: Turn on both the modem and router, waiting for them to fully boot up.
- Access the admin interface: Connect to the router (usually via a web browser) using the default IP address and login credentials.
- Update firmware: Check for and install any available firmware updates.
- Configure settings: Set up your network name (SSID) and password. For dual-band routers, consider using different SSIDs for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks.
- Enable security: Set your WiFi encryption to WPA2 or WPA3 if available.
- Optimize 5 GHz settings: Enable features like beamforming and MU-MIMO if your router supports them.
- Test your network: Connect various devices and test your speeds to ensure everything is working correctly.
Remember to consult your router’s manual for specific instructions, as the setup process can vary between brands and models.

How often should you update your router’s firmware?
It’s a good practice to check for firmware updates every few months. Many modern routers can automatically download and install updates, which is the most convenient option. Regular updates can improve performance, add new features, and patch security vulnerabilities, helping to keep your network safe and running smoothly.
Maximizing Your 5 GHz Network’s Performance: Pro Tips and Tricks
To get the most out of your new 5 GHz router, consider implementing these advanced techniques:
- Use WiFi analyzer tools to identify the least congested channels in your area.
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize important traffic like video calls or gaming.
- Experiment with antenna positioning to optimize coverage in specific areas of your home or office.
- Consider setting up a guest network to keep your main network secure.
- Use a mesh WiFi system for larger homes to ensure consistent 5 GHz coverage throughout.
- Regularly update your devices’ WiFi drivers to ensure compatibility with the latest router features.
By fine-tuning your router’s settings and optimizing your network setup, you can squeeze every bit of performance out of your 5 GHz connection.

Is it worth investing in a WiFi range extender for 5 GHz networks?
While WiFi range extenders can be useful for expanding coverage, they often come with a performance penalty. For 5 GHz networks, a better solution is usually a mesh WiFi system, which can provide seamless coverage without significant speed loss. If you’re experiencing dead spots in your 5 GHz coverage, consider upgrading to a mesh system rather than adding a traditional range extender.
As we look to the future of wireless networking, the 5 GHz band continues to play a crucial role. With the advent of WiFi 6E and the opening of the 6 GHz band, we can expect even faster speeds and less congestion in the coming years. However, 5 GHz routers remain an excellent choice for most users today, offering a significant upgrade over older 2.4 GHz technology.
By understanding the benefits of 5 GHz routers, carefully considering your options, and optimizing your setup, you can dramatically improve your home or office network performance. Whether you’re a casual user, a dedicated gamer, or a professional working from home, a high-quality 5 GHz router can provide the speed, reliability, and features you need to stay connected in our increasingly digital world.

What Is a 5 GHz WiFi Router and Why It Matters
A 5 GHz WiFi router is capable of broadcasting a wireless signal using the 5 GHz frequency band, which offers faster speeds and less interference compared to the commonly used 2.4 GHz band. With more devices connecting to home networks, upgrading to a 5 GHz router provides a better experience for bandwidth-heavy activities like 4K streaming, online gaming, and video calls.
How 5 GHz Band Offers Faster Speeds Than 2.4 GHz
The 5 GHz band provides more available bandwidth and channels than 2.4 GHz, allowing routers to deliver faster throughput speeds. While 2.4 GHz maxes out around 300 Mbps, 5 GHz can support up to 1 Gbps with modern WiFi standards. This makes it ideal for households with multiple devices accessing high bandwidth applications.
Ideal for Reducing WiFi Interference in Congested Areas
With fewer devices currently using the 5 GHz spectrum, there is less congestion and interference from neighboring networks. The shorter range of 5 GHz also helps minimize interference issues. This results in more reliable connectivity and less buffering or lag times.
Supports Newer WiFi Standards Like 802.11ac

Newer standards like 802.11ac are designed to exclusively use the 5 GHz band to provide faster speeds. A 5 GHz router allows you to benefit from these latest advancements in WiFi technology and performance.
Provides More Available Channels Than 2.4 GHz
The 5 GHz band has 24 non-overlapping channels versus just 3 in 2.4 GHz. More channels means networks can better distribute devices across different frequencies to reduce congestion and bottlenecks.
Works Best for Shorter Distances and Less Wall Penetration
The tradeoff with 5 GHz is reduced range compared to 2.4 GHz. The shorter wavelengths have more difficulty penetrating walls and solid objects. As a result, 5 GHz works better for smaller homes and apartments.
Top Benefits of Upgrading to a 5 GHz Capable Router
Upgrading to a dual band or 5 GHz-only router provides the following improvements:
- Faster top speeds and throughput performance
- Support for latest WiFi standards and technology
- Less interference and congestion when connecting multiple devices
- More reliable streaming, gaming and video calling
- Ability to create separate SSIDs for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks
Factors to Consider When Selecting a 5 GHz Router

Key factors to evaluate include:
- WiFi standards support – Look for 802.11ac or WiFi 6
- MU-MIMO and beamforming capabilities
- Processor speed and memory
- Antenna design and amplifier
- QoS traffic shaping features
- Number of Ethernet ports needed
- Security protocol support
Comparing Single vs Dual Band 5 GHz Routers
Dual band routers provide the flexibility of both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Single band 5 GHz routers maximize performance, but older 2.4 GHz only devices would need an extender. Consider your device mix and coverage needs when deciding.
Reviewing Top Brands for Reliable 5 GHz Performance
Top brands include Linksys, NETGEAR, ASUS, TP-Link, and Google Nest. Compare specs between models and read customer reviews on 5 GHz reliability when choosing.
Assessing Your Budget and Internet Speed Needs
5 GHz routers range from $50 basic models to $200+ high-end gaming routers. Determine how much speed and features you need for the best value. Aim for a router rated higher than your internet package’s top speeds.
Considering Extras Like Antenna Design, Ports and Software
Look for external antennas for better range and performance. Have enough Ethernet ports for wired connections. Manageability through apps can provide added controls and visibility into your network.
How to Set Up and Configure a New 5 GHz Router
Follow these steps when installing your new dual band router:
- Set up the router near the modem and connect it via Ethernet cable.
- Power on the router and log into the admin interface.
- Update the router firmware to latest available version.
- Set a unique network name and strong wireless password.
- Enable the 5 GHz band and set a different SSID.
- Configure WiFi encryption mode to WPA2 or WPA3.
Tips to Get the Best Coverage from Your 5 GHz Network
- Place the router in a central area elevated if possible.
- Minimize obstructions between devices and router.
- Use high-gain directional antennas to focus signal.
- Enable beamforming for targeted signal direction.
- Set 5 GHz channels to auto to avoid interference.
The Future of 5 GHz WiFi – What’s Coming Next

