What are isolation gowns. How do they protect healthcare workers and patients. Why are isolation gowns crucial in medical settings. What materials are used in isolation gowns. How are isolation gowns regulated. What are the key features of isolation gowns. How should isolation gowns be properly used.
Understanding Isolation Gowns: A Vital Component of Personal Protective Equipment
Isolation gowns serve as a critical line of defense in healthcare settings, forming an essential part of personal protective equipment (PPE). These specialized garments are designed to shield healthcare workers and patients from potential exposure to infectious agents and bodily fluids. But what exactly sets isolation gowns apart from ordinary medical attire?
Unlike standard lab coats or scrubs, isolation gowns are meticulously engineered and regulated as medical devices by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). They must meet rigorous performance standards to ensure they provide adequate protection in high-risk scenarios involving exposure to fluids, microbes, and particulates. The primary function of these gowns is to create a reliable barrier between pathogens and the wearer’s clothing, skin, and mucous membranes.

Key Functions of Isolation Gowns
- Prevent transmission of infections spread through contact or droplet routes
- Protect healthcare workers’ clothing from contamination
- Safeguard patients from potential contaminants carried by healthcare providers
- Maintain hygiene standards and reduce healthcare-associated infections
Research has consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of isolation gowns in infection control. Studies have shown that proper use of these protective garments correlates with lower rates of antibiotic-resistant organisms and Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infections in hospital settings.
Regulatory Standards and Classifications for Isolation Gowns
To qualify as a regulated medical device, isolation gowns must adhere to specific requirements outlined by the FDA. Various standards organizations, including ASTM International, have developed performance testing procedures to ensure the quality and efficacy of these protective garments.
How are isolation gowns classified? The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) has established a classification system known as AAMI PB70, which categorizes isolation gowns based on their level of protection. Manufacturers must validate that their products meet the designated AAMI levels through standardized test methods.

AAMI PB70 Classifications
- Level 1: Minimal risk, basic care, standard hospital medical unit
- Level 2: Low risk, blood draw, suturing, intensive care unit, pathology lab
- Level 3: Moderate risk, arterial blood draw, inserting an IV line, emergency room, trauma
- Level 4: High risk, long, fluid-intensive procedures, surgery, pathogen resistance
These classifications help healthcare facilities select the appropriate level of protection for specific procedures and risk levels. The testing process evaluates various metrics, including microbial penetration resistance, fluid resistance, seam strength, breathability, flammability, and overall durability.
Applications of Isolation Gowns in Healthcare Settings
Isolation gowns are omnipresent in a wide range of medical environments, from hospitals and clinics to laboratories and long-term care facilities. Their versatility and protective properties make them indispensable in numerous healthcare scenarios.
Common Uses of Isolation Gowns
- Patient care in isolation precautions
- Surgical procedures
- Laboratory work in molecular biology and microbiology
- Hazardous material handling
- Autopsy and mortuary procedures
- Visitor protection in contagious patient rooms
- Home care and assisted living infection control
In each of these applications, isolation gowns play a crucial role in maintaining a sterile environment and preventing the spread of infectious agents. Their use extends beyond healthcare professionals to include visitors and caregivers in various settings, underscoring their importance in comprehensive infection control strategies.
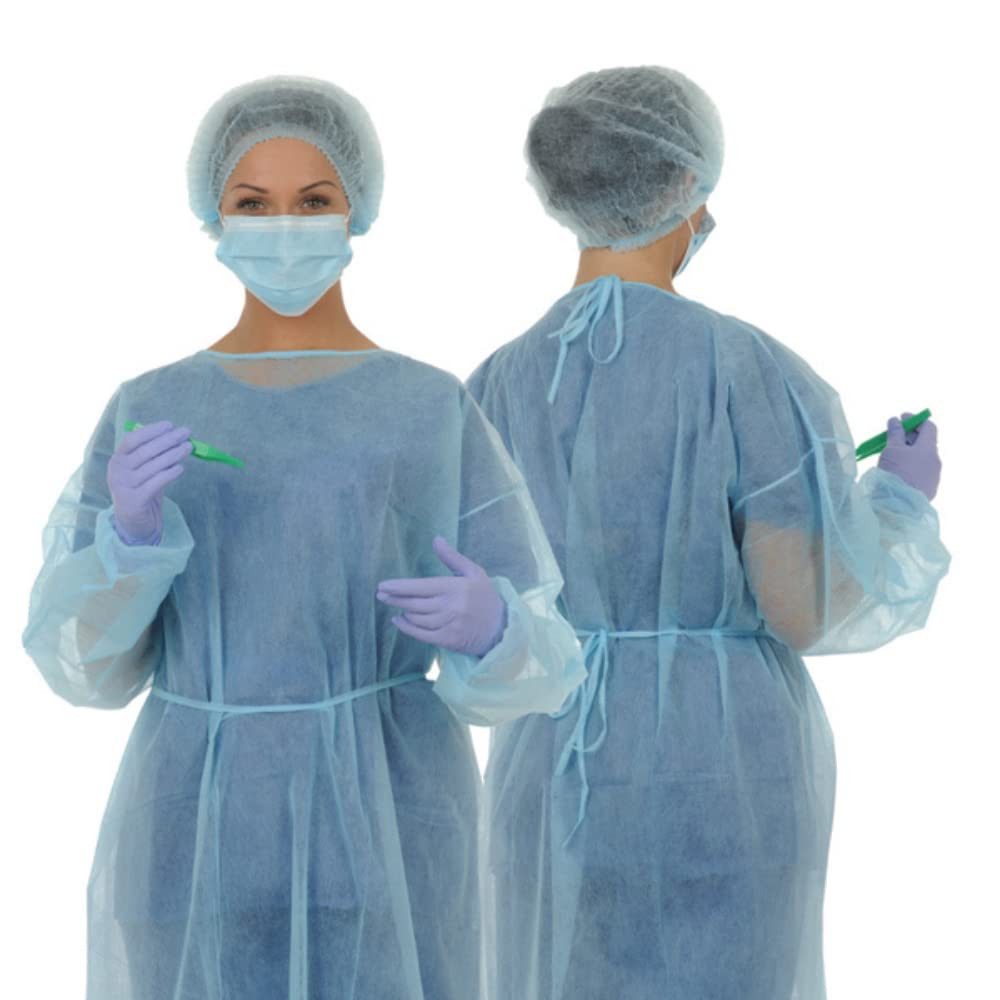

