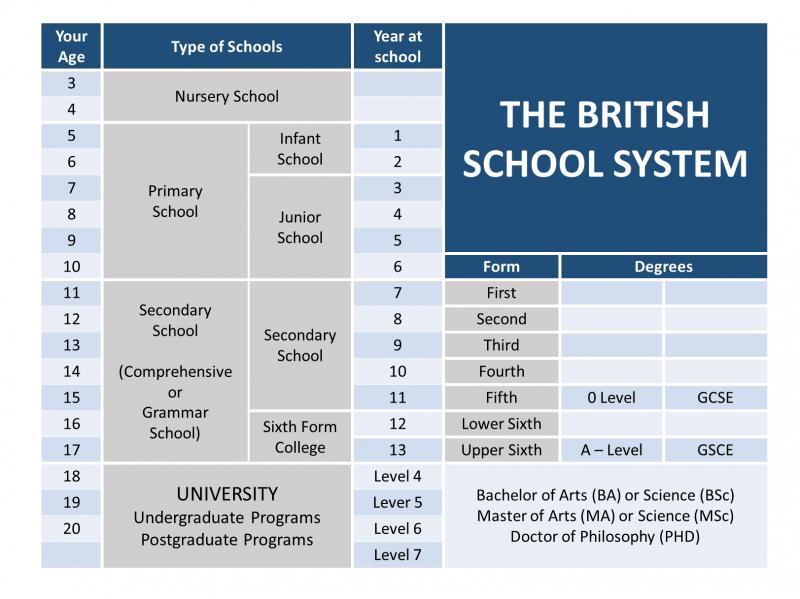
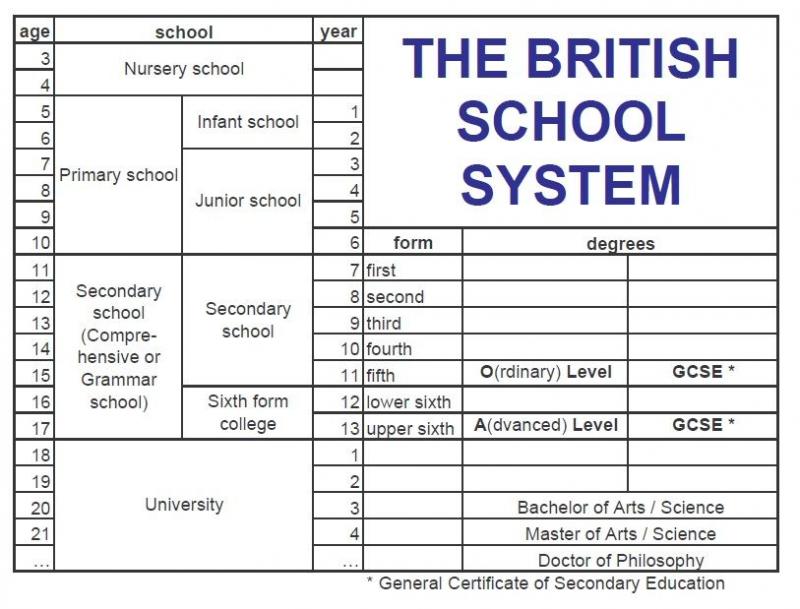
How are Cornerstone Charter Schools outperforming public schools. What strategies do they employ to achieve academic success. Why are parents choosing Cornerstone Charter Schools for their children. How does the rigorous curriculum at Cornerstone Charter Schools prepare students for the future. What role does data-driven instruction play in Cornerstone Charter Schools’ success.
The Rise of Cornerstone Charter Schools: A New Era in Education
Cornerstone Charter Schools have emerged as a formidable force in the education sector, experiencing unprecedented growth over the past decade. From a modest beginning with just a few schools, this network has expanded to over 100 institutions across 15 states, captivating parents and students alike with their unique approach to education.
The rapid expansion of Cornerstone Charter Schools can be attributed to their distinctive educational philosophy, which emphasizes a return to fundamental academic principles. These schools have garnered attention for their intensive focus on core subjects, disciplined learning environment, and impressive performance metrics.

The Cornerstone Difference: Academic Intensity
At the heart of Cornerstone Charter Schools’ success lies their unwavering commitment to academic excellence. Unlike traditional public schools that often offer a broad range of subjects and extracurricular activities, Cornerstone schools maintain a laser-like focus on core academic subjects such as mathematics, science, reading, and writing.
This intense academic concentration has both advocates and critics. Supporters argue that this approach equips students with essential skills needed to thrive in an increasingly competitive world. Critics, however, express concerns about the potential lack of creative and emotional development opportunities.
Innovative Teaching Methods: Engaging the Modern Learner
Cornerstone Charter Schools pride themselves on employing cutting-edge instructional techniques to keep students engaged and motivated. Their classrooms are dynamic environments where traditional lecture-style teaching is replaced with interactive and immersive learning experiences.

- Active learning strategies
- Technology integration
- Peer-to-peer learning
- Flipped classroom approach
- Project-based learning
These innovative teaching methods aim to transform students from passive recipients of information into active participants in their educational journey. By incorporating elements such as songs, chants, and physical movement into lessons, Cornerstone teachers strive to make learning both enjoyable and effective.
The Role of Technology in Cornerstone Classrooms
Technology plays a pivotal role in the Cornerstone educational model. From interactive whiteboards to educational apps and online learning platforms, these schools leverage digital tools to enhance the learning experience and prepare students for a technology-driven world.
Community Engagement: A Pillar of Cornerstone’s Success
Cornerstone Charter Schools recognize that education extends beyond the classroom walls. They place a strong emphasis on parental involvement and community partnerships, creating a supportive ecosystem for student success.

Parents are expected to actively participate in their child’s education, from attending school events to reinforcing disciplinary standards at home. This high level of parental engagement fosters a strong home-school connection, which is crucial for student achievement.
Moreover, Cornerstone schools forge partnerships with local businesses and community organizations, providing students with real-world learning opportunities. These collaborations not only enrich the educational experience but also help students develop practical skills and understand the relevance of their studies to the world beyond school.
The Selective Admission Process: Ensuring Student Readiness
One of the distinguishing features of Cornerstone Charter Schools is their selective admission process. Unlike public schools that typically admit students based on geographical boundaries, Cornerstone schools employ a rigorous application and selection procedure.
- Review of prior academic performance
- Standardized test scores
- Personal interviews
- Recommendations from previous teachers
This selective approach has sparked debate in educational circles. Supporters argue that it ensures a student body capable of thriving in Cornerstone’s demanding academic environment. Critics, however, contend that this practice may exclude students who could benefit from the schools’ resources and teaching methods.

