How do disposable surgical gown materials impact patient and staff safety. What AAMI standards should be considered for surgical gowns. Which fabric properties are crucial for optimal protection. How does gown construction affect safety and comfort. Why is proper gown use and disposal essential for infection control.
The Importance of Disposable Surgical Gown Materials in Ensuring Safe Surgeries
Disposable surgical gowns play a pivotal role in maintaining a sterile environment during surgical procedures. These gowns serve as the final barrier against potentially harmful microorganisms and bodily fluids, protecting both patients and medical professionals. The material used in these gowns is a critical factor in determining their effectiveness.
Selecting the right disposable surgical gown material involves considering various factors to ensure optimal protection. This article explores nine key aspects to consider when choosing surgical gown materials, helping healthcare facilities make informed decisions to enhance safety in the operating room.

Understanding AAMI Standards for Surgical Gown Fabrics
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) has established crucial guidelines for evaluating the protective properties of surgical gowns. These standards are based on the gown’s ability to resist fluid penetration, providing a clear framework for assessing their effectiveness.
AAMI Levels Explained
AAMI rates surgical gowns on a scale from Level 1 to Level 4, with Level 1 offering the lowest fluid resistance and Level 4 providing the highest. For most surgical procedures, AAMI Level 3 gowns are recommended. These gowns are designed to resist moderate to high amounts of fluid exposure, striking a balance between protection and comfort.
Can AAMI Level 3 gowns provide sufficient protection for most surgical procedures. Yes, AAMI Level 3 gowns offer a high level of protection against microbe transmission while maintaining breathability and comfort, making them suitable for a wide range of surgical procedures.
Comparing Fabric Weights and Properties for Optimal Protection
The weight and properties of fabrics used in disposable surgical gowns significantly impact their protective performance. Understanding these characteristics is essential for selecting the most appropriate gown for specific surgical needs.
Fabric Weight Considerations
Fabric weight is typically measured in grams per square meter (GSM). Heavier fabrics tend to offer better durability and fluid imperviousness, while lighter materials provide enhanced breathability and flexibility. The ideal gown material strikes a balance between these properties, ensuring both protection and comfort.
Common Disposable Gown Fabrics
- Polypropylene: Excellent liquid barrier properties
- Polyester: Provides strength, softness, and comfort
- Spunlace (SMS): Offers a balance of protection and breathability
Do heavier fabric weights always provide better protection. Not necessarily. While heavier fabrics often offer better fluid resistance, they may compromise breathability and comfort. The ideal gown material combines optimal protection with wearability.

Evaluating Gown Construction and Design for Enhanced Safety
The construction and design of disposable surgical gowns play a crucial role in their protective capacity and overall performance. Several key features contribute to a gown’s effectiveness in maintaining a sterile barrier.
Critical Design Elements
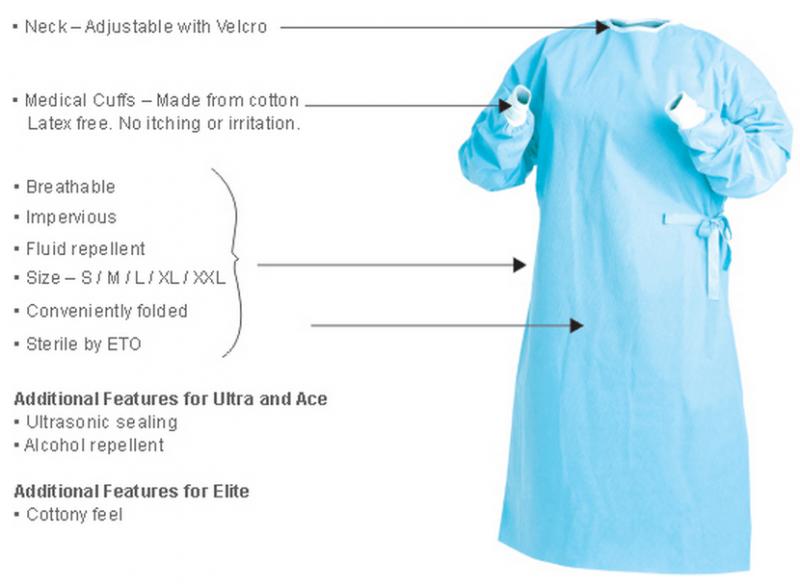
- Reinforced seams: Prevent fluid penetration at vulnerable points
- Knit cuffs: Provide a secure fit around the wrists
- Thumb loops: Help keep sleeves in place during movement
- Ergonomic design: Allows for a full range of motion
- Back and side vents: Improve air circulation and breathability
How does proper sizing and fit contribute to gown effectiveness. Optimal sizing and fit are critical for complete coverage, preventing gaping or tearing that could compromise the sterile barrier. A well-fitted gown ensures protection without restricting movement.