The rollout of WiFi 6E will unlock new 6 GHz channels, providing even faster speeds up to 9.6 Gbps. Wider adoption of 5 GHz will reduce congestion as more devices upgrade. Mesh systems can also better blanket homes with 5 GHz for full coverage. The future looks bright for the still developing 5 GHz band and routers taking advantage of its benefits.
What Is a 5 GHz WiFi Router and Why It Matters
A 5 GHz WiFi router can broadcast a signal using the less crowded 5 GHz frequency band. This opens up more bandwidth and faster speeds compared to the standard 2.4 GHz band that most routers use. With the growing number of connected devices in homes today, upgrading to a 5 GHz capable router provides a better experience for bandwidth-hungry activities like 4K streaming, online gaming, video calls and more.
How 5 GHz Band Offers Faster Speeds Than 2.4 GHz
The 5 GHz band has a clear speed advantage over the commonly used 2.4 GHz frequencies. But why exactly is 5 GHz WiFi able to deliver faster throughput and better performance? Here are some of the key technical reasons:
More Available Bandwidth

The 5 GHz frequencies have a lot more bandwidth available compared to the narrower 2.4 GHz channels. More bandwidth means more data can be transmitted at one time. Think of it like adding more lanes to a highway to allow more cars to flow through faster.
Supports Faster WiFi Standards
Newer WiFi standards like 802.11ac and WiFi 6 are designed to work exclusively on the 5 GHz band in order to achieve multi-Gigabit speeds. The technologies and capabilities of these standards can’t be taken full advantage of on the more limited 2.4 GHz frequencies.
Offers More Non-Overlapping Channels
While the 2.4 GHz band only has 3 non-overlapping channels, the 5 GHz band has up to 24 available channels depending on region. More channels means networks can better segment and isolate user traffic to reduce bottlenecks and interference.
Higher Throughput thanks to Wider Channels
In addition to more channels, 5 GHz channels are also wider than 2.4 GHz. For example, a standard 20 MHz channel on 2.4 GHz provides around 150 Mbps max while a 40 MHz channel on 5 GHz offers over 300 Mbps.
256 QAM Support
5 GHz networks can make use of 256 QAM modulation which encodes more data bits per waveform. 2.4 GHz maxes out at 64 QAM, limiting throughput. So a 5 GHz router can push more data through the pipe at once.
Beamforming for Targeted Signals
Some 5 GHz routers support beamforming, allowing the signal to be directed right at the client device. This increases range and bandwidth over the omnidirectional output from 2.4 GHz antennas.
Less Interference and Congestion
With 2.4 GHz being used by most routers, Bluetooth, microwaves, cordless phones, and more, interference can be an issue. The 5 GHz band has far less traffic, boosting speeds and reliability.
Ideal for Shorter Distances
While 5 GHz doesn’t go as far as 2.4 GHz, it’s ideal for smaller homes and apartments. The shorter range means faster falloff, so devices can get full bandwidth instead of congesting a crowded network.
Key Takeaways on 5 GHz vs 2.4 GHz Performance
In summary, by utilizing greater bandwidth, newer WiFi standards, beamforming, and less interference, 5 GHz wireless signals can offer substantially faster throughput speeds compared to the overused 2.4 GHz spectrum. For the best home networking experience, upgrade to a modern dual band or 5 GHz-exclusive router.
Next Steps for Faster WiFi Speeds

Ready to upgrade your WiFi and enjoy the boost 5 GHz can provide? Be sure to check out our top router picks and installation guide to help select the right model and get set up with faster speeds in no time.
What Is a 5 GHz WiFi Router and Why It Matters
A 5 GHz capable router can broadcast wireless signals using the less crowded 5 GHz band, enabling faster speeds and less interference compared to standard 2.4 GHz networks. With more smart home devices connecting, upgrading to 5 GHz WiFi provides a better experience.
Ideal for Reducing WiFi Interference in Congested Areas
One of the major benefits of 5 GHz routers is reduced interference from neighboring WiFi networks and devices. The 5 GHz band provides a less congested environment compared to overutilized 2.4 GHz frequencies. Let’s look at why 5 GHz WiFi performs better in high-interference areas.
Avoiding the Crowded 2.4 GHz Spectrum
The 2.4 GHz spectrum is cluttered with traffic from WiFi routers, Bluetooth devices, microwaves, cordless phones, wireless cameras, Zigbee smart home products, and more. With so many devices trying to share the airwaves, interference is inevitable.
Shorter Range Limits Interference

5 GHz signals don’t travel as far as 2.4 GHz thanks to shorter wavelengths that have difficulty penetrating walls and obstructions. This smaller coverage area minimizes interference from neighboring networks.
More Channel Options
The 2.4 GHz band only has 3 non-overlapping channels, forcing networks to share frequencies leading to crosstalk. 5 GHz has over 20 available channels, allowing better channel segmentation.
Automatic Channel Switching
Some 5 GHz routers automatically switch channels when interference is detected, always finding the clearest path. 2.4 GHz networks typically stick to preset channels.
Beamforming Focuses Signal
Beamforming technology available on some 5 GHz routers concentrates the signal directly at devices instead of broadcasting in all directions. This avoids interference while improving range and bandwidth.
OFDMA Support
WiFi 6 routers utilizing 5 GHz can take advantage of OFDMA to divide bandwidth into sub-carriers, effectively giving each device its own channel further reducing interference between clients.
How to Optimize 5 GHz to Reduce Congestion
Here are some additional tips to minimize interference on a 5 GHz network:
- Ensure router placement is central and elevated if possible.
- Adjust antenna angles to focus signal where needed.
- Enable MU-MIMO simultaneous streaming.
- Set 5 GHz band to 20/40 MHz wide channels.
- Use a WiFi analyzer to identify the clearest channels.
- Set 5 GHz channel to auto to avoid crowding.
The Bottom Line
While no WiFi band is completely immune to interference, the 5 GHz spectrum provides a much less congested environment, especially in apartment buildings and densely populated areas. Less interference means faster speeds, lower latency, and reliable connectivity for modern smart home demands. Make the move to 5 GHz WiFi and leave frustration behind!
Looking for the perfect 5 GHz router upgrade? Check out our top picks here and get the dual band or 5 GHz-only model that fits your needs and budget.
What Is a 5 GHz WiFi Router and Why It Matters