Are Cornerstone Schools Truly Accessible to All?
The selective admission process of Cornerstone Charter Schools raises important questions about educational equity and access. While these schools aim to create an environment conducive to high achievement, there are concerns that this approach may inadvertently perpetuate educational disparities.
Extended Learning Time: Maximizing Educational Opportunities
Cornerstone Charter Schools operate on an extended schedule that significantly surpasses the typical public school calendar. Students attend classes six days a week, with the academic year often stretching to 200 days – far beyond the standard 180-day school year.
The school day at Cornerstone institutions is also longer, typically running from 8 AM to 4 PM. Additionally, many schools offer mandatory after-school tutoring sessions for students who require extra support. This extended learning time is based on the principle that increased exposure to academic content leads to improved outcomes.

The Impact of Extended Learning Time on Student Well-being
While the extended schedule at Cornerstone schools aims to maximize learning opportunities, it also raises concerns about student well-being and work-life balance. Critics argue that such intense schedules may lead to burnout and stress among students and teachers alike.
High Expectations and Strict Discipline: The Cornerstone Approach
Cornerstone Charter Schools are known for their high academic expectations and stringent disciplinary policies. Students face rigorous coursework, frequent assessments, and strict grading standards. The schools maintain that this challenging environment prepares students for the demands of higher education and the professional world.
Discipline is a cornerstone of the Cornerstone approach. Students are required to wear uniforms and adhere to strict behavioral codes. Infractions can result in detentions or suspensions, reflecting the schools’ belief that a structured environment is crucial for academic success.

The Debate on Strict Discipline in Education
The strict disciplinary approach employed by Cornerstone schools has sparked debate in educational circles. Proponents argue that it creates a focused learning environment and instills important life skills. Critics, however, contend that such stringent policies may be too authoritarian and fail to address the underlying causes of behavioral issues.
Data-Driven Instruction: Personalizing the Learning Experience
At the core of Cornerstone Charter Schools’ educational model is a strong emphasis on data-driven instruction. These schools employ advanced analytics to continually assess student performance and tailor teaching strategies accordingly.
Students undergo frequent online assessments, providing teachers with real-time data on their progress. This information allows educators to identify areas of weakness, modify lesson plans, and provide targeted support where needed. Students are also encouraged to track their own progress, fostering a sense of ownership over their learning journey.

The Potential Drawbacks of Data-Centric Education
While data-driven instruction offers numerous benefits, it has also faced criticism. Some educators and parents worry that an overemphasis on quantitative metrics may overshadow other important aspects of education, such as creativity, critical thinking, and social-emotional development.
Addressing Diverse Learning Needs: Cornerstone’s Approach to Inclusivity
Despite their reputation for selectivity and academic rigor, Cornerstone Charter Schools have made efforts to accommodate students with diverse learning needs. While most Cornerstone schools do not offer self-contained special education programs, they provide various forms of support for students with learning differences.
- Differentiated instruction
- Paraprofessional support
- Assistive technology
- English Language Learner programs
These accommodations aim to ensure that students with diverse learning needs can access the challenging curriculum and thrive in the Cornerstone environment. However, the effectiveness of these measures in fully supporting all students remains a topic of ongoing discussion and evaluation.

The Challenge of Balancing Rigor and Inclusivity
Cornerstone Charter Schools face the ongoing challenge of maintaining their high academic standards while also ensuring inclusivity for students with diverse learning needs. This balance is crucial for the schools to fulfill their mission of providing excellent education to a broad range of students.
The Future of Education: Lessons from Cornerstone Charter Schools
The rapid growth and success of Cornerstone Charter Schools offer valuable insights into the future of education. Their focus on academic rigor, innovative teaching methods, and data-driven instruction has yielded impressive results, attracting attention from educators, policymakers, and parents alike.
However, the Cornerstone model also raises important questions about educational equity, student well-being, and the balance between academic achievement and holistic development. As the education landscape continues to evolve, the experiences of Cornerstone Charter Schools provide a rich source of data and inspiration for ongoing discussions about best practices in education.

Can the Cornerstone Model Be Replicated in Public Schools?
One of the most intriguing questions arising from the success of Cornerstone Charter Schools is whether their model can be effectively implemented in traditional public school settings. While some elements of the Cornerstone approach may be adaptable, factors such as funding, regulatory requirements, and diverse student populations present significant challenges to wholesale adoption of the model.
Nonetheless, many public schools are exploring ways to incorporate aspects of the Cornerstone approach, such as extended learning time, data-driven instruction, and increased parental involvement. The ongoing dialogue between charter and public schools may lead to innovative hybrid models that combine the strengths of both systems.
The Impact of Cornerstone Charter Schools on Educational Policy
The success of Cornerstone Charter Schools has not gone unnoticed by policymakers and education reformers. Their model has influenced discussions about school choice, accountability measures, and the role of standardized testing in education.

Advocates of the Cornerstone model argue that their success demonstrates the potential of alternative educational approaches and the importance of school choice. Critics, however, caution against using charter school performance as a blanket argument for privatization of education, pointing out the unique circumstances and selective nature of many charter schools.
The Role of Charter Schools in Educational Innovation
Cornerstone Charter Schools, like many charter schools, serve as laboratories for educational innovation. Their ability to operate with greater autonomy than traditional public schools allows them to experiment with new teaching methods, curricula, and organizational structures. This flexibility can lead to valuable insights and practices that may benefit the broader education system.
However, it’s crucial to consider the context in which these innovations occur. The selective nature of many charter schools, including Cornerstone, means that their successes may not be directly transferable to all educational settings. Nonetheless, their experiences provide valuable data and ideas for improving education across all types of schools.

Parental Perspectives on Cornerstone Charter Schools
The rapid growth of Cornerstone Charter Schools is largely driven by parental demand. Many parents are attracted to the schools’ promise of academic excellence, structured learning environment, and track record of sending graduates to top colleges.
For these parents, Cornerstone schools offer an alternative to public schools that they perceive as underperforming or unable to meet their children’s needs. The schools’ emphasis on discipline, hard work, and measurable results aligns with many parents’ visions of what education should entail.
The Trade-offs of Choosing a Cornerstone Education
While many parents are enthusiastic about the Cornerstone model, others express concerns about the potential drawbacks. The intense academic focus, long school hours, and strict disciplinary policies may not be suitable for all students. Some parents worry about the lack of emphasis on arts, sports, and other extracurricular activities that contribute to a well-rounded education.

