How do isolation gowns protect healthcare workers. What are the different levels of isolation gowns. Why is polypropylene the preferred material for disposable gowns. How do surgical and non-surgical gowns differ. What are the AAMI standards for isolation gowns. How should isolation gowns be properly used and disposed of. What are the latest advancements in isolation gown technology.
The Evolution and Significance of Isolation Gowns in Healthcare
Isolation gowns have become an indispensable component of personal protective equipment (PPE) in healthcare settings. These disposable garments serve as a crucial barrier between healthcare providers and potential contaminants, effectively preventing the transmission of infections and safeguarding both patients and medical staff.
The history of isolation gowns dates back to the 1970s when they were primarily made of cloth or paper materials. However, as the need for more effective infection control measures grew, disposable options gained popularity due to their enhanced protection and convenience. Today, disposable polypropylene SMS gowns have become the industry standard, offering an optimal balance of protection, comfort, and cost-effectiveness.

What makes SMS gowns so effective?
SMS refers to the three-layered spunbond-meltblown-spunbond nonwoven fabric used in modern isolation gowns. This innovative construction provides an ideal bacterial barrier while maintaining breathability and comfort for the wearer. The outer and inner spunbond layers offer strength and softness, while the meltblown middle layer acts as the primary barrier against fluids and microorganisms.
Understanding the Four Levels of Isolation Gowns
Isolation gowns are categorized into four distinct levels based on the degree of protection they provide. This classification system helps healthcare professionals choose the appropriate gown for specific situations and risk levels.
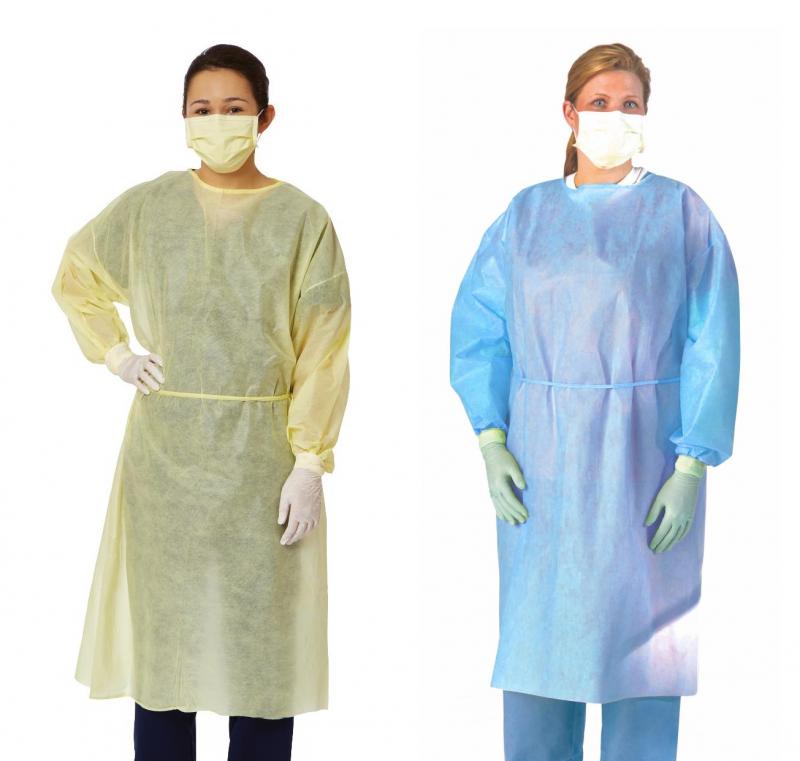
- Level 1: Minimal risk, suitable for basic care of patients without infections
- Level 2: Low risk, designed for protection against blood and body fluid exposure
- Level 3: Moderate risk, offering protection against large splashes of blood or other fluids
- Level 4: High risk, intended for use with hazardous materials and aerosol-transmitted diseases
Among these, Level 2 gowns are the most commonly used in routine patient care settings. They provide 360-degree protection against moderate fluid splashes while maintaining good breathability and comfort for extended wear periods.

What are the key features of Level 2 isolation gowns?
Level 2 disposable isolation gowns possess several important characteristics that make them ideal for everyday use in healthcare environments:
- Constructed with SMS polypropylene material
- Fluid-resistant with a hydrostatic head pressure greater than 20 cm
- Equipped with thumb/finger loops to secure sleeves
- Knit cuffs for enhanced comfort and protection
- Compliant with AAMI PB70 standard for Level 2 barrier performance
Surgical vs. Non-Surgical Isolation Gowns: Key Differences
While both surgical and non-surgical isolation gowns provide Level 2 protection, surgical gowns offer additional features to meet the stringent requirements of operating room environments.
How do surgical gowns differ from non-surgical options?
Surgical gowns are designed with several enhancements:
- Reinforced seams and higher fluid resistance (AAMI PB70 Level 3)
- Extended coverage in the back and under the arms
- Sterile and lint-free construction
- Often available in blue color instead of yellow
These additional features make surgical gowns suitable for use in operating rooms where maintaining a sterile field is critical. Non-surgical gowns, on the other hand, are sufficient for routine patient care in wards, clinics, and other settings where surgical asepsis is not required.

AAMI Standards: Ensuring Quality and Performance
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) plays a crucial role in setting testing methods and performance requirements for medical gowns in the United States. These standards ensure that isolation gowns meet specific criteria for protection and durability.
What are the AAMI requirements for Level 2 gowns?
To comply with AAMI PB70 guidelines, Level 2 gowns must demonstrate a minimum hydrostatic head pressure of 20 cm. This measurement indicates the gown’s ability to resist fluid penetration under pressure, ensuring adequate protection for healthcare workers.
It’s important to note that a higher price does not always equate to better protection. Less expensive gowns from reputable suppliers can meet AAMI standards while providing good value through optimal barriers, strength, and comfort.
Reusable vs. Disposable Isolation Gowns: Weighing the Options
Healthcare facilities must consider various factors when choosing between reusable cloth gowns and disposable options. Both types have their advantages and drawbacks, and the decision often depends on specific institutional needs and priorities.
What are the pros and cons of reusable and disposable gowns?
Reusable gowns:
- Lower long-term costs
- Reduced environmental impact
- Require laundering and storage facilities
- Potential risk of cross-contamination if not properly processed
Disposable gowns:
- Higher initial costs
- Definitive infection control with no reprocessing necessary
- Convenient and time-saving
- Increased waste generation
Factors such as initial cost, convenience, storage space, environmental impact, and infection risks all play a role in determining the best choice for a particular healthcare facility.
Polypropylene: The Material of Choice for Disposable Gowns
Polypropylene has emerged as the preferred material for disposable isolation gowns due to its unique combination of properties that make it ideal for healthcare applications.
Why is polypropylene so well-suited for isolation gowns?
The advantages of polypropylene include:
- Strong yet lightweight and breathable
- Naturally hydrophobic, repelling fluids effectively
- Can be manufactured into fine fibers for excellent bacterial filtration
- Low-linting fabric, reducing contamination risks
- Cost-effective material for large-scale production
These properties allow polypropylene SMS gowns to strike an optimal balance between protection, comfort, and affordability, making them the go-to choice for disposable isolation gowns in healthcare settings.

Proper Usage and Disposal: Maximizing Protection
To ensure the effectiveness of isolation gowns and maintain a safe healthcare environment, proper usage and disposal procedures must be followed meticulously.
How should healthcare workers use and dispose of isolation gowns?
Follow these guidelines for optimal gown usage:
- Select the appropriate level of gown for the specific task or procedure
- Fasten neck and waist ties securely to ensure full coverage
- Overlap the gown with gloves and eyewear to create a complete barrier
- Remove the gown carefully to prevent contamination
- Dispose of the gown immediately after use in designated waste containers
Proper donning and doffing techniques are crucial for maximizing safety. Healthcare workers should be trained in these procedures to minimize the risk of self-contamination during gown removal. Additionally, gowns should be discarded after each patient encounter to prevent the spread of infections between patients.
Innovations in Isolation Gown Technology
As healthcare needs evolve and technology advances, researchers and manufacturers continue to innovate in the field of isolation gowns. These developments aim to enhance protection, improve comfort, and address environmental concerns.

