How do solar powered thermometers benefit gardeners. What factors should be considered when choosing a solar thermometer. How can temperature data be used to protect plant health.
The Advantages of Solar Powered Thermometers in Gardening
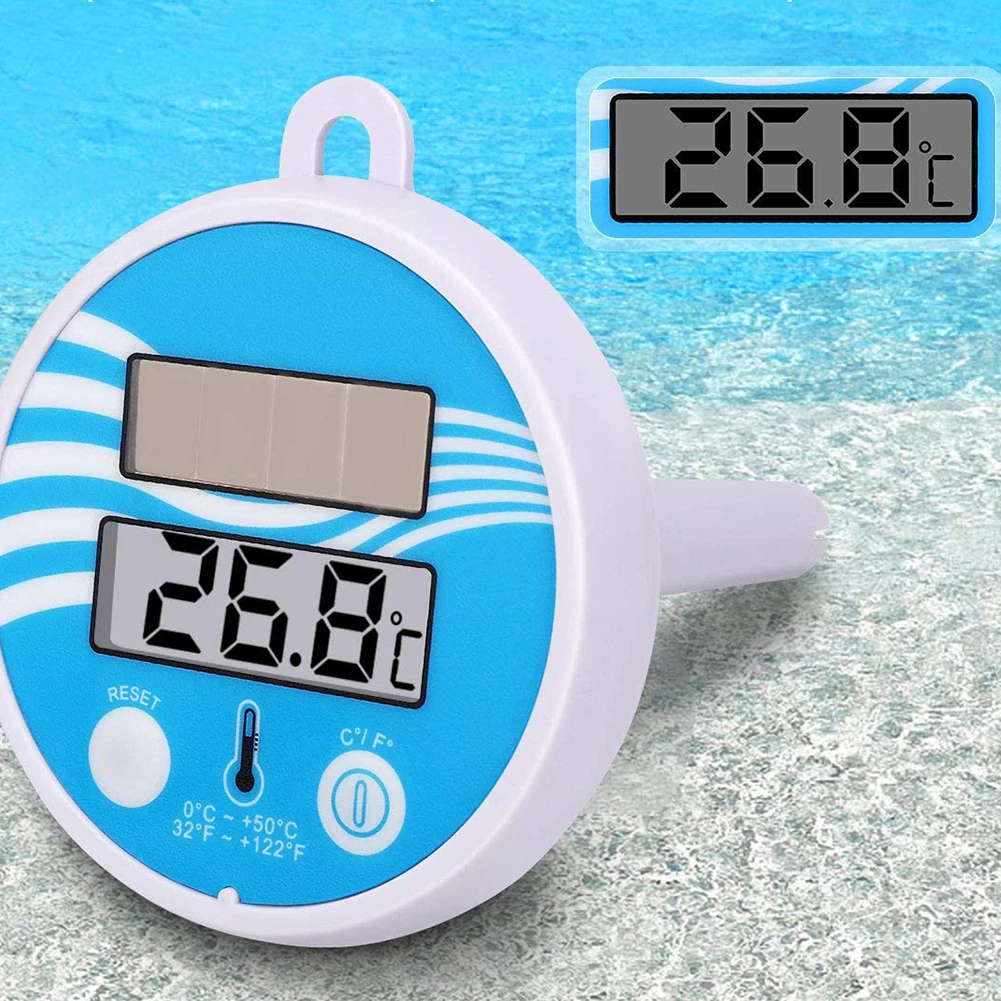
Solar powered thermometers have revolutionized the way gardeners monitor and manage their outdoor spaces. These innovative devices harness the power of the sun to provide accurate temperature readings without the need for batteries or electrical connections. By utilizing solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity, these thermometers offer a sustainable and low-maintenance solution for temperature monitoring in gardens and yards.
The benefits of using solar powered thermometers in gardening are numerous:
- Continuous temperature monitoring without battery replacements
- Ability to track daily temperature fluctuations
- Identification of frost risks for sensitive plants
- Determination of optimal planting times based on soil temperature
- Guidance for proper watering schedules
- Monitoring of heat waves and extreme temperature events
- Comparison of sun exposure in different garden areas
- Prevention of plant damage due to temperature extremes
Is a solar powered thermometer suitable for all garden types? Solar powered thermometers can be used in various garden settings, from small urban balconies to large rural properties. Their versatility and ease of installation make them an excellent choice for gardeners of all levels of experience.

Selecting the Ideal Solar Thermometer for Your Garden
When choosing a solar powered thermometer for your garden, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure you select the most suitable device for your needs:
Display Type
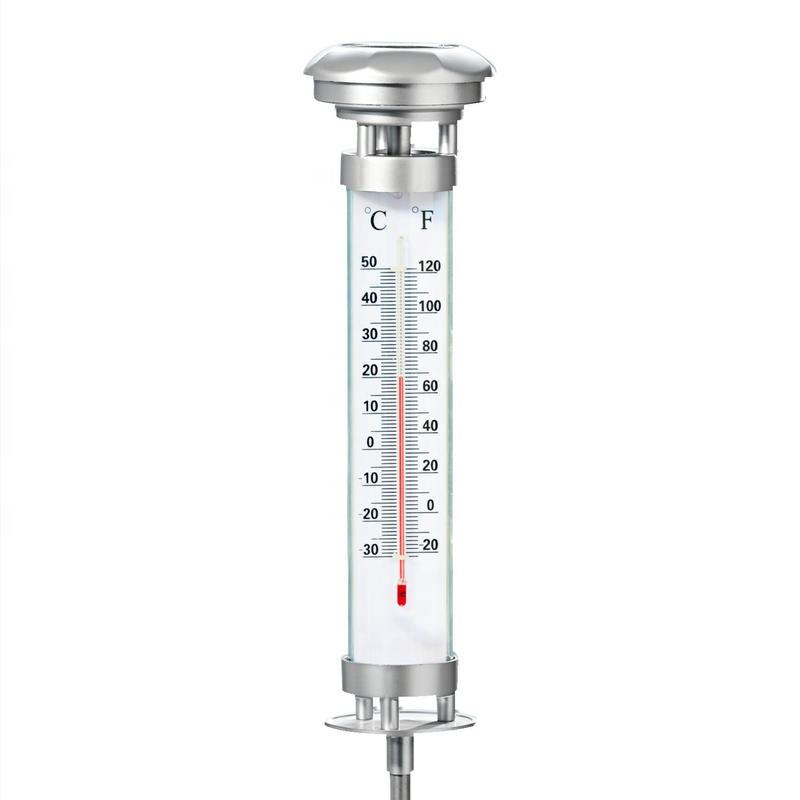
Solar thermometers come with different display options. Analog dial displays offer simplicity and ease of reading, while digital models often provide additional features such as minimum and maximum temperature tracking. Consider which type of display will be most convenient for your gardening routine.
Temperature Range
Ensure the thermometer’s temperature range is appropriate for your climate. A range of -20°F to 110°F (-29°C to 43°C) is suitable for most regions, but gardeners in extreme climates may need to look for models with broader ranges.
Accuracy
For reliable temperature measurements, look for thermometers with an accuracy of ±1°F (±0.5°C). This level of precision is crucial for making informed decisions about plant care and protection.