Additionally, the selective admission process and potential for high student turnover (as students who struggle to meet the schools’ standards may leave) can create a sense of instability or exclusivity that some parents find problematic.
Teacher Experiences in Cornerstone Charter Schools
Teachers play a crucial role in the success of Cornerstone Charter Schools, and their experiences offer valuable insights into the strengths and challenges of this educational model. Many teachers are drawn to Cornerstone schools by the opportunity to work in a highly focused academic environment with motivated students and supportive administration.
The schools often provide extensive professional development opportunities, allowing teachers to continually refine their skills and stay abreast of the latest educational research and techniques. The data-driven approach also appeals to many educators who appreciate the ability to track student progress in real-time and adjust their teaching strategies accordingly.

The Challenges of Teaching in a High-Pressure Environment
While many teachers thrive in the Cornerstone environment, others find the intense focus on academic achievement and data to be challenging. The extended school hours and rigorous curriculum can lead to burnout, and some teachers feel pressure to prioritize test preparation over more holistic approaches to education.
Additionally, the strict disciplinary policies and high expectations for student behavior can create a demanding classroom management environment. Teachers must navigate the delicate balance between maintaining order and fostering a positive, supportive learning atmosphere.
The Long-Term Impact of Cornerstone Education on Students
As Cornerstone Charter Schools continue to grow and graduate more students, researchers are beginning to examine the long-term impacts of this educational model. Early data suggests that Cornerstone graduates often perform well in college admissions and demonstrate strong academic skills in higher education settings.
However, more comprehensive studies are needed to fully understand the effects of a Cornerstone education on students’ overall development, career trajectories, and life outcomes. Questions remain about how well the intense academic focus prepares students for the diverse challenges they may face in their personal and professional lives.
Beyond Academics: Assessing Social and Emotional Development
While Cornerstone Charter Schools excel in academic preparation, there is ongoing debate about how well they support students’ social and emotional development. Critics argue that the intense focus on academics may come at the expense of other important life skills, such as creativity, empathy, and resilience.
Proponents of the Cornerstone model, however, contend that the schools’ emphasis on discipline, hard work, and personal responsibility instills valuable character traits that serve students well in all aspects of life. As more long-term data becomes available, a clearer picture of the holistic impacts of a Cornerstone education may emerge.
The Role of Technology in Cornerstone Charter Schools
Technology is a cornerstone of the Cornerstone Charter Schools’ educational approach. These institutions leverage cutting-edge digital tools and platforms to enhance instruction, assess student progress, and prepare learners for a technology-driven world.
From interactive whiteboards and tablets in classrooms to sophisticated learning management systems, Cornerstone schools integrate technology at every level of the educational experience. This tech-savvy approach not only facilitates more engaging and personalized learning but also equips students with essential digital literacy skills.
Balancing Screen Time and Traditional Learning Methods
While technology plays a crucial role in Cornerstone schools, there is ongoing discussion about striking the right balance between digital and traditional learning methods. Some educators and parents express concerns about excessive screen time and the potential loss of important analog skills like handwriting and face-to-face communication.
Cornerstone schools are continually refining their approach to technology integration, aiming to harness the benefits of digital tools while preserving the value of traditional educational practices. This balance is crucial for preparing students for a world where both digital and analog skills are important.
Financial Aspects of Cornerstone Charter Schools
The financial model of Cornerstone Charter Schools is an important aspect of their operation and growth. As publicly funded institutions, these schools receive per-pupil funding from state and local governments. However, they often supplement this funding through private donations, grants, and partnerships with businesses and foundations.
This hybrid funding model allows Cornerstone schools to invest in resources and programs that may not be available in traditional public schools. However, it also raises questions about equity and the allocation of educational resources.
The Debate Over Charter School Funding
The funding of charter schools, including Cornerstone, is a topic of ongoing debate in educational policy circles. Supporters argue that charter schools provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional public schools, delivering strong academic results with similar or lower per-pupil spending.
Critics, however, contend that charter schools divert resources from public school systems, potentially exacerbating educational inequalities. The financial sustainability of the charter school model, particularly for schools that rely heavily on private funding, is also a subject of scrutiny.
Introduction to cornerstone charter schools and their rapid growth
Have you noticed those new charter schools popping up around your neighborhood lately? The ones with names like Excellence Academy or Pinnacle Prep? Chances are those belong to one of the fastest growing charter school networks in the country – the Cornerstone Charter Schools.
These schools pride themselves on “getting back to basics” with their intense focus on academics, discipline, and performance. And parents are eating it up. Cornerstone Charter Schools have exploded over the past decade, growing from just a handful of schools to over 100 today across 15 states. So what’s behind their meteoric rise?
They Focus Like a Laser on Academics
When you walk into a Cornerstone Charter, don’t expect to see students painting murals or playing instruments. These schools are intense academic hothouses, with the focus relentlessly on math, science, reading, and writing. Forget about extras like art, music, or recess – every minute is designed to prepare students for testing and college prep.
Critics argue this laser academic focus leaves little room for creativity or emotional development. But Cornerstone contends their approach gives students the tools to succeed in today’s rigorously academic and competitive world.
Teachers Have a Whole Bag of Tricks
Cornerstone teachers are highly trained in cutting-edge instruction techniques to keep kids engaged and learning. Expect active, fast-paced classrooms with teachers peppering their lessons with songs, chants, and physical movement. They make extensive use of technology, online games, and digital learning tools to capture kids’ interest.
There’s no sitting passively taking notes in these classrooms! Cornerstone teachers use proven techniques like peer-to-peer learning, flipped classrooms, and project-based learning to ensure kids are actively absorbing the material.
Parents and Community are Key Partners
Parental involvement is huge in Cornerstone schools. Parents are expected to participate in school activities, enforce discipline at home, and fully engage in their child’s education. This strong home-school partnership keeps kids on track.
Cornerstone also partners closely with community organizations and local businesses to provide additional learning opportunities. Students may work on projects for local companies or non-profits, combining academics with real-world experience.
Getting In Is Tough
Cornerstone Charter Schools are selective in who they admit. There are no neighborhood boundaries – students apply from across the region. But the application process is rigorous, with admissions based on prior grades, test scores, interviews, and recommendations. Only the most motivated students get in.
Critics argue this “cherry picking” stacks the deck by only accepting the best students. But Cornerstone contends their admissions process ensures students are prepared to handle the schools’ fast pace and high expectations.
Non-Stop Schooling
Once you’re in, get ready for a tightly packed school calendar. Cornerstone students attend school 6 days a week and as many as 200 days per year – much longer than a typical public school. The school day is longer too, usually 8am to 4pm daily, plus mandatory after school tutoring for students who need it.
Exhausting for both students and teachers, but Cornerstone believes there’s no substitute for putting in the time when it comes to academic achievement.
High Pressure and Strict Discipline
Academic expectations are sky-high at Cornerstone schools. Students face heavy workloads, regular testing, and strict grading. Countless homework assignments and intense pressure to ace standardized tests.
Discipline is serious business too. Students wear uniforms, follow strict behavior codes, and can face detention or suspension for slacking or acting up. Critics argue the atmosphere is too authoritarian, but Cornerstone maintains discipline is essential for academic progress.
Data Drives Everything
Data analytics drive instruction at Cornerstone schools. Students are tested frequently with online assessments, giving teachers real-time data to modify lessons and target weak areas. Kids track their own progress continuously against educational goals.
Some argue this data obsession takes the humanity out of education. But Cornerstone leverages data to ensure each child masters the material before moving to the next level.
Accommodations for Special Needs