Materials and Design Features of Isolation Gowns
The effectiveness of isolation gowns relies heavily on their materials and design. Manufacturers employ a range of synthetic materials and innovative construction techniques to create gowns that balance protection, comfort, and functionality.
Common Materials Used in Isolation Gowns
- Nonwoven polypropylene
- Spunbond-meltblown-spunbond (SMS) polypropylene
- Polyethylene
- Polyester
- Mixed synthetic fabrics
Some isolation gowns feature coated or laminated materials to enhance fluid resistance. The choice of material involves careful consideration of factors such as breathability, strength, and barrier performance to ensure optimal protection without compromising wearer comfort.
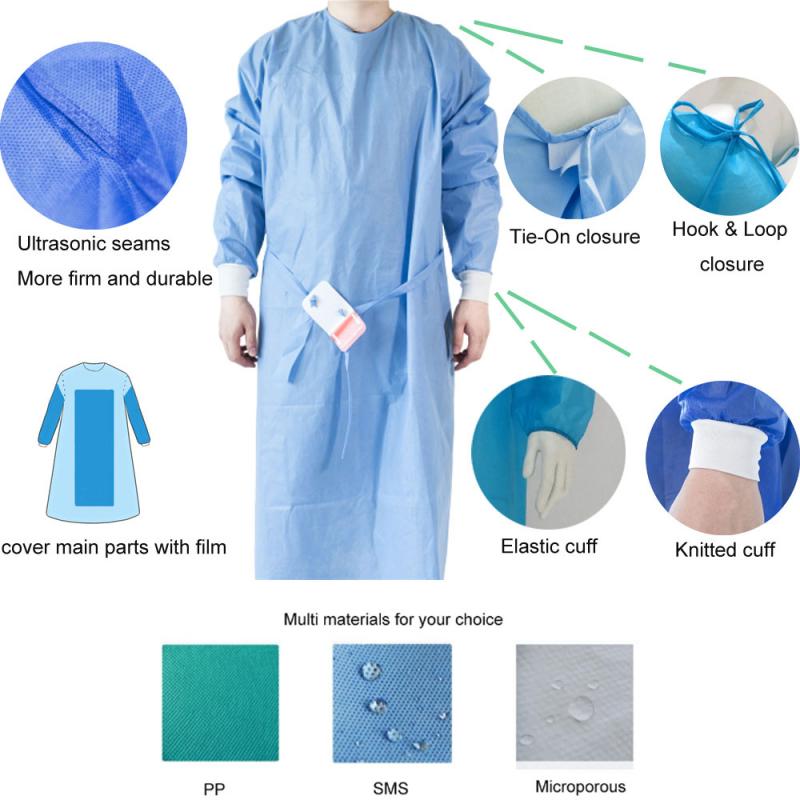
Key Design Elements of Isolation Gowns
- Full back coverage with secure neck fastening
- Pouch sleeves with fitted or elastic cuffs
- Neck and waist ties or closures
- Reinforced seams for durability
- Knit cuffs for comfort and enhanced coverage
- Varying lengths from hip to mid-calf
- Optional features like thumb loops and kick pleats for improved mobility
These design elements work in concert to provide comprehensive coverage and protection while allowing healthcare workers to perform their duties efficiently. The range of available designs spans from basic, all-purpose gowns to highly specialized surgical gowns engineered for specific procedures.

Disposable vs. Reusable Isolation Gowns: Weighing the Options
When it comes to isolation gowns, healthcare facilities have two primary options: disposable and reusable gowns. Each type has its own set of advantages and considerations, and the choice often depends on factors such as cost, sustainability goals, and specific use cases.
Disposable Isolation Gowns
Disposable gowns offer several benefits that make them a popular choice in many healthcare settings:
- Convenience of single-use protection
- Elimination of cross-contamination risks associated with laundering
- Reduced storage and inventory management requirements
- Consistent performance with each new gown
However, disposable gowns also present challenges, particularly in terms of environmental impact and long-term cost considerations.
Reusable Isolation Gowns
Reusable gowns have gained popularity in recent years, driven by sustainability concerns and potential cost savings:
- Reduced environmental footprint
- Lower long-term costs for healthcare facilities
- Potentially more comfortable for extended wear
- Improved availability during supply chain disruptions
The primary challenge with reusable gowns lies in ensuring proper laundering and maintenance to prevent pathogenic spread between uses. Healthcare facilities must have robust processes in place to clean and sterilize these gowns effectively.
Proper Donning and Doffing Techniques for Isolation Gowns
The effectiveness of isolation gowns in preventing infection transmission relies heavily on proper donning (putting on) and doffing (removing) techniques. Healthcare workers must follow specific protocols to ensure they maximize protection and minimize the risk of contamination.
Donning an Isolation Gown
- Perform hand hygiene before handling the gown
- Select the appropriate gown size
- Hold the gown with the opening at the back
- Insert arms into the sleeves, ensuring the gown covers from neck to knees
- Secure the neck and waist ties
- Ensure full coverage of the torso
- Don other PPE items like gloves and mask after the gown
Doffing an Isolation Gown
- Assume the gown and gloves are contaminated
- Untie all ties or unfasten all closures
- Peel the gown away from the neck and shoulders
- Turn the contaminated outer surface inward
- Fold or roll the gown into a bundle
- Discard in an appropriate waste container
- Perform hand hygiene immediately after removing the gown
Proper technique is crucial to maintain the integrity of the protective barrier and prevent accidental contamination during the removal process. Regular training and practice sessions can help healthcare workers master these essential skills.
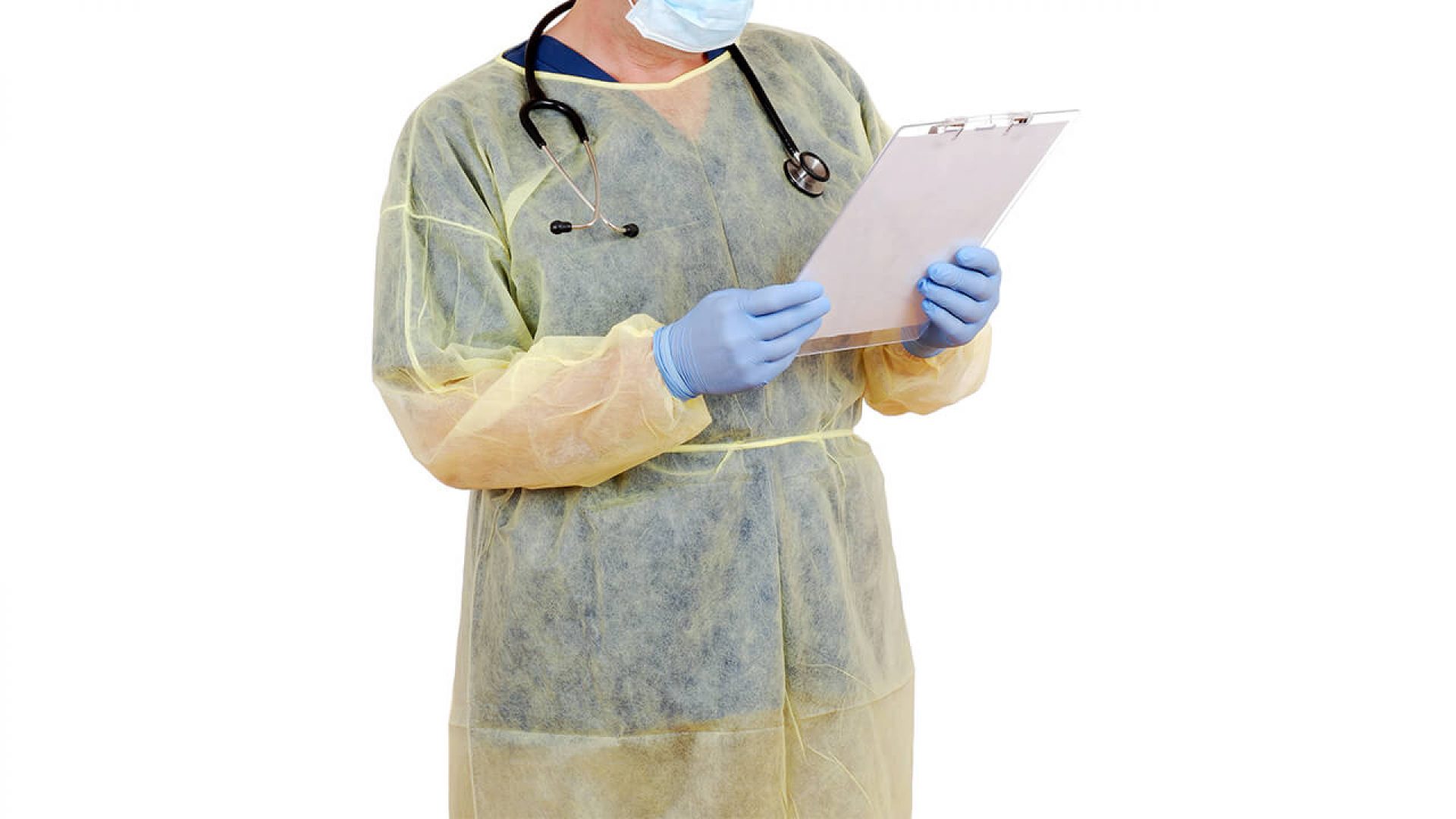