What are the latest advancements in isolation gown technology?
Some recent innovations in disposable gown technology include:
- Enhanced fluid resistance and breathability through advanced material engineering
- Antimicrobial treatments to provide an additional layer of protection
- RFID tags for improved inventory management and tracking
- Development of environmentally sustainable materials to reduce ecological impact
- Improved gown designs for better coverage and ease of use
These advancements reflect the ongoing efforts to enhance the performance of isolation gowns while addressing the evolving needs of healthcare professionals and environmental concerns.
How do antimicrobial treatments enhance gown effectiveness?
Antimicrobial treatments applied to isolation gowns can provide an additional layer of protection by actively inhibiting the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms on the gown’s surface. This feature can be particularly beneficial in high-risk environments or during prolonged wear, helping to reduce the potential for cross-contamination.
The Role of Isolation Gowns in Infection Prevention Strategies
Isolation gowns play a crucial role in comprehensive infection prevention strategies within healthcare settings. Their effectiveness in reducing the spread of pathogens highlights the importance of proper selection, use, and disposal of these protective garments.
How do isolation gowns contribute to overall infection control?
Isolation gowns contribute to infection control in several ways:
- Creating a physical barrier between healthcare workers and potential contaminants
- Reducing the risk of cross-contamination between patients
- Protecting healthcare workers’ clothing from contamination
- Serving as a visual reminder of infection control practices
- Complementing other PPE components for comprehensive protection
When used in conjunction with proper hand hygiene, gloves, masks, and other protective equipment, isolation gowns form an integral part of a multi-faceted approach to infection prevention in healthcare facilities.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability Efforts
As the use of disposable isolation gowns continues to increase, concerns about their environmental impact have prompted efforts to develop more sustainable solutions.
How are manufacturers addressing the environmental impact of disposable gowns?
Several initiatives are underway to mitigate the environmental footprint of isolation gowns:
- Development of biodegradable or compostable gown materials
- Implementation of recycling programs for polypropylene gowns
- Exploration of reusable gown options with improved infection control properties
- Optimization of manufacturing processes to reduce waste and energy consumption
- Research into alternative, eco-friendly materials that maintain protective properties
These efforts aim to balance the critical need for effective infection control with growing environmental concerns, paving the way for more sustainable healthcare practices in the future.
Training and Education: Ensuring Proper Use of Isolation Gowns
The effectiveness of isolation gowns in preventing infections relies heavily on proper use by healthcare personnel. Comprehensive training and education programs are essential to ensure that staff members understand the importance of correct gown selection, donning, and doffing procedures.

What should be included in isolation gown training programs?
Effective training programs for isolation gown use should cover:
- Understanding the different levels of gowns and their appropriate applications
- Proper techniques for donning and doffing gowns to prevent contamination
- Recognition of when gown changes are necessary during patient care
- Correct disposal procedures and infection control practices
- The role of isolation gowns in overall infection prevention strategies
Regular refresher courses and competency assessments can help maintain high standards of gown usage and contribute to a safer healthcare environment for both patients and staff.
The Future of Isolation Gowns in Healthcare
As healthcare continues to evolve, so too will the design and application of isolation gowns. Future developments are likely to focus on enhancing protection, improving comfort, and addressing environmental concerns.
What trends are shaping the future of isolation gowns?
Several trends are influencing the future direction of isolation gown development:

- Integration of smart technologies for real-time monitoring of gown integrity
- Development of reusable gowns with advanced antimicrobial properties
- Customization of gowns for specific medical procedures or environments
- Exploration of nanotechnology to enhance barrier properties
- Increased focus on ergonomic designs to improve wearer comfort and mobility
These advancements aim to create isolation gowns that not only provide superior protection but also address the practical needs of healthcare workers and the growing emphasis on sustainability in medical practices.
As research continues and technology progresses, isolation gowns will undoubtedly play an increasingly sophisticated role in infection prevention strategies. Healthcare facilities must stay informed about these developments to ensure they are utilizing the most effective and appropriate protective equipment for their staff and patients.
Introduction to Isolation Gowns and Their Importance
Isolation gowns are a critical form of personal protective equipment (PPE) used in healthcare settings. These disposable gowns create a barrier between the wearer and potential contaminants, preventing the transmission of infections and keeping both patients and providers safe. Understanding the different types, levels, materials, and proper usage of isolation gowns is key for effective infection control.
Isolation gowns first came into widespread use in the 1970s and were initially made of cloth or paper materials. Disposable options became more common over time as they offered greater protection and convenience. Today, disposable polypropylene SMS gowns are the most prevalent. SMS refers to the three layered spunbond-meltblown-spunbond nonwoven fabric, which provides an ideal bacterial barrier.
The Different Levels of Isolation Gowns
Isolation gowns are categorized into four levels according to the degree of protection they provide:
- Level 1 – Minimal risk, for basic care of patients with no infections
- Level 2 – Low risk, for blood and body fluid exposure
- Level 3 – Moderate risk, for large splashes of blood/fluids
- Level 4 – High risk, for hazardous materials and aerosol-transmitted diseases
Level 2 gowns are the most commonly used option in routine patient care. They provide 360-degree protection against moderate fluid splashes with good breathability and comfort for prolonged wear.
Key Properties of Level 2 Isolation Gowns
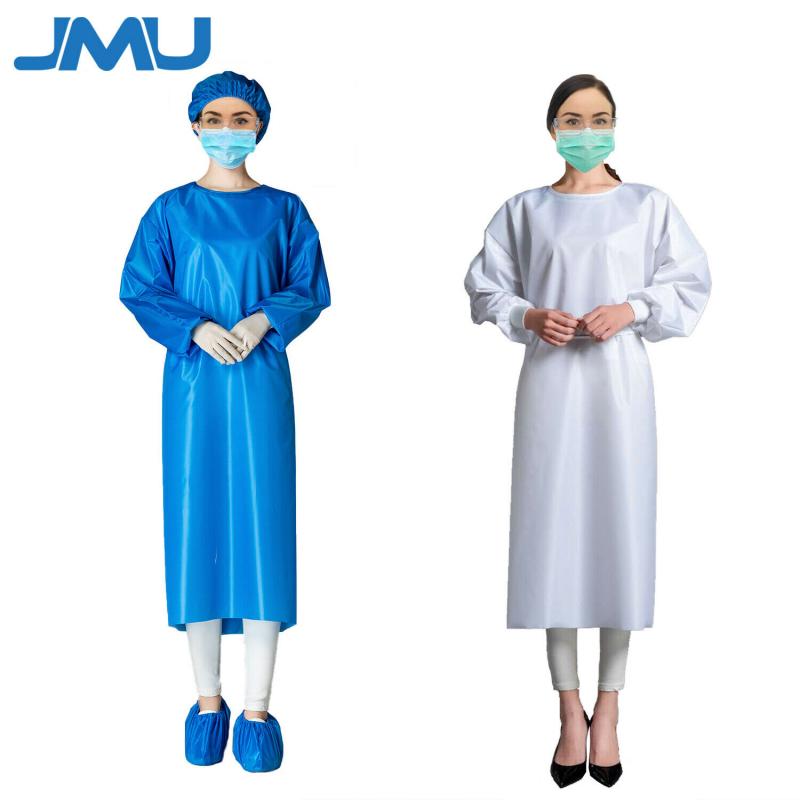

Level 2 disposable isolation gowns have several important features:
- Constructed with SMS polypropylene material
- Fluid resistant with hydrostatic head pressure >20 cm to resist fluid penetration
- Thumb/finger loops to anchor sleeves
- Knit cuffs for comfort and protection
- Meets AAMI PB70 standard for level 2 barrier performance
The spunbond outer and inner layers provide strength and softness. The meltblown middle layer acts as the barrier against fluids and microorganisms. The gown construction fully covers the arms and bodice front and back.
Differences Between Surgical and Non-Surgical Gowns
While both surgical and non-surgical isolation gowns provide level 2 protection, surgical gowns offer some additional features:
- Reinforced seams and higher fluid resistance (AAMI PB70 Level 3)
- Extra coverage in the back and under the arms
- Sterile and lint-free
- Often blue color instead of yellow
Surgical gowns are worn in the OR. Non-surgical gowns are sufficient for routine patient care in wards, clinics, and other settings where surgical asepsis is not required.
AAMI Standards for Performance
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) sets testing methods and performance requirements for medical gowns in the United States. AAMI Level 2 gowns must demonstrate a minimum hydrostatic head pressure of 20 cm to pass AAMI PB70 guidelines.
Higher price does not always mean better protection. Less expensive gowns from reliable suppliers can meet AAMI standards while providing good value through optimal barriers, strength, and comfort.
Reusable vs. Disposable Gown Options
Both reusable cloth and disposable isolation gowns have pros and cons:
- Reusable gowns cost less over time but require laundering and risk cross-contamination.
- Disposable gowns are more expensive but offer definitive infection control with no reprocessing necessary.
Factors like initial cost, convenience, storage space, environmental impact, and infection risks determine the best choice for a particular facility.
Polypropylene Material in Disposable Gowns
Polypropylene is the preferred material for disposable isolation gowns today. Advantages of polypropylene include:
- Strong yet lightweight and breathable
- Naturally hydrophobic to repel fluids
- Can be made into fine fibers for excellent bacterial filtration
- Low-linting fabric
- Cost-effective material
Polypropylene SMS gowns balance protection, comfort, and affordability.
Proper Usage and Disposal
To get the most out of isolation gowns:
- Select the right level of gown for the task
- Fasten neck and waist ties securely
- Overlap gown with gloves and eyewear
- Remove carefully to prevent contamination
- Dispose of immediately after use
Proper donning and doffing techniques maximize safety. Gowns should be discarded after each patient encounter.
The Evolving Technology of Medical Gowns
Some new advances in disposable gown technology include:
- Improved fluid resistance and breathability
- Antimicrobial treatments
- RFID tags for inventory management
- Environmentally sustainable materials
Researchers continue to innovate gown materials and designs to enhance protection and comfort while controlling costs.
Isolation gowns serve a critical infection prevention role. Understanding the levels, properties, and proper use of disposable polypropylene SMS gowns enables healthcare personnel to protect themselves and their patients from dangerous pathogens in a comfortable and cost-effective manner.
Isolation gowns are a critical component of personal protective equipment (PPE) used in healthcare settings. With the spread of infectious diseases like COVID-19, the use of disposable isolation gowns has become increasingly important for infection control. But not all gowns provide the same level of protection. Understanding the different ANSI/AAMI levels of disposable isolation gowns can help healthcare facilities choose the right gown for their needs.
Different Levels of Isolation Gowns (Levels 1-4)
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) has established four levels of performance for protective apparel like disposable isolation gowns, ranging from Level 1 (low barrier) to Level 4 (highest barrier). Higher levels indicate better protection for healthcare workers against the transfer of microorganisms and body fluids.
Level 1 Disposable Isolation Gowns
Level 1 gowns provide the lowest level of protection and are suitable for minimal risk situations. A single use isolation gown or an SMS gown (spunbond-meltblown-spunbond nonwoven fabric) is typically Level 1. These ppe level 2 gowns provide a basic barrier against very light splashes and sprays of body fluids or contaminants.
Level 1 isolation gown level disposable gowns are commonly used for basic care of patients without active bleeding or drainage. Procedures such as blood pressure checks, injections, collecting urine samples, or reading vitals would call for a Level 1 gown.
Level 2 Disposable Isolation Gowns