Weather Resistance
Since the thermometer will be exposed to the elements, choose a model with waterproof and rustproof construction. This ensures durability and longevity in outdoor conditions.
Remote Sensing Capabilities
Some solar thermometers feature wireless sensors that allow for temperature monitoring in remote locations. This can be particularly useful for large gardens or areas with varied microclimates.
Solar Cell Size
The size of the solar cell affects the device’s ability to capture sunlight and generate power. Larger cells generally provide more consistent operation, especially in areas with limited sunlight.
Can solar powered thermometers function in partially shaded areas? While solar powered thermometers perform best with direct sunlight exposure, many models can still operate effectively in partially shaded locations. However, it’s important to position the device to maximize sunlight exposure to the solar cell for optimal performance.
Maximizing the Use of Your Solar Thermometer
To get the most out of your solar powered thermometer, proper installation and use are essential. Follow these tips to ensure accurate and reliable temperature data:
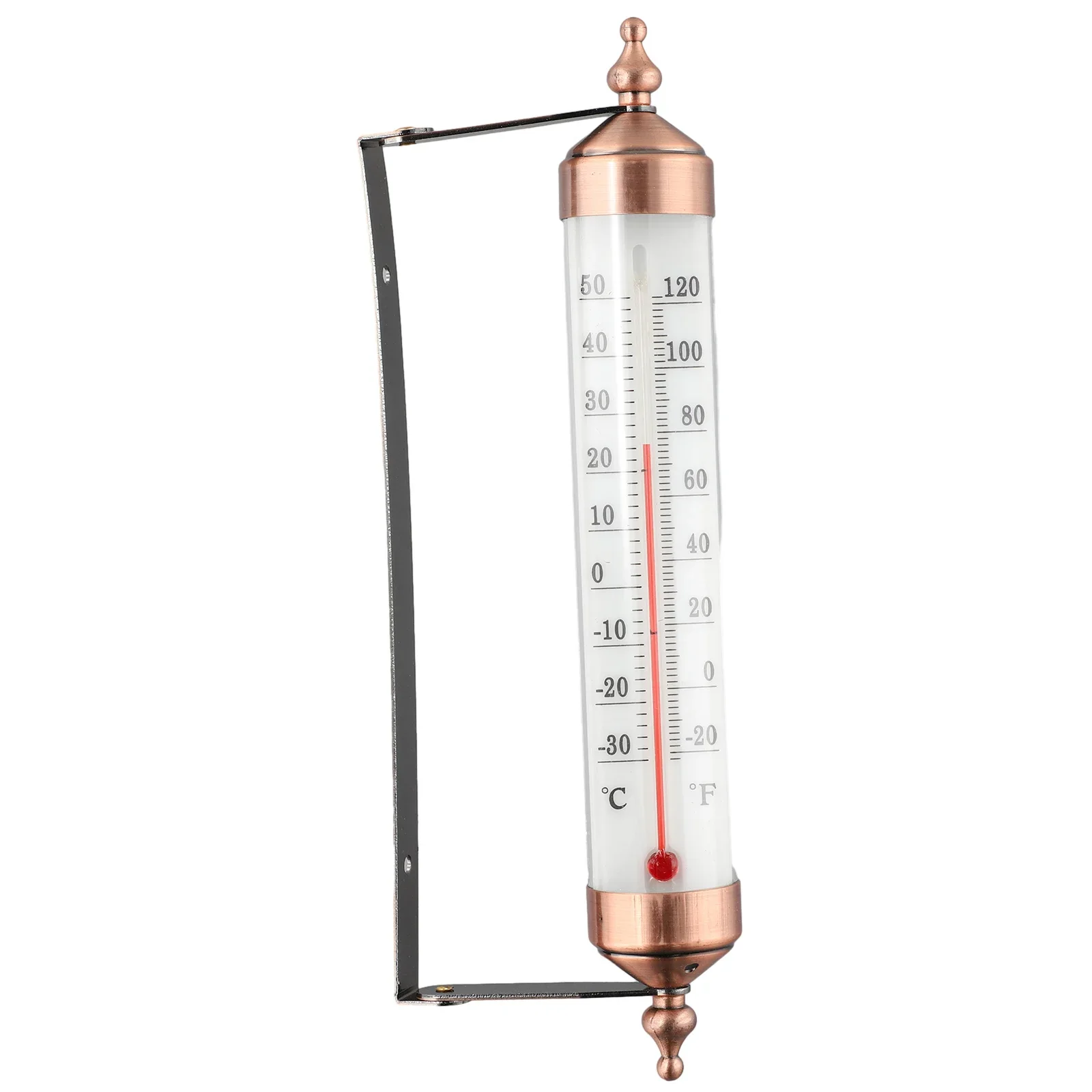

- Mount the thermometer vertically on a stable surface such as a wall, post, or railing.
- Position the device to receive ample sunlight throughout the day.
- Verify accuracy by comparing readings with other reliable thermometers.
- Take multiple readings throughout the day to observe temperature patterns.
- Record daily minimum and maximum temperatures for trend analysis.
- Adjust the thermometer’s location seasonally to accommodate changing sunlight patterns.
- Use temperature readings to inform watering, planting, and plant protection decisions.
How often should temperature readings be taken? While continuous monitoring is ideal, taking readings at least three times a day (morning, midday, and evening) can provide valuable insights into your garden’s temperature fluctuations.
Leveraging Temperature Data for Optimal Plant Health
The temperature data collected from your solar powered thermometer can be invaluable in maintaining and improving the health of your plants. Here are some ways to utilize this information:

Soil Temperature Monitoring
Use soil temperature readings to determine the best time for planting various crops. Many plants have specific soil temperature requirements for optimal germination and growth.
Frost Date Identification
By tracking temperature trends, you can identify the last frost date in spring and the first frost date in fall. This information helps in planning your growing season and protecting sensitive plants.
Heat Wave Management
Recognize extreme heat events early and take preventive measures such as providing shade or increasing watering to protect your plants from heat stress.
Watering Schedule Optimization
Adjust your watering routine based on temperature readings. Higher temperatures generally require more frequent watering to prevent plant dehydration.
Microclimate Identification
By comparing temperature readings from different areas of your garden, you can identify microclimates and make informed decisions about plant placement based on their temperature preferences.