A 5 GHz WiFi router can broadcast wireless signals using the less crowded 5 GHz frequency band, enabling faster speeds and less interference compared to standard 2.4 GHz networks. With more devices connecting, upgrading to 5 GHz provides a better experience.
Supports Newer WiFi Standards Like 802.11ac
One key advantage of 5 GHz routers is the ability to take advantage of newer WiFi standards designed specifically for the 5 GHz frequencies. These standards offer major speed and performance improvements not possible on crowded 2.4 GHz networks.
802.11ac – Gigabit WiFi Speeds
802.11ac was the first standard to push WiFi into true gigabit territory by exclusively utilizing the 5 GHz band’s wider channels and better propagation. 802.11ac routers can deliver over 1 Gbps speeds at short ranges.
WiFi 6 – Next Generation Improvements
The latest WiFi 6 standard (802.11ax) also depends on 5 GHz to achieve multi-gigabit performance along with advanced features like OFDMA simultaneous transmission.
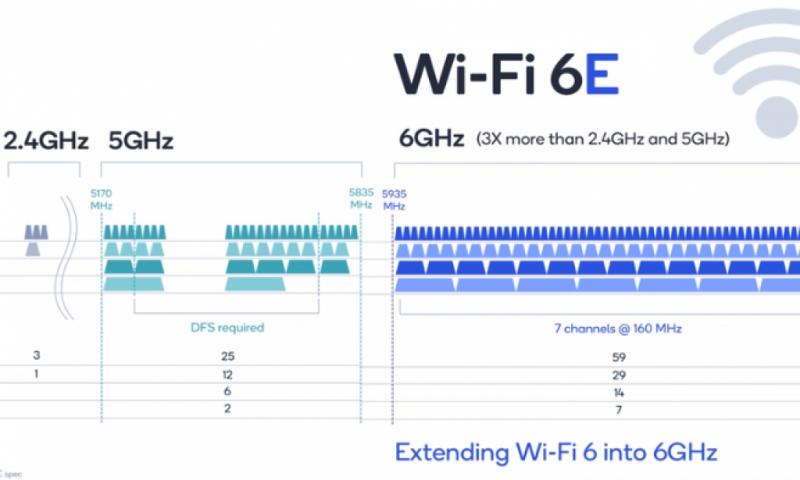
WiFi 6E – Unlocking 6 GHz Band

Emerging WiFi 6E routers will add the new 6 GHz band to 5 GHz for incredible speed and capacity. This is only possible by building on existing 5 GHz technology.
More Bandwidth and Channels
These standards capitalize on the 5 GHz band’s wider channel sizes (up to 160 MHz) and higher channel count compared to limited 2.4 GHz spectrum.
256 QAM Support
5 GHz networks can also use more complex 256 QAM modulation to encode more data per waveform compared to 64 QAM max on 2.4 GHz.
MU-MIMO Multi-User Streaming
Technologies like MU-MIMO allow simultaneous transmission to multiple clients at once, boosting throughput significantly.
Real-World Speed Improvements
In real-world usage, the speed difference enabled by 5 GHz WiFi standards is substantial:
- 802.11ac – Up to 1.3 Gbps vs 450 Mbps on 802.11n 2.4 GHz
- WiFi 6 – Up to 4.8 Gbps vs 600 Mbps on 802.11ac
And Multi-user MU-MIMO pushes speeds even higher by transmitting to multiple devices concurrently.
Why 5 GHz Unlocks Better Performance
By leaving behind the slower, overcrowded 2.4 GHz frequencies, the newer standards can maximize throughput using 5 GHz in several key ways:
- Less interference and congestion
- More available bandwidth per channel
- Higher order modulation for increased data density
- Advanced multi-user transmission technologies
The result is WiFi officially entering the gigabit era with 5 GHz as the key enabler.
Conclusion
To enjoy the performance of the latest ultra-fast WiFi standards, upgrading to a modern 5 GHz router is essential. Leave network congestion behind and experience the full potential of next generation WiFi technology.
What Is a 5 GHz WiFi Router and Why It Matters
A 5 GHz capable router can broadcast wireless signals using the less crowded 5 GHz frequency band, enabling faster speeds and less interference compared to standard 2.4 GHz networks. With more devices connecting, upgrading to 5 GHz WiFi provides a better experience.
Provides More Available Channels Than 2.4 GHz

One advantage of 5 GHz WiFi is the significantly higher number of available channels versus the very limited channel selection on 2.4 GHz networks. Having more channels to choose from allows 5 GHz routers to reduce congestion and interference.
Just 3 Non-Overlapping 2.4 GHz Channels
The 2.4 GHz band only has 11 total channels, but only 3 of them don’t overlap – channels 1, 6, and 11. This means all 2.4 GHz networks in an area are sharing one of these 3 crowded frequencies.
Over 20 Non-Overlapping 5 GHz Channels
In contrast, the 5 GHz band has over 20 non-overlapping channels available, providing much greater flexibility in channel planning and segmentation.
Prevents Adjacent Channel Interference
With only 3 channels, 2.4 GHz networks often end up interfering even if not on the exact same channel. The abundance of 5 GHz channels prevents this adjacent channel crosstalk.
Allows Channel Optimization
You can optimize 5 GHz channel selection around neighboring WiFi networks to minimize interference, not possible on 2.4 GHz.
How 5 GHz Utilizes the Additional Channels

Here are some of the ways 5 GHz routers take advantage of so many additional channels:
- Automatic channel switching to avoid congestion
- Creates separate 5 GHz network away from existing 2.4 GHz traffic
- Higher throughput thanks to larger 40/80/160 MHz channel widths
- Ability to dedicate channels for faster backhaul links on mesh networks
- Segment clients across channels to reduce bottlenecks
The Result: Faster Speeds, Less Interference
By moving to the less populated 5 GHz spectrum with 20+ channel options, modern WiFi routers can deliver both faster throughput thanks to wide channel bandwidths, while also minimizing interference through better channel planning and separation versus crowded 2.4 GHz networks.
To experience the full benefits, upgrade your router and devices to take advantage of the 5 GHz band’s expansive channel availability compared to the constraints of aging 2.4 GHz WiFi.
Ready for less WiFi frustration and faster speeds? Check out our top 5 GHz router picks here!
What Is a 5 GHz WiFi Router and Why It Matters
A 5 GHz capable router can broadcast wireless signals using the less crowded 5 GHz frequency band, enabling faster speeds and less interference compared to standard 2.4 GHz networks. With more devices connecting, upgrading to 5 GHz WiFi provides a better experience.
Works Best for Shorter Distances and Less Wall Penetration
One tradeoff with 5 GHz WiFi is that it doesn’t travel as far as 2.4 GHz, making it better suited for smaller homes and apartments. The shorter range does have benefits though in terms of higher throughput.
Shorter Wavelength Can’t Penetrate As Well
5 GHz wavelengths are shorter than 2.4 GHz, which makes them less able to pass through walls, floors, windows and other solid objects. This limits the effective range compared to 2.4 GHz.
Ideal for Smaller Homes and Apartments
Because of the reduced penetration ability, 5 GHz works best in smaller living spaces of around 500-1000 sq. ft. It can struggle to reach all corners of large homes unless repeaters are used.
Ensures Strong Signal Close to Router
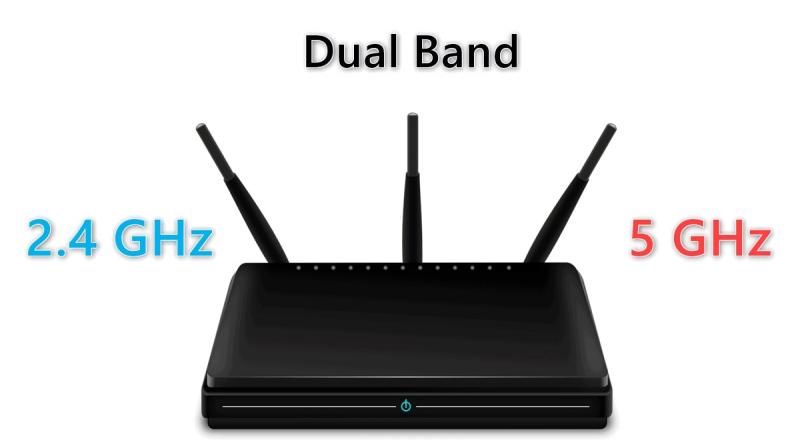

