How do fall safety apps protect workers in high-risk industries. What are the must-have features of fall protection apps. Why is fall prevention critical in 2023. How can technology reduce occupational fall incidents.
The Importance of Fall Protection in Today’s Workplace
Fall protection remains a critical concern in various industries, with falls consistently ranking as the leading cause of fatalities in construction. In 2020, nearly 300 workers lost their lives due to falls at job sites, accounting for over a third of all construction-related deaths. These sobering statistics underscore the urgent need for enhanced fall protection measures across multiple sectors.
Emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and advanced mobile applications, are revolutionizing fall safety programs. Fall protection apps leverage these innovations to provide real-time monitoring, instant communication, and life-saving data, effectively serving as an additional layer of security for workers operating at elevated heights.

High-Risk Industries for Fall Incidents
- Construction
- Transportation
- Manufacturing
- Utilities
- Agriculture
These industries face particularly high risks due to the nature of their work environments, which often involve ladders, scaffolds, rooftops, loading docks, elevated platforms, and other hazardous elevated work areas.
Understanding OSHA Requirements for Fall Protection
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that employers provide adequate fall protection when employees work at heights of 6 feet or more in construction and 4 feet or more in general industry. This includes the proper use of conventional fall protection systems such as guardrails, safety nets, and personal fall arrest equipment.
Fall safety apps complement these traditional measures by ensuring their correct implementation and providing comprehensive oversight. These technological solutions make it easier for companies to stay compliant with evolving OSHA regulations through robust real-time monitoring and data analysis.

Common Causes of Falls in the Workplace
- Improper climbing on or off equipment
- Slipping on slick surfaces or loose objects
- Loss of balance while overreaching or bending
- Structural collapse of platforms or scaffolds
- Equipment failures
- Absence of fall protection systems
- Inadequate training on hazards and proper equipment use
Understanding these common causes allows for targeted prevention strategies. Fall safety apps provide the necessary data visibility to identify risks and send real-time notifications to alert workers before an incident occurs.
The Economic Impact of Fall Incidents
Beyond the tragic loss of life, fall accidents impose a significant financial burden through medical expenses, litigation, and lost productivity. Occupational falls result in nearly 3 million emergency room visits annually, with costs ultimately passed on to consumers through higher prices for goods and services.
Can fall safety apps provide a cost-effective solution to this problem? Indeed, when compared to the devastating consequences of a fall incident, the investment in cutting-edge fall prevention technology offers an outstanding return on investment. By leveraging technology to prevent accidents proactively, these apps can significantly reduce both human and economic costs associated with workplace falls.
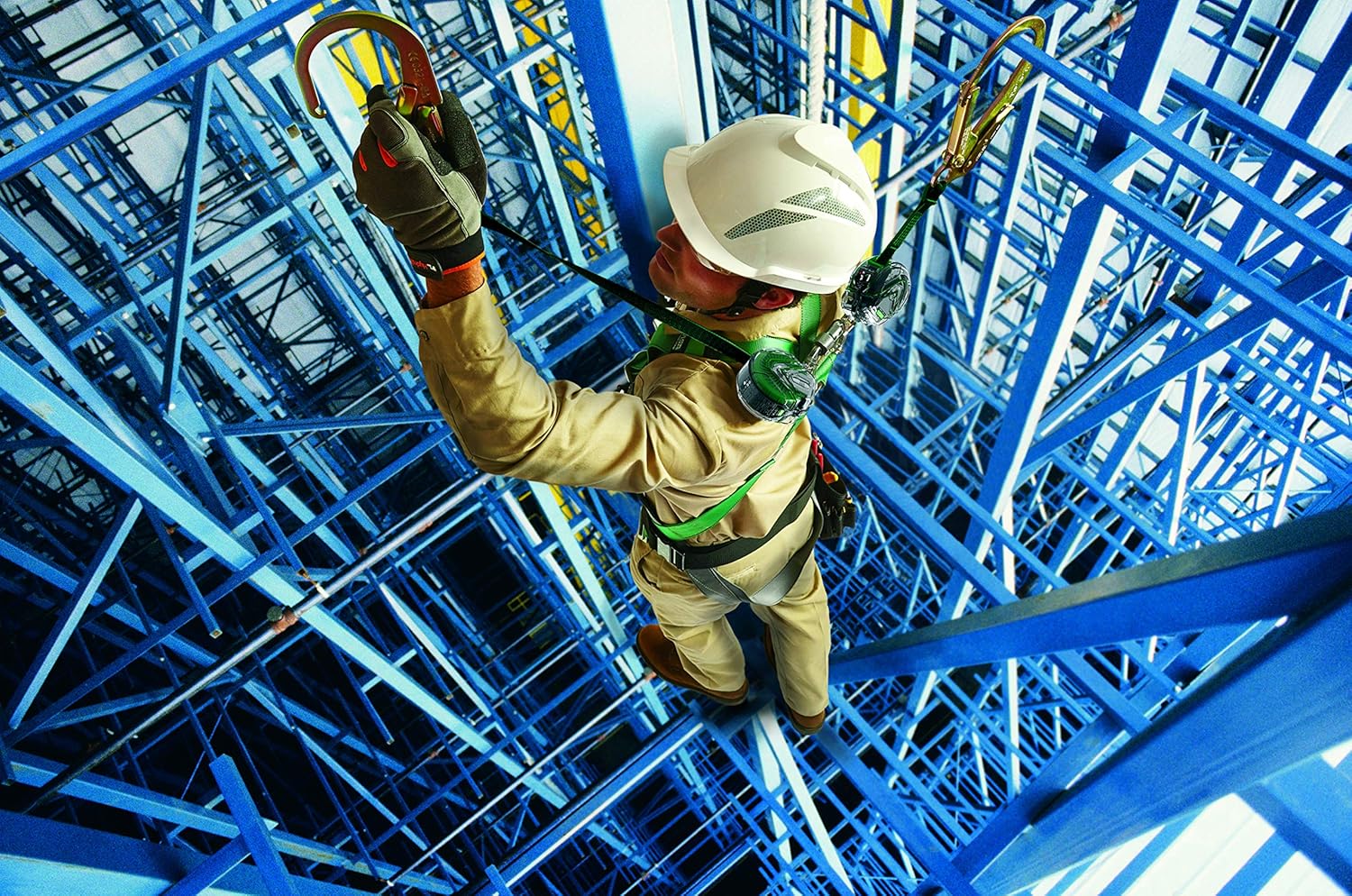

15 Essential Features of Effective Fall Safety Apps
To maximize worker protection, fall safety apps should incorporate a range of critical features. Here are 15 must-have components that can make a significant difference in preventing fall-related injuries and fatalities:
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
How do fall safety apps provide immediate hazard notifications? Advanced sensors and AI algorithms continuously analyze the work environment, instantly alerting workers and supervisors to potential fall risks. This real-time monitoring can detect unstable surfaces, improperly secured equipment, or workers approaching danger zones, allowing for immediate corrective action.
2. Geofencing and Location Tracking
Geofencing technology enables the creation of virtual perimeters around hazardous areas. The app can trigger alerts when workers enter or exit these predefined zones, ensuring they remain aware of their surroundings and potential risks. Additionally, location tracking aids in rapid response during emergencies, allowing rescuers to quickly locate and assist injured workers.