While most Cornerstone schools don’t offer self-contained special education, they do provide accommodations through differentiated instruction, paraprofessional support, and assistive technology for kids with learning differences. And English Language Learner programs help students from foreign backgrounds get up to speed.
Critics say Cornerstone lacks the staffing to properly serve kids with greater needs. But within their model, Cornerstone strives to make accommodations based on each student’s requirements.
College Obsessed
Everything at Cornerstone is geared towards college preparation, starting in elementary school. The intensive academics, high pressure testing, and rigorous workload aim to give students the study skills and mindset to thrive in higher education.
College pennants line the hallways as motivation. High schoolers take SAT/ACT prep courses and practice college admissions essays. Counselors actively guide families through the application process.
Critics contend students are pushed too hard too young without enough balance. But Cornerstone sees rigorous college focus as giving their mostly disadvantaged students a ticket to advancement.
Who Runs These Schools Anyway?
Here’s an interesting fact about Cornerstone Charter Schools – they’re managed by a for-profit corporation, Cornerstone Management Group. CMG handles curriculum, hiring, school policies, and business operations for all Cornerstone schools.
This tight centralized control is key to replicating the Cornerstone model quickly across the U.S. But critics contend an educational system shouldn’t be run by a corporation focused on the bottom line.
Big Money Behind Them
Running a successful charter school network takes a lot of startup capital. The money fueling Cornerstone’s expansion comes from big donors and Wall Street backers enthused by their academic results.
Wealthy philanthropists, hedge fund managers, foundations and investment banks have pumped hundreds of millions into CMG to target rapid growth. Their financial muscle lets Cornerstone scale up faster than local public schools can.
Real Estate Wheels Greased
Finding facilities is one of the biggest challenges for new charter schools. But Cornerstone’s deep-pocketed financial backers allow CMG to lease, build, and renovate impressive campuses far quicker than a traditional public school could.
This gives Cornerstone a big advantage over crowded urban schools housed in aging buildings. For families in these areas, the shiny new Cornerstone campuses are a big draw.
Hiring the Best Talent
Cornerstone attracts top teaching talent by offering merit-based pay, performance bonuses, and stock options – compensation public schools can’t match. Teachers are highly motivated and closely monitored for results.
Critics contend merit pay leads to excessive teaching to the test. But to Cornerstone, rewarding standout teachers is part of their free market-based approach to education.
Intense Lobbying
CMG hires dozens of lobbyists to promote charter-friendly policies at the local, state, and national level. Their deep pockets give them influence over regulations governing charter schools.
Critics argue this unfairly tilts the regulatory playing field against public schools. But Cornerstone contends they are just working within the system to advocate for their organization.
But Aren’t These Schools Creaming Off Top Students?
The most common criticism leveled at charter school networks like Cornerstone is that by selectively admitting motivated students with engaged parents, they “cream off” the top students from public schools, leaving them drained of talent and leadership.
There may be some truth to this. But supporters counter that Cornerstone Charter Schools are giving vital opportunities to disadvantaged students let down by failing public schools in their neighborhoods.
Rather than letting poor but capable students slip through the cracks, Cornerstone is nurturing the abilities of these motivated kids to unlock their potential.
Draining Resources?
There’s also criticism that charters siphon funding from traditional public schools as enrollment shifts to charter networks. Proponents counter this “rising tides lifts all boats” – competition from charters motivates local public schools to innovate and improve.
Research on these dynamics is mixed, but competition from high-performing charter networks like Cornerstone certainly disrupts the status quo – by design.
The Segregation Question
Since many Cornerstone Charter Schools serve predominantly low-income minority populations, some argue they lead to increased racial isolation compared to more diverse public schools.
Supporters counter that parents have chosen these schools because they offer a quality alternative to dysfunctional neighborhood schools. And lifting up disadvantaged communities should take priority over integrating students.
Scalability Concerns
With their aura of exclusivity and Harvard-style admissions, can the Cornerstone model scale to serve all families seeking their services? Supporters believe Cornerstone is bringing innovation that can transform public education as a whole.
But replicating Cornerstone’s atmosphere of academic intensity may prove difficult beyond a limited scope. As the network grows, maintaining quality control will be an increasing challenge.
Where Are Cornerstone Charter Schools Headed?
If growth continues as rapidly as the last decade, Cornerstone Charter Schools are on pace to become a major force in public education over the next 10 years. But some big questions remain about their expansion.
Will their laser academic focus continue to deliver standout results as they scale? Can their model work for students with moderate to severe disabilities? Will public school systems embrace their innovations or view them as unwanted disruption?
While such questions remain, one thing is clear – the Cornerstone Charter School revolution shows no signs of slowing down.
Cornerstone charter schools’ focus on academic excellence
If there’s one thing that sets Cornerstone charter schools apart, it’s their hardcore, no-nonsense focus on academics. These schools are on a mission to prep students for college, and they let nothing get in the way of that goal.
From the moment students set foot in a Cornerstone charter, the expectations are sky-high. We’re talking serious homework loads, intense standardized test prep starting in elementary school, and strict grading against rigorous benchmarks.
Forget about flaky electives like drama or shop class. Every minute of the school day is geared toward building skills in math, science, English, and critical thinking. I’m talking a boot camp style academic environment.
Now don’t get me wrong – a lot of parents welcome this intense approach. They feel public schools have gotten soft and aren’t preparing kids for the global economy. And studies show Cornerstone students consistently outscore their public school peers on standardized tests.
But critics argue that placing such extreme focus on rote academics and testing comes at the expense of creative self-expression. They contend childhood should be a time for play, emotional development, and exploring interests – not just prepping for college exams day-in and day-out.
As a former public school teacher myself, I see merits to both viewpoints. But there’s no denying Cornerstone’s laser academic focus yields measurable results for students determined to excel.
Tough Grading
Grading is no joke at Cornerstone schools. We’re talking standards that would make Marine drill instructors blush. Getting a B is considered borderline failure in many cases.
Students constantly track their own progress on skills mastery checklists, working to fill in all the boxes. Teachers do “data deep dives” into regular assessment results, tweaking lesson plans to target weaknesses.