The upside of the shorter range is clients close to the 5 GHz router can get very fast speeds with minimal attenuation, avoiding congestion.
Helps Minimize Interference
Limiting coverage area also keeps the 5 GHz signal contained, preventing interference with neighboring networks.
Tips for Extending 5 GHz Range
There are some techniques that can help extend the usable range of 5 GHz coverage:
- Position router in a central elevated location
- Use detachable high-gain directional antennas
- Enable beamforming signal focusing
- Set channels to 20 MHz width
- Use mesh network nodes to repeat the signal
The Right Tool for the Job
While 2.4 GHz is better for covering larger homes due to penetration ability, 5 GHz is ideal for smaller spaces where faster speeds near the router are key. Play to the strengths of each band and enjoy the best WiFi experience.
Ready to upgrade to faster 5 GHz WiFi? Check out our top router recommendations here!
Upgrading to a 5 GHz capable router can provide a number of benefits for your home WiFi network. With more devices connecting wirelessly than ever before, having a router that can provide faster speeds and greater bandwidth is becoming increasingly important. Here are some of the top benefits of getting a router capable of using the 5 GHz band:
Faster Speeds

The 5 GHz band offers faster maximum wireless speeds compared to the more commonly used 2.4 GHz band. 5 GHz is less congested and can support wireless speeds over 1 Gbps with the latest WiFi technologies like WiFi 5 and WiFi 6. This means you can get faster transfers and downloads over WiFi. For example, you may be able to download a full HD movie in under a minute compared to several minutes on 2.4 GHz.
Less Interference
The 5 GHz band has more available channels that don’t overlap with each other as much as the limited number of 2.4 GHz channels. This means less interference from your neighbors’ WiFi networks. You’ll get stronger signals and more consistent performance even in densely populated areas. With 2.4 GHz, all the routers in an apartment building for example are likely competing for the same small set of channels which results in slower speeds.
Better Support for Multiple Devices
The extra bandwidth on the 5 GHz band allows it to handle more connected devices at the same time. If you have a lot of devices at home, like laptops, tablets, phones, media streamers, smart home gadgets, and gaming consoles, having them all share a 2.4 GHz network can result in congestion and slowdowns during peak usage times. With 5 GHz, there is enough bandwidth to go around for everyone.
Access to Newer Technologies
Some of the latest wireless innovations are only available on the 5 GHz bands. For example, the fastest speeds of over 1 Gbps come from technologies like 160 MHz channel bonding which requires 5 GHz. WiFi 6E which taps into new 6 GHz spectrum is also 5 GHz based. If you want to future proof your network, upgrading to a 5 GHz router will allow you to take advantage of new technologies as they emerge.
Better Performance for High-Bandwidth Uses
5 GHz WiFi performs better than 2.4 GHz when transferring large files, streaming high resolution media, online gaming, and other bandwidth intensive tasks. The fatter pipeline of 5 GHz means less lag and buffering when doing data intensive activities. For example, 4K/8K video streaming, VR gaming, or video conferencing will all benefit greatly from having a 5 GHz network.
Useful for Smart Homes
Modern smart home devices like security cameras, video doorbells, and appliances rely on WiFi to connect to your network and the internet. These devices often need to send and receive a lot of data, like with HD video monitoring. A 5 GHz router will be able to handle all the wireless traffic generated by your connected smart home efficiently.
Dual Band Capabilities

5 GHz routers usually support both 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz bands simultaneously in a single device (dual band). That means you can connect devices that only use 2.4 GHz like some smart home gadgets or older laptops, while still getting 5 GHz performance from newer devices. Dual band also allows you to set up different SSIDs and settings for each band.
Better Range than 2.4 GHz
Surprisingly, 5 GHz WiFi often has greater range than 2.4 GHz especially when using beamforming antennas. The shorter wavelength of 5 GHz frequencies allows for more targeted signal direction. Obstacles like walls and metal surfaces that easily block 2.4 GHz signals have less impact on 5 GHz. With the right router, you may be able to get 5 GHz coverage across your entire home and yard.
Support for Wider Channels
5 GHz allows for channel widths of up to 160 MHz compared to just 20 or 40 MHz on 2.4 GHz. Wider channels mean more data can be transferred at once. The latest WiFi 6 routers can combine two 80 MHz channels for blisteringly fast 160 MHz connections over 5 GHz. This kind of speed isn’t possible on the narrower 2.4 GHz channels.
Backwards Compatible

WiFi standards that use the 5 GHz band like 802.11ac and 802.11ax are fully backwards compatible with older devices. For example, your 802.11ac 5 GHz router will still work with 802.11n or 802.11g devices, but they will simply be limited to their maximum speeds and features. Upgrading your router to 5 GHz won’t strand older 2.4 GHz only devices.
More Resilient Security
The additional bandwidth of 5 GHz means it can support the latest WPA3 security protocol which adds enhanced encryption and other protections. WPA3 would slow down 2.4 GHz networks too much, but 5 GHz has the capacity to handle the extra processing required. More advanced security keeps your network and devices safe.
As you can see, upgrading to a router capable of 5 GHz WiFi unlocks a ton of benefits from faster speeds to expanded capacity and next-gen features. With work, school, entertainment and smart homes now relying on WiFi, having a robust and modern wireless network is more important than ever. The 5 GHz band is less crowded and delivers major advantages over the aging 2.4 GHz spectrum. For the best home WiFi experience, choosing a router with great 5 GHz support should be at the top of your list.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a 5 GHz Router
In 2023, upgrading to a 5 GHz router can provide a major boost in WiFi performance and reliability. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds, lower interference, and more bandwidth compared to crowded 2.4 GHz networks. With more devices than ever relying on home WiFi, getting the most out of your wireless network is crucial. However, not all 5 GHz routers are created equal. Several key factors should be evaluated when choosing a router capable of leveraging 5 GHz WiFi.
WiFi Standards and Channels
Newer WiFi standards like 802.11ac and 802.11ax operate solely on 5 GHz and are optimized for speed, capacity, and coverage. An 802.11ac or WiFi 5 router supports channels up to 160 MHz wide, while WiFi 6 / 802.11ax devices can use 160 MHz or even 80+80 MHz channels for blazing throughput over 1 Gbps. However, client devices need compatible WiFi radios to realize the benefits. An 802.11ax router will still work well with older 802.11ac, n, g, b, and a devices too, just at reduced performance.
Within the 5 GHz band, DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) channels are also important. DFS automatically switches channels to avoid interference from radar systems, resulting in more reliable connections. However, DFS support is required for access to many 5 GHz channels. So opting for a router with comprehensive DFS support ensures you can leverage more of the 5 GHz spectrum.
Antennas and Beamforming