The Role of Proper Gown Use and Disposal in Infection Control
While the material and construction of disposable surgical gowns are crucial, proper use and disposal techniques are equally important in maintaining a sterile environment and preventing contamination.
Key Aspects of Proper Gown Use
- Correct donning procedures
- Appropriate doffing techniques
- Proper disposal methods
- Consistent staff training on gown protocols
Why are disposable surgical gowns advantageous for infection control. Disposable gowns offer single-use convenience, eliminating the need for laundering and reducing the risk of cross-contamination. This streamlines the process and enhances overall safety in surgical settings.
Differentiating Protection Levels: Not All Gowns Are Created Equal
It’s crucial to understand that not all disposable surgical gowns provide the same level of protection against fluids and microbes. The protective performance of a gown depends on various factors, including the material used and its construction.
Comparing Common Gown Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Polyester | Lightweight, comfortable, breathable | Lower fluid resistance |
| Polypropylene | Excellent fluid repellence, good barrier protection | Can be noisy, less pliable |
| Spunlace (SMS) | Balance of protection and breathability | Higher cost |
Is it cost-effective to choose cheaper surgical gowns. While it may be tempting to opt for less expensive gowns, this often results in compromised safety. Investing in high-quality gowns rated at AAMI Level 3 or higher is crucial for ensuring adequate protection against moderate to high fluid exposure.

Innovative Materials and Technologies in Surgical Gown Development
The field of surgical gown materials is continually evolving, with new technologies and innovative fabrics emerging to enhance protection and comfort. These advancements are reshaping the landscape of surgical safety.
Cutting-Edge Developments in Gown Materials
- Nanofiber technologies: Enhancing fluid resistance while maintaining breathability
- Antimicrobial fabrics: Incorporating agents to actively combat microorganisms
- Smart textiles: Integrating sensors for real-time monitoring of contamination risks
- Biodegradable materials: Addressing environmental concerns associated with disposable gowns
How are these innovations impacting surgical safety. These advancements are leading to gowns that offer superior protection, improved comfort, and enhanced functionality, ultimately contributing to safer surgical environments and better outcomes for patients.
Environmental Considerations in Disposable Surgical Gown Selection
While the primary focus of surgical gowns is safety and protection, the environmental impact of disposable gowns is an increasingly important consideration for healthcare facilities.

Balancing Safety and Sustainability
The healthcare industry is exploring ways to reduce the environmental footprint of disposable surgical gowns without compromising on safety. This includes:
- Developing biodegradable gown materials
- Implementing recycling programs for certain gown components
- Exploring reusable gown options with advanced cleaning technologies
- Optimizing gown usage to reduce waste
Can environmentally friendly surgical gowns provide adequate protection. Yes, many eco-friendly gown materials are being developed to meet or exceed AAMI standards while reducing environmental impact. However, it’s crucial to thoroughly evaluate these options to ensure they meet all safety requirements.
The Impact of Surgical Gown Selection on Healthcare Economics
Choosing the right surgical gown material not only affects safety but also has significant economic implications for healthcare facilities. Understanding the full cost picture is essential for making informed decisions.