No slacking or coasting allowed here. Students quickly learn they must put in maximum effort to make the grade. Supporters applaud this high level of accountability. Critics argue it creates unhealthy stress.
Testing Mania
Standardized test prep is baked into the Cornerstone curriculum from kindergarten on up. Expect practice testing several times per year, with intensive test prep courses beginning junior high.
Math and English lessons tightly align with state testing standards. Students learn tricks and strategies for excelling on multiple choice and essay sections. The goal is college-ready test scores.
Some feel this test-centric focus encourages superficial learning. But Cornerstone stands by it as the path to academic excellence most valued by top universities.
Rigorous Course Loads
Cornerstone students carry heavy course loads across the academic spectrum – think multiple AP classes for high schoolers. The homework requirements are massive too – expect 3+ hours per night.
They offer few open electives or study halls where students can catch a break. Every class must build college-prep academic skills, not just “fun stuff.” It’s a demanding pace requiring focus and time management skills.
Critics argue students need more balance between school work and personal time. But Cornerstone considers their rigorous approach key to getting into top colleges.
Laser Teaching Methods
Sitting passively and taking notes is not how Cornerstone teachers roll. They use cutting-edge instruction models to hammer home lessons and keep kids engaged.
Expect personalized digital content, project-based learning, peer-to-peer teaching, and active participation. Teachers function more as coaches than lecturers in this style.
Some feel these teaching methods focus more on delivery rather than depth. But Cornerstone stands by them as critical to reaching today’s learners and maximizing performance.
The intense academic environment at Cornerstone Charter Schools isn’t for everyone. But for motivated students looking to ace the test and get into a top university, few can match the rigorous preparations these schools provide.
It’s academics on steroids – precisely what many striving families are looking for.
Innovative teaching methods used in cornerstone charters
Walk into a typical public school classroom and you’re likely to see a familiar scene – students sitting at desks, passively listening to a teacher lecture at the front of the room. But step into a Cornerstone charter school and get ready for something completely different.
See, Cornerstone teachers toss out the traditional classroom playbook. Instead, they use cutting-edge methods to actively engage students and deliver lessons in the most impactful way possible. This innovative approach is a big part of what sets Cornerstone schools apart.
From personalized digital learning tools, to project-based learning, peer tutoring, and flipped classrooms, these schools are pedagogical petri dishes. The focus is on innovating new ways to educate, not dusty old teaching traditions.
Customized Digital Learning
Technology is huge in Cornerstone classrooms. Students work at their own pace through adaptive digital curriculums that tailor lessons to their individual strengths and weaknesses. Sophisticated data analytics enable continuous feedback.
Supporters say this digital approach personalizes learning far better than one-size-fits-all lectures. But critics argue too much screen time hampers social development.
Peer-to-Peer Learning
Rather than endless lectures from a teacher’s mouth, Cornerstone students spend much of their time learning collaboratively in small groups. They complete projects together, peer tutor struggling learners, and even co-teach lesson modules.
Proponents believe peer learning builds teamwork and retention. Critics contend students may reinforce each others’ misconceptions and shortcomings.
Flipped Classrooms
The flipped classroom model is used extensively at Cornerstone schools. Students gain first exposure to new material through videos, readings, and interactive modules outside school. In-class time is then spent on projects applying the knowledge, with the teacher coaching.
Supporters say this “homework in class, lectures at home” approach increases engagement. Critics argue it puts too much burden on parents.
Learning by Doing
You won’t find students sitting passively and endlessly taking notes at a Cornerstone school. Instruction emphasizes learning through hands-on application – conducting science experiments, building models, doing group projects, and practicing skills interactively.
Proponents believe active participation cements learning. Critics contend students need more explicit instruction at times.
The intense academic focus at Cornerstone schools isn’t innovative in itself. What’s trailblazing is how they leverage technology, customized instruction, and interactive methods to deliver that rigorous content as effectively as possible. It reflects their willingness to throw out the old classroom playbook and embrace new models that work.
Are these teaching innovations miracle cures or just flashy bells and whistles? The debate continues. But Cornerstone is fully committed to innovating more effective ways of educating students for the 21st century.
Parental involvement and community partnerships
At many public schools, getting parents actively involved can be like pulling teeth. But at Cornerstone charter schools, engaged parents are expected to be key partners in their child’s education.
These schools make parent participation a core part of their model. From volunteer committees, to homework monitoring, to fundraising drives – parents are enlisted to help maximize student success.
Cornerstone also partners closely with local businesses and nonprofits on programs that enrich student learning. These community ties give students real-world educational experiences.
Parent Participation Mandatory
When students enroll at Cornerstone, parents must sign a pledge to stay actively involved in their academics and school activities. That means things like enforcing homework time, attending parent-teacher conferences, and serving on volunteer committees.
Supporters say engaged parents are key to student achievement. Critics argue not all parents can participate equally due to jobs and other barriers.
Non-Stop Communication
Get ready for a fire hose of school emails, phone calls, and progress reports as a Cornerstone parent. The schools maintain constant contact to update parents on assignments, grades, and issues as they arise.
Proponents believe this keeps parents fully informed. But some see it as micromanagement or nagging.
Fundraising Duty
Charter schools operate on tight budgets, so Cornerstone parents are enlisted as fundraisers. From donation drives to gala events, parents are expected to chip in time and money to support school programs.
Supporters say this builds community engagement. Critics argue it burdens working class families.
Leveraging Community Partners
Cornerstone partners with local businesses, colleges, nonprofits, and community groups on programs that provide real-world educational experiences. Students may intern at companies, collaborate with professors, or help solve problems facing local organizations.
Advocates say these partnerships bring education to life. Opponents argue companies shouldn’t shape school priorities.
Parent and community involvement is baked into the Cornerstone model. Supporters applaud it for engaging families and enriching academics. But it also puts burdens on parents that not all can meet equally.
Regardless, few can deny that Cornerstone parents tend to be a highly motivated bunch. Their energy and participation is a major asset fueling these schools’ success.
Rigorous student admission standards at cornerstone charters