Antenna design directly impacts WiFi range and coverage. Many 5 GHz routers now utilize multiple high-gain antennas and advanced beamforming technologies like MU-MIMO to focus signals towards connected client devices. This enhances range while reducing dead spots. Positioning external antennas properly to reduce obstruction can further optimize coverage. Just adding more antennas doesn’t necessarily equal better performance, so focus on routers with proven antenna implementations.
Processor and Memory
A faster processor and more memory enable a router to handle higher throughputs and multiple connections without lag or buffering. High-end 5 GHz routers designed for gaming and 4K streaming are equipped with quad or octa-core processors and 256MB to 1GB of RAM. Even if you don’t need bleeding edge performance, don’t skimp here – underpowered routers can struggle with bandwidth-heavy tasks.
Port Capabilities
Having an appropriate number of capable ports is essential for connecting devices via ethernet. Look for routers offering at least four gigabit LAN ports, allowing wired speeds up to 1000 Mbps to multiple devices simultaneously. Newer 2.5G and even 5G/10G LAN ports are also emerging for ultra high-speed NAS and infrastructure connections. Just one WAN port is typical, but dual WAN offers failover or load balancing across multiple internet links.
Network Security

Protecting your home network should be a priority. Modern 5 GHz routers include comprehensive wireless encryption via WPA3, WPA2, WPS support, and other security standards. Multi-user (MU) QoS helps prevent network congestion and prioritizes traffic. Firewall, VPN passthrough, DNS filtering, and other advanced features help keep unwanted traffic out. Make sure any router under consideration has the latest wireless and network security available.
WiFi Mesh and Roaming
WiFi mesh systems are surging in popularity, using multiple access points to blanket homes in strong 5 GHz signals. Mesh routers amplify coverage via dedicated wireless backhaul between nodes, providing seamless roaming. Tri-band routers dedicate one 5 GHz radio for backhaul, while the other two radios handle client traffic. Mesh networks are easy to install and flexible, scaling to multi-story dwellings. Just be prepared to pay more compared to standalone routers.
Built for Speed
If ultra-fast speeds are your goal, look for routers specifically designed for high performance. For example, gaming routers tout extremely low latency while also handling massive throughput without lag spikes or jitter. Other routers boast multi-gig WAN/LAN ports to fully harness fiber optic and 5G internet. High speed doesn’t come cheap, so have realistic expectations for the internet speeds you’ll actually receive.
Advanced Features
Today’s leading edge routers come packed with an array of advanced capabilities via customized firmware and apps. This includes full VPN servers for securing remote connections, robust parental controls, anti-malware scanning, device prioritization, media servers, and more. While enticing, these extras may go unused by many households with basic needs. Focus on core networking capabilities first before paying extra for cutting edge features.
Ease of Use
A router loaded with every feature imaginable does you no good if the interface is convoluted and confusing. Ease of usespans from quick setup to intuitive QoS and firewall menus. Phillips head screws on the enclosure’s exterior speed hardware access during installation. Some vendors even offer helpful mobile apps. Don’t settle for less than a straightforward user experience.
Price
As with most technology, routers are available at a wide range of price points. High-end gaming and mesh routers can cost $400 to $600, while budget options run under $50. In general, you get what you pay for – rock bottom pricing typically means compromised performance or missing features. Aim for a middle ground around $150 to $250 for a high quality dual or tri-band AC/AX router with robust connectivity to unlock 5 GHz advantages.
By evaluating factors like WiFi standards support, hardware specs, security protections, ease of use and price, you can zero in on an optimal 5 GHz router tailored to your wireless needs, budget, and home setup. Taking the time to make an informed decision will ensure your next router investment serves your household well into the future. The Additional performance and capabilities of 5 GHz WiFi make the upgrade worthwhile!
Comparing Single vs Dual Band 5 GHz Routers

With more devices and bandwidth-heavy applications relying on home WiFi, upgrading to a 5 GHz router can significantly improve performance. But should you choose a single band or dual band 5 GHz model? While both provide benefits over crowded 2.4 GHz networks, dual band routers offer greater flexibility and capacity.
Single Band 5 GHz
As the name implies, single band 5 GHz routers only operate on the 5 GHz frequency range, typically channels 36-165. Without a 2.4 GHz radio, all connected devices communicate exclusively over 5 GHz. This avoids interference and congestion from legacy 2.4 GHz networks and devices like cordless phones, microwaves, or Bluetooth accessories. Single band routers also dedicate full WiFi resources to 5 GHz clients for maximum throughput.
However, single band means no 2.4 GHz support. Many smart home devices, media streamers, cameras, and older phones still rely on 2.4 GHz only. A single band 5 GHz router won’t work at all for these clients unless you add a separate 2.4 GHz access point. Single band models also have reduced range compared to dual band, as 5 GHz frequencies don’t penetrate walls and obstacles as well. Placement and positioning becomes more crucial.
Dual Band 5 GHz