Innovations and Future Trends in Isolation Gown Technology
As healthcare needs evolve and technology advances, the field of isolation gown design continues to innovate. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring new materials, construction techniques, and features to enhance protection, comfort, and sustainability.
Emerging Technologies in Isolation Gowns
- Antimicrobial fabrics that actively neutralize pathogens
- Smart textiles with embedded sensors for real-time monitoring
- Biodegradable materials for eco-friendly disposable options
- Improved breathability without compromising barrier properties
- Enhanced durability for reusable gowns
These innovations aim to address current challenges in isolation gown use, such as heat stress during prolonged wear, environmental concerns, and the need for more precise infection control measures.
Future Directions in Isolation Gown Research
Research efforts are focusing on several key areas to improve isolation gown performance and usability:
- Development of more sustainable materials and production processes
- Integration of isolation gowns with other PPE components for seamless protection
- Customization options to better fit diverse body types and medical procedures
- Exploration of new testing methods to evaluate gown effectiveness against emerging pathogens
As healthcare facilities face evolving challenges, including new infectious diseases and antibiotic-resistant organisms, the continued advancement of isolation gown technology will play a crucial role in maintaining safety and infection control standards.

The Impact of Isolation Gowns on Healthcare Economics and Sustainability
The use of isolation gowns extends beyond immediate infection control benefits, influencing healthcare economics and environmental sustainability efforts. Understanding these broader impacts is crucial for healthcare administrators and policymakers.
Economic Considerations
Isolation gowns represent a significant expense for healthcare facilities. Factors affecting the economic impact include:
- Initial purchase costs of gowns
- Storage and inventory management expenses
- Disposal costs for single-use gowns
- Laundering and maintenance costs for reusable gowns
- Potential savings from reduced healthcare-associated infections
While the upfront costs can be substantial, the long-term economic benefits of preventing infections and reducing hospital stays can offset these expenses. Healthcare facilities must carefully analyze their usage patterns and infection rates to determine the most cost-effective approach to isolation gown procurement and use.

Environmental Impact and Sustainability Efforts
The environmental footprint of isolation gowns, particularly disposable options, has become a growing concern in the healthcare industry. Efforts to address this issue include:
- Development of more environmentally friendly disposable materials
- Increased adoption of reusable gowns to reduce waste
- Implementation of recycling programs for certain gown components
- Exploration of alternative sterilization methods to reduce energy consumption
- Life cycle assessments to guide more sustainable manufacturing processes
Balancing infection control needs with environmental responsibility presents an ongoing challenge for healthcare facilities and gown manufacturers. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in healthcare, we can expect to see continued innovation in this area.
The role of isolation gowns in healthcare extends far beyond their immediate protective function. These essential garments represent a complex intersection of medical science, materials engineering, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, so too will the design and implementation of isolation gowns, ensuring they remain a cornerstone of infection control and patient safety strategies.
What is an Isolation Gown?
Isolation gowns are a critical component of personal protective equipment (PPE) used in healthcare and laboratory settings. These disposable or reusable garments create a barrier to prevent potential exposure to infectious agents and body fluids. But what exactly are isolation gowns, and why are they so vital for safety?
An isolation gown is a protective coverall designed specifically for medical procedures. Unlike ordinary lab coats or scrubs, isolation gowns are regulated as medical devices by the FDA. They must meet stringent performance requirements for high-risk scenarios involving fluid, microbe, and particulate exposure. Quality isolation gowns are engineered with specific materials and construction to provide full coverage of the torso and limbs.
Serving As a Protective Barrier
When worn properly, the isolation gown acts as a shield between pathogens and the wearer’s clothes, skin, and mucous membranes. Gowns protect healthcare staff from acquiring infections that can be spread by contact or droplet routes. They also prevent contamination of garments that will be worn outside of the patient’s room. Additionally, isolation gowns keep patients safe from exposure to outside contaminants the provider could carry.
Because isolation gowns form a barrier, they play a critical role in maintaining hygiene and preventing healthcare-associated infections. Numerous studies have demonstrated their effectiveness for infection control. Proper gown usage has been associated with lower rates of antibiotic-resistant organisms and C. difficile in hospitals.
Meeting Regulatory Standards

Not just any lab coat or coverall qualifies as an isolation gown. To serve as regulated medical devices, these garments must satisfy requirements outlined by the FDA. Performance testing procedures have been developed by ASTM International and other standards organizations.
Isolation gowns are evaluated for their level of protection based on AAMI PB70 classifications. Manufacturers must validate that their products meet the designated AAMI levels through standardized test methods. This involves assessing metrics like microbial penetration, fluid resistance, seam strength, breathability, flammability, and durability.
Healthcare Applications
Isolation gowns are ubiquitous in hospitals, clinics, and other patient care settings. Doctors, nurses, and other staff don these protective coveralls when caring for patients in isolation precautions. They are also required for handling infectious materials in the lab or operating room.
Specific applications include:
- Isolation precaution gowns
- Surgical gowns
- Lab coats for molecular biology, microbiology, etc.
- Hazmat suits
- Autopsy/mortuary gowns
Additionally, visitors may need to wear isolation gowns for entering rooms of contagious patients on contact or droplet precautions. In assisted living or home care, gowns help caregivers safely interact with clients battling infections.
Materials and Design Features