Unlike public schools that must accept all students in their zone, Cornerstone charter schools can carefully select who gets admitted through a rigorous application process. This selectivity is controversial, but also key to Cornerstone’s success.
Getting into a Cornerstone school is no easy feat. The application requires good grades, test scores, essays, interviews, and recommendations. Only the most motivated students make the cut.
Supporters say this ensures students are prepared for Cornerstone’s fast pace and high expectations. But critics argue it unfairly “creams” the top students from public schools.
Top Test Scores Needed
Standardized test scores are a huge factor for Cornerstone admission. Applicants must submit their latest scores and have percentiles well above average to qualify. This filters for students who test well right off the bat.
Proponents believe testing objectively identifies prepared students. Critics say it ignores late bloomers with potential.
Straight A’s Preferred
Like the test score filter, Cornerstone also uses prior grades to identify motivated students. Applicants must submit their last two years of report cards showing consistently high marks to be competitive.
Supporters say past grades predict future effort. Critics argue grades can be influenced by outside factors like teaching quality.
Essays and Interviews
In addition to quantitative data, Cornerstone’s application requires short essays and in-person interviews to gauge student drive and attitude. Communication skills and critical thinking are evaluated.
Proponents believe this screens for genuine interest and fit. Critics say interviews and essays can introduce bias.
Teacher Recs a Must
All students must submit two teacher recommendations along with their Cornerstone application. These confidential recs provide an outside perspective on work ethic and behavior.
Supporters say teacher insights help identify deserving students. Critics argue recs often just reflect grades.
Cornerstone’s selective admissions ensure the schools get students fully prepared and motivated to thrive in their rigorous academic environment. But critics argue it tilts the playing field by skimming the cream of the crop from public schools.
Regardless, the admissions standards establish Cornerstone as an academic home for strivers looking to be challenged to their full potential.
Longer school days and extended school years
Thought your kid put in long hours at their public school? Cornerstone students endure schedules that make a typical public school look like a part-time gig.
We’re talking school years that last up to 200 days, six day school weeks, and eight to ten hour school days packed with instructional time. It’s an academic marathon designed to accelerate learning.
Supporters applaud the extended time as key to Cornerstone’s outcomes. But critics argue the grueling pace leads to burnout.
200 Days of School Per Year
While most public schools max out around 180 instructional days per year, Cornerstone students are in school up to 200 days annually. That’s nearly an extra month of education each year.
Proponents say this extended time is crucial for accelerating academics. Critics argue students need breaks to recharge.
Mandatory Summer School
Summer vacation? Forget about it. Cornerstone students attend mandatory academic summer school to prevent learning loss. Required summer reading lists are rigorous too.
Supporters say this minimizes the summer slide. Critics argue kids need unstructured downtime in summer.
Six Day School Weeks
Most schools operate on a five day weekly schedule. But Cornerstone students attend classes six days a week, Monday through Saturday, for maximum instructional time.
Proponents argue the six-day weeks pack in more learning. Critics say they leave little time for family.
Eight to Ten Hour School Days
In addition to the extended calendar, Cornerstone school days run nearly two hours longer than average public schools. The extensive schedule is dominated by instructional time.
Advocates say longer days equal more learning. Critics argue it causes burnout.
There’s no denying Cornerstone students spend WAY more time in school than their public peers. Supporters see this as a key advantage. But even the most motivated kids struggle with schedules this packed and non-stop.
High expectations and accountability for students and teachers
Cornerstone charter schools operate on a principle of extremely high expectations paired with strict accountability up and down the organization. For both students and teachers, performance is closely monitored.
Students face heavy workloads, rigorous grading, and regular assessment of progress against goals. Teachers must demonstrate concrete learning gains in their classrooms through data.
Supporters say mutual accountability fuels Cornerstone’s outcomes. But critics argue it leads to excessive pressure.
No Excuses for Students
Cornerstone students hear one message loud and clear: “no excuses.” Regardless of background, difficulties, or obstacles, students are expected to excel academically through hard work and perseverance.
Advocates say this “no excuses” mindset instills grit. Critics argue some students need more support.
Intensive Data Tracking
Student progress at Cornerstone schools is constantly measured through assessments, grades, and goal tracking. Struggling students face mandatory tutoring, homework support, and parent conferences.
Proponents believe data accountability identifies and helps struggling students. Critics argue it causes unhealthy stress.
Merit-Based Pay for Teachers
Teacher compensation at Cornerstone schools ties heavily to student performance metrics. Big bonuses can be earned for exceeding learning goals.
Supporters say merit pay attracts top teaching talent. Critics argue it leads to “teaching to the test.”
Data Driven Evaluation
Like students, teachers are closely evaluated using data tied to student learning gains. Teachers who fail to meet quantifiable goals face retraining or replacement.
Proponents believe data accountability ensures effective teaching. Critics argue it diminishes teacher creativity.
The intense mutual accountability system at Cornerstone schools drives outcomes but also criticism that students and teachers face excessive top-down pressure.
But for better or worse, this laser focus on quantifiable results is fundamental to the Cornerstone model.
How cornerstone charters measure student progress
If data is the fuel that powers Cornerstone charter schools, student assessment is the engine. These schools are obsessive about constantly measuring and tracking student progress through a barrage of tests, metrics, and goal tracking.
Supporters argue this data-driven approach maximizes student growth and identifies weak spots. But critics contend it leads to excessive testing and stress.
Monthly Benchmark Assessments
Students at Cornerstone schools take benchmark assessments at least monthly to gauge progress in each subject. Results are used to tailor instruction and target weak areas.
Proponents believe frequent testing spots learning gaps early. Critics argue it detracts from meaningful learning.
Data Walls Track Growth
“Data walls” displaying each student’s scores, growth, and goals are prominently displayed in Cornerstone classrooms. Students are motivated to move their performance markers upward.
Advocates say public data motivates students. Critics argue it causes unhealthy competition.
Sophisticated Analytics Spot Trends
Cornerstone schools utilize advanced data systems to aggregate and analyze assessment results. Overall class and school trends are used to modify curriculums and teaching practices.
Supporters believe identifying broad problem areas drives improvement. Critics argue it overly relies on data to make teaching decisions.
Students Set Targets