Economic Factors to Consider
- Initial purchase cost of gowns
- Potential reduction in healthcare-associated infections
- Staff productivity and comfort
- Disposal and waste management costs
- Potential liability risks associated with inadequate protection
How does investing in high-quality surgical gowns impact long-term healthcare costs. While premium gowns may have a higher upfront cost, they can lead to significant savings in the long run by reducing infection rates, improving staff efficiency, and minimizing liability risks.
In conclusion, selecting the right disposable surgical gown material is a critical decision that impacts patient safety, staff protection, and overall healthcare outcomes. By considering factors such as AAMI standards, fabric properties, gown construction, and proper usage protocols, healthcare facilities can ensure they are providing optimal protection during surgical procedures. As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, the field of surgical gown materials continues to evolve, offering new opportunities to enhance safety while addressing sustainability challenges. Ultimately, investing in high-quality, appropriate surgical gowns is an investment in better patient care and more efficient healthcare delivery.
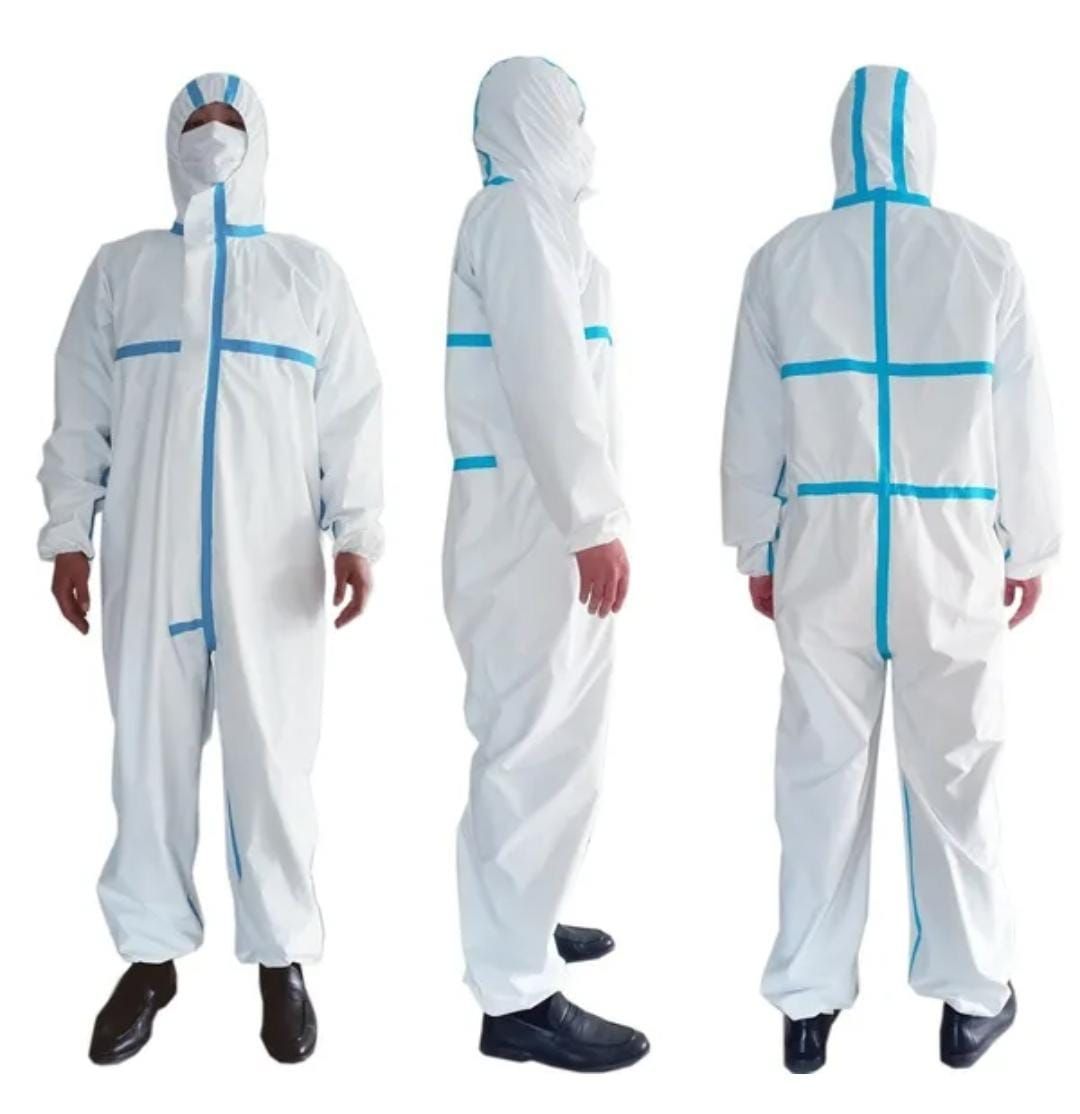

Disposable Sterile Gowns Offer Crucial Barrier Protection During Surgery
When it comes to safeguarding patients and medical professionals during surgical procedures, the material used for disposable sterile gowns is arguably one of the most important considerations. After all, these gowns serve as the last line of defense against dangerous microbes and infectious bodily fluids. But with so many options on the market, how can you determine which disposable surgical gown provides the right level and type of protection?