3. Customizable Safety Checklists
Digital checklists streamline the process of equipment inspections and safety protocol adherence. These customizable lists ensure that all necessary safety measures are taken before work at height begins, reducing the likelihood of oversights that could lead to accidents.
4. Wearable Integration
Integration with wearable devices, such as smart helmets or safety vests, enhances the app’s ability to monitor worker safety. These wearables can detect falls, measure vital signs, and even assess worker fatigue, providing a comprehensive picture of each individual’s well-being throughout the workday.
5. Incident Reporting and Analysis
In the event of a near-miss or accident, the app should facilitate quick and easy incident reporting. This feature allows for thorough analysis of safety trends, enabling companies to identify patterns and implement targeted improvements to their fall protection strategies.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning for Enhanced Fall Protection
How can artificial intelligence improve fall safety measures? AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected by fall safety apps to predict potential hazards before they manifest. By identifying patterns in worker behavior, environmental conditions, and equipment usage, these intelligent systems can provide proactive recommendations to prevent falls.

For example, AI-powered fall safety apps might:
- Predict when equipment is likely to fail based on usage patterns and maintenance history
- Identify high-risk times of day or weather conditions that correlate with increased fall incidents
- Suggest optimal routes for workers to navigate elevated areas safely
- Personalize safety recommendations based on individual worker profiles and historical data
6. Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment
By leveraging historical data and real-time inputs, fall safety apps can employ predictive analytics to assess the likelihood of fall incidents under various conditions. This feature enables proactive risk management, allowing safety managers to allocate resources more effectively and implement preventive measures before accidents occur.
7. Augmented Reality (AR) Safety Visualization
AR technology can overlay safety information directly onto a worker’s field of view, highlighting potential hazards, safe paths, and proper equipment placement. This immersive approach to safety education and awareness can significantly reduce the risk of falls by providing context-specific guidance in real-time.

Communication and Collaboration Features in Fall Safety Apps
Effective communication is crucial for maintaining a safe work environment, especially when it comes to fall protection. Fall safety apps should incorporate robust communication features to ensure that all team members are well-informed and can collaborate effectively in hazardous situations.
8. Instant Messaging and Voice Communications
Secure, in-app messaging and voice call capabilities allow workers to quickly communicate potential hazards, request assistance, or coordinate safety measures without leaving their work area or removing safety equipment.
9. Emergency Response Coordination
In the event of a fall or other emergency, the app should facilitate rapid response coordination. This feature might include automated alerts to emergency services, guidance for on-site first responders, and real-time updates to all relevant personnel.
10. Team Safety Dashboards
Centralized dashboards provide supervisors and safety managers with a comprehensive overview of all workers’ locations, safety statuses, and potential risks. These dashboards enable quick decision-making and resource allocation to maintain a safe working environment.

Training and Education Components of Fall Safety Apps
Continuous education and training are essential for maintaining a strong safety culture and ensuring that all workers are equipped with the knowledge and skills to prevent falls. Fall safety apps can play a crucial role in delivering and reinforcing this important information.
11. Interactive Safety Training Modules
How can fall safety apps improve worker education? By incorporating interactive training modules, apps can provide engaging, multimedia-rich content that helps workers understand fall risks, proper equipment usage, and best practices for working at height. These modules can be tailored to specific job roles and updated regularly to reflect the latest safety standards and regulations.
12. Gamification of Safety Practices
Gamification elements, such as point systems, badges, and leaderboards, can incentivize workers to engage with safety content and adhere to best practices. This approach not only makes safety training more enjoyable but also encourages healthy competition and recognition for safety-conscious behavior.

13. Virtual Reality (VR) Fall Simulation
VR technology can provide immersive, risk-free environments for workers to practice fall prevention techniques and emergency responses. These simulations offer a safe way to experience and learn from potentially dangerous scenarios without real-world consequences.
Data Management and Compliance Reporting
Effective fall protection requires meticulous record-keeping and compliance with regulatory standards. Fall safety apps can streamline these processes, making it easier for companies to maintain accurate records and demonstrate their commitment to worker safety.
14. Automated Compliance Reporting
How do fall safety apps simplify regulatory compliance? By automatically generating compliance reports based on real-time data collected through the app, companies can easily demonstrate adherence to OSHA and other regulatory requirements. This feature saves time, reduces paperwork, and ensures that all necessary safety documentation is up-to-date and readily available.

15. Data Analytics and Insights
Advanced data analytics tools within the app can process vast amounts of safety-related information to uncover trends, identify areas for improvement, and measure the effectiveness of fall protection strategies over time. These insights enable data-driven decision-making to continuously enhance safety protocols and reduce fall risks.
Integrating Fall Safety Apps into Existing Safety Programs
While fall safety apps offer powerful new tools for protecting workers, it’s essential to integrate them effectively into existing safety programs. This integration ensures that the technology complements rather than replaces traditional safety measures and human oversight.
Key considerations for successful integration include:
- Providing comprehensive training on app usage and features
- Aligning app-based protocols with existing safety procedures
- Ensuring buy-in from all levels of the organization, from frontline workers to upper management
- Regularly reviewing and updating app settings to reflect changing work conditions and safety requirements
- Encouraging feedback from users to continually improve the app’s effectiveness
By thoughtfully incorporating fall safety apps into their overall safety strategy, companies can create a more robust and responsive fall protection program that leverages the best of both technological innovation and human expertise.