In addition to top-down goals, Cornerstone students set their own academic growth targets in collaboration with teachers. They track progress against these through portfolios and conferences.
Proponents argue it teaches goal setting skills. Critics say self-set goals can lack rigor.
Cornerstone’s intense data-driven culture is foundational to its approach. Yet critics argue students are more than test scores and data points. It’s an ongoing debate.
Special education and ELL programs in cornerstone charters
Unlike public schools required to serve all students, most Cornerstone charter schools don’t offer extensive special education or English language learner (ELL) programming. But they do implement targeted accommodations and supports.
While not equipped for students with intensive needs, Cornerstone aims to make their rigorous model accessible for motivated students through differentiated instruction, paraprofessional support, and assistive technology.
Inclusion Model
Most Cornerstone schools serve special education students through an inclusion model integrating them into general classrooms with individualized accommodations from teachers. No separate special day classes are offered.
Advocates argue inclusion promotes normalization. Critics contend some students need more intensive services.
Paraprofessional Support
Cornerstone schools often provide paraprofessional aides for individual students who require assistance for learning or behavioral issues to function in the general classroom.
Supporters say paras allow more students to be included. Critics argue they lack specialized training.
Assistive Tech Focus
Cornerstone makes extensive use of assistive technology like audiobooks, text readers, speech recognition, and other tools to support diverse learning needs among students.
Proponents argue technology enables personalization. Critics say low-tech solutions shouldn’t be ignored.
ELL Instruction
English language development is supported through small group instruction and tutoring after school and on Saturdays. Dual-language materials are used when possible.
Advocates say this promotes ELL success within the model. Critics argue language barriers require more intensive ELL-specific instruction.
While lacking robust special education programs, Cornerstone aims to make its model accessible to motivated students through accommodations and inclusive support.
College prep and career readiness in cornerstone charters
Preparing students for higher education and careers is a central part of the Cornerstone Charter School mission. College readiness activities permeate the curriculum from elementary onwards.
From SAT prep courses to college essay writing to vocational training, Cornerstone students receive intensive support to succeed at the next level.
College Pennants Everywhere
Walk the halls of any Cornerstone school and you’ll see college pennants lining the walls. Classrooms are named after the alma maters of staff. It’s college immersion from an early age.
Advocates say surrounding students with college imagery builds aspirations. Critics argue it narrows how success is defined.
SAT and ACT Prep Classes
All Cornerstone high school students take intensive prep classes for college entrance exams like the SAT and ACT. Strong scores unlock scholarships, so test excellence is emphasized.
Supporters applaud preparing students for college exams. Critics contend prep can reach excessive levels.
Admissions Essay Writing
Cornerstone English classes work extensively on crafting the perfect college admissions essay. Counselors provide feedback on drafting compelling personal narratives.
Proponents argue good essays develop writing skills. Critics say formulaic essays can inhibit student voice.
Career Exposure
Guest speakers, company tours, job shadow days, and vocational courses provide Cornerstone students exposure to careers. The aim is graduating with purpose.
Supporters say it builds real-world readiness. Critics argue career exploration should be broader.
While intense, few can deny Cornerstone’s college and career focus equips students with skills to excel at the next level.
Cornerstone charter school management and governance
Unlike traditional public schools, Cornerstone Charter Schools are not managed by local government districts. Instead, they are operated by a private nonprofit organization called Cornerstone Management Group (CMG).
This centralized management is key to Cornerstone’s ability to replicate its model quickly while maintaining consistent standards. But critics argue education shouldn’t be privatized.
Centralized Control
CMG oversees all curriculum, policies, hiring, training and operations for Cornerstone schools nationwide. Principals have autonomy over their campus but must adhere to CMG’s model.
Proponents say centralization maintains quality control. Critics contend it stifles local innovation.
Private Nonprofit Management
As a 501(c)3 nonprofit, CMG is governed by a board of directors consisting of philanthropists, educators, and business leaders. They guide the strategic vision for Cornerstone schools.
Supporters argue nonprofit status attracts talent. Critics say it lacks public accountability.
Scaling Rapidly
With itstight organizational control, CMG can replicate the Cornerstone model much faster than a traditional district. New locations just plug into the system.
Advocates say consistent replication expands options for families. Critics argue charter networks undermine traditional public schools.
CMO Compensation Model
CMG ties executive and principal compensation heavily to school performance metrics like test scores and enrollment, unlike public schools.
Supporters say performance pay attracts talent. Critics argue it warps educational priorities.
CMG’s centralized nonprofit management fuels Cornerstone’s growth. But critics question whether education should be privatized.
Funding and facilities for cornerstone charter schools
Launching and operating charter schools requires major upfront investments. Cornerstone has leveraged large-scale private funding to quickly expand its facilities and programs.
This financial backing gives Cornerstone an advantage in serving families through state-of-the-art campuses and offerings that traditional districts struggle to match.
Major Philanthropic Support
Massive contributions from deep-pocketed philanthropists, foundations, and impact investors have built up Cornerstone’s coffers. This empowers rapid growth and campus development.
Proponents argue philanthropic dollars expand options for families. Critics contend it gives disproportionate influence to donors.
Drawing Wall Street Dollars
In addition to philanthropy, Wall Street heavy hitters have directed millions in investment capital to fuel Cornerstone’s expansion. They see the network as a sound moneymaking opportunity.
Supporters say investors increase access for students. Critics argue schools shouldn’t be investment vehicles.
Upscale Campuses
Flush with outside funding, Cornerstone builds impressive modern campuses with advanced facilities, technology, and learning spaces far exceeding the average public school building.
Proponents argue beautiful campuses inspire students. Critics say funds should go to instruction, not bells and whistles.
Enrichment Programs
Robust budgets allow Cornerstone to offer academic enrichment programs like robotics teams, internships, and project-based learning that resource-strapped district schools can’t match.
Supporters believe enrichment opportunities benefit students. Critics contend they advantage charters over traditional schools.
Cornerstone’s ample outside financing fuels the rapid growth and polished campuses that distinguish the network in many communities.
Critics’ concerns about cornerstone charters: cream skimming and segregation