Dual band wireless routers contain two radios – one for 2.4 GHz and one dedicated to 5 GHz. This provides the flexibility to connect a wide variety of devices across both bands while reducing interference between the frequencies. Dual band routers also allow you to separate IoT devices from bandwidth-hungry 5 GHz clients, balancing load across the networks. Having both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz available allows seamless roaming as well.
The trade-off is that a dual band router splits WiFi resources between the bands, so the maximum link rate for 5 GHz clients will be reduced. However, most dual band models offer at least AC1200 class speeds – plenty for most homes. Several high-end gaming and mesh platforms also pack dedicated radios for each band to achieve the best of both worlds.
Which is Better for My Needs?
Here are a few key factors to consider when deciding between single and dual band 5 GHz:
- Client device compatibility – Dual band if you have 2.4 GHz only devices, single if all clients have 5 GHz
- Range and coverage – Dual band has better penetration through walls and obstacles
- Bandwidth needs – Single for max 5 GHz throughput, dual if you need both bands
- Roaming – Dual allows automatic band steering and transition between bands
For most homes today, dual band AC1200+ routers provide the best blend of speed, coverage, and compatibility. However, here are a few instances where single band 5 GHz routers make sense:
- You only need 5 GHz and all clients support it
- Maximizing 5 GHz bandwidth is critical (i.e. high speed online gaming)
- Adding dedicated WiFi just for smart home devices on 2.4 GHz
- Smaller apartments or dwellings with minimal obstructions
Single band routers can still work well in these targeted cases. Just be aware of the limitations compared to more flexible dual band models before purchasing.
Key Considerations for 5 GHz
Whichever you choose, look for the latest WiFi 6 (802.11ax) standard for optimal performance on 5 GHz. Other features like DFS support, beamforming, mu-MIMO, Processor power and RAM will also enhance real-world speeds and capacity regardless of bands. Don’t neglect security either – WPA3 encryption, firewall protection, and other safeguards are a must today. Finally, prioritize easy setup, management and robust QoS when evaluating router options. This ensures you’ll get the most from your 5 GHz network.
Upgrading to a new AC or AX router with 5 GHz support is one of the best ways to boost home WiFi capabilities. Choosing between single vs dual band depends on your clients, layout, and performance goals. Evaluating key differences like compatibility, speed, and roaming will lead you to the ideal 5 GHz router for your unique needs.
With internet usage booming in recent years, having a fast and reliable WiFi connection at home has become more important than ever. For the best speeds, many tech experts recommend using a wireless router capable of tapping into the 5 GHz frequency band. But with so many router brands and models available, how do you know which ones reliably deliver those blazing 5 GHz speeds?
In this article, we’ll review the top router brands to consider for getting the most out of the 5 GHz WiFi spectrum. We’ll look at key factors like speed, range, number of antennas, processor power, and extra features. Brands like Netgear, TP-Link, Asus, Linksys, and Synology consistently earn high marks across these criteria.
Why Choose a 5 GHz Router?

First, let’s quickly cover what makes 5 GHz routers so appealing. The 5 GHz band offers faster maximum speeds and less network congestion than the more common 2.4 GHz band. With 5 GHz, you can enjoy reduced lag and buffering when streaming HD video, faster file downloads and uploads, and smoother online gaming.
The one downside is that 5 GHz signals don’t travel as far as 2.4 GHz ones. But for most homes, the speed trade-off is worth it. Many modern routers let you use both bands simultaneously to get the best of both worlds.
Key Factors in a Reliable 5 GHz Router
When comparing top brands for 5 GHz performance, keep these factors in mind:
- Speed range – Look for maximum speeds of at least 1,300 Mbps on 5 GHz. Top-tier routers boast speeds upwards of 2,000 or even 4,000 Mbps.
- Range – More antennas (4-6) extend the 5 GHz signal further from the router.
- Processor – A 1.5 GHz quad-core processor or faster helps the router handle high speeds.
- Features – QoS, MU-MIMO, beamforming, and USB ports are useful extras.
- Price – Expect to pay $100-250+ for a high-end 5 GHz router.
Reviews of the Best 5 GHz Router Brands

Netgear
With their Nighthawk line, Netgear consistently delivers some of the fastest and most reliable 5 GHz routers on the market. The RAX120 Nighthawk AX6000, for example, hits speeds up to 4.8 Gbps on the 5 GHz band. It sports eight high-powered antennas and a powerful 1.8 GHz quad-core processor to handle the maximum throughput.
Useful features include USB 3.0 ports for connecting external drives, QoS for prioritizing devices and apps, and Netgear Armor for protecting against cyber threats. Netgear routers work with all major cable modems and ISPs. The only downside is the higher price, but you get what you pay for.
TP-Link
For budget-minded shoppers, TP-Link offers reliable 5 GHz routers at more affordable prices. The Archer AX73 hits AX5400 WiFi speeds up to 5.4 Gbps on the 5 GHz band. The four large antennas use Beamforming technology to extend range and stability.
While not as advanced as Netgear’s offerings, the AX73 still includes useful extras like USB 3.0 ports, QoS, and TP-Link HomeCare for parental controls and antivirus. Reliable 5 GHz speeds don’t have to break the bank.
Asus
Gaming routers like Asus’s RT-AX88U are optimized for low lag on the 5 GHz channels. This router uses Broadcom’s WiFi 6 chipset to reach speeds up to 6 Gbps on the 5 GHz band. The eight antennas fold out to improve range and stability.
For gaming, the RT-AX88U includes Adaptive QoS to prioritize game traffic, a gaming port for lower latency connections, and WTFast game acceleration software. The Armoury Crate app lets you monitor traffic and tweak settings. Reliable wired and wireless speeds make this a go-to choice for serious gamers.
Linksys
Linksys has upgraded many of its most popular routers to support faster 5 GHz WiFi. The Linksys Atlas Max 6 Dual-Band Mesh router hits AX6000 speeds up to 4.8 Gbps on the 5 GHz band. Four external antennas come equipped with beamforming technology to focus the signal.
This Linksys router includes useful features tailored for smart homes. There’s built-in support for Linksys’s Velop mesh WiFi system for extending range, along with Linksys Intelligent Mesh Technology. Compatibility with Amazon Alexa allows for WiFi-enabled voice commands.
Synology

Finally, Synology’s RT6600ax router proves you don’t need flashy gaming features to get reliable 5 GHz speeds. The sleek, understated RT6600ax uses a triple core 1.8 GHz processor to deliver AX6000 speeds up to 4.8 Gbps on the faster 5 GHz channels.
Four internal antennas provide WiFi coverage up to 5,500 square feet. Synology’s SRM operating system allows for one-touch network security scans, traffic monitoring, QoS controls, and VPN server setup. If you want top 5 GHz performance without the gaming frills, this Synology router delivers.
The Takeaway on 5 GHz Routers
Hopefully this overview provides a good starting point for choosing a router than can take full advantage of 5 GHz WiFi. The top brands like Netgear, TP-Link, Asus, Linksys, and Synology combine fast 5 GHz speeds with useful features and reliable connections.
Look for modern standards like WiFi 6, plenty of high-gain antennas to extend range, powerful processors, QoS for traffic shaping, and extras like USB ports. Investing in a quality 5 GHz router pays off with faster speeds, less congestion, and more stable coverage throughout your home.
Assessing Your Budget and Internet Speed Needs When Looking for the Best 5 GHz Routers in 2023
Assessing Your Budget and Internet Speed Needs