Level 2 sms isolation gowns provide a moderate barrier for low to moderate risk situations. These level 2 disposable gowns are meant for procedures where there is a bit more fluid exposure, though not a high spray or splash risk. This could include things like insertion of IVs or catheters, or any direct patient care.
Level 2 gown disposable isolation gowns may also be worn when caring for patients on contact precautions when pathogens are spread by direct or indirect contact. A non surgical isolation gowns or ppe yellow gown would provide sufficient coverage and protection.
Level 3 Disposable Isolation Gowns
Level 3 gowns feature the best balance of protection and durability. These disposable ppe gowns provide substantial coverage and offer a high barrier against splashes and sprays of fluids. Moderate to high fluid exposure risk calls for a Level 3 gown.
Medical disposable gowns meeting Level 3 standards would be worn for surgeries or invasive procedures. Cloth isolation gowns are also rated Level 3 and can withstand the rigors of laundering and reuse.
Level 4 Disposable Isolation Gowns
Level 4 gowns provide maximum protection against blood, body fluids, and pathogens. These specialized disposable blue gowns must meet the highest barrier protection standards.
Situations that demand Level 4 include major surgery, trauma care, or any procedure where heavy volumes of fluid exposure is likely. Aami level 2 isolation gowns and disposable surgery gowns would meet this level of protection.
A Level 4 disposable gown like certain level 2 surgical gowns is often paired with a face shield for critical procedures. These disposable gowns represent the highest level of disposable apparel protection available.
Choosing the Right Disposable Isolation Gown
Healthcare facilities need to provide the appropriate level of protective apparel for specific tasks and risks. While disposable options at each level serve a purpose, Level 3 gowns emerge as the most versatile choice suitable for a wide range of medical procedures.
Popular options like polypropylene isolation gowns offer the durability of a reusable gown with the convenience of disposables. Disposable barrier gowns with reinforced seams also withstand the demands of frequent use.
For more hazardous situations, a level 4 isolation gown, medical gowns level 2, or ppe isolation gown would be prudent. Blue isolation gowns are a common color for maximum protection disposable gowns.
While gown level dictates the barrier protection, there are other factors to consider as well.
- Comfort – Does the gown move with the wearer to prevent self-contamination?
- Coverage – Does the disposable gown provide full coverage of arms and body front?
- Donning/doffing – Is the gown easy to put on and remove properly?
- Fit – Does the gown provide optimal fit for the intended user?
The COVID-19 pandemic put a spotlight on the critical role of proper PPE in infection control. With limited reusable gown inventory, many facilities turned to disposable isolation gowns near me to meet the surge demand. Both protective gowns ppe and standard disposable gowns for patients became heavily utilized to prevent spread.
While cloth and reusable gowns are ideal when supply allows, disposable isolation gowns prove indispensable for flexibility and immediate protection. Keeping stock on hand of different disposable isolation gowns near me ensures healthcare staff have the right protective apparel when it matters most.
Key Features of Level 2 Isolation Gowns
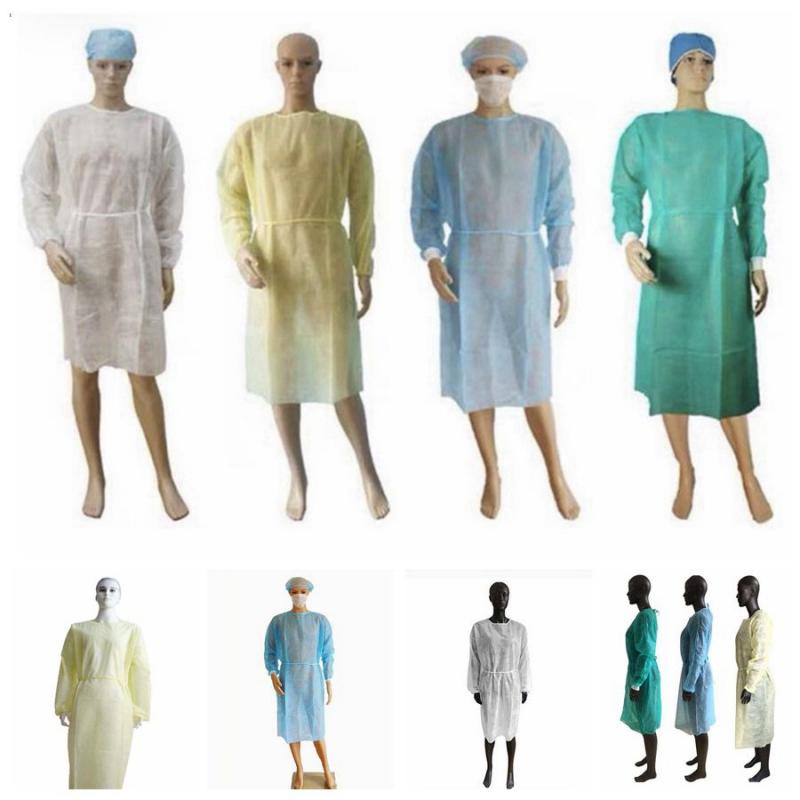

Personal protective equipment (PPE) like isolation gowns are essential for keeping healthcare workers safe while caring for patients. Not all gowns offer the same level of protection though. Level 2 isolation gowns provide moderate barrier protection and are commonly used for basic care of COVID-19 patients, as well as other isolation precautions.
Here are some key features of disposable Level 2 isolation gowns:
- Made of lightweight fabric like spunbond-meltblown or polypropylene to provide breathability.
- Seams are sewn and bound or taped for added strength.
- Full sleeve coverage with fitted cuffs at wrists.
- Closed front with ties or back closure.
- Provides moderate barrier protection against fluid penetration.
- Meets or exceeds AAMI PB70 standard for level 2 barrier performance.
- Single-use for one wear only.
- Available in standard and extra-large sizing to get the right fit.
- May have knit cuffs or elastic wrists for comfort and protection.
- Optional thumb loops to anchor sleeves while working.
- May be fluid resistant, fluid proof, or neither (AAMI level 2 minimum).
Level 2 isolation gowns are the workhorse disposable gowns for many healthcare environments. They balance breathability and comfort with protective features to aid compliance. Proper donning, fit, and doffing enhances the level of protection as well. Many facilities provide disposable level 2 isolation gowns as part of routine PPE along with gloves, masks, and eye protection.
These moderate barrier disposable gowns help create a safer environment for healthcare personnel to interact closely with patients. They also reassure patients that precautions are being taken for their safety. Having the proper protective apparel is an important factor in keeping contagious illnesses contained. Healthcare workers can focus on providing care when they feel confident in the safety equipment their facility provides.
Disposable isolation gowns have been heavily utilized worldwide during the COVID-19 pandemic. As PPE supplies ran dangerously low, ability to procure quality level 2 gowns became mission critical. While cloth and reusable gowns play an important role, the majority of isolation gowns in healthcare are still disposable. Manufacturers stepped up production while ensuring they could still meet key standards like AAMI PB70 guidelines.
Many facilities had to implement crisis capacity protocols when PPE was severely limited. But as supply chains stabilize, proper use of disposable level 2 gowns and other PPE is getting back on track. Protocols around extended use and reuse of isolation gowns are also being refined. And new innovations in barrier fabrics and reusable designs continue advancing as well.
Whether used for COVID-19, flu, C.diff, MRSA, or other infectious threats, isolation gowns will remain an essential component of safe care. Disposable level 2 gowns strike an effective balance between safety requirements, cost, and performance. As risks continue evolving, isolation gown technology will keep advancing to protect those who dedicate their lives to protecting ours.
single use isolation gowns,sms gown,ppe level 2 gowns,isolation gown level,sms isolation gowns,level 2 disposable gowns,level 2 gown,non surgical isolation gowns,ppe yellow gown,disposable ppe gowns,medical disposable gowns,cloth isolation gowns,disposable blue gowns,aami level 2 isolation gowns,disposable surgery gowns,level 2 surgical gowns,disposable gowns,polypropylene isolation gowns,disposable barrier gowns,level 4 isolation gown,medical gowns level 2,ppe isolation gown,blue isolation gowns,disposable isolation gowns near me,protective gowns ppe,disposable gowns for patients
AAMI Standards for Medical Isolation Gowns