To get optimal safety and coverage, there are several key factors to take into account when selecting disposable sterile gown materials:
Understand AAMI Standards for Surgical Gown Fabrics
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) has established testing methods and performance guidelines for evaluating the protective properties of surgical gowns based on their ability to resist fluid penetration. Gowns are rated on a scale from Level 1 (lowest fluid resistance) to Level 4 (highest resistance).
For most surgical procedures, AAMI Level 3 gowns are recommended. They are rated to resist fluid penetration from moderate to high amounts of fluid exposure, providing a high level of protection from microbe transmission while maintaining breathability and comfort.
Compare Fabric Weights and Properties
Fabric weight, or grams per square meter (GSM), can vary widely between disposable surgical gowns. Heavier weight fabrics tend to be more durable and impervious to fluids. Lighter weight materials offer better breathability and range of motion, but may sacrifice some protective performance.
Common disposable gown fabrics include polypropylene and polyester. Polypropylene offers great liquid barrier properties, while polyester provides strength, softness and comfort. The ideal option combines the best of both fabrics.
Evaluate Gown Construction and Design
How a gown is engineered and constructed plays a big role in its protective capacity and durability. Features like reinforced seams, knit cuffs, and thumb loops help prevent fluid penetration while also making the gowns more comfortable to wear.
An ergonomic gown design allows for full range of motion, while back and side vents improve air circulation and breathability. Optimal sizing and fit are also critical for complete coverage without gaping or tearing.
Prioritize Proper Use and Disposal

While gown material is important, proper donning, doffing, and disposal techniques are also key to avoiding contamination. This requires consistent gown training and protocols to ensure sterile fields are maintained.
Disposable surgical gowns streamline the process with single-use convenience, eliminating the need for laundering and potential cross-contamination issues.
By understanding AAMI standards, comparing fabric properties, and evaluating construction quality, facilities can provide their staff with disposable sterile gowns that offer the right balance of protection, comfort, and convenience for safe surgical care.
Not All Gowns Provide Equal Levels of Protection From Fluids and Microbes
When prepping for surgery, it’s easy to assume that any disposable gown will provide sufficient barrier protection. Unfortunately, that’s not always the case. Significant differences exist between surgical gown materials and how well they safeguard against infectious fluids and microorganisms.
Disposable gowns are made from a range of fabrics like polyester, polypropylene, and spunlace. Each material offers distinct properties that determine its protective performance:
Polyester
Lightweight and comfortable, polyester gowns tend to be very breathable. However, they generally provide less resistance against fluid penetration compared to other fabrics. Polyester works better when combined with films or laminates to boost imperviousness.
Polypropylene
Known for its naturally hydrophobic qualities, polypropylene repels aqueous fluids extremely well. It offers excellent barrier protection even as lightweight fabric. Unfortunately, polypropylene gowns can be noisy and less pliable.
Spunlace
Spunlace, or spunbond-meltblown-spunbond (SMS), provides great liquid resistance thanks to its multi-layered construction. It strikes a nice balance between breathability and protection. However, spunlace tends to be more expensive than other disposable fabrics.