Isolation gowns come in a range of materials, including nonwoven polypropylene, spunbond-meltblown-spunbond (SMS) polypropylene, polyethylene, polyester, and mixed synthetics. Some feature coated or laminated materials for enhanced fluid resistance. Choices balance factors like breathability, strength, and barrier performance.
Key design elements include:
- Full back coverage with fastening behind the neck
- Pouch sleeves with fitted or elastic cuffs
- Neck and waist ties or closures
- Reinforced seams
- Knit cuffs for comfort and coverage
Lengths vary from hip to mid-calf. Some isolation gowns integrate thumb loops and kick pleats for ease of movement. Choices range from basic designs to highly engineered surgical gowns.
Disposable vs. Reusable Options
Both disposable and reusable isolation gowns are common. Disposable gowns provide convenience and single-use protection. They prevent cross-contamination risk from laundering errors. However, reusable gowns have sustainability benefits and lower long-term costs.
Reusable isolation gowns are gaining popularity. These are constructed from durable, fluid-resistant fabrics. However, proper laundering is essential for reusables to prevent pathogenic spread between uses.
Donning and Doffing Technique
To work effectively, isolation gowns must be put on, worn, and removed properly. The CDC provides guidelines for donning and doffing PPE.
Key pointers when donning an isolation gown:
- Perform hand hygiene
- Face the back opening of the gown
- Secure neck and waist ties
- Ensure coverage of torso from neck to knees
- Put on other PPE like gloves and mask after gown
To doff the gown safely:
- Untie ties
- Peel gown away from shoulders, rolling inside-out
- Avoid contact of outer surface with body
- Dispose of in designated container
- Wash hands immediately
Proper technique is vital for avoiding gown breaches and accidental exposure when caring for isolated patients.
The Bottom Line
Isolation gowns provide critical protective barriers for healthcare staff and patients. Their material and construction targets fluid and microbe exposure risks. While essential for safety, they must be donned, worn, and disposed of properly to work. Isolation gowns continue to evolve with new styles and engineered fabrics that balance protection, comfort, and sustainability.
Purpose of the Medical Isolation Gown
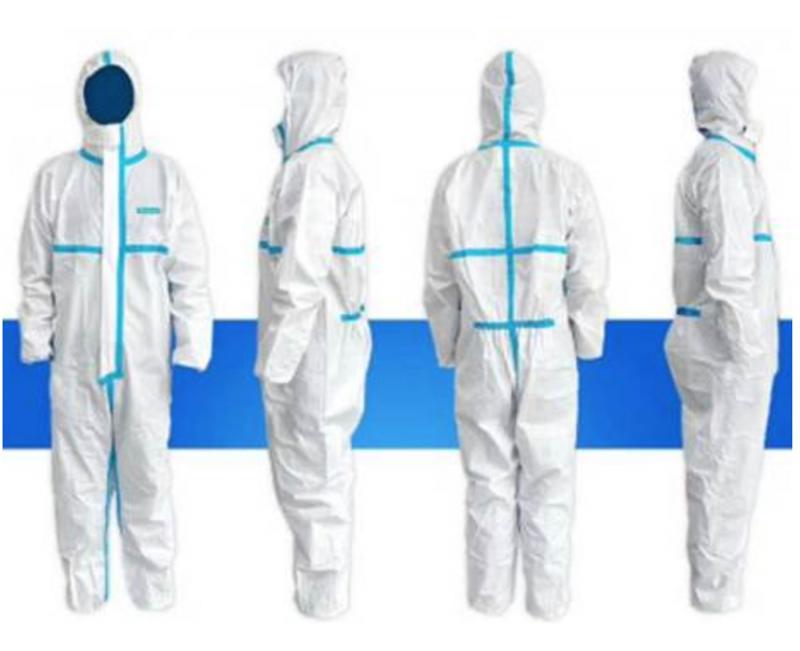

Isolation gowns serve a critical purpose in healthcare – to protect. By creating a barrier between pathogens and the wearer’s body, the gown prevents potential transmission of infectious agents. Understanding the key objectives of isolation gowns provides insight into their life-saving role.
First and foremost, the purpose of an isolation gown is to shield medical personnel. Doctors, nurses, lab techs, and other staff interact closely with sick patients daily. Without proper protective apparel, they would be at high risk of contracting transmissible diseases. Proper gown usage safeguards healthcare workers from acquiring infections on the job.
Additionally, isolation gowns prevent clinicians from spreading pathogens they may carry to vulnerable patients. Say a nurse has a MRSA infection but isn’t exhibiting symptoms. Wearing a gown creates a protective barrier to stop asymptomatic carriage and transmission to immunocompromised patients.
The gown also serves to maintain hygiene standards in patient care. When worn over street clothes, the isolation gown prevents contact between external surfaces and the patient environment. This helps uphold sanitation protocols, especially in sterile spaces like the OR.
By preserving clinician and patient safety, isolation gowns support infection prevention efforts. Gowns create a tangible barrier to disrupt contact, droplet, and fluid-borne modes of disease transmission. Facilities with robust gown protocols see lower healthcare-associated infection rates.
Additionally, isolation gowns uphold patient dignity and privacy. The coverage they provide preserves modesty and avoids exposing the body unnecessarily during examinations or procedures.
Proper isolation gowns must balance several objectives:
- Protect staff by preventing pathogen exposure
- Protect patients by controlling spread from providers
- Enable compliance with hygiene and sanitation protocols
- Preserve patient privacy and dignity
In short, medical isolation gowns provide critical protective barriers to break infection transmission routes. They safeguard healthcare workers while letting them deliver needed hands-on care safely. When used correctly, isolation gowns are simple but lifesaving tools.
Regulations and Standards