With the proliferation of devices and applications that require robust internet connectivity, having a high-speed wireless router capable of utilizing the 5 GHz band has become almost essential for many households. However, before purchasing a new 5 GHz router, it’s important to assess both your budget and your actual internet speed needs. Doing so will help ensure you get the right router for your situation, without overspending. Here are some key factors to consider:
Take Stock of Your Devices
First, take an inventory of the devices that will be connecting to your router. The more devices you have, the more bandwidth you’ll need. Make a list of each device – smartphones, tablets, computers, smart home gadgets, gaming consoles, etc. Consider not just what you have now, but what you may add in the coming years. Newer routers have technology to handle dozens of devices.
Estimate Your Usage
Next, think about how you use the internet. Do you mostly browse the web and check email? Or do you stream lots of high definition video and play online games? Streaming HD video and gaming require faster speeds of at least 25-50 Mbps. Downloading large files also benefits from faster connections. If your household does a lot of high bandwidth activities, opt for a faster router.
Understand Your Connection Speeds
You also need to understand your internet plan speeds. Most connections are asymmetric – the download speed is much faster than the upload. Look at your plan and your monthly statements. For the most part, your router can’t exceed your plan’s maximum speeds. If you are paying for 150 Mbps download but your router can handle 300 Mbps, you won’t see any benefit. Match your router capabilities with your plan.
Budget Accordingly
Higher performance routers cost more. Budget 5 GHz routers start around $50-75, while high-end gaming routers run up to $300. For moderate use, a good mid-range router in the $80-150 range will suffice. The latest WiFi 6 routers cost over $200. Consider paying more if you have lots of devices or need fast speeds. Think if the investment is worthwhile.
Leave Room to Upgrade
Finally, consider your growth needs. You may start with basic web browsing and streaming, but that could change over time. Buying a more powerful router now leaves room to upgrade your internet plan later without replacing the router. Spend a bit more for a high-performance router even if you don’t need it yet.
Key Factors When Shopping for a 5 GHz Router

Once you’ve assessed your budget and speed requirements, you can start shopping for a 5 GHz router. Here are some key specifications and factors to keep in mind:
Dual-Band with 5 GHz Support
Look for a dual-band router supporting both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band generally has longer range, while 5 GHz is faster but has shorter range. Dual-band routers allow devices to connect on either frequency. Confirm the router explicitly states 5 GHz support – don’t assume dual-band means 5 GHz.
Top Speeds
Check the maximum speeds on the 5 GHz band – often over 1000 Mbps on high-end routers. Match this with your internet plan’s speeds. For most, 600 Mbps or better is sufficient. WiFi 6 routers boast speeds up to 4800 Mbps!
MU-MIMO & Beamforming
Look for MU-MIMO and beamforming features. MU-MIMO allows a router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously. Beamforming focuses the signal towards each connected device. Together these technologies enhance overall speed and connectivity.
Processor & Antennas

A faster processor helps manage all the traffic and requests going through the router. More high-gain antennas provide wider coverage and better reception. Four good external antennas are ideal.
Quality of Service
QoS or Quality of Service allows you to prioritize traffic so important activities like gaming or streaming don’t lag. This is a key feature if you have lots of users and devices competing for bandwidth.
Security Protocols
Encrypt your network traffic and protect against attacks. Look for WPA3 WiFi encryption and firewall protection at a minimum. VPN server support provides added security.
WiFi Standards
Newer WiFi 6 (802.11ax) routers support faster speeds and handle more devices, but are more expensive. WiFi 5 (802.11ac) routers are a good alternative for many. Avoid older 802.11n routers if possible.
By taking the time to realistically assess your budget and speed needs, you can find the ideal 5 GHz wireless router for your home or office. Focus on dual-band support, speed capabilities, QoS, MU-MIMO, beamforming, processor power, antennas, and security. Investing in the right router gives you performance and room to grow.
Considering Extras Like Antenna Design, Ports, and Software When Shopping for the Best 5 GHz Routers
Considering Extras Like Antenna Design, Ports and Software
While core specs like dual-band support and maximum speeds are critical when selecting a new 5 GHz router, you’ll also want to evaluate some of the extra features and design factors that can impact performance and functionality. Carefully considering elements like antenna design, ports, and software can help you choose a router that best fits your needs.
Antenna Design
Antenna design affects WiFi range and coverage. Look for these key antenna features when shopping for a 5 GHz router:
- Number of antennas – Typically between 2 to 8. Four is optimal for good omnidirectional coverage.
- External antennas – Better reception than internal antennas.
- Position and orientation – Vertical antennas provide broader coverage.
- High gain – Focuses and boosts the wireless signal strength.
- Beamforming – Focuses the signal to WiFi devices.
Positioning external high-gain antennas vertically and 45 degrees apart provides a strong 360 degree signal pattern. Choose routers promoting antenna technology like this.
Ports

Evaluate the type and number of ports, both LAN and internet. Look for:
- Gigabit LAN ports – At least four. Prioritize gigabit over slower 10/100 Mbps.
- WAN port – Look for gigabit WAN rather than slower alternatives.
- USB port – For attaching printers and storage drives.
The more LAN ports, the more wired devices you can connect. USB ports add expandability. Make sure the ports match your needs.
Software & Firmware
User-friendly software helps you manage the advanced features and settings of 5 GHz routers:
- Web interface – For monitoring usage and configuring settings.
- Mobile app – Manage your network remotely via smartphone.
- QoS controls – Prioritize traffic and devices.
- Guest networks – Provide separate SSIDs for guests.
- Parental controls – Limit access for kids.
- Firewall and security – Protect your network.
- Automatic firmware updates – Ensure you have the latest features and fixes.
Evaluate whether the router’s software meets your needs. Look for QoS software if you need to prioritize streaming or gaming traffic. Automatic firmware updates keep your router secure.
Other Features

Some additional features that may be beneficial include:
- VPN support – Secure remote access with Virtual Private Networking.
- Link aggregation – Use two LAN ports together for faster speeds.
- WiFi mesh – Extend coverage with mesh satellite units.
- Bluetooth – Connect to Bluetooth devices like speakers.
Consider extras like these that add functionality tailored for gaming, security, media streaming, or other needs. Identify features that will enhance how you use your home network.
Taking a holistic view of antenna design, ports, software, and supplemental features ensures you select a 5 GHz router that truly fits your budget, speed needs, and functionality wants. Don’t just look at specs – look at the overall package. Finding the right blend gives you the best WiFi experience.
How to Set Up and Configure a New 5 GHz Router
How to Set Up and Configure a New 5 GHz Router
Congratulations, you’ve purchased a new dual-band 5 GHz wireless router to boost your home WiFi speeds! But before you can enjoy lightning fast downloads and lag-free gaming and streaming, you’ll need to properly set up and configure your new equipment. Follow this step-by-step guide to get your new 5 GHz router installed correctly and optimized for top performance.
Step 1 – Position the Router
Start by placing your router in an ideal location for WiFi coverage. The best spots are centrally located in the home and elevated, like on a high shelf or table. Keep the router away from objects that can interfere with wireless signals like metal, mirrors, thick walls, and microwave ovens. Position it away from competing electronics. Place it near your modem if connecting wirelessly.
Step 2 – Connect the Hardware
Next, connect the physical hardware. Use the included Ethernet cable to connect your broadband modem to the router’s WAN or internet port. Connect wired devices like computers and game systems to the router’s LAN ports. Attach the antennas and point them upward. Plug in the power cable last to turn it on. LED lights on the router should turn on if it powers up correctly.
Step 3 – Configure with the Web Interface
The easiest way to configure the router is via the web interface. Connect wirelessly or via Ethernet cable from a computer. Open a browser and enter the router’s default gateway IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Enter the default username and password when prompted. You can now access the settings and change the SSID, encryption type, passwords, and more.
Step 4 – Update Firmware
Check the current firmware version and update to the latest if available. Updated firmware provides security fixes and new features. Find the firmware update section in the web interface. Download the firmware file to your computer, then use the interface to browse to the file and install it. Reboot the router after an update.
Step 5 – Set Up & Name Networks
Using the web interface, configure your wireless networks. Name each network by creating an SSID. Configure one SSID for the 2.4 GHz band and another for the faster 5 GHz band. For example “YourNetworkName_2G” and “YourNetworkName_5G”. Set a secure password for each WiFi network. Enable encryption like WPA2 or WPA3.
Step 6 – Configure QoS Settings
To prioritize gaming and streaming, configure Quality of Service settings. Via the interface, enable QoS and Traffic Prioritization features. Specify priority device types, like Xbox or PS5. Set higher bandwidth percentages for priority devices. This prevents bandwidth hogging and lag.
Step 7 – Set Up Guest Network