While Cornerstone touts its results, critics argue the network’s selective admissions and demographic trends raise red flags around equity and systemic impact.
By targeting top-performing students, are Cornerstone schools improving education overall or simply benefiting certain demographics?
Skimming Off Top Students?
A common criticism of Cornerstone is they “cream skim” – siphoning off the most motivated students from traditional schools through selective enrollment, thus disadvantaging the students left behind.
Supporters counter this gives overlooked strivers opportunities. But critics argue it harms equity.
Recruiting High Achievers
Relatedly, critics argue Cornerstone deliberately recruits and markets to high-achieving demographics, shaping the type of students in their applicant pool.
Proponents say they seek motivated students wherever found. But critics contend recruitment has skewed access.
Segregating Students?
Data shows Cornerstone schools typically serve predominately low-income, minority populations. Critics argue this leads to increased racial and economic isolation.
Supporters counter they are serving disadvantaged communities. But critics argue segregation is harmful.
Widening Achievement Gaps?
Some argue that while Cornerstone students progress, achievement gaps may worsen as traditional schools struggle with departing top performers and reduced funding.
Proponents say rising tides lift all boats. Critics argue gaps are widening.
Cornerstone firmly defends its merits, but concerns persist around equity, systemic effects, and the network’s responsibilities to students as a whole.
Responses to critics from cornerstone charter advocates
Supporters of Cornerstone acknowledge critiques but argue the network is doing vital work providing quality options for underserved communities. How do they counter common criticisms?
Serving High-Potential Students
Regarding cream-skimming concerns, Cornerstone argues they are expanding opportunities by properly nurturing strivers failed by neighborhood schools. Their selectivity identifies motivated students, not just privileged ones.
Critics argue this still harms equity. But Cornerstone contends they help students based on effort, not demography.
Driving Systemic Improvements
In response to concerns about weakened traditional schools, Cornerstone contends their success forces districts to improve through competition and that their practices can be adopted by other schools.
Critics argue they disrupt systems. But Cornerstone says they are drivers of innovation.
Advancing Disadvantaged Students
Regarding segregation concerns, Cornerstone notes most of their students come from disadvantaged backgrounds. They are focused on serving marginalized populations.
Critics argue they isolate minorities. But Cornerstone says outcomes show model works for underserved groups.
Expanding Family Choice
Finally, supporters argue Cornerstone offers choice and high-quality options to families failed by assigned district schools. The network empowers parents to find the best fit for their child.
Critics argue choice favors savvy families. But proponents tout the benefits of options.
Cornerstone argues persistently that ultimately they expand opportunities to disadvantaged students. The debate continues.
The future of cornerstone charters and their implications for education
Over the last decade, cornerstone charter schools have seen explosive growth across the country. These independently-operated public schools receive public funding but have more flexibility and autonomy than traditional public schools when it comes to their curriculum, budget, staffing and operations. Cornerstone charters emphasize a rigorous, back-to-basics curriculum with an emphasis on math, science, literature and foreign languages. They typically have longer school days and school years than traditional public schools. Cornerstone charters are also known for their strict disciplinary policies and focus on moral character development.
So why are cornerstone charters expanding so rapidly when many public schools are struggling? Quite simply, cornerstone charters get results. Multiple studies have shown that students at cornerstone charters consistently outperform their peers at traditional public schools on standardized tests in reading, writing and math. Cornerstone charters boast higher graduation rates and lower dropout rates. Their students also gain admission to selective colleges at much higher rates. Clearly, the cornerstone model works for the students enrolled in these schools.
However, the growth of cornerstone charters has significant implications for public education more broadly. Here are some of the key issues to consider:
Access and equity
There are concerns that cornerstone charters “cream” the best students from traditional public schools, leaving a disproportionate number of struggling students behind. Cornerstone charters are allowed to cap enrollment, and they often have selective admissions criteria and long waiting lists. This means access may be limited for English language learners, students with disabilities and low-income families. More data is needed on the student demographics at cornerstone charters compared to neighboring district schools to fully understand equity issues.
Funding and resources
Every student who enrolls in a cornerstone charter means less funding and resources for the nearby traditional public school district. Critics argue that siphoning money away from public school districts can exacerbate existing inequities. However, supporters counter that the funding should follow the student, and that competition introduces accountability and motivation for school districts to improve their outcomes.
School choice and alternatives
Cornerstone charters provide an attractive school choice option for families dissatisfied with their local schools. But choice advocates caution that families need legitimate alternatives, not just an escape route. Shuttering and replacing dysfunctional district schools with charters alone will not fix underlying issues. Cornerstone charters may be part of the solution, but more holistic reforms are needed.
Scalability and expansion
The cornerstone model has proved successful, but can it maintain quality at scale? Cornerstone charters are still just a fraction of the overall K-12 landscape. If they continue growing, will they be able to find enough qualified teachers willing to work longer hours under their strict policies? Will the model sustain as founders retire and schools mature and evolve?
Innovation and best practices
Perhaps the greatest opportunity is for cornerstone charters to innovate and share best practices that can benefit all schools. For example, cornerstone charters tend to emphasize phonics in early literacy. If their methods boost reading scores, they could share strategies with district schools. Increased data transparency and collaboration between charters and districts could lift all boats.
While debates will continue about the merits of cornerstone charters, the reality is they are rapidly expanding. Instead of ideological battles over school choice, the focus should be on ensuring all types of schools are held to high and equitable standards, share innovations that work, and collaborate to serve all students’ needs. If cornerstone charters continue outpacing district school performance, they will place more competitive pressure on traditional schools to improve. This could motivate needed reforms in public education, but policymakers must ensure improvements reach all demographics. Overall, cornerstone charters show the potential of high-standards schools, but they are just one part of giving every student access to an excellent education.