The Future of Fall Protection Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of fall safety apps are likely to expand even further. Future developments may include:
- Advanced biometric monitoring to detect fatigue or other physical conditions that may increase fall risk
- Integration with autonomous drones for aerial inspections of high-risk areas
- Improved AI algorithms for more accurate prediction and prevention of fall hazards
- Enhanced AR and VR capabilities for even more immersive safety training and hazard visualization
- Greater integration with smart building systems and IoT devices for comprehensive workplace safety management
How will these advancements shape the future of workplace safety? As fall protection technology becomes more sophisticated and integrated, we can expect to see a continued decrease in fall-related incidents and injuries. This progress will not only save lives but also contribute to more efficient and productive work environments across all industries where fall hazards are present.

In conclusion, fall safety apps represent a significant leap forward in protecting workers from one of the most persistent and dangerous workplace hazards. By combining real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and interactive training features, these apps provide a comprehensive solution to fall prevention that goes far beyond traditional safety measures. As companies increasingly adopt and integrate this technology, we can look forward to safer work environments and fewer fall-related tragedies in the years to come.
When it comes to protecting your workers from dangerous falls, a fall safety app can make all the difference. With advanced technology literally in the palms of their hands, employees have an extra layer of security against falls – the leading cause of fatalities in construction. So how exactly will a fall safety app safeguard your crew? Let’s explore the must-have features you never knew could prevent injuries and save lives.
Introduction: Why Fall Protection Is Critical In 2023
Falls remain the number one killer in construction year after year. In fact, falls account for over a third of all construction fatalities, with nearly 300 workers dying from falls at job sites in 2020 alone. These alarming statistics make it clear – fall protection must be a top priority for every contractor and company in 2023.
With emerging technologies like AI, IoT sensors and advanced mobile apps, new solutions are available to dramatically improve fall safety programs. Fall protection apps leverage these cutting-edge innovations to provide real-time monitoring, instant communication and life-saving data to keep workers protected at elevation.
While safety ropes, harnesses and guardrails are essential equipment, a fall safety app acts like an extra set of eyes watching over the worksite. By combining the latest hardware with powerful software, fall protection enters a new era where injuries and fatalities can be prevented before they occur.
Stats On Fall Injuries Show The Need For Prevention

The numbers speak for themselves – occupational falls result in nearly 3 million emergency room visits annually. Beyond the tragic loss of life, fall accidents impose a tremendous financial toll through medical expenses, litigation, and lost productivity.
Falls from elevation aren’t just a problem in the building trades either. Transportation, utilities, manufacturing and agriculture all carry significant fall hazards that must be addressed. The costs of these incidents ultimately get passed on to consumers through higher prices.
With such a heavy human and economic burden, investment in cutting-edge fall prevention is imperative. Fall safety apps provide inexpensive protection compared to the devastating consequences of an incident. By leveraging technology to avoid accidents in the first place, apps deliver outstanding ROI.
Top 5 High-Risk Industries For Falls On The Job
While falls can happen virtually anywhere, these five industries face especially high risks:
- Construction – ladders, scaffolds, rooftops
- Transportation – loading docks, truck beds, catwalks
- Manufacturing – elevated work platforms, catwalks, conveyors
- Utilities – power line towers, utility poles
- Agriculture – silos, grain bins, barn lofts
Companies in these sectors would benefit tremendously by implementing a robust fall protection app to protect their at-height workers. With detailed data and improved safety accountability, apps provide a lifeline for workers in high hazard environments.
OSHA Requirements For Fall Protection You Must Follow

Under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations, employers must provide adequate fall protection when employees are working at heights of 6 feet or more in construction and 4 feet or more in general industry.
This includes proper use of conventional fall protection systems like guardrails, safety nets and personal fall arrest equipment. Now, add fall safety apps to the mix for the ultimate protection.
Apps ensure safety measures are correctly implemented and provide oversight to guarantee no at-risk worker is overlooked. Staying compliant with evolving OSHA rules is much easier with technology performing robust real-time monitoring.
How Do Falls Happen? Common Causes To Be Aware Of
Understanding why and how falls occur is crucial to prevent them. Many construction accidents result from:
- Climbing on or off equipment improperly
- Slipping on slippery surfaces or loose objects
- Losings balance while overreaching or bending
- Structural collapse of platforms or scaffolds
- Equipment failures like ladder rung breaks
- Absence of fall protection systems
- Lack of training on hazards and proper equipment use
Once you know the mistakes that lead to falls, you can take strategic action to avoid them. Apps provide the data visibility to pinpoint risks and the real-time notifications to alert workers before an incident happens.
Preventing Falls From Ladders And Scaffolds
Ladders and scaffolds account for the majority of elevated falls. Safety apps can reduce these incidents through:
- Checklists ensuring proper ladder positioning and scaffold assembly
- Alerts when inspection findings aren’t resolved
- Notifications if non-compliant equipment is being utilized
- Confirming fall protection is worn with 100% compliance
- Auditing training status for equipment operation
- Proximity sensing to prevent working too close to edges
With a full view of crew activities, apps provide unsurpassed visibility to prevent falls from these ubiquitous hazards.
Guardrails And Safety Nets: Passive Fall Protection
Guardrails and safety nets are examples of passive fall protection – they don’t require any action by workers to be effective. Apps verify these systems are properly implemented:
- Confirming guardrails meet height and strength requirements
- Checking safety nets are certified and installed correctly
- Making sure net perimeter areas are barricaded
- Enforcing safe distance compliance from guardrail edges
- Mandating the use of tethers for tools and materials near edges
With apps actively monitoring the work environment, passive systems offer better protection.
Personal Fall Arrest Systems: Active Fall Protection

Harnesses, lanyards and retractable lifelines comprise personal fall arrest systems. As active protection, they require proper donning and use by individual workers to be effective. Apps provide support through:
- Electronic inspection checklists for equipment
- Alerts when wear and damage is detected
- Tracking fall protection inventory in real-time
- Enforcing harness exam and fit requirements
- Confirming double lanyard tie-off when transitioning
- Mandating anchor point load testing and certification
Apps ensure active fall protection performs optimally by prompting and guiding correct usage each step of the way.
Proper Use And Inspection Of Safety Harnesses
Harnesses are the most vital PPE for fall protection, but require thorough inspection and proper donning to work effectively. Apps facilitate compliance by:
- Providing digital harness inspection forms
- Tracking overdue harness inspections and removals
- Confirming fit with photo evidence and mandatory check-in
- Blocking access if harness isn’t verified before heading to site
- Enforcing weight limits and expiration dates
- Limiting harness use to certified personnel only
With apps managing each detail, workers can just focus on the job knowing their harnesses will perform right if a fall occurs.
Training Workers On Fall Hazards And Protection