Personal protective equipment (PPE) like isolation gowns are essential for protecting healthcare workers and patients from the spread of infections in medical settings. With growing concerns around contagious illnesses like COVID-19, there is increased focus on the standards and testing methods used to ensure isolation gowns provide adequate protection.
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) is an organization that develops consensus standards for medical devices, including PPE like isolation gowns. AAMI standards help define minimum performance requirements as well as testing methods to evaluate critical safety attributes.
Levels of Isolation Gowns
AAMI standards classify isolation gowns into four levels based on the gown material’s ability to resist penetration by blood and other potentially infectious fluids:
- Level 1 – Minimal risk, for basic care tasks involving no fluid exposure risk
- Level 2 – Low risk, for basic care tasks with mild fluid exposure risk
- Level 3 – Moderate risk, for invasive procedures with moderate fluid exposure risk
- Level 4 – High risk, for procedures where heavy fluid exposure is likely
Higher gown levels indicate better fluid resistance and are recommended for procedures or situations with greater risk of contamination. For example, a Level 4 gown would be worn when performing surgery, while a Level 1 gown may be suitable for brief patient interaction with no fluid contact.
Material Performance Tests
To receive an AAMI classification, isolation gown materials must meet established criteria in tests evaluating:
- Resistance to fluid penetration – Synthetic blood is pressed against the material using standard test methods and pressures. No fluid leakage can occur.
- Resistance to microbial penetration – The material is challenged with a viral microbe to assess if pathogens could breach the material when exposed to fluid.
- Resistance to abrasion – The material is subject to rubbing forces to determine durability and assess if abrasion could compromise fluid resistance.
- Tensile strength – Forces are applied to test if the material will tear or rip when stressed.
Based on the level of performance in these tests, the isolation gown can be assigned a rating from Level 1 to Level 4 in accordance with AAMI criteria.
Design and Performance Requirements
- Coverage – Gowns must protect all at-risk areas, like arms, torso, and lower legs.
- Sizing – A range of sizes must be available to fit various body shapes and sizes.
- User safety – Gowns cannot be made with materials that may harm the user, like razor-sharp edges.
- Flammability – Gowns must resist ignition and slow the spread of flames.
The gown design must also allow for easy fastening at the neck and wrists so that the healthcare worker can properly secure the gown.
Selecting the Right Isolation Gown

With AAMI standards in place, healthcare facilities can better identify isolation gowns that offer the level of protection needed for specific clinical workflows. Some key points to consider when selecting isolation gowns include:
- Evaluate the anticipated amount of fluid exposure for the planned procedure or patient interaction.
- Consult manufacturers’ product data to match the gown level to the expected risk level.
- Select the right gown type for the task – surgical, cover, or reinforced gowns offer different degrees of coverage and durability.
- Consider characteristics like stretch and breathability for comfort during extended wear.
- Assess features such as thumb loops, extended cuffs, and back closure for ease of use.
Proper isolation gown selection, use, and disposal are all critical for reducing disease transmission risks. With AAMI standards guiding gown design, production, and testing, healthcare providers can have greater confidence that isolation gowns will perform as expected to help protect staff and prevent infections.
Disposable isolation gowns serve a vital role in infection control across healthcare settings. These single-use garments provide barrier protection from biological contaminants for both medical personnel and patients. Understanding key considerations around disposable gown selection, proper use, and standards compliance is essential for facilities seeking to optimize isolation gown effectiveness.
Types of Disposable Isolation Gowns
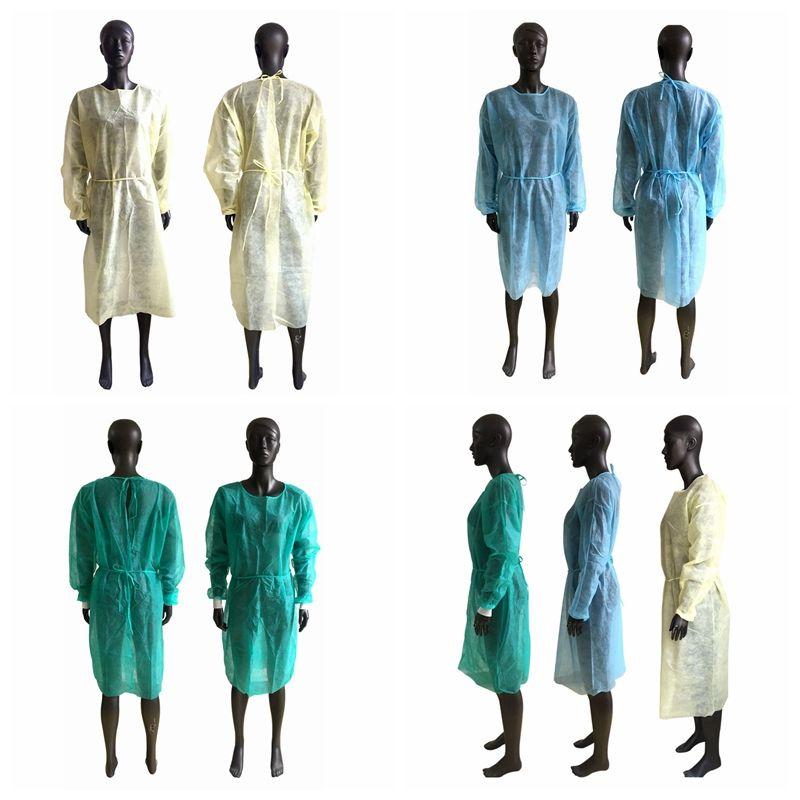