How can temperature data help in preventing plant diseases? Many plant diseases thrive in specific temperature ranges. By monitoring garden temperatures, you can anticipate potential disease outbreaks and take preventive measures, such as adjusting watering practices or applying protective treatments.
Exploring Advanced Features of Solar Powered Thermometers
As technology advances, solar powered thermometers are incorporating more sophisticated features to provide gardeners with enhanced monitoring capabilities:
Wireless Connectivity
Some models offer Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity, allowing you to access temperature data remotely through smartphone apps or web interfaces.
Data Logging
Advanced solar thermometers may include built-in data logging features, storing temperature readings over time for detailed analysis and trend identification.
Multiple Sensor Support
Certain systems support multiple wireless sensors, enabling simultaneous temperature monitoring in various garden zones from a single base station.

Integrated Weather Stations
Some solar powered devices combine thermometer functionality with other weather monitoring features such as humidity sensors, rain gauges, and wind speed meters.
Do solar powered thermometers require any maintenance? While solar powered thermometers are generally low-maintenance, occasional cleaning of the solar panel and sensor to remove dust and debris can help ensure optimal performance and accuracy.
Integrating Solar Thermometers with Smart Garden Systems
The integration of solar powered thermometers with smart garden systems opens up new possibilities for automated plant care and environmental control:
Automated Irrigation
By connecting solar thermometers to smart irrigation systems, watering schedules can be automatically adjusted based on temperature readings, ensuring plants receive the right amount of water in varying conditions.
Climate Control
In greenhouse settings, solar thermometers can be linked to ventilation and heating systems to maintain optimal growing temperatures automatically.

Frost Protection
When integrated with protective coverings or heating elements, solar thermometers can trigger automatic frost protection measures when temperatures approach freezing.
Data-Driven Gardening
By combining temperature data with other environmental sensors, gardeners can create comprehensive databases to inform future planting decisions and optimize growing conditions.
How can solar powered thermometers contribute to energy efficiency in gardening? By providing accurate temperature data, these devices can help optimize the use of heating, cooling, and irrigation systems in gardens and greenhouses, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and improving sustainability.
The Future of Solar Powered Thermometers in Horticulture
As technology continues to evolve, the future of solar powered thermometers in horticulture looks promising. Some potential developments include:
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Future models may incorporate AI algorithms to provide predictive temperature forecasting and personalized plant care recommendations based on historical data and current conditions.

Enhanced Energy Storage
Improvements in solar cell and battery technology could lead to more efficient energy capture and storage, ensuring uninterrupted operation even during extended periods of low light.
Miniaturization
Advancements in electronics may result in smaller, more discreet solar thermometers that can be easily integrated into various garden elements without disrupting aesthetics.
Expanded Sensor Capabilities
Future solar powered devices may incorporate additional sensors to measure factors such as soil moisture, nutrient levels, and light intensity, providing a more comprehensive view of garden conditions.
Will solar powered thermometers eventually replace traditional battery-operated models in gardening applications? While solar powered thermometers offer numerous advantages, they are likely to coexist with battery-operated models for the foreseeable future. Each type has its strengths, and the choice will depend on individual gardener preferences and specific application requirements.

In conclusion, solar powered thermometers represent a significant advancement in garden monitoring technology. By providing accurate, continuous temperature data without the need for battery replacements or electrical connections, these devices empower gardeners to make informed decisions about plant care and protection. As technology continues to evolve, solar powered thermometers are poised to play an increasingly important role in promoting sustainable and efficient gardening practices.
Introduction to Solar Powered Thermometers for Gardening
For many gardeners, knowing the temperature in your garden or backyard is crucial information. The outdoor temperature impacts everything from when to plant certain crops to protecting sensitive plants from frost or extreme heat. Traditional thermometers often require batteries or electricity to operate, but solar powered thermometers offer a great battery-free option to monitor temperatures right in your garden.
Solar powered thermometers utilize a solar cell to convert sunlight into electricity that powers the thermometer. This allows them to provide temperature readings day and night without ever needing battery changes. Solar thermometers come in many styles from simple dial displays to digital models with min/max temperature tracking. They are also available as indoor/outdoor models with an external sensor that can be placed right where you need to measure while the main unit stays protected indoors.
Using a solar thermometer in your yard or garden provides many useful benefits:
- Monitor daily temperature fluctuations in your garden.
- Track minimum and maximum temperatures to understand temperature variability.
- Identify risk of frost or freezing temperatures for sensitive plants.
- Determine ideal times to plant based on soil temperature.
- Make sure plants are watered properly based on temperature.
- Identify and track heat waves or extreme heat events.
- Compare amount of sun exposure in different parts of your yard.
- Prevent damage to plants by excessive heat or cold.
- No batteries to replace since power comes from the sun.
Solar powered thermometers are easy to install and use. Most models mount right onto a wall or post. Try placing them in different parts of your yard to monitor microclimates. Position them in full sun versus shade, near the house versus an open field, or surrounded by concrete versus soil and grass. Comparing temperatures around your property can help identify the best growing sites.
Choosing the Right Solar Thermometer
With many options available, keep these factors in mind when selecting a solar thermometer:
- Display Type – Simple dial displays are easy to read while digital models allow minimum and maximum tracking.
- Temperature Range – Match the range to your climate needs like -20° to 110°F for most areas.
- Accuracy – Look for +/- 1° accuracy for reliable temperature measurements.
- Weatherproof – Ensure waterproof and rustproof construction for outdoor use.
- Remote Sensor – Models with wireless sensors allow monitoring remote locations.
- Size of Solar Cell – Larger cells can capture more sunlight for power.
Consider getting a model with remote probe that can be placed in your garden while the main unit is in a convenient spot. An indoor/outdoor thermometer lets you track both areas. Digital models with min/max memory are useful for noting record temperatures each day.
Using Your Solar Thermometer