Education is essential – an untrained worker is an unsafe worker. Apps reinforce fall protection training through:
- Mobile-friendly training materials and quizzes
- Verification that critical topics were completed
- Notifications when retraining is required
- Confirming competency with hands-on evaluations
- Tracking credentials like competent person certifications
- Access deactivation when training lapses
With apps monitoring all educational requirements, you can trust workers have the knowledge to stay protected from falls.
By merging the capabilities of mobile technology with fall safety expertise, apps provide a simple yet powerful way to reduce risks and prevent fatalities. While nothing can fully eliminate falls, comprehensive apps minimize hazards before they become accidents. Equipping your workforce with an app ensures they have the tools and knowledge needed to make it home safely each day.
When it comes to protecting workers at height, the numbers speak for themselves: we need better fall prevention. Let’s take a closer look at the data driving the urgent need for modern solutions like safety apps.
Stats On Fall Injuries Show The Need For Prevention
You’ve likely seen the tragic headlines – a roofer plunges from faulty scaffolding. An electrician falls from a utility pole without proper fall arrest. A construction laborer trips into an unguarded elevator shaft.
While the stories always differ, the endings are the same: shattered lives, grieving families and companies forever changed. The latest statistics on occupational falls paint a dire picture:
- Falls account for over a third of construction fatalities annually
- Over 800 fall deaths occur in general industry each year
- Almost 3 million emergency room visits result from jobsite falls annually
- $70 billion is spent on medical costs, litigation, and lost productivity from falls
Clearly, falls remain the foremost cause of serious injury and death on the job across every major industry. Traditional safety measures alone are not moving the needle on reducing fall accidents. Advanced solutions are desperately needed.
That’s where fall safety apps come in. By combining mobile technology with data analytics, apps provide the real-time insight and oversight needed to prevent falls proactively. Instead of relying on passive equipment like guardrails, apps take active measures like alerts and check-ins to verify protection at all times.
For companies struggling to lower their fall incident rates, apps offer a paradigm shift. You can’t manage what you don’t measure – apps provide the on-site intelligence to pinpoint risks and prevent them from becoming reality.
Fall protection is a complex, ever-evolving challenge. But new tools are emerging to simplify the process and provide life-saving checks and balances. For less than the cost of a single fall accident, apps deliver the layers of protection that returning workers home safely demands.
The fallen will never be forgotten. But leveraging powerful technology solutions means fewer memorial services, smaller OSHA fines and most importantly – workers making it home to their loved ones after a hard day’s work.
Falls claim so many lives and inflict so much suffering each year. But data-driven apps are here to turn the tide. By stopping falls before they happen, these innovative new platforms are creating a future where no family receives that devastating call. A future where the only number that counts is zero – zero falls.
When it comes to fall hazards, some jobs are riskier than others. Here’s a look at the top 5 industries with the highest risk of falls from elevation:
Top 5 High-Risk Industries For Falls On The Job

Working at heights is hazardous across all occupations, but these sectors see the most elevated falls each year:
- Construction
- Transportation and Warehousing
- Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Agriculture
Let’s examine why working conditions in these industries make falls more likely to occur:
Construction
Construction workers face fall hazards daily while working on:
- Roofing
- Scaffolding
- Ladders
- Open window and door edges
- Elevator shafts
- Unprotected skylights
Falls account for 1 in 3 of the near 1000 annual construction fatalities. Safety oversight on diverse job sites with multiple crews is difficult, leading to accidents.
Transportation and Warehousing
Workers in transportation handle cargo at elevation and risk falling from:
- Loading docks
- Truck beds
- Conveyors
- Catwalks
- Storage racks
Hectic schedules and pressure to work quickly can result in risky behaviors. Forklift rollovers from docks also cause many deaths.
Utilities

Utilities workers are exposed to falls while working on:
- Power line towers
- Utility poles
- Cell towers
- Wind turbines
Harsh weather conditions and remote locations make elevated work more dangerous. Proper safety equipment and training is essential.
Manufacturing
Factory workers face fall risks when working on:
- Elevated work platforms
- Catwalks
- Conveyors
- Cranes
- Mezzanines
Complex machinery, slick surfaces from oil and water, and obstructed views can all lead to tragic falls.
Agriculture
Farm workers encounter fall hazards when working in:
- Grain silos
- Grain bins
- Barn haylofts
- Elevated tractor cabs
Remoteness of work areas and small workforces make establishing proper safety protocols difficult.
While the work is vastly different, what these 5 industries share is above-ground work exposing them to risks of fatal falls. But safety apps are coming to the rescue…
When it comes to preventing falls at height, OSHA sets the standards all employers must comply with. Let’s examine the key OSHA regulations for fall protection and how safety apps can facilitate compliance.
OSHA Requirements For Fall Protection You Must Follow
Under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) rules, employers have a duty to protect workers from fall hazards. Failure to comply can result in injuries, deaths and severe OSHA fines.
Here are the essential OSHA requirements on fall protection that companies must follow:
- Provide fall protection at 6 feet for construction work
- Provide fall protection at 4 feet for general industry work
- Ensure proper use of fall protection systems
- Inspect and maintain fall protection equipment
- Develop and enforce a written fall program
- Train workers to recognize fall hazards
- Supervise workers exposed to fall risks
These obligations can be challenging to meet, especially on remote jobsites with limited supervision. That’s where fall safety apps come in.
Apps provide digital oversight to ensure OSHA rules are consistently followed. Features like checklists, alerts and automatic tracking provide real-time data to document enforcement.
For example, apps can:
- Prompt workers to inspect equipment before use
- Require harness fit checks before going on site
- Alert supervisors if guardrails are inadequate
- Confirm anchors are load-tested and certified
- Deliver refresher training when due
- Restrict access if requirements aren’t met
By automating compliance tracking, apps enable companies to easily satisfy demanding OSHA regulations. Workers are empowered to make smarter decisions with policy guidance at their fingertips.
When OSHA inspectors arrive, apps provide the documentation needed to demonstrate diligent enforcement of the agency’s fall rules. Fines, project shutdowns and litigation can be avoided.
In our modern world, technology is changing how we work. OSHA recognizes this reality and encourages innovative new tools to enhance jobsite safety. Fall protection apps lead the way in leveraging technology to prevent worker injuries and deaths from elevation.
To prevent falls, you first need to understand what causes them. Here are the most common reasons workers fall from elevation on the jobsite:
How Do Falls Happen? Common Causes To Be Aware Of