Disposable isolation gowns are available in a range of materials, configurations, and sizes to meet different clinical needs:
- SMS gowns – Made of spunbond-meltblown-spunbond nonwoven polypropylene, offering a breathable option for basic isolation needs.
- Polyethylene gowns – Offer durability and excellent fluid resistance but can be hot to wear for long periods.
- Non-woven polyester gowns – Provide breathability and comfort for extended wear.
- Reinforced/surgical gowns – Designed with extra material in critical areas for high fluid exposure during surgeries or trauma care.
Disposable gown construction can also vary, with options like back-fastening or side-fastening gowns, sleeve and neck closure types, and enhanced coverage around wrists and arms.
Selecting the Appropriate Gown Level
Healthcare organizations should choose disposable isolation gowns rated to the appropriate level for the intended use:
- Level 1 – Minimum risk exams where there is no fluid exposure expected.
- Level 2 – Procedures with low fluid volumes such as drawing blood or giving injections.
- Level 3 – Moderate risk situations involving larger fluid volumes or potential splashes.
- Level 4 – High fluid exposure procedures where heavy liquid staining is expected.
Referencing AAMI standards helps define the right protective level needed. Proper gown selection reduces transmission risks for both healthcare personnel and patients.
Proper Usage Guidelines
- Select the correct size to allow for full coverage without impairing movement.
- Fasten the gown securely at the neck and waist to prevent any openings.
- Put on the isolation gown before entering the patient care area.
- Use appropriate hand hygiene practices before and after gowning.
- Take care not to contaminate sleeves and outer surface when reaching for supplies.
- Remove gown slowly by pulling at the neck and rolling the dirty outer surface inward.
- Dispose of used gowns promptly in designated contaminated waste bins.
Following usage and disposal guidelines is vital for reducing transmission risks when wearing isolation gowns.
Standards and Regulations
Key standards and guidelines apply to disposable isolation gowns:
- FDA product codes cover surgical isolation gowns (FQH) and nonsurgical isolation gowns (OYZ) for marketing and regulation.
- AAMI PB70 standard classifies liquid barrier performance levels from 1 to 4.
- ANSI/AAMI PB70 standard establishes quality assurance and performance requirements.
- OSHA recommends isolation gowns for avoiding bloodborne pathogen exposure under 29 CFR 1910.1030.
Selecting disposable isolation gowns that properly conform to current standards helps provide healthcare personnel with suitable protection during patient care while supporting regulatory compliance.
The Importance of Disposable Isolation Gowns
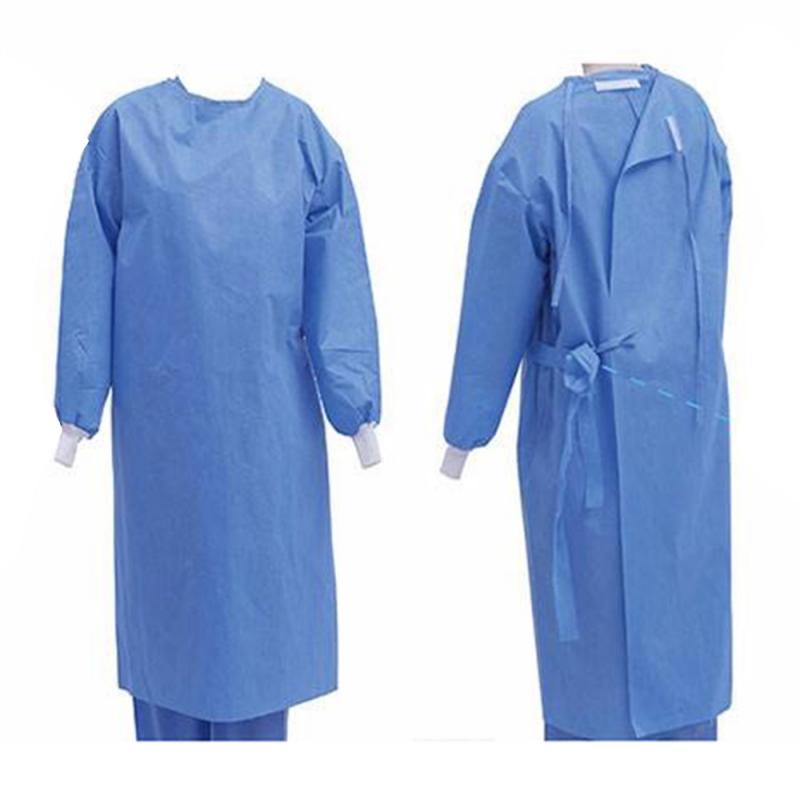
When used correctly, disposable isolation gowns provide critical barrier protection and can prevent the transmission of infectious diseases in healthcare environments. Key benefits provided by disposable gowns include:
- Offer effective fluid-resistant coverage of clothing and skin.
- Help avoid direct contact contamination from biological fluids and pathogens.
- Provide complete coverage of arms and body front for standard isolation precautions.
- Reduce the risk of infectious disease transfer between patients and healthcare personnel.
- Support quick and frequent gown changes between patient contacts.
- Facilitate easier disposal compared to reprocessing reusable gowns.
With vigilant disposable isolation gown selection, usage, and disposal, healthcare organizations can better safeguard against transmission of infectious illnesses in patient care settings.
Pros and Cons of Disposable vs. Reusable Gowns
Medical gowns are a critical piece of personal protective equipment for healthcare workers. Facilities must choose between disposable isolation gowns for one-time use or reusable cloth gowns that can be laundered and reused. There are important trade-offs to consider when selecting between disposable and reusable options.
Disposable Gown Advantages

Disposable isolation gowns offer several benefits:
- Provide guaranteed protection – Each gown is worn only once, avoiding reuse risks.
- Facilitate rapid gown changes between patients to limit cross-contamination.
- Reduce laundry facilities needed since no reprocessing is required.
- Prevent improper laundering issues that could lead to cross-contamination.
- Eliminate gown deterioration and tearing over time with reuse.
- Offer consistent and reliable level of protection with each new gown.
- Provide a cooler option for healthcare workers compared to cotton fabrics.
The single-use nature of disposable gowns ensures a fresh protective barrier with each patient encounter to limit transmission risks.
Disposable Gown Disadvantages
There are some downsides to consider with disposable isolation gowns:
- Generate large volumes of healthcare waste needing disposal.
- Lead to higher overall costs over time compared to reusable options.
- Require careful gown sizing to get a proper fit for adequate coverage.
- Can be less durable and prone to tearing if quality standards aren’t met.
- Don’t permit a custom fit like tailored reusable gowns allow.
While disposable gowns provide infection control benefits, the trade-off is greater waste generation and expense over time.
Reusable Gown Advantages
Reusable isolation gowns offer some unique benefits:
- Lower environmental impact by reducing total waste produced.
- Lower overall long-term costs through repeated laundering and reuse.
- Allow custom-fit tailoring for better coverage and mobility.
- Made of cotton or polyester materials, providing user comfort.
- Can be designed with antimicrobial treatments to enhance protection.
- May be more durable than disposable options.
With proper care and handling, reusable gowns can offer years of use at lower overall expense and waste output.
Reusable Gown Disadvantages
Reusable gowns also have some limitations to consider:
- Carry risk of transferring pathogens if improperly laundered between uses.
- Fibers can degrade over time, reducing liquid barrier effectiveness.
- Cotton reusable gowns are hotter than disposable options.
- Require proper on-site laundry facilities and processes.
- Must be inspected and taken out of use when damaged.
- Higher upfront purchase cost per gown than disposables.
To mitigate risks of contamination, reusable gown programs require stringent oversight and control measures from handling to washing.
Key Factors in Selecting Gown Type

Choosing between disposable and reusable isolation gowns involves assessing:
- Available laundry, staffing, and quality control resources.
- Ability to separate contaminated gown processing from other linens.
- Clinical risks and consequences associated with potential cross-contamination.
- Upfront costs versus long-term cost savings with reusable gowns.
- Waste disposal capacity and sustainability initiatives targeting waste reductions.
For maximum infection control, disposable gowns provide guaranteed barrier protection for each use. Reusables may offer advantages related to sustainability and long-term costs but require diligent oversight.
Best Practices for Gown Programs
To optimize isolation gown use, healthcare facilities should:
- Train clinical staff on proper selection, use, and disposal for the gown type chosen.
- Have defined policies for what gown level is required for various types of interactions.
- Routinely inspect reusable gowns for damage and track useful life.
- Adhere strictly to laundering requirements if using reusable gowns.
- Audit and monitor gown use practices regularly.
- Consider using both reusable and disposable options depending on risk levels and tasks.
With clear procedures and quality oversight, both disposable and reusable gown programs can provide much-needed barrier protection within healthcare settings.
The Importance of Isolation Gowns