Once you’ve selected the right solar thermometer, install it properly for reliable temperature data. Here are some tips for setup and use:
- Mount the thermometer vertically on a wall, post, or railing.
- Allow ample sunlight exposure to the solar cell.
- Check for accuracy by comparing to known accurate thermometers.
- Take periodic readings throughout the day for comparisons.
- Note daily minimum and maximum temperatures.
- Track and compare temperature trends over time.
- Relocate as needed for seasonal monitoring needs.
- Use readings to guide watering, planting, and protection decisions.
With a quality solar thermometer properly sited in your yard, you’ll have the temperature data needed to make informed choices for your garden’s health. Monitoring conditions allows you to plant at optimal times, water adequately as temperatures rise, and protect plants when extreme heat or cold threatens.
While sunlight powers the thermometer itself, the temperature measurements also provide insight into how much sun reaches different parts of your yard. Track sun exposure in open and shady areas to determine ideal planting sites based on sunlight needs. Watching temperature variability even from morning to afternoon can reveal microclimates to utilize.
Using Temperature Data for Plant Health
Armed with thorough temperature data from your yard, you can make management decisions that protect the health of all your plants. Here are some ways to utilize the readings:
- Monitor soil temperature and only plant outdoors when soil reaches the recommended minimum for that crop.
- Identify the date of last frost in spring and first frost in fall to determine growing season length.
- Recognize extreme heat events and safeguard plants with shade covers or extra misting.
- Water adequately as temperatures rise to prevent drought stress.
- Watch for cold snaps in spring and fall and protect sensitive plants with covers.
- Note areas that collect frost easily based on minimum temperatures and avoid planting there.
The detailed temperature history from your thermometer provides insights into yard conditions that impacts plant health. You can pick ideal planting sites, determine safe planting dates, and respond quickly to dangerous temperature swings.
Enhance Your Backyard Environment
In addition to guiding planting and management, monitoring yard temperatures can reveal opportunities to enhance your overall backyard environment. Some ideas include:
- Add windbreaks, trellises, or shade structures to reduce wind and heat impact.
- Select heat tolerant plant varieties if high temperatures are a consistent issue.
- Increase watering or mulch bare areas if soil temperature is too extreme.
- Relocate plants if their current site shows unsuitable temperature patterns.
- Supplement sun exposure with movable reflectors in shady planting locations.
Your thermometer provides the data to identify issues and make landscape improvements. Address problems through design changes, equipment additions like shade cloth, and selecting plants suited to each microclimate.
Enjoy Hassle-Free Temperature Tracking
Solar powered thermometers provide a convenient way to monitor backyard temperatures without having to rely on electricity or batteries. They give gardeners, hobby farmers, and anyone who spends time outdoors the data needed to understand conditions and protect plants.
With no cables or batteries to hassle with, solar thermometers require minimal maintenance. Just check periodically that any remote sensors remain securely positioned and clean the solar cell if dust buildup occurs. Download data if your model allows recording. Otherwise simply glance at the display anytime to get current readings.
Solar power allows these rugged thermometers to keep working indefinitely with just an occasional cleaning. Place one in your yard and within a few days you’ll have a much better understanding of the temperatures your plants experience. Utilize this new knowledge to support a healthier, more productive garden and make improvements for a better backyard environment.
How Do Solar Powered Thermometers Work?
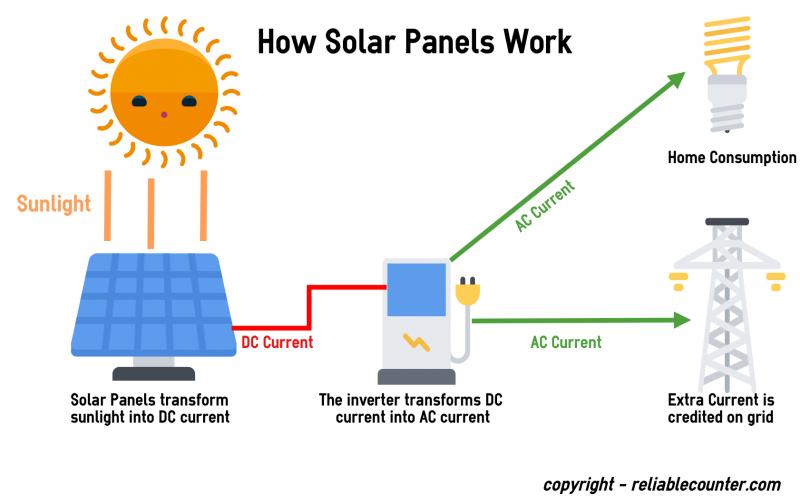
Solar powered thermometers are a great way to monitor temperatures in your garden, greenhouse, or backyard without needing batteries or wiring. But how do these handy devices actually work? The key is in converting sunlight into electricity to power the thermometer.
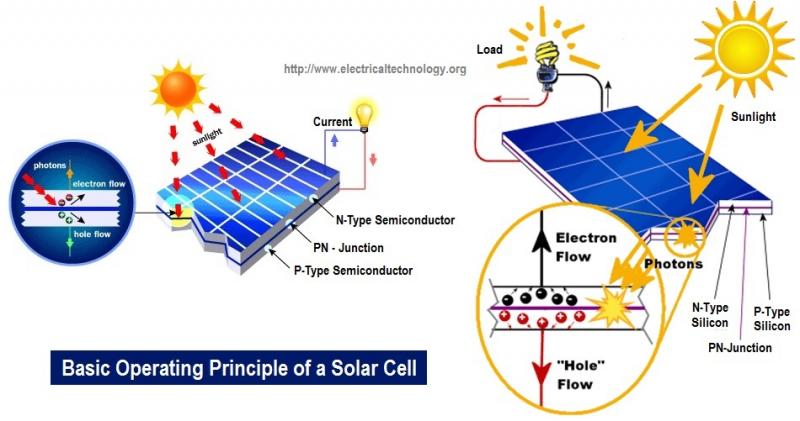
Solar thermometers use a photovoltaic solar cell, typically made from silicon crystals. The solar cell contains positive and negative semiconductor layers that create an electric field. When sunlight hits the cell, the energy knocks electrons free in the silicon, allowing them to flow and generate electric current.
The solar cell is encased behind a clear plastic or glass cover and mounted on the thermometer. Angling the cell perpendicular to the sun’s rays maximizes exposure and power generation. The small solar panel can be just a few inches in size to several inches on larger models.
The electricity from the solar cell charges a storage capacitor or rechargeable battery inside the thermometer. This stored power runs the thermometer’s temperature sensor, display, and internal clock if applicable. The photovoltaic process converts enough sunlight into electricity to operate the thermometer continually.
Key Components
Here are the main internal components that allow a solar thermometer to harness the sun’s energy:
- Solar Cell – Made of silicon semi-conductors that generate electric current when exposed to sunlight.
- Battery or Capacitor – Stores energy from the solar cell to power the thermometer at night.
- Temperature Sensor – Measures ambient temperature using a thermistor or other sensor.
- Microchip – Converts sensor data and controls the thermometer display.
- LCD Display – Displays current, min, and max temperatures as applicable.
These components work together to convert sunlight, take temperature measurements, store data, and display the readings onscreen. Advanced models may also include a data logging function to record temperatures over time.
How Solar Power Generation Works
The key to the technology is in the special solar cell or panel. Solar cells are made from thin layers of silicon crystal wafers that have been treated to form positive and negative semiconductor materials. When combined together, these create an electric field across the cell.
As photons from sunlight strike the solar cell, their energy knocks electrons loose within the silicon crystal structure. The electrons can then flow freely, generating a DC electric current. Metal conductive plates on the cell collect the current and transfer it to charge the thermometer’s battery or capacitor.
A single solar cell produces less than 2 watts of power. But the minimal energy needs of a thermometer allow the small solar cell to capture sufficient sunlight to operate it. The cell’s dark color also helps absorb more light to maximize efficiency.
Getting Power at Night
But how does a solar powered thermometer keep working at night or on cloudy days? That’s where the internal battery or capacitor comes in. These storage devices charge up with electricity from the solar cell during daylight hours.
At night, the stored energy powers the thermometer’s temperature sensing, memory, display, and clock functions. Newer lithium batteries can run for months between charges. The solar cell recharges the battery during any daylight to maintain continuous operation.
For simple thermometers without any memory or clock, a capacitor may be used instead of a battery. Capacitors charge and discharge more rapidly. But frequent sunlight is needed to replenish them. Batteries work better for features like min/max temperature memory.
Typical Voltage Requirements
Solar cells provide relatively low voltage and current. But that’s perfect for powering low-energy electronics like calculators, watches, and thermometers. Here are some typical voltage requirements:
- Single solar cell – 0.5V
- LCD display – 3-5V
- Thermometer microchip – 3-12V
- Thermistor sensor – 1-2V
The solar cell and battery or capacitor together can easily provide the 5-12V DC needed for the display, sensor, and internal chips. The system needs only milliwatts of power for continuous operation.
Optional Remote Probes
Higher end solar thermometers include a remote temperature probe on a cord. This allows placing the probe in one location, like a garden, while the main unit stays protected from the elements on your porch.
Running the probe cable back to the display takes some additional voltage – around 16-20V. So these models utilize larger solar cells and bigger batteries. The probe contains just the temperature sensor while the electronics stay with the display.
Remote probes let you monitor temperature anywhere within reach of the probe wire length. Signals transmit digitally back to the display so long runs don’t affect accuracy.
Advantages of Solar Power
Using the power of the sun provides many excellent benefits for thermometers and other outdoor electronics:
- No batteries to replace
- No wiring required
- Easy installation anywhere
- Lower environmental impact
- Minimal maintenance required
- Long operating life
- Resistant to weather and moisture
As solar technology continues to evolve, the number of power-generating applications keeps growing. Solar thermometers demonstrate how this renewable energy can provide off-grid electricity even on a small scale. Just a few inches of solar cell can run an entire thermometer indefinitely!
Choosing an Efficient Solar Thermometer
When selecting a solar powered thermometer, keep an eye on solar cell size and battery capacity. A larger cell and battery will typically last longer between charges. Consider these factors:
- Solar cell size – Larger is better to collect more sunlight.
- Solar cell efficiency – Look for monocrystalline silicon cells.
- Battery capacity – Higher mAH rating means more storage.
- Rechargeable lithium battery – Lasts through more charge cycles.
- Remote probe – Requires more power capacity.
Higher quality solar cells and sufficient onboard battery storage will provide years of reliable service. Carefully mounting the unit to maximize sun exposure is also important.
Put the Power of the Sun to Work for You
Solar powered thermometers utilize innovative photovoltaic technology to harness free solar energy. The sun powers the included temperature sensor and display all day and night. No costly battery replacement is ever needed.
Understanding how these devices work can help you select the best model and properly install it for optimum sunlight exposure. Tap into the limitless power of the sun to monitor temperatures anywhere outside. Let a solar powered thermometer provide the data you need for gardening, outdoor projects, and managing backyard environments.
Key Features of Solar Powered Outdoor Thermometers
Solar powered thermometers are a convenient way to monitor outdoor temperatures without running electrical wires or replacing batteries. These handy devices use solar cells to convert sunlight into power for measuring and displaying accurate temperature readings day and night.
Today’s solar thermometers offer a wide range of features to suit different needs. Here are some of the key options to consider when choosing an outdoor solar thermometer:
Display Types
Solar thermometers are available with several display options:
- Analog dial – Simple and easy to read at a glance.
- LCD digital – Shows precise temperature and added data like min/max.
- LED digits – Large lighted numbers visible in low light.
Digital LCD offers the most information with min/max memory, moon phase icons, time and date, etc. But classic analog dials maintain a nostalgic look with retro appeal.
Temperature Range
Match the measurement range to your climate needs. Common options include:
- -40° to 120°F
- -20° to 140°F
- -30° to 165°F
Wider temperature ranges let you use the thermometer year-round in more extreme conditions. However, most models work well for typical climates between -20° to 120°F.
Remote Probes
Higher end models offer a remote probe on a cord allowing you to position the probe while the display stays protected. Probe lengths range from 3 to 50 feet. Some have wireless probes that transmit on radio frequencies back to the display. Probes let you measure temperature in specific microclimates.
Accuracy
Look for accuracy of ±1°F or better. High quality sensors ensure your temperature data is reliable.
Measurement Units
Most thermometers allow switching between Fahrenheit and Celsius units.
Solar Cell Size
Larger solar cells collect more sunlight. Cells can range from just a few inches up to 6 inches on some models. Bigger is generally better for power capacity.
Mounting Options
Convenient mounts like hang holes, desktop stands, wall brackets, or magnets allow flexible positioning.
Backlighting
Lighted, glow-in-the-dark, or backlit displays remain easy to read at night.
Min/Max Temperature Memory
Save daily highs and lows with max/min memory features. Review date/time of past extremes.
Trend Arrows
See whether temperatures are rising, falling, or steady with handy trend indicators.
Weather Forecast Icons
Some models estimate upcoming weather based on pressure and display a forecast icon.
Humidity Readings
Add-on sensors can track humidity levels along with temperatures.
Clock/Calendar
View time and date along with your temperature data.
Color-coded Bar Graph
Graphical bars indicate temperatures through color zones like blue for cold, green for normal, red for hot.
Weatherproof Construction
Durable, waterproof enclosures withstand outdoor environments.
Wireless Transmission
Bluetooth or radio transmission sends data wirelessly from probe to display.
With the variety of feature options, you can find just the right solar thermometer to suit your needs and budget. Determine which added capabilities would be most useful for how you want to utilize the temperature data.
Top Use Cases
Beyond basic air temperature monitoring, solar thermometers offer helpful solutions for:
- Gardening – Track soil temperatures for planting. Monitor extremes that could damage plants.
- Backyard microclimates – Compare sun vs shade areas, near structures vs open zones, ground level vs raised beds.
- Outdoor cooking – Perfect grilling by monitoring ambient temp, surface temp, and internal food temp.
- Swimming pools – Ensure proper water temperature for health and enjoyment.
- HVAC monitoring – Compare indoor vs outdoor temperatures around homes or buildings.
- Weather stations – Track rainfall, wind, barometric pressure along with air temperature.
- Solar efficiency – Monitor solar panel temperature which impacts energy output.
Take advantage of a thermometer’s data logging, alarms, and remote probes to customize it for your particular needs. Choose display qualities like backlit digits or color-coded bars that make the data most useable.
Ideal Locations to Monitor