Construction sites are chaotic environments filled with hazards. It’s no surprise falls are the leading cause of worker deaths in the industry. But many falls can be prevented by recognizing what causes them in the first place. Here are the primary reasons workers fall from height:
- Climbing on/off equipment: The ascent and descent from ladders, scaffolds and rooftops accounts for many falls. Proper 3-point technique is essential.
- Slipping: Loose materials, oil spills, weather hazards can all lead to lost footing and falls.
- Loss of balance: Overreaching and bending are major factors in falls. Maintaining stability is key.
- Structural collapse: Faulty scaffolds, guardrails and roofs can give way and lead to accidents.
- Equipment failures: Ladder rung breaks, worn rope snaps, malfunctioning elevators cause falls.
- No fall protection: Lack of guardrails, safety nets, harnesses and anchors is a common factor.
- Lack of training: Untrained workers are unaware of hazards and proper equipment use.
Now that we know what causes falls, let’s look at how safety apps can help avoid these pitfalls and keep workers protected.
First, apps provide digital checklists for safe equipment use. Workers are guided step-by-step through proper ladder positioning, scaffold assembly, roof access – preventing climbing errors.
Next, apps track housekeeping and maintenance issues. Alerts notify supervisors of trip hazards or inadequate guardrails to fix issues before an accident.
Apps also confirm fall protection is used through geo-fencing, check-ins, and PPE inspections. Compliance is no longer optional.
Speaking of compliance, apps act like a coach, walking workers through safe work practices. Guidance and resources are always available to reference.
Finally, apps enforce training and certifications required for elevated work. Untrained workers are identified before they set foot on site.
Falls don’t have to be an inevitable part of construction. By tackling the root causes with apps, workers can return home safe each day.
Ladders and scaffolds present major fall hazards on jobsites. But safety apps provide effective safeguards against accidents when working on these ubiquitous tools.
Preventing Falls From Ladders And Scaffolds

No construction site would function without ladders and scaffolds. But working at height on them accounts for many deadly fall tragedies annually.
Ladders seem simple, but improper setup and use leads to thousands of injuries each year. Scaffolds are complex structures assembled on-site, leaving ample room for error.
Thankfully, fall safety apps provide a comprehensive system to prevent accidents when working on these elevated platforms. Let’s look at some key ways apps help avert ladder and scaffold falls:
- Digital checklists guide proper ladder positioning and scaffold assembly
- Equipment inspections identify faults like missing ladder rung clips
- Alerts notify if faulty items are not fixed promptly
- Non-compliance alerts if improper equipment is utilized
- Confirms fall protection is worn before ascending
- Enforces training credentials for equipment use
- Prevents working too close to unprotected edges
With ladders and scaffolds involved in over half of elevated falls, apps provide a fool-proof system to avoid these preventable accidents.
First, apps remove guesswork by providing illustrated guidance on safe setup. Workers of all experience levels have expert advice on hand.
Next, apps digitize inspections so no hazard goes undetected. Faulty ladders can be tagged out before an incident occurs.
Speaking of incidents, apps enforce training requirements for equipment use. No more untrained workers winging it on complex scaffold systems.
And apps add oversight on the ground with geo-fencing to prevent work too close to unprotected edges. Authorized locations are clearly defined.
Ladders and scaffolds are a fact of life on the jobsite. But with apps safeguarding their use, workers can ascend with confidence knowing their protection is guaranteed.
Guardrails and safety nets prevent falls passively without worker action. Let’s explore how apps verify these systems are properly installed and utilized.
Guardrails And Safety Nets: Passive Fall Protection
Unlike harnesses and lanyards, guardrails and safety nets work to prevent falls automatically – no action required by employees. But passive systems are only effective when installed and used correctly.
Guardrails seem simple in concept, but even experienced crews can make mistakes assembling them on site. Safety nets involve meticulous installation and maintenance to catch falling workers.
This is where safety apps excel. Apps provide digital oversight on the ground to confirm guardrails and nets meet requirements. Here are some of the safeguards apps deliver:
- Confirming top rails and mid-rails meet minimum height standards
- Checking net perimeter areas are properly barricaded
- Validating net installation was done by certified riggers
- Enforcing safe distance compliance from guardrail edges
- Mandating use of tool tethers near unprotected sides
- Alerting when repairs or recertification are needed
With so many moving parts on dynamic jobsites, apps provide an extra layer of protection to verify these critical last lines of defense are optimized.
First, apps digitize inspections so flaws in guardrails or nets are detected early when easier to fix. Daily checks become effortless.
Next, apps monitor authorized work zones in relation to leading edges. Barriers and controlled access prevent falls.
Apps also prompt routine maintenance and recertification activities to avoid lapses. Compliance is simplified.
In fast-paced, high-risk work environments, things inevitably get missed. But apps fill the gaps to ensure passive systems provide maximum protection.
Unlike passive systems, personal fall arrest equipment requires proper use by workers to provide protection. Let’s look at how apps facilitate correct utilization.
Personal Fall Arrest Systems: Active Fall Protection

Personal fall arrest systems like harnesses, lanyards and SRLs depend on appropriate use by individual workers to deliver safety. Worker actions dictate if the gear performs properly or fails when needed most.
With so many steps required to don, adjust, secure and inspect these active systems, errors can occur. Apps provide the oversight to prevent mistakes.
Here are some of the ways apps ensure personal fall arrest equipment works effectively:
- Digital forms guide and record equipment inspections
- Alerts notify supervisors when wear/damage is detected
- Inventory tracking ensures adequate gear is available
- Enforces harness fit checks before going on site
- Confirms double tie-off when transitioning between anchors
- Verifies anchor certification and load testing
Instead of relying on workers to remember every step, apps provide prompts, guidance and documentation for correct use of active arrest systems.
First, apps digitize clumsy paper inspection forms so defects can be spotted early before equipment failures. Photos validate conditions.
Next, apps enforce proper harness donning and fit through mandatory check-in procedures before the workday begins. No shortcuts allowed.
Throughout shifts, apps guide technicians through compliant safety practices like double tie-offs when moving between anchors.
With so many details involved, apps enable active fall arrest systems to work reliably all day, every day.
Safety harnesses are only effective when properly inspected, fitted and worn. Let’s look at how apps provide oversight on these crucial processes.
Proper Use And Inspection Of Safety Harnesses