For isolation gowns to fulfill their protective purpose, they must meet stringent regulations. In the U.S., the FDA designates isolation gowns as Class I medical devices.
Manufacturers must adhere to FDA quality system regulations for design, validation, manufacturing, and labeling. Gowns marketed for medical use undergo thorough performance testing per AAMI/ANSI standards.
Key standards include:
- AAMI PB70 – performance requirements for protective apparel
- ASTM F1670 – standard test method for resistance of materials used in protective clothing to penetration by synthetic blood
- ASTM F1671 – standard test method for resistance of materials used in protective clothing to penetration by blood-borne pathogens
Additionally, facilities must follow CDC guidelines for proper gown use to fulfill safety objectives.
With stringent regulations and standards, isolation gowns reliably provide their critical protective barrier function in healthcare settings.
Isolation gowns aren’t just a routine part of PPE – they serve specific purposes vital to healthcare delivery and safety. When engineered and worn correctly, they prevent infections that can derail lives and careers. Though often taken for granted, the isolation gown’s barrier protection plays an indispensable role in safe patient care.
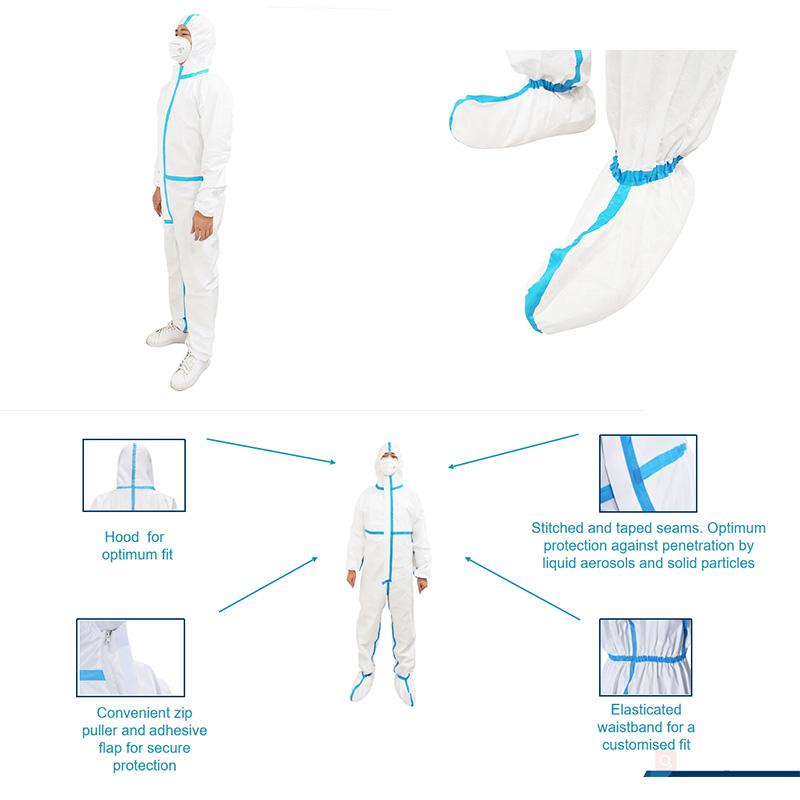
Materials Used to Make Protective Gowns
Creating an effective isolation gown requires selecting the right materials. Gown fabrics and components must balance critical factors like barrier protection, breathability, strength, and comfort.
Here are key materials used in medical isolation gown construction:
Nonwoven Polypropylene
Spunbonded polypropylene is a popular choice for disposable isolation gowns. This nonwoven fabric offers a breathable, fluid-resistant barrier at low cost. It’s naturally hydrophobic, repelling liquids away from the surface. Polypropylene gowns provide moderate fluid protection suitable for basic isolation needs.
SMS Polypropylene
SMS stands for spunbond-meltblown-spunbond polypropylene. This is a polypropylene nonwoven with an added meltblown layer. The meltblown polypropylene acts as a filter, providing enhanced fluid resistance compared to spunbond alone. SMS polypropylene disposable gowns offer greater barrier protection for surgical and hazardous applications.
Polyethylene

Polyethylene films and laminates provide high liquid barrier performance. However, they lack breathability. Polyethylene isolation gowns are common as contraband covers in operating rooms. They’re also used for extremely hazardous scenarios requiring maximum protection.
Polyester and Cotton Blends
For reusable gowns, polyester/cotton blends are a popular choice. The polyester provides durability and protection, while the cotton improves comfort. However, polyester/cotton blends generally provide less fluid resistance than synthetic nonwovens. They require laundering after each use to prevent cross-contamination.
Coatings and Laminates
Some isolation gowns feature coatings or laminates for enhanced barrier performance. For example, spunbond polypropylene can be coated with polyurethane for increased fluid resistance. Laminates combine layers like spunbond fabric and meltblown film.
Reinforced Seams
Gown seams are points of potential fluid breach. Many isolation gowns feature seams bound with polyurethane tape or specialty stitching. This reinforcement minimizes the risk of seam failures and fluid exposure through gaps.
Cuffs and Bands
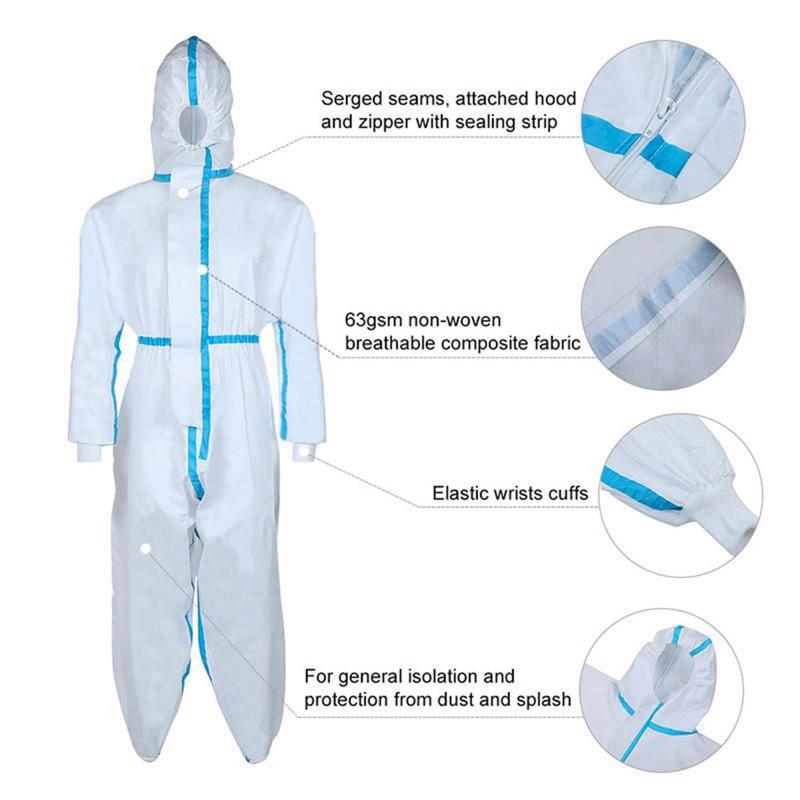
Knit cuffs, collar bands, and waistbands improve fit and coverage. Polyester and other synthetics are common. In some cases, the cuffs include an inner absorbent layer to wick away moisture.
Ties and Fasteners
Most isolation gowns secure with neck and waist ties. Twill ties offer durability. Some feature alternative closures like velcro, buttons, or snap tabs.
Material selection balances factors like barrier effectiveness, breathability, flexibility, and cost. No single material is ideal – the right choice depends on the specific use case and risk level involved.
With the availability of advanced fabrics and reinforcements, isolation gowns continue to evolve. The latest provide better protection and comfort, for improved safety and wearability.
Sustainability
Sustainability is an increasing priority in isolation gown production. Environmentally-friendly materials include:
- Biopolymers from renewable sources instead of polyolefins
- Recycled polypropylene
- Organic cotton
Some eco-friendly approaches include:
- Minimizing material waste in production
- Reusable/recyclable materials
- Energy and water conservation in manufacturing
The latest isolation gowns balance safety with reduced environmental impact. Proper reuse and recycling programs also improve sustainability.
Isolation gowns must be thoughtfully engineered to fulfill their protective purpose. Material selection considers barrier effectiveness, breathability, comfort, and environmental impact. With new fabric technologies and production practices, isolation gowns continue advancing to better safeguard healthcare personnel.
Features of a High-Quality Gown
Not all isolation gowns are equal when it comes to quality and protection. So what distinguishes a high-level isolation gown?
Here are key features to look for in a superior protective medical gown:
AAMI Level 3 or 4 Performance
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) establishes performance guidelines for protective apparel. AAMI Level 3 and 4 gowns provide moderate to high fluid barrier protection for surgical and hazardous applications.
Optimized Fabric and Construction
The right textile engineering provides effective defenses. Top gowns opt for materials like SMS polypropylene or polyethylene laminates. They also incorporate reinforced seams, knit cuffs, and other protective features.
Full Back and Sleeve Coverage
A quality isolation gown offers complete coverage – front, back and sleeves. Back openings secure with neck and waist ties or closures. Snug cuffs prevent sleeve rolldown.
Comfort Features