Some key spots to position solar thermometers include:
- Garden beds – Track soil temperature.
- Both sunny and shady areas – Compare temperature difference.
- Near structures – Monitor radiant heat effects.
- Under roof eaves – Check attic ventilation.
- On poles at various heights – Profile air temperature gradients.
- Interior rooms with external probes – Compare indoor vs outdoor.
- Entryways – See impact when opening doors.
- Near HVAC systems – View effects of air intake and distribution.
Utilize multiple thermometers or models with remote probes to monitor temperature diversity across your property. Identify microclimates and vertical temperature layers.
Added Capabilities
Many solar thermometers include extra functions beyond just temperature measurement:
- Humidity – Add humidity data with sensors that also track %RH.
- Time – Integrated clocks display current time.
- Date – Calendar shows day, month and year.
- Weather forecasting – Icons estimate upcoming conditions based on pressure.
- Moon phase – See the eight phases of the moon cycle.
- PC interface – Download logged data to a computer for further analysis.
- Smartphone connectivity – Bluetooth syncs data to your phone.
Depending on your needs, extras like humidity readings, weather forecasting icons, moon phases, and downloadable data can add helpful functionality.
Installation Tips
Proper installation ensures your solar thermometer provides reliable temperature data. Follow this advice:
- Mount vertically on a wall with screws.
- Allow unobstructed sunlight onto the solar cell.
- Position out of direct rain and snow impact.
- Allow adequate air circulation around the sensor.
- Check accuracy by comparing to a known accurate thermometer.
- Consider a rain shade if mount spot gets heavy precipitation.
Take time to identify the optimal mounting location before installing your thermometer. Maximize solar exposure while protecting from harsh weather effects.
Solar powered thermometers offer endless options for tracking outdoor temperatures. Select features like remote probes, min/max memory, and smartphone syncing to build a versatile temperature monitoring station.
Monitor Day and Night Temperatures in Your Garden
Keeping an eye on temperatures in your garden can make all the difference when it comes to protecting your plants. Wide fluctuations between daytime highs and nighttime lows can stress plants at critical growing stages. A solar powered thermometer allows you to easily track temperatures without any wiring or batteries to deal with.
These innovative garden thermometers harness energy from the sun to power their display. A solar cell converts sunlight into electricity that runs the thermometer. This means you can place them anywhere in your yard without worrying about access to outlets. They are completely self-contained.
Benefits of Solar Powered Thermometers
Solar thermometers offer several advantages for monitoring garden temperatures:
- Provide day and night readings – Continue working even after sundown.
- Allow placement anywhere – Position in multiple garden beds or zones.
- Require no wiring – Save time and hassle.
- Operate maintenance-free – No battery changes needed.
- Resist weather – Durable for outdoor conditions.
- offer clear display – Large digits visible from a distance.
These hassle-free garden temperature gauges make it simple to keep tabs on conditions in your yard. The versatility of solar power means you can mount them on fences, posts, and walls to track temps precisely where you need them.
Ideal for Monitoring Day and Night Differences
Outdoor plants can experience a roller coaster of temperatures throughout the day. A sunny afternoon might reach 85°F (29°C), while nighttime could drop as low as 55°F (13°C). This 30 degree swing places strain on plants as their metabolism struggles to adjust. Extremes during critical growth stages can hamper development.
A solar powered outdoor thermometer lets you quantify the variance your garden experiences over 24 hours. Most models have min/max features to record the full range. Seeing just how low or high it gets allows you to interpret impacts and take protective actions.
For example, if a cold snap is imminent, you could deploy protective covers or move pots to sheltered areas. Or you may need to provide shade if afternoon peaks climb too high. Catching problems early guards against slow growth and plant loss.
Ideal for Multiple Garden Zones