If desired, create a separate SSID and WiFi password just for guests. Enable the guest network option in the interface to create an additional network name and password that keeps guests off your main network. Set appropriate bandwidth allowances.
Step 8 – Test Speeds & Coverage
Test your wireless speeds and coverage. Connect devices and use speed tests in multiple locations to verify desired bandwidth, especially for the 5 GHz network. If any rooms or areas lack signal, try repositioning the router, antennas, or devices to improve coverage.
Following these steps helps ensure your new 5 GHz router is set up correctly and ready to deliver the speed, performance, and connectivity you want. Take time to configure QoS, guest networking, security protocols, and parental controls tailored for how you use the internet. Enjoy your faster WiFi!
Tips to Get the Best Coverage from Your 5 GHz WiFi Network
Tips to Get the Best Coverage from Your 5 GHz Network
The 5 GHz band on your shiny new dual-band router provides faster speeds but shorter range compared to 2.4 GHz. Don’t let spotty or weak 5 GHz coverage negate the speed benefits of your router purchase. Use these tips to optimize your setup and get the best WiFi coverage from your router’s 5 GHz network:
Centralize the Location
Position your router as centrally in your home as possible to allow the 5 GHz signals to radiate in all directions with minimal obstacles. Place it on an upper floor if you have a multi-story home. Keep it elevated in an open area for best dispersion.
Adjust Antennas Properly
Experiment by pointing the antennas in different directions to see if coverage improves. Generally, vertical positioning works best to push the signal downwards throughout your home. Avoid bunching or tangling antennas too close together.
Don’t Block the Signals
Keep the router clear of objects that can absorb or disperse the wireless signals. Maintain an open path since walls, floors, cabinets, and other obstacles impede 5 GHz range. Avoid positioning near electronics, appliances, and metal materials too.
Upgrade Antennas if Needed

If the included antennas don’t provide sufficient reach, upgrade to higher gain aftermarket antennas. Look for antennas rated for 5 GHz frequencies with at least 5dBi or more gain. Position the new antennas for optimal coverage.
Install Antenna Boosters
In addition to upgrading the antennas themselves, also consider adding antenna booster accessories. These amplify the wireless signal for greater range and penetration through walls and floors. Position boosters around your home.
Add a Wireless Extender
For particularly stubborn WiFi dead zones, add a wireless range extender for the 5 GHz band. Set it up closer to the weak coverage area to pick up and rebroadcast the router’s 5 GHz signals.
Enable Beamforming
Make sure the beamforming feature is enabled in your router’s settings. Beamforming focuses and strengthens the direction of the WiFi signals to each device, enhancing range and performance.
Connect Devices Closer
If certain devices still struggle with 5 GHz signal strength due to their location, try moving them closer to the router. Shortening the distance required for a solid 5 GHz connection helps.
Avoid Band Steering
Turn off your router’s band steering or smart connect function, which tries to force devices onto 5 GHz. Let devices connect to 2.4 GHz if the signal is stronger, since dual-band allows either frequency.
Adjust Quality of Service
Give priority in QoS settings to devices farther from the router that need strong 5 GHz signals. Reduce bandwidth for closer devices so distant ones get a boost.
Tweaking router placement, antennas, wireless extenders, beamforming, band steering, QoS, and device locations helps enhance your overall 5 GHz wireless footprint and performance. Get better range to take advantage of those blazing fast 5 GHz network speeds!
The Future of 5 GHz WiFi – What’s Coming Next
The Future of 5 GHz WiFi – What’s Coming Next
With a new 5 GHz router, you’re enjoying blazing fast speeds today. But what does the future hold for 5 GHz WiFi technology? Let’s look at emerging advancements that will shape the next generation of speedy 5 GHz wireless networking.
WiFi 6E
WiFi 6E is an enhanced version of WiFi 6 that adds support for the new 6 GHz band. This massive chunk of spectrum has 14 additional 80 MHz channels, free from interference from legacy devices. WiFi 6E routers and devices will unlock multi-gigabit speeds surpassing 5 GHz capabilities.
4096 QAM Modulation
Current 5 GHz routers use 256 QAM modulation. New 4096 QAM boosts throughput by encoding more data per waveform. Combined with wider 160 MHz channels, 4096 QAM will significantly enhance speeds.
OFDMA Technology
OFDMA allows a router to split channels into sub-carriers, enabling simultaneous transmissions to multiple devices at once. Coupled with MU-MIMO, OFDMA will optimize traffic capacity in congested environments.
Improved Beamforming
Beamforming will continue improving by focusing signals even more precisely at each client. This strengthens signals at farther distances for better 5 GHz range and penetration.
10 Gbps LAN Support
Future routers will incorporate multi-gig ethernet LAN ports supporting speeds beyond 1 Gbps. This prepares for internet service upgrades without becoming a LAN bottleneck.
AI-Driven WiFi Management
Expect routers to use artificial intelligence to analyze network traffic patterns and usage behaviors. AI will automatically optimize settings and channels for optimal performance.
Easy Mesh Networking
Mesh systems will become more mainstream with models dedicated for 5 GHz backhaul. Consumers will easily increase range by adding nodes.
Improved Security
Security will continue improving with longer encryption keys and passwords, plus frontier technologies like quantum encryption. This prevents hacking of 5 GHz networks.
6 GHz and Faster Backbone Upgrades

Service providers are building out 6 GHz and fiber backbones to deliver multi-gigabit internet speeds to homes and businesses. This powers next-gen 5 GHz/6 GHz routers to their full potentials.
New Use Cases
Faster 5 GHz will enable new use cases like high-resolution wireless video streaming and virtual/augmented reality. Gaming will benefit from lag-free connectivity and rapid cloud compute.
The WiFi landscape will change dramatically in coming years thanks to new spectrum, higher throughput modulation, expanded channels, multi-gig hardware, and backbone upgrades. Today’s 5 GHz routers are just the start of an ultra fast wireless future!