The highest-rated isolation gowns balance protection with comfort. Breathable fabrics, knit bands, and user-friendly closures make them less stifling and restrictive.
Custom Sizing
One-size gowns can fit poorly. Optimal isolation apparel comes in a tailored size range for better coverage and mobility.
Specialty Fabric Reinforcements
Strategically-placed fabric reinforcements enhance gown performance. Examples include coated chest panels, reinforced hems and seams, and absorbent inner cuff layers.
Conformance to Standards
Quality isolation gown manufacturers validate their products meet AAMI PB70 guidelines. They maintain proper FDA medical device registration and Quality System Regulation compliance.
Clinical Evidence
Scientific literature and clinical evaluations validate the protective efficacy of the gowns in real-world settings.
Manufacturer Reputation
Opt for gowns from recognized infection control brands with a track record of quality.
While cheaper isolation gowns have their place, healthcare workers in high-risk roles need superior protection. Seek gowns designed and tested for maximum barrier performance, coverage, ease-of-use and comfort.
Cost Considerations
Higher-tier isolation gowns carry a price premium, but offer enhanced safety for hazardous applications. However, they can be costly to stock in bulk.
To balance cost and protection, facilities often utilize a gown strategy:
- AAMI Level 1-2 gowns for general patient care
- AAMI Level 3-4 gowns for surgery, isolation rooms, etc.
This selective deployment minimizes expenses while providing robust protection where needed most.
Isolation gown quality makes a real difference in infection control. Seeking the right features and performance data helps healthcare facilities select apparel equal to their clinical risks.
Why Choose Disposable vs Reusable?
When selecting isolation gowns, healthcare facilities face a key decision – disposable or reusable? Both offer advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits of Disposable Isolation Gowns
Disposable gowns are the prevalent option in most hospitals today. Here are their main advantages:
- Convenience – No laundering required
- Infection control – Fresh sterile barrier every time
- Cost-effective for occasional use
- Wide variety of options
Disposables eliminate cross-contamination risks from gown reuse. Simply discarding used apparel prevents spreading pathogens. Disposable gowns also require no laundry infrastructure, simplifying use.
Benefits of Reusable Isolation Gowns
Reusables offer some distinct advantages as well:
- Environmental benefit – Less waste
- Cost savings long-term
- Often more durable and comfortable
Reusable gowns have an initial higher cost but get utilized for dozens or hundreds of cycles. They generate far less waste compared to disposables. The sturdy fabrics tend to offer greater comfort and breathability over repeated use.
Drawbacks of Disposable Gowns
The main limitations of disposables include:
- Recurring costs of constant replenishment
- Generate large volumes of healthcare waste
- Often less breathable than reusable options
While convenient, the supply costs add up significantly over time. The large quantities of gown waste disposables generate is also an environmental concern.
Drawbacks of Reusable Gowns
Reusables also have some limitations:
- Laundering required between every use
- Risk of residual contamination if laundering inadequate
- Higher upfront investment
Effective reusable gown protocols require a laundry facility, staffing, and quality control. If laundering proves subpar, gowns could spread pathogens between uses.
The Right Choice Depends

Choosing disposable versus reusable isolation gowns depends on factors like:
- Clinical setting and risk levels
- Gown usage patterns
- Availability of laundry services
- Environmental objectives
- Budget constraints
For sporadic isolation needs, disposables often make sense. For routine surgery and isolation precautions, reusables may provide better value and sustainability.
Healthcare facilities must weigh upfront costs with longevity, infection risks, and waste generation to select the optimal isolation gown strategy.
Standards for Performance Testing
For isolation gowns to provide effective barrier protection, they must meet stringent performance criteria. Several key standards guide isolation gown testing and validation.
AAMI PB70
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) publishes the pivotal PB70 standard. This establishes required characteristics and classification levels for protective apparel:
- Level 1 – Minimal risk
- Level 2 – Low risk
- Level 3 – Moderate risk
- Level 4 – High risk
Higher AAMI levels demand greater liquid barrier performance and coverage. Most surgical and isolation gowns meet AAMI Level 3 or 4 criteria.
ASTM Standards

The American Society for Testing and Materials publishes key test methods for evaluating protective apparel:
- ASTM F1670 – Synthetic blood penetration resistance
- ASTM F1671 – Viral penetration resistance
- ASTM F1359 – Flexibility and ergonomics
These standardized techniques assess critical gown performance metrics using simulated test conditions.
FDA Requirements
As Class I medical devices, isolation gowns sold in the U.S. must adhere to FDA regulations, including:
- Compliance with Quality System Regulations (QSRs)
- Registration and listing with the FDA
- Following consensus standards like AAMI PB70
FDA reviews manufacturing procedures, specifications, testing data, labeling, and other documentation to ensure regulatory compliance.
Independent Testing
Third-party testing provides added validation of gown performance claims. Groups like Underwriters Laboratories (UL) apply standardized techniques per AAMI and ASTM protocols.
Additionally, purchasers often conduct in-house testing to confirm gowns meet needs before making major inventory commitments.
Real-World Evidence
Clinical implementation studies offer real-world evidence of isolation gown performance. Analyses show reduced infection rates associated with proper use of tested gowns.
Following rigorous standards ensures isolation gowns provide consistent, reliable barrier protection for both healthcare staff and patients.
AAMI Levels of Protective Apparel
Not all isolation gowns provide equal barrier protection. The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) establishes four levels of performance for protective medical apparel:
AAMI Level 1
Level 1 gowns are suitable for minimal risk situations. Examples include basic care of stable patients without infections or contagious fluids.
They provide minimal fluid resistance. Level 1 apparel includes basic exam gowns and isolation gowns made of untreated fabrics like cotton.
AAMI Level 2
Level 2 isolation gowns offer low barrier protection for procedures where there may be light amounts of fluid exposure. This could include working with controlled bodily fluids.
They provide moderate fluid resistance capabilities. Common materials meeting Level 2 criteria include spunbond-meltblown and breathable polyethylene fabrics.
AAMI Level 3