Yards and gardens often contain a patchwork of microclimates. An area against a brick wall may bake in afternoon sun, while a shaded zone nearby remains quite cool. Other factors like wind exposure, proximity to structures, and soil moisture also influence local conditions.
A single backyard thermometer can’t capture this variability. The best way to monitor your whole landscape is deploying thermometers in each distinct zone. Solar models allow this flexibility without complication.
You can quickly establish temperature profiles for your vegetable garden, perennial beds, orchards, and more. This allows making informed horticultural decisions tailored to each section of your yard. You’ll know which areas need shade cloth or extra water when heat spikes.
Models for Every Situation
Solar thermometers come in diverse designs to suit any garden setup. Here are some top options:
- Mini solar thermometers – Compact and lightweight models stick into soil or mount on stakes. Ideal for tight spaces.
- Solar powered rain gauges – Combine temperature and rainfall tracking. Help quantify water needs.
- Wireless thermometer systems – Allow remote monitoring from your phone or indoors.
- Large dial thermometers – Feature vivid displays that are easy to read from across your yard.
- Indoor/outdoor models – Monitor both environments on one unit. Great for greenhouses and enclosed gardens.
Look for models with convenient min/max memories so you don’t have to check at precise times to catch peak highs and lows. Waterproof construction is also ideal for enduring all weather conditions through the seasons.
Get the Whole Picture with Temperature Data
Solar thermometers are an indispensable tool for any gardener wanting to keep close tabs on conditions throughout the yard. The insights they provide can help diagnose issues and allow preventive action before damage or decline occurs.
These solar powered indoor outdoor thermometer options deliver convenience, flexibility, and reliability. Position them in hot spots and cold corners to quantify the microclimates your garden experiences. Taking temperature data to the next level allows making proactive improvements for better plant health and productivity all season long.
Place Solar Thermometers in Sunny and Shady Areas
Monitoring temperatures in different parts of your garden can provide valuable insights into the microclimates you have. Placing solar powered thermometers in both sunny and shady areas lets you easily track temperature variations throughout the day and season.
Solar powered thermometers are a great option for any gardener looking to keep tabs on temperatures impacting their plants. These devices charge up in daylight and run off that stored energy to display current, high, and low temperature readings. They’re durable, require no batteries or wiring, and can be placed anywhere needed.
Benefits of Using Solar Powered Thermometers