Gown durability, seam strength, cuff design, and fit can also impact protective performance. Trying to save money on cheaper gowns often backfires in the form of compromised safety.
That’s why it’s so important to choose a surgical gown rated at AAMI Level 3 or higher. These gowns are proven to resist moderate to high amounts of fluid, including pressurized streams, protecting staff in the event of unexpected fluid exposure during surgery.
Don’t take chances – the right disposable surgical gown material makes all the difference in providing a crucial safeguard for patients and medical professionals.
When it comes to safeguarding patients and staff during surgery, not all disposable gowns provide equal protection. Cheaper gowns made from inadequate materials carry the risk of leaking and strike-through. Selecting an AAMI Level 3 rated gown made from fluid-resistant fabrics like polypropylene or spunlace offers optimal barrier performance against infectious fluids and microbes for safer surgical care.
Understanding AAMI Gown Level Standards for Fluid Resistance

When selecting surgical gowns, one of the most important considerations is the gown’s level of fluid resistance. This is measured using standards established by AAMI (Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation).
AAMI has specific testing methods to rate the performance of protective apparel like gowns. There are four levels of fluid resistance:
Level 1 – Minimal Fluid Resistance
Level 1 surgical gowns provide minimal barrier protection against fluids. They are suitable for procedures where fluids and bacterial contamination are minimal, like basic physical exams.
Level 2 – Low Fluid Resistance
Level 2 gowns resist light amounts of fluid spray. They can be used for minimally invasive procedures where small spills may occur. Level 2 is still too low for major surgical procedures.
Level 3 – Moderate Fluid Resistance
Level 3 gowns provide moderate fluid resistance, protecting from splashes and sprays of bodily fluids during regular surgical procedures. This is the minimum recommended level for most surgeries.
Level 4 – High Fluid Resistance
Level 4 surgical gowns demonstrate the highest fluid resistance. They maintain barrier protection even when exposed to high-pressure streams or splashes of fluids that can penetrate through other materials.
Level 4 gowns are ideal for long procedures where exposure to copious amounts of fluid is expected, or for infectious diseases requiring maximum precautions.
Understanding these AAMI standards makes it easier to select a surgical gown with the right level of fluid resistance. While cost is a factor, opting for a gown that matches the anticipated amount of fluid exposure helps minimize contamination risks and protects both staff and patients.
Following AAMI guidelines on surgical gown levels ensures you choose appropriate protective apparel for the right amount of fluid resistance. Focus on Level 3 or 4 gowns to provide suitable barrier performance for most routine and complex surgical procedures.
Level 3 Gowns Recommended for Moderate to High Fluid Procedures
When preparing for surgery, one key decision is selecting the right level of fluid resistant gowns to protect staff from dangerous exposures. For most procedures, AAMI Level 3 surgical gowns provide the optimal balance of barrier performance and comfort.
Compared to Level 1 and 2 gowns, Level 3 disposable sterile gowns are engineered to resist larger volumes of fluid penetration. This makes them ideal for the majority of medium to high fluid surgeries including:
- Orthopedic procedures like joint replacement surgery
- Ob/Gyn and caesarean section births
- Cardiac catheterization lab procedures
- Invasive spinal and neurological procedures
- General abdominal surgery
- Kidney dialysis and transplant procedures
- Emergency trauma surgery
While Level 4 gowns provide the highest fluid resistance, the extra protection often isn’t necessary for routine surgery. Level 3 gowns still withstand high velocity spray, splash exposure and accidental soaking to keep staff safe.
Compared to lower levels, Level 3 disposable sterile gowns are proven to sustain longer liquid contact without leaking through fabrics. Reinforced facings and bound edges prevent strike-through and wicking.
For day-to-day surgical cases, Level 3 AAMI rated gowns offer the ideal balance of breathability, comfort, and trusted barrier performance. Facilities can optimize safety and cost-efficiency simply by aligning gown selection with the anticipated fluid amounts expected during surgery.