Level 3 designates moderate risk protection for procedures with larger volumes of fluid exposure. This includes hazards like blood splashes.
Level 3 gowns demonstrate moderately high liquid barrier performance. They are suitable for surgical gowns and isolation needs involving copious contagious fluids.
AAMI Level 4
Level 4 represents high risk. These gowns provide maximum barrier protection from bodily fluids under pressures, splashes or sprays.
Level 4 apparel prevents blood or infectious fluid penetration for over an hour. These gowns are essential for highly hazardous situations like trauma surgery or infectious disease outbreaks.
Selecting the Right AAMI Level
Healthcare facilities must evaluate the types of fluid exposure risks staff encounter to select appropriate AAMI-rated apparel:
- Level 1 – Exams, non-infectious patient contact
- Level 2-3 – Normal surgery, isolation rooms
- Level 4 – Trauma, infectious disease, hazmat treatment
Referencing AAMI classifications helps procurement officers match gown barrier performance to clinical needs.
The AAMI PB70 standard empowers facilities to choose protective apparel equal to their safety requirements. Understanding AAMI levels helps healthcare settings select optimal isolation gowns for diverse hazardous scenarios.
Which Industries Use Isolation Gowns?

While most associated with healthcare, isolation gowns are utilized across many workplace settings where hazardous fluids or materials must be handled safely.
Healthcare
Healthcare facilities rely extensively on disposable and reusable isolation gowns. Doctors, nurses, techs, and other personnel don them when interacting with patients in isolation precautions or performing surgical procedures.
Laboratory
Research and diagnostic labs require extensive PPE to protect staff. Isolation gowns provide a key safeguard when handling biological specimens like tissue, blood, and microorganisms.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Workers in pharmaceutical plants often wear isolation gowns when exposed to potent or hazardous active drug ingredients, especially during handling and cleanrooms operations.
First Responders
EMS and other first responders keep isolation apparel on hand for responding to accidents or crime scenes with bodily fluids present.
Mortuary Services
Mortuary workers and autopsy personnel rely on very high-level gowns for protection when preparing deceased bodies.
Tattooing and Piercing
Tattoo artists and body piercers wear isolation gowns over clothes along with gloves and face shields to prevent exposure while working.
Salons and Spas
Isolation gowns provide a hygienic barrier for certain nail care, waxing, and facials treatments.
Industrial and Hazmat
Specialty isolation gowns protect industrial workers and hazardous material cleanup crews from caustic chemicals and toxic materials.
Food Manufacturing
Butchers, seafood processors, and other food personnel utilize protective apparel to shield from the ingredients they handle.
Any scenario involving potential splashes, sprays or exposure to hazardous liquids calls for protective isolation gowns. They safeguard personnel across healthcare, industrial, laboratory and emergency response settings.
Preventing Infections in Healthcare Settings

Isolation gowns play a pivotal role in infection control efforts in hospitals, clinics, and other patient care settings. When used properly, they form a key barrier to help prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
How Isolation Gowns Prevent Transmission
Isolation gowns guard against both contact and droplet transmission of pathogens:
- Contact – Gowns provide a cleanable barrier between clinician garments and patient
- Droplet – Gowns protect against pathogenic droplets contacting skin or clothing
By blocking exposure routes, isolation gowns break the chain of infection spread.
Evidence for Reducing HAIs
Numerous studies correlate proper isolation gown use with lower HAI rates:
- Cutting MRSA, VRE, and C. diff infections in ICUs
- Reduced surgical site infections for orthopedic and cardiac procedures
- Lower risk of contamination for vascular access and catheterization
Conscientious gown use also improves hand hygiene compliance by raising awareness of contamination risks.
Guidelines for Healthcare Settings
To optimize infection prevention, facilities should:
- Follow CDC guidelines for isolation gown use
- Select appropriate AAMI level gowns for specific risks
- Reinforce proper donning, doffing, and disposal
- Monitor compliance with gowning protocols
Staff education and competency validation help ensure isolation practices are followed consistently.
The Bottom Line
Isolation gowns provide a simple but effective safeguard against pathogen transmission in healthcare environments. Along with other PPE, they help protect patients, clinicians, and the larger community from dangerous HAIs when used properly.
As medical apparel technology and clinical evidence continue advancing, isolation gowns will persist as a cornerstone of infection prevention best practices.
Proper Usage Guidelines for Medical Personnel
To provide effective barrier protection, isolation gowns must be utilized correctly by healthcare personnel. Medical facilities should establish evidence-based guidelines and provide training on proper selection, donning, wearing, and disposal of gowns.
When to Use Isolation Gowns
Guidelines should advise healthcare workers to gown up for:
- Surgical procedures
- Contact with patients on isolation precautions
- Handling bodily fluids or potentially infectious material
- Any situation with risk of splashes or sprays of fluids
Selecting Appropriate Gowns
Educate staff to choose the right gown level for the clinical scenario, based on AAMI guidelines and fluid exposure risks. This optimizes protection while avoiding gown overuse.
Proper Donning and Doffing
Train personnel on CDC-recommended gown donning and doffing protocol to prevent contamination:
- Perform hand hygiene before donning
- Secure gown ties neck and waist for full coverage
- Remove gown slowly with ties/cuffs inside to contain surfaces
- Dispose in designated receptacle
- Wash hands immediately after removal
Following Isolation Precautions
Reinforce proper usage of gowns for patients requiring contact or droplet isolation, including signage and cart supplies.
Prioritizing High-Risk Scenarios
Reserve Level 3-4 gowns for surgery, trauma, hazmat response, infectious disease, and other high-fluid-risk situations.
Consistent guidelines combined with competency checks optimize isolation gown use. This ensures protection for both staff and patients.
Donning and Doffing Techniques
To provide contamination protection, isolation gowns must be put on and removed properly. Healthcare workers should follow evidence-based techniques for safe gown donning and doffing.
Donning or Putting on the Isolation Gown
The CDC provides the following protocol for safely donning an isolation gown:
- Perform hand hygiene
- Select appropriate gown for planned patient interaction
- Open gown fully and inspect for damage
- Face the back opening of the gown
- Secure ties at neck and waist for complete coverage
- Ensure gown wraps around the back and fully covers torso
- Put on other PPE like gloves and masks after gown
Doffing or Removing the Isolation Gown