Isolation gowns are a foundational component of personal protective equipment for healthcare personnel. Whether following a disposable or reusable model, facilities must provide access to functional gowns meeting AAMI standards. This critical protective gear limits the spread of infections, safeguards patients, and reduces safety risks for frontline healthcare workers.
Polypropylene Material Used in Disposable Gowns
Disposable isolation gowns are a key piece of personal protective equipment used across healthcare settings. Many disposable gowns utilize polypropylene as the primary material to offer an effective fluid barrier. Understanding the properties and manufacturing of polypropylene provides useful insight into disposable gown construction and performance.
What is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer made from the monomer propylene. As a plastic, it can be melted and reformed into different shapes. Key traits of polypropylene include:
- Resistance to fatigue and flexing
- Low density and weight
- Resistance to chemical solvents and acids/bases
- Withstands sterilization by autoclaving, gamma radiation, etc.
- Low moisture absorption
- Resistance to staining from fluids and microbes
These attributes make polypropylene a fitting material for manufacturing disposable medical gowns.
Use in SMS Gowns
A common disposable gown construction uses an SMS material structure. SMS stands for:
- S – Spunbond polypropylene
- M – Meltblown polypropylene
- S – Spunbond polypropylene
Spunbond polypropylene forms a strong, durable fabric. Meltblown polypropylene creates a filtration layer to inhibit fluid movement. Combined into an SMS composite, the material offers breathability and high fluid barrier performance perfect for disposable gowns.
Manufacturing Process
Polypropylene gown materials follow a meltblown extrusion fabrication process:
- Polymer resin pellets are loaded into an extruder.
- The extruder melts the pellets at temperatures around 500°F.
- The molten plastic is forced through small nozzles surrounded by high velocity air.
- The fast-moving air draws the extruded plastic into extremely fine filaments.
- The filaments land and bond on a collecting belt, forming a nonwoven web.
- The spunbond and meltblown webs are stacked and thermally bonded into the final SMS material.
This nonwoven fabrication method allows tuning of the gown material’s thickness, weight, and pore size to achieve the right breathability and barrier performance.
Advantages of Polypropylene
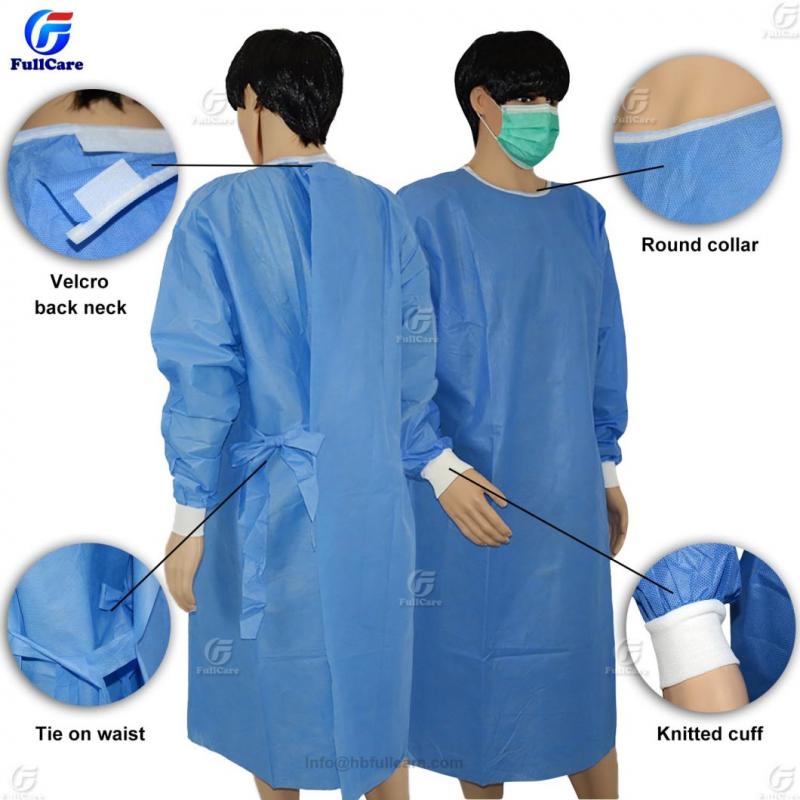
- Provides effective barrier against fluids and pathogens
- Low material density creates lightweight, comfortable gowns
- Breathability allows air circulation and cooling
- Won’t degrade or release chemicals after sterilization
- Resists abrasion during donning and wear
- Stable material properties across a range of storage conditions
Polypropylene’s durability, chemical resistance, and filtering abilities make it an ideal base material for disposable medical gowns.
Limitations of Polypropylene Gowns
While having many strengths, polypropylene also has some limitations including:
- Poor heat resistance – gowns can’t be autoclaved for sterilization
- High flammability requiring added flame retardant chemicals
- Limited stretch and drape compared to fabrics like cotton
- Susceptible to UV radiation degradation over time
- Not as environmentally sustainable as reusable natural fiber gowns
Special care must be taken to protect polypropylene gowns from heat damage during disposal. The material also shares common environmental drawbacks of plastics.
Evaluating Isolation Gown Materials
While polypropylene has advantages for disposable gown construction, other materials like polyethylene and polyester also have benefits. All gown materials should be assessed on properties like:
- Fluid imperviousness and splash protection
- Bursting strength and abrasion resistance
- Comfort and breathability for extended wear
- Environmental stability across storage and use conditions
- Drape, stretch, and ease of mobility
Polypropylene makes an excellent choice given its balanced performance across these metrics of critical importance for isolation gowns.
The Future of Polypropylene Gowns
Polypropylene will continue seeing widespread use in disposable isolation gowns given its proven barrier protection and comfort. However, addressing environmental concerns may require exploring alternative materials like bioplastics or recycled polymers. Continued innovation in isolation gown materials and manufacturing will be crucial for better balancing sustainability and performance.
Yellow PPE Gowns for Contact Precautions
In healthcare settings, patients placed under contact precautions require staff to wear personal protective equipment like gowns and gloves. Yellow disposable gowns are commonly used for contact precaution scenarios to prevent transmitting infectious illnesses between patients and healthcare workers.
Contact Precautions Overview
Contact precautions aim to limit the spread of contagious diseases easily transferred by touch or physical contact. They apply when patients are known or suspected to be harboring certain infectious agents that can contaminate the environment and staff. Common situations requiring contact precautions include:
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
- Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE)
- Candida auris yeast infections
- Norovirus outbreaks
- Multiple drug-resistant bacteria
Under contact precautions, staff must wear a gown and gloves for all interactions involving contact with the patient or their surroundings.
Why Yellow Gowns?

Yellow disposable gowns serve an important visual cue to clearly identify patients needing transmission-based precautions. Seeing the yellow gown prompts staff to take critical infection control steps:
- Puts on gown and gloves before entering room
- Only wears PPE in the isolation room then disposes before leaving
- Uses dedicated disposable equipment when possible
- Disinfects reusable gear before using on other patients
- Practices careful hand hygiene procedures
The yellow color helps reinforce that special handling is required to prevent spreading contagious illnesses.
Gown Features and Materials
Disposable yellow isolation gowns offer robust barrier protection thanks to features like:
- Water-resistant spunbond-meltblown fabrics
- Reinforced stitches along seams
- Knit cuffs with elastic wrists
- Attached thumb loops
- Full back closure with ties
- Extended neck and waist ties
- AAMI Level 2 or 3 barrier performance
Materials like polypropylene and polyethylene provide fluid resistance while knit components enhance comfort and mobility.
Proper Gown Use and Disposal