Harnesses represent the last line of defense against falls. But they can’t provide protection if they aren’t rigorously inspected, correctly fitted to each user, and worn properly all day. Too many steps exist for mistakes to creep in.
This is where fall safety apps save the day. By digitizing usage workflows, apps promote proper harness practices through:
- Digital inspection checklists for defects
- Tracking overdue inspections and removals
- Mandatory harness fit checks before work
- Blocking access if checks aren’t completed
- Monitoring weight limits and expiration dates
- Permitting use by authorized workers only
Instead of relying on workers to remember key steps, apps guide users through compliant processes that optimize harness effectiveness.
First, apps transform clumsy paper-based inspections into intuitive digital formats. Photos validate equipment conditions for remote review.
Next, apps enforce proper fit through mandatory check-in procedures where workers photograph harnesses donned correctly.
Even after shifts start, some workers remove harnesses in the field – apps prevent this by integrating with wearables that alert if a harness is taken off.
Harnesses seem simple, but are intricate life-saving devices. Apps provide the oversight needed for harnesses to perform their best when needed most.
Training Workers On Fall Hazards And Protection
When it comes to workplace safety, preventing falls should be a top priority for any business. After all, falls are the leading cause of worker fatalities, accounting for over 300 deaths per year in the U.S. alone. While falls can occur in many work environments, construction sites are especially hazardous, with around 30% of fall-related worker deaths occurring in construction.
Thankfully, with proper training and preventative measures in place, falls are highly preventable. Let’s explore some of the key things employers should do when training their workers on fall hazards and protection.
Conduct Thorough Fall Hazard Assessments
Before providing fall protection training, employers must first identify potential fall hazards at their work sites. This involves carefully analyzing each work area and task to pinpoint risks, such as unprotected edges, skylights, wall openings, steep roofs, unsound flooring, and more. For construction sites, hazard assessments should be conducted regularly as the site changes and evolves.
Establish Clear Fall Protection Policies

Once hazards have been identified, written fall protection policies and procedures must be put in place. These policies should clearly outline the required protective systems and devices to be used, such as guardrails, safety nets, personal fall arrest systems, covers for floor holes, and proper use of ladders and scaffolds. Policies should also specify who is responsible for proper set up and maintenance of equipment, conducting inspections, enforcing rules, and training workers.
Provide Training on Hazard Recognition
Workers must be educated on how to recognize fall hazards unique to their jobs. For example, those working on roofs should know that skylights and roof edges pose risks. Flagging or marking hazards, and putting warning signs in hazardous areas can also help alert workers to potential dangers. Additionally, training should cover how to report unsafe conditions that could lead to falls.
Demonstrate Proper Use of Fall Protection Equipment
Classroom-style training should be paired with hands-on demonstrations of proper equipment use. Employers should provide detailed instructions and let workers practice putting on harnesses, setting up guardrails, using lanyards, and more. It’s crucial that workers fully understand how to correctly wear and adjust equipment for maximum protection. Trainers should observe workers during practice to ensure proper use.
Educate on Access Equipment Hazards

Ladders, scaffolds, aerial lifts and other access equipment also carry serious fall risks if used unsafely. Employers must train workers on following safe practices, such as maintaining 3 points of contact on ladders, properly erecting scaffolds, and keeping aerial lift platforms from getting too close to edges or overreaching. Only properly trained workers should operate access equipment.
instill a Safety-First Mindset
While knowledge of policies and equipment use is crucial, fostering a culture of safety among workers is equally important. When providing fall protection training, emphasize that safety should come before productivity or shortcuts. Instill the mindset that protecting oneself from falls on the job isn’t optional – it’s an absolute must. Workers should be encouraged to speak up when they notice hazards or room for improvement in safety practices.
Provide Ongoing Training
A one-time training session is not enough. To keep knowledge and skills sharp, employers should provide fall protection refresher training regularly, such as annually. Also provide additional targeted training when new equipment is introduced or procedures change. When new workers arrive, make sure they receive comprehensive training before exposure to fall hazards. Ongoing training helps ensure safe habits become second nature.
Inspect and Enforce
It’s essential that employers enforce fall protection rules consistently after proper training has been given. Work sites should be monitored to ensure workers are following training, wearing proper gear, and using equipment correctly. Routine inspections of equipment are also critical for identifying any damaged or defective parts in need of replacement. Failure to consistently enforce safe practices can lead to complacency and accidents.
When it comes to fall risks, being proactive is a must in order to save lives and prevent injuries. Follow these tips to make fall protection training as effective as possible. Pair knowledge with frequent refreshers, demonstrations, and enforcement to ensure your workers make safety their first priority when working at heights.
Conducting Thorough Fall Protection Assessments
Preventing falls should be a top concern for any business where employees work at heights. After all, falls are the leading cause of worker fatalities, accounting for hundreds of deaths annually. While falls can happen across many industries, construction sites see a disproportionate amount – about 30% of fall-related worker fatalities occur in construction. The good news is that with proper fall protection assessments and safety measures, these incidents can be significantly reduced.
Let’s take a closer look at how to conduct thorough fall hazard evaluations to keep workers safe.
Involve Key Staff in Assessments
Fall protection assessments should involve management, supervisors, and floor staff alike. Managers can provide big-picture insight into site layouts, schedules, and safety protocol. Supervisors possess in-depth knowledge of day-to-day operations and can help pinpoint hazards. Rank and file employees who do the hands-on work are also invaluable, as they may notice dangers that supervisors miss.
Conduct Initial and Ongoing Site-Wide Assessments
A full work site evaluation looking for fall hazards should be done prior to starting any new construction project. Potential dangers like unprotected edges, openings in floors and walls, steep roofs, unsound surfaces, and lack of guardrails should be identified and addressed before work begins. On an active site, monthly assessments should continue as conditions change and new structures go up.
Analyze Specific Tasks and Work Areas
In addition to big picture site assessments, it’s critical to closely examine each distinct work area and task. For example, roofers face hazards like skylights and unprotected sides and edges. Mechanical contractors working in lift buckets must assess ground conditions and electrical lines. Assessors need extensive knowledge of all job roles to identify dangers unique to each.
Document Findings Thoroughly