To safely remove the gown without contamination:
- Untie all ties
- Pull gown away from neck and shoulders, touching inside only
- Turn contaminated outside surface inward
- Roll into a bundle and discard
- Wash hands thoroughly
Avoiding Errors
Mistakes to avoid include:
- Letting sleeves drag over clean hands or surfaces
- Touching outer surface of gown during removal
- Allowing gown to fall open and contaminate clothing
- Not securing ties for complete coverage
Proper technique protects clinicians and prevents spreading contaminants. Facilities should train staff on proper donning and doffing protocols.
Advantages of Different Gown Styles
Isolation gowns come in a variety of styles, each with pros and cons. Choosing the right gown design depends on the specific needs of the scenario.
Standard Tie Gowns
Classic isolation gowns use ties at the neck and waist. Benefits include:
- Allow custom fitting for different body types
- Enable adjustment if ties become loose
- Easy for most providers to put on correctly
Drawbacks are risk of ties dragging and potential for neck and waist gaps if tied loosely.
Snap/Tab Closure Gowns
Some isolation gowns use snap or tab closures instead of ties. Advantages:
- Prevent issues with tying loose or unevenly
- Streamline donning and doffing
- Eliminate dangling components
The fixed nature of closures can hamper fit and accommodating different body sizes though.
Reinforced Surgical Gowns
Specially engineered surgical isolation gowns offer features like:
- Specified zones of optimal barrier protection
- Reinforced seams and hems
- Knit cuffs for coverage and comfort
But surgical gowns come at a price premium. They are overkill for lower-risk scenarios.
The Right Choice Depends
Factors influencing optimal isolation gown style include:
- Fluid exposure risk level
- Cost constraints
- Donning/doffing considerations
- Provider preferences
Matching gown advantages to clinical needs results in the best protective solution.
Common Sizing Options

Finding the right fit is important for isolation gowns to provide proper coverage without impeding movement. Gowns come in standard sizes but also offer sizing flexibility.
Standard Sizing
Many manufacturers size gowns like other apparel:
- Small
- Medium
- Large
- Extra Large
- 2X/3X Large
Standard sizing provides a simpler ordering and stock system. But it may not suit all body shapes optimally.
Custom Sizing
Some gowns come in expanded size options for better fit:
- Numerical sizes like 32, 34, 36, etc.
- Short, regular and tall lengths
Custom sizing improves coverage and mobility but complicates inventory management with more SKUs.
One Size Options
“One size fits most” gowns cater to a wide range of body types. Benefits include:
- Fewer gown options to purchase and stock
- Often feature adjustable/expandable components
- Suitable for visitors who need temporary gowns
One size gowns provide less tailored fit for healthcare personnel though.
Accommodation Using Adjustable Features

Most gown sizes tie or close in ways that enable some size adaptability. Tailoring fit to the individual wearer is key for optimal protection.
With many sizing and adjustment choices available, facilities can outfit personnel with well-fitting isolation apparel.
Care and Maintenance Considerations
To maintain protective performance over time, isolation gowns require proper care and handling. This applies to both disposable and reusable options.
Disposable Isolation Gowns
For disposables, considerations include:
- Avoid excessive folding or crumpling during storage
- Store in a cool, dry place and avoid direct sunlight
- Inspect packaging and gowns periodically for damage
- Follow manufacturer expiration dates for gown stock
- Discard used gowns promptly in designated hazardous waste
Reusable Isolation Gowns
Caring for reusable gowns requires:
- Checking for staining/damage before washing
- laundering separately with proper disinfectant
- Ensuring thorough drying to prevent mildew
- Mending or removing from service if damaged
- Following number of safe reuses recommended
Workplace Handling
In the healthcare setting:
- Stock gowns in and dispense from a clean, dry area
- Prevent contamination of unused stock during storage
- Remove visibly soiled gowns from circulation immediately
Proper care, maintenance, and handling preserves the protective qualities and lifespan of both disposable and reusable isolation gowns.
The Bottom Line
While just one piece of PPE, isolation gowns provide an essential safeguard. Paying attention to gown specifications, quality, and care helps ensure this critical protective barrier remains intact.
Innovations in Isolation Gown Design
As medical apparel technology evolves, new isolation gown designs continue emerging to better protect healthcare personnel. Key innovations aim to enhance barrier effectiveness, improve comfort and use, and address environmental concerns.
Advanced Materials
New gown fabrics and composites include:
- Nanofiber spunbond nonwovens for superior liquid resistance
- Bio-based materials like PLA from renewable sources
- Graphene laminates with exceptional bacterial filtration
These enhance protective qualities while reducing environmental impact.
Strategic Reinforcements
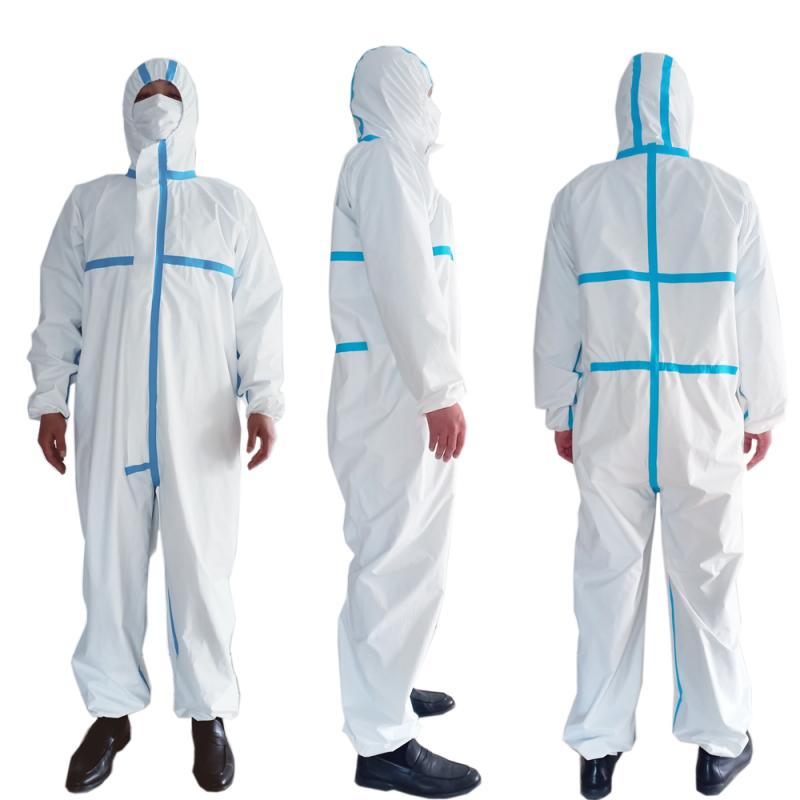

Selectively reinforcing specific zones optimizes gown performance:
- Coated chest panels for maximal fluid protection
- Reinforced hems, seams, and knit cuffs
- Moisture-wicking inner cuff layers
Targeted reinforcements focus protective features where needed most.
Improved Fit and Mobility
New designs provide better freedom of movement:
- Articulated elbows and shoulders
- Athletic-inspired fabrics with 4-way stretch
- Knit fabric waistbands for flexibility
These ergonomic elements help reduce fatigue and improve clinical workflows.
Sustainability
Eco-conscious innovations include:
- Biodegradable and recyclable materials
- Reusable/reprocessable gown models
- Zero-waste manufacturing methods
New isolation gowns protect people and the planet for a better future.