Selecting AAMI Level 3 rated disposable sterile gowns provides suitable fluid barrier protection for the majority of medium to high exposure surgeries. The moderate fluid resistance withstands splashes while maintaining comfort and reliability.
Factors like Fabric Weight Impact Gown Durability and Breathability

When evaluating disposable sterile gowns, an important factor to consider is fabric weight. Heavier gown materials tend to provide greater durability and fluid resistance. But increased weight can also impact breathability and comfort during long surgeries.
Disposable gown fabric weights are measured in grams per square meter (GSM). Here’s how common material weights compare:
- Lightweight – <50 GSM
- Medium Weight – 50-80 GSM
- Heavy Weight – 80-120+ GSM
Lightweight gowns with lower fabric density breathe easier and allow for greater mobility. But they sacrifice some liquid barrier performance and tear strength that heavier materials provide.
Heavier weight disposable gowns are highly impervious to fluid and stand up well to rigorous activity and abrasion. But they can feel hot, stiff, and uncomfortable when worn for long periods.
The ideal gown combines a lightweight feel with targeted reinforcement of high-exposure areas. Stitching higher weight panels along the front, sleeves, and chest provides extra protection and durability only where it’s needed.
Ergonomic designs with panels of breathable fabric under the arms, around the neck, and across the back also improve air circulation and comfort in hot environments.
Selecting disposable sterile gowns that balance weight and breathability ensures adequate barrier coverage without sacrificing mobility and comfort during surgery.
Fabric weight impacts the durability and breathability of disposable sterile gowns. While heavier materials improve fluid resistance, lightweight fabrics enhance comfort and ventilation. Optimal protection combines reinforced panels in high-exposure areas with breathable fabrics in mobility zones.
Reinforced and Bound Seams Prevent Fluid Strike-Through

When evaluating disposable sterile gowns, one critical area that impacts barrier performance is the seam construction. Seams are vulnerable points where fluids can leak through if not properly reinforced.
Disposable surgical gown seams are constructed in several ways:
- Bound seams have an extra strip of material folded over and stitched for 4-ply thickness.
- Serged seams are finished with an overlock stitch pattern.
- Taped seams are covered with impervious tape during assembly.
Reinforced seams provide an extra barrier against fluid penetration through needle holes or stitching gaps. They reduce the risk of dangerous fluid strike-through.
Quality disposable sterile gowns also orient seam openings in a direction away from expected fluid exposure areas. This strategic seam construction minimizes the chance for fluids to leak through.
Gowns with double-stitched inverts and standing finishes ensure seam edges lay flat against the body without wicking moisture underneath.
Don’t underestimate the importance of seam integrity. Reinforced stitching and binding prevent fluid tracking to the inside layer, keeping healthcare staff dry and protected.
Proper disposable sterile gown construction means sealing all potential leakage points. Reinforced seams and strategic seam orientation provide an essential safeguard against dangerous fluid strike-through during surgery.
Reinforced and bound seams are a critical disposable gown feature. The extra stitching prevents fluids from penetrating needle holes or gaps, reducing strike-through risk and keeping surgical staff protected.
Opting for Disposable Over Reusable Can Avoid Cross-Contamination
When selecting protective apparel for surgery, many hospitals debate between disposable sterile gowns versus reusable cloth gowns. While reusable may seem eco-friendly, disposables better safeguard patients and staff against dangerous cross-contamination.
Reusable surgical gowns require diligent laundering between each use to eliminate infectious bodily fluids and microbes. However, studies show mechanical washing doesn’t fully remove all bioburden even after disinfection.
Trace amounts of blood, tissue, and viruses can still remain embedded in the reusable fabric. These organisms often end up cross-contaminated to the next patient.
Disposable sterile gowns eliminate this risk. After surgery, disposable gowns are simply discarded using proper containment procedures. Fresh, sterile gowns are then donned for the next case.
Disposables also provide better protective performance thanks to engineered fabrics and seam constructions. Their impervious barriers better withstand splash and spray exposure from fluids.
While disposables create more waste, the single-use convenience improves infection control. For high risk procedures, the safety of patients and staff outweighs sustainability factors.