- Select the proper size gown for full coverage
- Fasten neck and waist ties securely
- Ensure cuffs fit snugly over wrists
- Use gowns only in designated isolation area
- Remove slowly and carefully to avoid contamination
- Dispose of gowns in infectious waste containers
Following protocol prevents carrying pathogens outside the isolation environment.
Advantages of Disposable Yellow Gowns
- Visual cue reinforces need for enhanced precautions
- Fluid-resistant construction provides barrier protection
- Easy disposal reduces transmission risks
- Lightweight materials improve comfort
- Allow quick gown changes between patients
- Eliminate need to reprocess contaminated reusable gowns
Yellow disposable gowns make following contact precaution requirements simpler for hospital staff.
Potential Limitations
- More expensive than reusable options long-term
- Generate extra healthcare waste for facilities
- Often made of plastics like polypropylene rather than sustainable fabrics
- Can feel impersonal to patients
- Require proper gown sizing to achieve full coverage
While very useful for infection control, disposable yellow gowns share some common environmental and cost concerns with medical plastics.
Maximizing Yellow Gown Effectiveness
- Provide staff training on proper contact precaution procedures
- Have defined policies guiding use of yellow gowns
- Store gowns properly to avoid damage or deterioration
- Audit and monitor contact precaution compliance
- Use gowns as part of a comprehensive infection prevention program
Combining visual indicators like yellow gowns with rigorous processes helps enhance contamination prevention and mitigate risks during contact precaution scenarios.
Isolation Gowns: How Are Disposable Gowns Keeping Us Safe?
Blue Disposable Patient Gowns vs. Hospital Gowns
Personal protective equipment (PPE) has become an essential part of healthcare and frontline work during the COVID-19 pandemic. One key piece of PPE is the isolation or surgical gown, designed to provide an extra barrier against pathogens and prevent contamination. Healthcare facilities typically use two main types of isolation gowns: reusable cloth hospital gowns and disposable paper or plastic gowns. Disposable gowns have become more prevalent in recent years due to their convenience and ability to help control infections. But how do disposable patient gowns compare to traditional hospital gowns when it comes to safety and effectiveness?
Disposable isolation gowns are designed for single use only and then discarded after care of each patient. They are constructed using materials like spunbond-meltblown-spunbond (SMS) polypropylene, which creates a breathable yet fluid-resistant barrier. Some key advantages of disposable gowns include:
- Helps reduce risk of cross-contamination between patients compared to reusable gowns
- Provides constant barrier protection with each new gown
- Wide range of styles for different medical procedures and risk levels
- Can be easily disposed of after use following proper protocols
- Often made to be lightweight and comfortable for extended wear
Standard reusable hospital gowns are made from cotton, polyester blends or treated polyester. They are laundered after each use and reused. Benefits of cloth hospital gowns include:
- More durable and cost-effective over multiple uses
- May be more breathable and comfortable for patients
- Can be customized with hospital logos or designs
However, reusable gowns carry a higher risk of retaining and spreading pathogens if laundry procedures are not followed properly. The CDC recommends disposable gowns as the safest option, especially when interacting with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients. Disposable gowns are also preferred for sterile procedures, high splash risk situations, and when working with immunocompromised patients.
Types of Disposable Isolation Gowns
Disposable isolation gowns fall into different categories based on their construction, fabric, and level of protection:
- Level 1 – Basic fluid resistance for minimal risk situations
- Level 2 – More fabric weight and coating for moderate fluid exposure
- Level 3 – Highest liquid barrier with coated fabric and sleeves
- Level 4 – Meet highest standards for surgical gowns
Level 1 disposable gowns provide baseline protection for routine patient interaction. They have basic fluid repellency rated at a hydrostatic pressure of at least 10 cm to resist water-based splashes or sprays. Level 2 gowns offer more moderate barrier protection, with coated or laminated fabric tested at a hydrostatic pressure of at least 20 cm.
Higher tiers like Level 3 feature coated sleeves and closures to prevent fluid penetration through often contaminated areas. Level 4 surgical gowns are sterilized and used for sterile procedures. When selecting isolation gowns, workers should assess the level of precautions needed based on anticipated exposure to blood, bodily fluids, or pathogens. Those performing invasive medical procedures may need Level 3 or 4 gowns, while Level 1 or 2 is appropriate for routine care.
Proper Use of Disposable Gowns
To get the most protection from disposable isolation gowns:
- Select the right gown level for the procedure
- Ensure proper size for good coverage
- Fasten neck and waist ties securely
- Pull gown away from body before removing to avoid contamination
- Remove carefully by rolling inside-out and avoid shaking
- Dispose of used gowns properly in designated containers
It’s important that disposable gowns are put on and taken off correctly to reduce risk. Gowns should fully cover the torso, arms, back and legs as needed. Ties must be fastened snuggly to prevent exposure while working. When doffing, workers should first pull the gown forward and away from the body without disturbing the outer contaminated surface. Sleeves should be pulled inside-out and the gown rolled into a bundle for safe disposal or laundering if reusable. Proper PPE techniques, hand hygiene and disinfecting surfaces are also critical for health and safety.
The Importance of PPE in Infection Control
Disposable isolation gowns are a fundamental piece of personal protective equipment for healthcare workers. Along with gloves, masks, respirators and eye protection, gowns provide an essential barrier against infectious diseases and contamination. During an outbreak like COVID-19, proper use of disposable gowns is one strategy facilities employ to limit the spread. Medical grade disposable gowns certified to FDA and AAMI standards can give staff confidence when treating sick patients. While PPE shortages have complicated pandemic response, increased production and new innovations in gown construction are helping meet the high demand. Ultimately, disposable isolation gowns are a prime example of how medical technology continues to evolve to address emerging risks. Proper use of disposable gowns and other PPE based on current guidelines remains key for protecting both healthcare personnel and the patients in their care.
Isolation gowns are a critical component of personal protective equipment (PPE) utilized by healthcare workers. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for disposable isolation gowns skyrocketed, leading to significant shortages. This shone a spotlight on the debate between disposable vs. cloth options. When considering isolation gowns, healthcare facilities must weigh factors like cost, availability, sustainability, comfort, and protection.
Cloth Isolation Gowns vs. Disposable Options
Disposable isolation gowns are the dominant choice in most healthcare settings today. These gowns are made from synthetic materials like polypropylene which provide an impermeable barrier against fluids and contaminants. Disposable gowns are designed for single use, after which they are disposed of. This eliminates concerns about laundering and reuse. Disposable options from reputable manufacturers generally provide adequate protection according to FDA standards. However, extensive reuse during PPE shortages has raised some doubts about durability and barriers breaking down over time.
Cloth isolation gowns, usually made of cotton or cotton-blend fabrics, were more commonly used in healthcare facilities prior to the advent of disposables. Reusable cloth gowns can be laundered and sterilized for repeated uses. Cloth lacks the impermeable barrier of synthetics, but can provide adequate protection when combinations of materials are used, such as in SMS gowns (non-woven spunbond-meltblown-spunbond polypropylene). However, after repeated laundering and sterilization cycles, cloth gowns are more likely to degrade and lose protective properties compared to disposable options. Maintaining a sufficient inventory of cloth gowns to allow for laundry turnover can also be logistically challenging for facilities.
Factors to Consider
When deciding between cloth and disposable isolation gowns, administrators need to weigh several factors:
- Cost – Disposables often cost more per gown, but reuse and laundering cloth gowns incur significant hidden costs.
- Availability – Disposables may be more readily available, while cloth has inventory constraints.
- Protection – Both can offer adequate barrier protection if proper materials and quality standards are met.
- Comfort – Clinicians often report preferring cloth over disposables for better air circulation.
- Convenience – Disposables require no laundering or sterilization procedures.
- Waste – Disposables produce more waste compared to reusable cloth gowns.
- Compliance – Disposables guarantee single use for infections control.
The Case for Disposable Isolation Gowns
Healthcare facilities have almost universally transitioned to disposable isolation gowns in recent decades for good reason. Disposables offer some clear benefits:
- Reliable impermeable synthetic barrier against infectious fluids.
- No concerns about loss of protection with reuse over time.
- Convenient single-use with no laundering required.
- Easily sourced from a range of manufacturers.
- Uniform quality and protection standards.
- Guaranteed sterile right out of the package.
- Allows facilities to provide personal gowns to staff.
- Avoids cloth inventory management challenges.
- Wide selection of sizes and styles for preferences.
These advantages explain the ubiquity of disposable gowns in hospitals today. They alleviate many of the logistical headaches of maintaining cloth gown inventories. Disposables also provide reliable protection shift after shift. For clinicians, disposable gowns mean always having sterile protection available when interacting with infectious patients. However, disposable gowns come with environmental costs due to plastic waste. They also suffered severe shortages during COVID-19 as supply chains were disrupted.
The Remaining Case for Cloth Isolation Gowns
While cloth isolation gowns have been mostly phased out, some arguments remain for their use:
- Much lower environmental impact without plastic waste.
- Potentially lower long-term costs taking laundering into account.
- Less prone to supply chain shortages.
- Reusability makes them ideal emergency backup option.
- Often greater durability and withstands abrasion.
- Usually more breathable and air-permeable for comfort.
- Cotton and cotton blends have natural antibacterial properties.
Healthcare administrators evaluating isolation gown options should still consider the potential benefits of reusable cloth gowns. While disposables are generally more convenient and readily available, cloth gowns hedge against supply shortages. Therequisite laundry operations also provide jobs. And eliminating single-use plastic gown waste is an environmental consideration. Facilities with in-house laundry operations could potentially realize cost savings from reusable cloth over time. However, to ensure proper protection, cloth gowns require stringent oversight on laundering, inspection for defects, and retirement criteria.
The Verdict
When all factors are weighed, disposable isolation gowns are the right choice for most healthcare facilities today. Their impermeable synthetic barriers provide essential protection for frontline staff against infectious fluids. Disposable gowns mitigate concerns about reuse, laundering, and inventory management associated with cloth alternatives. The convenience, reliability, availability, and quality control of disposables make them the standard for good reason. However, reusable cloth isolation gowns still have a place as an emergency backup option not subject to supply chain shortages. Prudent facilities should maintain a small inventory of cloth gowns for contingency planning. And for those with the resources to properly launder, inspect, and cycle reusable cloth gowns, they remain a reasonable choice with environmental benefits to consider.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an unprecedented demand for disposable isolation gowns in healthcare settings. As PPE supplies ran short, facilities struggled to find available gowns, let alone affordable options. Now that supply has stabilized, buyers need dependable sources for quality gowns at reasonable prices. Factors like materials, manufacturing standards, and seller reliability must be balanced against costs when sourcing essential PPE.