Written documentation provides critical evidence that assessments have been done, and makes it easier to develop safety plans and track accountability. For each area and task, record details like the location, project phase, hazards observed, affected workers, and recommended controls. Photos and videos are also useful documentation tools. Keep detailed reports on file for reference.
Get Input from Workers
Workers performing the hands-on labor often notice potential fall hazards that supervisors can miss. Before assessments, gather input from staff on any concerns they have about their work environment. Set up a system where employees can anonymously report hazards without fear of reprisal. Consider and validate all worker concerns.
Use Heigh-Specific Assessment Tools
Specialized assessment forms can help identify hazards unique to working at certain heights. For example, a roofing hazard assessment checklist would include items like skylight protections, guards for openings, and slide guards for steep slopes. Customized tools provide consistency and ensure inspectors don’t overlook height-specific risks.
Mark and Flag Identified Hazards
Clearly marking or flagging off dangerous areas after identifying fall risks makes workers aware of hazards. Use warning signs, tape, cones or barricades to restrict access to hazardous areas. Mark floor and wall openings and post signs. Keep marked areas off limits until proper fall protection controls have been implemented.
Verify Controls are in Place
It’s not enough to just identify risks – appropriate fall protection systems like guardrails, safety nets or personal fall arrest systems must actually be installed. Assessors should confirm that engineering and administrative controls laid out in safety plans are fully implemented before work proceeds. Controls should also undergo routine inspection and maintenance.
Provide Ongoing Assessor Training
Conducting quality fall hazard assessments requires specialized skills and expertise. Provide initial and periodic refresher training to key personnel involved in assessments. Education should cover fall protection regulations, equipment, inspection techniques, documentation requirements, and more. Well-trained assessors are essential for identifying dangers.
Regular, thorough fall hazard evaluations are crucial to preventing worker falls. Following these best practices will help assessors conduct high-quality evaluations that drive effective safety programs and create a culture of fall prevention.
Features Of An Effective Fall Safety Mobile App

For companies with workers at height, investing in a dedicated fall safety mobile app can significantly improve prevention and response. But not all safety apps are created equal. The most effective ones have key features that empower employees to take fall protection into their own hands.
Let’s look at some must-have capabilities that set leading fall safety apps apart.
Hazard Identification and Reporting
A core app feature should allow workers to quickly snap photos or take videos of potential fall hazards they spot at the worksite. Useful additions include adding voice memos explaining the danger, and auto-tagging photos with date, time and geo-location data. The app should enable one-touch reporting that instantly alerts safety managers for quick resolution.
Equipment Inspections
Conducting and documenting regular gear inspections is a crucial safety process. Apps can simplify this by providing customizable digital checklists for examining components like harnesses, lanyards, anchor points and more. Employees can complete and submit detailed inspection reports right from their smartphone.
Access to Safety Data

OSHA mandates that companies maintain and share certain safety records with workers upon request. A mobile app provides anytime, anywhere access to documentation like training logs, inspection checklists, and incident reports. This data empowers employees with safety insights.
Training Resources
The ability to deliver fall protection training content directly through the app keeps safety top of mind. Alerts can remind workers to complete training modules and brief quizzes on topics like equipment use, hazard recognition, and safe work practices.
Company Policy Review
At any time, employees should be able to pull up digital copies of your company’s safety policies and procedures for fall prevention and response. Quick access ensures workers can reference policies on the go if there are ever any uncertainties.
Incident Reporting
If a fall or other safety incident does occur, the app should enable one-button incident reporting to immediately notify safety staff. The app can even guide employees through the reporting process using interactive prompts and checklists.
Post-Incident Analysis
Detailed reports provide valuable data to prevent future incidents. The app should allow managers to supplement employee-submitted reports with additional details, photos or root cause analysis. Aggregated reporting data also helps identify ongoing safety weaknesses.
Emergency Response Tools
In the event of a fall emergency, built-in tools can be lifesavers. An SOS button can alert nearby coworkers trained in rescue techniques. Location tracking pinpoints the injured worker, and time stamps document the swiftness of response.
Two-Way Messaging
For non-emergencies, two-way messaging enables safety managers and field employees to communicate about hazards, inspections or training requirements. Quick messaging helps tie the reporting loop and keeps all stakeholders engaged.
Automated Notifications and Alerts
App-triggered notifications eliminate reliance on memory. Alerts can remind workers to complete inspections, training or corrective actions on time. Safety managers also receive notifications when hazards are identified or incidents reported.
Collaborative Capabilities
Tools like group messaging boards allow everyone to discuss safety issues and solutions. Location-based discussions foster collaboration among coworkers in the same area, team or crew. A sense of collective involvement boosts participation.
Leveraging a comprehensive mobile app shows employees that safety is a top priority. Features that engage workers and provide helpful resources lead to improved reporting, documentation and analysis – ultimately preventing falls before they happen.
Real-Time Monitoring And Alerts For At-Risk Workers
For companies with employees working at heights, real-time safety monitoring provides an invaluable protective net. Advanced wearable devices now allow managers to track workers remotely and get alerts if they enter potentially dangerous scenarios.
Let’s explore how real-time monitoring capabilities are transforming fall protection programs today.
Detect Unsafe Proximity to Hazards
Wearable safety devices with built-in GPS tracking can detect when a worker ventures too close to an unprotected edge or other fall hazard. If they cross a pre-set virtual barrier, the manager receives an immediate alert to the risk so they can intervene.
Monitor Use of Fall Protection Gear
Sensors can confirm that employees have properly equipped their mandated harnesses, lanyards or self-retracting lifelines. If a worker disengages their gear or begins working at height without it, managers are alerted to address non-compliance.
Analyze Real-Time Fall Risk
Advanced algorithms factor in multiple data points like hazard proximity, equipment engagement and even weather conditions to calculate a worker’s live fall risk score. Managers can then take corrective actions to mitigate high risk scenarios before an incident occurs.
Detect Slips and Falls
Built-in accelerometers can automatically detect falls and alert safety managers within seconds. This allows for immediate remote response, even if the worker is incapacitated and unable to call for help themselves.
Track Response Time
Metrics like time stamps and location data let managers monitor and improve average response times. Analyzing the time between an alert and on-site intervention provides accountability and visibility into the effectiveness of emergency protocols.
Facilitate On-Site Rescue
When a fall or injury does occur, real-time location tracking guides rescuers quickly to the worker’s on-site coordinates. This expedites time-sensitive on-site emergency response and improves outcomes.
Monitor Lone Workers Remotely
For roofers, service technicians or other lone workers at height, real-time status updates provide reassurance and rapid emergency notification. Safety managers can continually monitor lone workers remotely and react at the first sign of trouble.
Coordinate Automated Check-ins
To ensure continual safety, managers can configure automated periodic check-in alerts. If a check-in is missed, it could signify an emergency like a fall, heart attack or other serious condition needing rapid response.
Promote a Safety-First Culture
When workers know their gear engagement and hazard proximity is being monitored, it reinforces safety-first behaviors. Responsibility becomes shared between workers and managers, promoting mutual accountability.
Access Detailed Incident Reports