By opting for disposable over reusable gowns, facilities can reduce the risk of dangerous organism transmission often associated with laundered gowns. Improving patient outcomes is the top priority.
Disposable sterile gowns avoid the cross-contamination risks of reusable gowns that can still harbor traces of infectious fluids even after washing. Their single-use nature optimizes barrier protection and infection control for safer surgery.
Proper Donning/Doffing Technique Critical for Maintaining Sterility
While gown material is crucial, even the best disposable sterile gowns fall short if not worn correctly. Proper donning and doffing techniques ensure gowns maintain a sterile barrier throughout surgery.
Before gowning, strict hand hygiene must be performed and personal protective equipment like masks and eyewear donned first. Next:
- Open the gown fully and insert arms into sleeves without allowing outside surface to make contact.
- Secure the neck and waist ties while avoiding any gaping or openings.
- Ensure cuffs fully cover wrists and isolate gloves from exposure.
- Drape and adjust the gown to provide 360-degree coverage.
- Take care to not dislodge PPE underneath when moving.
For safe removal, a systematic procedure must also be followed:
- Untie waist ties then neck tie without allowing outside of gown to contact skin.
- Peel gown down each shoulder, rolling it away from the body.
- Dispose of immediately in proper contaminated waste receptacle.
- Wash hands thoroughly before touching anything else.
Proper techniques reinforce sterile principles and prevent dangerous exposure to contaminated gown exteriors. Consistent gown training ensures staff habits optimize protection.
More than just material, maximal disposable gown safety requires healthcare personnel to employ proper donning and doffing techniques for maintaining sterile fields.
Along with quality materials, donning and doffing disposable sterile gowns using meticulous technique is vital for preserving sterility and avoiding contamination during surgical procedures.
Fit Testing Ensures Proper Gown Sizing for Complete Coverage
Along with material selection and donning technique, properly fitted disposable sterile gowns are vital for total protective coverage. Facilities should conduct mandatory fit testing to match staff with optimal gown sizes.
Like respirators, finding the right gown size for each individual’s body type eliminates hazardous gaps or openings in coverage. Baggy gowns can billow out and expose underlying clothing or skin.
Conduct initial and annual fit tests for all personnel required to wear sterile gowns in surgery:
- Have test subject move and stretch as needed to mimic range of motion during procedures.
- Mark any areas where gown cuffs, neckline or ties gap away from skin.
- Compare coverage across available gown sizes and select the best fit.
- Document optimal size for each staff member’s reference.
Take care when sizing staff with varying body shapes and proportions. Consider length extensions for taller builds and bariatric sizes for fuller figures.
Proper disposable gown sizing eliminates gaps that defeat the sterile barrier. Fit testing maximizes coverage and safety for surgery teams.
Along with proper donning technique, conducting fit testing helps facilities match staff with the right disposable sterile gown size for their body type. Optimized sizing eliminates hazardous coverage gaps to maintain sterility.
Compare Materials Like Polypropylene vs Polyester for Strength and Comfort
Disposable sterile gowns are constructed using different synthetic materials that balance protective qualities with comfort and durability.
Two of the most common materials used are:
Polypropylene
- Naturally hydrophobic and repels fluids
- Offers excellent barrier against microbes
- Tends to be noisy and prone to static buildup
- Not as breathable or flexible as other materials
Polyester
- Smooth and soft for better comfort
- Allows more airflow for breathability
- Wicks moisture away from skin
- Can be weaker than polypropylene in durability
The ideal disposable gown combines polypropylene’s impervious qualities with polyester’s comfort. Constructing different panels using the best material for that body region optimizes both protection and wearability.
Make sure to compare materials used for isolation gowns versus surgical gowns. More breathable fabrics may work for quick examinations, but surgical settings require highly impervious materials for lengthy procedures with high fluid volumes.
Analyze disposable gown fabric contents to find the optimal balance of strength, comfort and barrier performance for the given clinical environment.
Compare protective qualities, comfort, and breathability when selecting disposable sterile gown materials like polypropylene vs polyester. The ideal surgical gown combines both fabrics’ strengths.