Here are some of the top benefits of using solar powered thermometers in your garden:
- Provide temperature data to help with planting decisions – Knowing the temperature range in different garden beds lets you choose plants suited to those conditions.
- Help protect plants from extreme heat or cold – By monitoring temps, you can take steps like providing shade cloth if an area gets too hot.
- Work in remote garden areas – No need to run power cords across your yard. Solar thermometers work anywhere with sun exposure.
- Operate maintenance-free – After initial placement, solar thermometers run themselves without any upkeep needed.
- Aid debugging garden issues – If plants struggle in one bed, comparing temps to other areas can help identify causes.
- Guide watering needs – Higher temperatures indicate beds that will need more frequent watering.
For just a small upfront investment, solar thermometers provide continuous temperature data to inform many gardening decisions. Their self-powering operation and wireless portability make them easy to use anywhere needed.
Ideal Placement Locations
When installing solar thermometers, consider these prime placement locations:
- Full sun areas – Position thermometers in sun-drenched garden beds and open areas without shade. Compare to shady zones.
- Partially shaded beds – Place under trees or shrubs providing patchy shade. Monitor sun/shade temperature differences.
- Greenhouses – Mount solar thermometers inside greenhouses to track conditions. Ensure adequate sun exposure.
- Microclimates – Identify and monitor mini-zones in your yard with distinct climates like against walls.
- Near plantings – Locate thermometers next to specimen plantings to monitor conditions right around them.
Aim for distributing thermometers across the different sunlight exposures in your landscape. This provides sufficient data to understand the temperature variances. Position them near plantings you want to closely monitor and in areas prone to excessive heat or cold.
Reading and Using the Temperature Data
Once your solar thermometers are in place, be sure to check them frequently. Look at both the current temperature and historical highs/lows. Over time, you’ll get a good feel for the temperature patterns in your garden.
Use this data to make informed gardening decisions:
- Choose plants suited to each area’s temperature range
- Add shade cloth, wall-o-waters, or cold frames if needed
- Tweak watering schedules based on temperatures
- Monitor for hot/cold spots that affect plant health
- Consider adding thermal mass like stones if temperatures fluctuate a lot
- Relocate plants if they seem poorly suited to an area’s temps
Also record key events like extreme hot/cold snaps, comparing them to the thermometer readings. Over time, the temperature history provided by your solar thermometers will help optimize how you garden in your unique climate.
Models for Sunny Areas vs. Shade
When purchasing solar thermometers, consider getting two models:
- Full sun thermometer – Choose a model made for direct sun exposure if placing in an unshaded area. Look for a wide temperature range (-40°F to 140°F or similar).
- Shade thermometer – For shady areas, select a thermometer designed for low light. It may have a smaller solar cell and capacitor to operate on less sunlight.
Having two specialized thermometers for sun and shade ensures each unit is optimized for the conditions in that garden zone. Plus you can compare readings to see the impact of sunlight on temperatures.
Ideal Features to Look For