Where to Find Affordable Disposable Isolation Gowns
Disposable isolation gowns are a key component of safe PPE protocols and critical for protecting healthcare workers. But with tightened budgets, finding affordable gowns can be a challenge. Here are some strategies for sourcing low-cost gowns without sacrificing quality:
Buy in Bulk Directly from Established Manufacturers
Purchasing gowns in bulk quantities directly from manufacturers provides the best opportunity for lower pricing. Cutting out distributor markups saves significantly. Partnering with domestic manufacturers also provides more supply chain stability. Large group purchasing organizations can negotiate discounted bulk contracts on behalf of hospital networks or state health systems.
Purchase Non-Surgical Isolation Gowns
For routine isolation precautions, less expensive non-surgical gowns provide adequate protection. They have basic fluid barriers but lack the durability and higher AAMI standards of surgical gowns. Reserving surgical gowns for ORs and procedures where greater exposure is anticipated makes purchasing more cost-effective.
Consider Reusable Options
While less convenient, reusable cloth isolation gowns can offer long-term savings over disposables with in-house laundering. Higher initial investments are offset over repeated uses. Make sure proper laundering protocols are established and inspect for wear.
Shop at Medical Supply Distributors
Well-established medical supply distributors can offer competitive pricing on bulk orders of isolation gowns. They often carry their own brands of quality gowns at lower price points. Comparison shop between distributors. Beware excessive markups of brand name gowns.
Purchase Previous Generation Products
Medical gown manufacturers regularly introduce newer upgraded versions. Last generation gowns are often discounted significantly when newer versions debut. Verify that protection levels are still adequate before purchasing older gown lines.
Consider foreign Manufacturers
Importing isolation gowns directly from manufacturers in regions like Asia and Latin America can yield substantial savings. Ensure rigorous quality control and verify responsible manufacturing standards are met.
Monitor for Coupons and Discounts
Keep an eye out for periodic coupons and discounts from major suppliers and distributors. Sign up for newsletters and sales alerts. Special savings deals are sometimes offered for large bulk orders.
Purchase Salvage Products
Lightly damaged or returned isolation gowns deemed still usable are often salvaged and resold at deep discounts. Carefully inspect for any breaches to barrier integrity before purchasing.
Use Group Purchasing Organizations
Joining a group purchasing organization provides leverage to negotiate discounted bulk contracts with manufacturers. This strategy yields lower pricing for smaller facilities pooling demand.
Balancing Cost, Quality, and Availability
The quest for the most affordable isolation gowns never ends for procurement teams. But cost savings must be balanced against product specifications, quality standards, and responsible sourcing. While paying a premium for brand names rarely makes sense, choosing the cheapest gowns without verifying their quality and supply chain could put frontline staff at risk. Take the time to thoroughly evaluate isolation gown options for performance, value, and integrity before purchasing. Prioritizing clinician safety and ethical manufacturing ultimately outweighs chasing every last dollar of savings.
Isolation gowns serve a critical infection control purpose in healthcare settings. By providing a protective barrier, disposable isolation gowns reduce the risks that nurses, doctors, and other clinicians face when interacting closely with potentially contagious patients. Understanding how isolation gowns work to minimize contact and fluid exposure is essential for proper utilization of this crucial PPE.
How Isolation Gowns Protect Healthcare Workers
Isolation gowns are designed to safeguard healthcare personnel against exposure to infectious agents and hazardous fluids. Worn as part of comprehensive PPE, isolation gowns provide multiple layers of protection:
Minimize Contact Transmission
Disposable isolation gowns provide a lightweight, breathable physical barrier between clinicians’ regular uniforms and patients. This first layer minimizes contact transmission of pathogens through touch. Tight-fitting wrists and elastic cuffs ensure gown sleeves don’t contact exposed skin.
Fluid-Resistant Material
Isolation gowns are constructed of fluid-resistant synthetics that provide an impermeable barrier against splashes or sprays of blood, respiratory droplets, or other potentially infectious fluids. Materials like spunbound-meltblown polypropylene repel fluids from penetrating through to clothes or skin.
Full Body Coverage
Proper isolation gowns extend well below the knees, with full sleeve coverage to protect the torso and extremities from exposure. Back closure styles ensure the back remains covered while gowning up.
Proper Sterile Technique
Following proper technique for putting on and removing isolation gowns ensures clinicians remain protected. Gowns are donned with the opening in the back, then secured at neck and waist. Upon removal, gowns are rolled inside-out and disposed of appropriately to contain contamination.
Used With Other PPE
Isolation gowns are always used in combination with gloves, mask, face shield or goggles. Combining protective layers enhances overall barrier effectiveness. Proper sequencing when donning and doffing PPE prevents self-contamination.
Disposed After Single Use
Unlike surgical gowns, isolation gowns are not intended for reuse. After wearing for one patient encounter, disposable isolation gowns are discarded to prevent transferring pathogens. New sterile gowns are donned for each interaction.
Proper Use Critical for Safety
To fully benefit from the protections isolation gowns offer, proper procedures must be rigorously followed each and every time. This includes:
- Selecting the appropriate type and size of isolation gown.
- Inspecting for damage before use.
- Always wearing under standard work attire.
- Securing neck and waist ties for complete coverage.
- Layering with other protective PPE like gloves and mask.
- Keeping gown sleeves from riding up while working.
- Being careful to not dislodge gown when bending over.
- Removing gown slowly with caution to contain contamination.
- Disposing of used gowns properly in infectious waste bins.
- Never reusing single-use disposable isolation gowns.
An Essential Last Line of Defense
Isolation gowns represent the last critical barrier between healthcare workers and infectious threats. When utilized properly alongside other protective gear, disposable isolation gowns contain and shield against exposures. Their impermeable materials and full coverage offer reliable protection shift after shift. Isolation gowns alleviate worries about contamination so clinicians can focus fully on delivering care. While often overlooked, proper use of isolation gowns is fundamental to the safety of all frontline staff.
Isolation gowns are a key component of safe PPE practices in healthcare settings. However, to realize their full protective benefits, proper usage and disposal protocols must be strictly followed. Understanding correct techniques for putting on, wearing, and removing isolation gowns is critical for avoiding inadvertent contamination.
Proper Usage and Disposal of Isolation Gowns
All PPE only works when utilized correctly every single time. Here are best practices for healthcare workers using isolation gowns:
Select Properly Sized Gown
Choose a gown that fully covers from neck to knees without constricting movement. Gowns should have a snug neck and elastic cuffs. Oversized gowns are prone to catch and expose skin. Undersized gowns can tear.
Inspect Before Donning
Examine isolation gown carefully for any holes, fraying, or breaches before putting on. Ensure all ties and fasteners are intact. Discard any gowns with concerning defects.
Put On Gown Correctly
With opening in back, secure neck closure first, then waist ties. Assistance donning gown ensures full coverage. Keep uniform sleeves and undergarments covered by gown.
Layer Appropriately With Other PPE
Gowns always go over regular work clothing but under other PPE like masks and face shields. Proper sequencing prevents contamination while gowning.
Keep Sleeves Rolled Down
Be vigilant that gown sleeves remain fully extended over wrists and any exposed skin during patient care. If sleeves ride up, immediately pull back down.
Take Care When Reaching or Bending
Move cautiously when reaching overhead or bending over to avoid dislodging gown. Have coworkers adjust gown if needed to maintain coverage.
Change Gown if Soiled
Immediately change isolation gown if it becomes contaminated with blood or fluids during use. Safe doffing prevents further exposure while changing.
Remove Gown Slowly and Deliberately
Unfasten ties and peel gown away from body without pulling over head. Roll gown inside-out as remove. Dispose in proper receptacle immediately.
Perform Hand Hygiene After Removal
Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after removing gown. Use alcohol-based sanitizer if soap unavailable. Never reuse single-use gowns.
Proper Disposal Critical for Safety
Used isolation gowns contain infectious hazards and must be discarded properly to avoid transmission risks. Follow these protocols for disposal:
- Dispose of gowns in designated healthcare risk waste bins.
- Never reuse disposable gowns even for same patient.
- Roll or fold gown in on itself when doffing to contain surfaces.
- Keep used gowns away from uniform or skin during removal.
- Double bag if waste bin is not nearby during doffing.
- Designate central regulated medical waste storage area.
- Follow regulated medical waste hauling and treatment.
Scrupulous gown disposal reduces pathogen load on surfaces and protects waste handlers. Combining prudent usage with proper disposal techniques ensures isolation gowns effectively deliver their critical barrier protection.
An Ounce of Prevention
Personal protective equipment fully safeguards only when utilized optimally every time. For disposable isolation gowns, proper usage and disposal procedures enable unfailing protection against hazardous exposures. Taking the extra seconds to gown up, wear, and doff gowns conscientiously eliminates preventable contamination risks. Following best practices preserves the integrity of isolation gowns as the indispensable final barrier defending healthcare workers.
The COVID-19 pandemic put isolation gowns in the spotlight. As PPE shortages disrupted supply chains, manufacturers raced to boost production. This unprecedented demand is driving new innovations to further improve isolation gown protections, convenience, and sustainability.
The Future of Isolation Gown Technology and Design
Isolation gowns are poised for significant advances building upon lessons learned during COVID-19. Here are some future trends and developments on the horizon for disposable isolation gowns:
Enhanced Fluid Resistance and Repellency
Expect new synthetics and material treatments to offer even greater impermeability against splashes, sprays, and droplets. Nanotech coatings may provide radical improvements in fluid resistance and repellency.
Improved Gown Integrity and Durability
New manufacturing techniques will strengthen gown materials against abrasion, catches, and tears during use without compromising comfort and breathability.
Superior Barrier Protections
New proprietary materials and hybrid fabric constructions will heighten contaminant protections for infection control. Some may integrate antimicrobial properties.
Innovative Fit and Fastening
Advances in garment design will optimize isolation gown tailoring, sleeve length, coverage, and closures to enhance range of motion while eliminating gaps.
Reduced Plastic Use
Sustainable manufacturing processes will minimize plastic content of disposable gowns and utilize more eco-friendly biodegradable materials.
Improved Launderability of Reusables
Enhanced cloth isolation gowns designs will better withstand repeated industrial laundering and sterilization while extending usable life cycle.
RFID Inventory Tracking
Embedding gowns with RFID chips will enable real-time inventory management, expiration monitoring, and location tracking to prevent shortages.
Video Instructions and Training
QR codes on gowns will link frontline staff to on-demand video tutorials on proper usage, improving compliance and minimizing misuse.
Usage Sensors and Analytics
Smart gowns may integrate sensors to monitor donning/doffing and transmit data to identify gaps in PPE protocols.
Balancing Innovation with Practicality
While advances driven by the pandemic hold much promise, new isolation gown technology must balance performance with pragmatism. Cost constraints in healthcare cannot be ignored. And unproven features that complicate use or impair core protective functions will face challenges. Any innovations must first do no harm. But by inspiring fresh design perspectives, COVID-19 will leave a lasting mark on the evolution of isolation gowns.