Data gathered by real-time monitoring systems provides detailed documentation and visualization of any near misses or confirmed falls. This data is invaluable for incident investigation, root cause analysis and prevention of recurrences.
The wealth of insights provided by real-time worker monitoring and alert technology enables proactive fall prevention and rapid emergency response. While upfront investment is required, the payoff in reduced injuries, workers’ comp claims and OSHA fines is significant. Most importantly, these systems help ensure employees make it home safe at the end of each workday.
Custom Checklists For Daily Equipment Inspections
For workers at heights, their fall protection equipment is their lifeline to safety. Harnesses, lanyards, tie-off points and other gear must be in flawless working order to be effective. That’s why comprehensive daily inspections are a must. But generic checklists often miss job-specific nuances. That’s where custom inspection tools come in.
Let’s look at how tailored digital checklists can take safety inspections to the next level.
Customize by Equipment Type

Harnesses, lanyards, anchor hooks and lifelines all have very different components to inspect. A generic checklist leads to missed steps. With a customizable app, inspectors can follow a checklist tailored to the exact type of fall arrest gear being examined that day.
Personalize by Work Environment
Roofers, manufacturers and telecom tower technicians face very different equipment hazards. Custom checklists allow you to specify environmental factors like heat, cold, moisture and caustic chemicals that can degrade gear integrity over time.
Adapt to Work Tasks
The strain of specialized tasks can damage equipment. Custom inspection forms can include loads from tool belts, awkward work positions, point loading, and repeated deployment and retraction during unique work procedures.
Note User Information
A standardized form captures key data like the equipment user’s name, employee ID and group. Photos of labeled equipment provides accountability for assigned gear. Knowing exactly who uses each piece provides critical traceability if issues arise.
Require Sign-Off
Requiring a digital signature or personal pin code to close the inspection ensures accountability. Workers must complete the entire checklist and accept responsibility that equipment is sound before going on site. Mandatory sign-off prevents skipped steps.
Flag Used Gear Due for Retirement
Checklists can automatically flag gear reaching expiration or removal dates per the manufacturer’s specs. Visual flags prompt inspectors to pull aging gear out of rotation to maintain reliability.
Link to Equipment Records
Digital inspection tools can access a database of equipment records including purchase dates, inspection, loading and maintenance history, and expiration timelines. This data aids decisions on retirement or maintenance.
Guide Photographic Evidence
Photos provide visual documentation of equipment condition, but can be easily missed. Inspection apps can prompt users with instructions for taking specific photos, like “buckle wear” or “tension cable fraying” to provide evidence.
Facilitate Instant Reporting

Submitting paper checklists can delay repairs. Digital forms enable instantaneous reporting to safety managers, and automated alerts for defects requiring immediate equipment removal from service.
Maintain OSHA Compliance
Customized inspection tools guarantee OSHA mandates are met, preventing citations. OSHA compliance officers can also access detailed equipment records as digital proof of diligent inspections.
Custom inspection checklists tailored to specific jobs, environments and equipment provide the backbone for proactive fall protection maintenance. When inspection forms are thoughtfully designed, equipment reliability and worker safety continue to rise.
Detailed Reporting For Improving Safety Programs
Having detailed reporting and analysis is crucial for any organization looking to improve their safety programs and reduce incidents. Without clear data and insights, it’s impossible to pinpoint problem areas or recognize what’s working well. Let’s explore some of the key ways detailed reporting can lead to better safety outcomes.
Identifying Trends and Problem Areas

Detailed reporting allows you to track and analyze incident data over time to identify any emerging trends or problem areas. For example, you may notice an uptick in slips and falls in a certain department or location. With this insight, you can then investigate further and implement targeted preventative measures like improving housekeeping or installing slip-resistant flooring.
In-depth reporting also enables you to categorize incidents by type, severity, contributing factors, etc. This classification exposes patterns that may have previously gone unseen. Perhaps most of your recordable incidents relate to improper machinery operation or occur during the third shift. Detailed analysis shines a light on systemic issues.
Evaluating Mitigation Strategies
After identifying an area for improvement, detailed reporting helps determine if your mitigation strategy is working. For instance, if you launched a large ergonomics training program for manufacturing employees, you’d expect to see a decrease in musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) over time. Granular data allows you to track leading and lagging indicators related to MSDs before and after the training rollout.
Similarly, you can use rich data to calculate return on investment for safety initiatives. If a certain project lowered incidents by 10%, exactly how much did that save in workers’ compensation costs and lost time? Quantify the benefits to justify future health and safety investments.
Monitoring Compliance and Programs
Say your organization recently instituted a comprehensive lockout/tagout program. Detailed reporting can tell you how often the program was followed versus violated. Or maybe you want to confirm that every employee received the proper PPE training. Granular data makes compliance monitoring and program oversight much easier.
In-depth analysis also assists with internal audits and external inspections. Regulators will be impressed by robust recordkeeping that proves your health and safety efforts are making a measurable difference. Accurate statistics are essential during an OSHA inspection too.
Pinpointing Needs for Training
When the data shows certain incident types spiking, that’s a clue that refresher training may be needed. For example, perhaps there was a rash of forklift-related damage after several new operators were hired. Detailed reporting enables you to connect training needs back to real-world evidence.
Granular data can also reveal if injuries are concentrated among newer hires or younger demographics. You can then tailor onboarding and mentoring to give those high-risk groups additional skills. Ongoing training should address not just what the regulations require, but what your reporting indicates.
Recognizing Opportunities for Improvement

Even when all the obvious metrics like incident rates and lost days look excellent, detailed reporting may uncover chances to get even better. For instance, leading indicators like near misses and unsafe conditions observed can point to potential weak spots before they lead to injuries.
Likewise, reporting may show certain sites, departments, or shifts outpacing others safety-wise. Look to your top performers for insights into best practices that could be replicated elsewhere. Data-driven benchmarking spreads positive gains throughout the organization.
Enhancing Your Safety Culture
Ultimately, detailed reporting contributes to a resilient safety culture focused on continuous improvement. When frontline workers know management is carefully tracking key safety parameters, it demonstrates how much these issues matter. Data transparency, regular reporting, and follow-through on addressing problem areas drives engagement around health and safety.
Furthermore, today’s workforce wants to see progress over time. Comprehensive reporting shows the link between their daily safety efforts and big-picture results. That fosters meaning and pride in preventative work.
In summary, detailed reporting provides the foundation for data-driven safety decisions and proactive, targeted risk reduction. Leveraging granular incident data, compliance statistics, training records, and leading indicators gives a holistic view of current strengths and opportunities. Safety improvement begins with insights derived from in-depth reporting across the organization.