When shopping for solar garden thermometers, keep these top features in mind:
- Wireless and portable – Choose thermometers with no wires so they can be easily moved.
- Weatherproof – Look for durable, waterproof thermometer housing and components.
- Current/min/max temps – Models that store historical highs and lows give more insights.
- Bright display – Pick thermometers with large, high contrast numbers for easy reading.
- Wide temperature range – Maximum and minimum readable temperatures suited to your climate.
- Easy installation – Magnetized backs, hanging holes, and stakes make placement simple.
High quality solar thermometers meeting these criteria will provide years of reliable temperature data for your garden spaces.
Getting Started with Solar Thermometers
Solar thermometers are a simple upgrade that offers valuable new insights for any gardener. Follow these tips to get started leveraging them in your yard:
- Order two specialized thermometers – one for sun and one for shade.
- Identify key sunny and shady areas to monitor across your landscape.
- Mount the thermometers in those locations at similar heights.
- Check readings at the same time daily to gather comparable data.
- Record temperatures along with key garden events and plant issues.
- Use the data to optimize your gardening practices for your microclimates.
In no time, you’ll be leveraging temperature data from your new solar thermometers to make better planting decisions, protect your plants, and boost your gardening success!
Use Solar Powered Indoor Outdoor Thermometers
Solar powered indoor/outdoor thermometers are a handy tool for any home or garden. These versatile devices display temperatures from both a wireless outdoor sensor and the main indoor unit. With no electrical wires or batteries required, they can provide temperature data from multiple locations to help optimize your home environment.
Having visibility into indoor and outdoor conditions lets you make informed heating, cooling, and gardening decisions. The outdoor sensor can be placed anywhere needed, while the indoor display provides at-a-glance monitoring. Let’s explore the benefits of using a solar powered indoor/outdoor thermometer and how to get the most out of this useful gadget.
Top Benefits of Solar Powered Indoor Outdoor Thermometers
Here are some of the key advantages of using a solar powered indoor/outdoor thermometer at home:
- Monitor indoor and outdoor temps from one display
- Quickly see if it’s warmer or cooler outside
- Track daytime heating and nighttime cooling cycles
- Identify the best times to ventilate or insulate your home
- Help optimize use of heaters, fans, and AC
- No wiring or batteries needed for operation
- Provides min/max temperature records
- Wireless sensor can be placed anywhere in your yard
- Simple installation with no setup needed
For very little investment, an indoor/outdoor thermometer provides data to help make your home more comfortable and efficient all year round.
Ideal Locations to Place the Outdoor Sensor
The key to getting useful readings from your solar thermometer is proper placement of the outdoor sensor. Consider these prime locations around your home:
- Patio or deck – Monitor temperature in your main outdoor living area
- Garden beds – Check conditions around your plants
- Play areas – Know when it’s too hot or cold for kids
- Poolside – Track ideal swimming temperatures
- Garage or shed – Get insights on outbuilding conditions
- Microclimates – Discover hot/cold spots around your home
Aim to place the sensor in a spot that will provide the most useful temperature data for how you use your yard. And ensure it gets adequate sun exposure so the solar power functions properly.
Getting the Most from Your Temperature Readings
Once your solar indoor/outdoor thermometer is set up, check it frequently and take note of temperature patterns. Here are some ways to use the readings:
- Open/close windows and doors when outside air is cooler
- Run fans and AC more at the hottest times of day
- Fire up the heater when indoor and outdoor temps drop
- Monitor outdoor lows for cold-sensitive plants
- Adjust automatic sprinkler schedules based on weather
- Identify the most comfortable outdoor areas to relax
- Know when to bring pets indoors due to heat or cold
Pay attention to the minimum and maximum temperature records too. These reveal temperature swings you may not see at a glance. All this data will help you make smart, informed decisions about your home.
Added Convenience of Digital Models
Many indoor/outdoor thermometers today offer digital displays with added features like:
- Backlit screen – Illuminated display is easy to read day or night.
- High/low alerts – Programmable to notify you when temps exceed set levels.
- Temperature trends – See if it’s getting hotter or colder over time.
- Weather forecasting – Icons indicate expected conditions.
- Humidity readings – Monitors indoor and outdoor humidity levels.
- Clock/calendar – Extra functions on the indoor display.
Digital models provide more insights than old-fashioned bimetallic coil thermometers. Just be sure to place the display where it’s easy to access and view.
Installation Tips
Installing a solar powered indoor/outdoor thermometer is quick and easy. Follow these tips:
- Select locations to place the outdoor sensor and indoor unit.
- Clean the installation surfaces and attach hardware.
- Insert batteries in the outdoor sensor for backup power.
- Ensure the sensor gets direct sun exposure.
- Sync the units following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Mount the indoor display in a visible spot you’ll check often.
Within minutes, your thermometer will spring to life! Set it up in the evening so the outdoor sensor charges fully in the morning sun.
Monitoring indoor and outdoor temperatures provides insights for creating a more comfortable, energy efficient home. With a solar powered indoor/outdoor thermometer, you’ll have the data you need conveniently in one glanceable display.
Solar Powered Weather Stations for Gardens
As a gardener, being aware of weather conditions can help you make better decisions for your plants. Installing a solar powered weather station in your garden provides continuous data to optimize your growing environment.
Solar weather stations measure much more than just temperature. By tracking factors like humidity, rainfall, wind and more, they give you valuable insights into the microclimate in your yard. Let’s explore how setting up a solar powered weather station can take your gardening to the next level.
Key Benefits of Solar Powered Garden Weather Stations
Some of the top benefits of using a solar powered weather station for your garden include:
- Monitor air temperature highs and lows
- Measure soil temperature at root level
- Track humidity which affects disease and growth
- Log wind speeds and direction
- Record rainfall amounts
- Get UV index readings for sun exposure
- Configure custom alarms for conditions
- Operate fully off-grid using solar power
- Easily move sensors around the garden
- Wireless connectivity to access data remotely
The comprehensive real-time data provides invaluable insights to support your gardening. And solar power lets you install sensors anywhere needed without electrical cords.
Ideal Locations to Place Sensors
Take advantage of the portability of solar sensors to place them in multiple microclimates within your garden, such as:
- Center of vegetable garden beds
- On sun-facing and shaded sides of trees
- Inside a greenhouse to monitor conditions
- Where frost may form first if susceptible plants are nearby
- Adjoining heat-loving plants like tomatoes and peppers
- Near moisture-sensitive succulents and cacti
Distribute sensors across your entire garden area to get sufficient weather data. And ensure they receive adequate sunlight for the solar panels to function.
Using Weather Station Data for Gardening
The real value of a weather station is using the data to inform your gardening. Here are some ways to leverage the readings:
- Water more frequently during hot, dry periods
- Use fans, misters, or shade cloth when too hot
- Add cold frames or row cover when temperatures drop
- Watch for patterns signaling disease-friendly conditions
- Plan planting timing and spacing based on microclimate data
- Adjust automatic sprinklers based on rainfall
- Apply extra sun protection when UV index is very high
Checking the weather station regularly and recording key events will provide insights to optimize your garden all season long. You’ll quickly learn to “listen” to what your weather data is telling you.
All-in-One Stations vs. Modular Sensors
When selecting a solar weather station, you have two main options:
- An integrated station with sensors built into one unit.
- A modular design allowing you to place individual sensors anywhere.
Integrated stations are more convenient but limit sensor placement flexibility. Modular systems allow fully customizing sensor locations but require more effort to install. Choose the right one based on your specific gardening needs and setup preferences.
Must-Have Features for Garden Weather Stations
Look for these useful features when picking a solar weather station:
- Sensors for temperature, humidity, rainfall, etc.
- Direct soil temperature probes
- Solar power and battery backup for sensors
- Weatherproof, durable construction
- LCD display with data history
- Custom high/low condition alerts
- Simple DIY installation
- App and cloud connectivity to monitor remotely
Advanced models meeting these criteria will provide detailed weather insights to support your gardening for years to come.
Installing Your Solar Weather Station

Follow these tips for smoothly setting up your new garden weather station:
- Select ideal locations to place sensors based on sun, plants and microclimates.
- Clean and level mounting surfaces.
- Assemble, power on, and sync devices per instructions.
- Ensure solar panels have sun exposure throughout the day.
- Use mounting hardware to install sensors and display base.
- Configure app and alerts to monitor data remotely.
In no time, you’ll be leveraging comprehensive weather data to make smarter decisions for your garden! A solar powered weather station is one of the best upgrades any gardener can make.
Protect Plants from Frost and Heat with Solar Thermometers
Temperature extremes like frost and intense heat can damage or kill garden plants. Using solar powered thermometers allows closely monitoring conditions so you can take steps to protect your vegetation.
With solar thermometers in place, you can keep a close eye on temperatures around your plants. This gives advance warning to shield them from harsh weather before it takes a toll. Let’s look at how tracking temps with solar thermometers helps safeguard your greens from both cold and hot weather.
Protecting Plants from Frost and Freezes
Frost is a threat during cooler growing seasons. A solar thermometer with a remote sensor placed among susceptible plants is an ideal early warning system. When temps start dropping near freezing, take action such as:
- Cover plants with cloches, cold frames, or row cover
- Move potted plants together and surround with insulation
- Water plants well before frost to retain heat in the soil
- Move plants indoors or under awnings/patios
- Use strings of incandescent lights to provide warmth
- Spray plant leaves with an insulating antifreeze spray
Without a thermometer, you may not notice freezing conditions until plant damage occurs. But solar models give advance notice to protect your vegetation.
Shielding Plants from Extreme Heat
Just like cold snaps, periods of extreme heat can wreak havoc in your yard. Solar thermometers let you take action once temperatures hit critical thresholds, such as:
- Adding shade cloths and screens over plants
- Applying reflective mulch to cool the soil
- Watering more frequently to reduce stress
- Misting leaves with water to lower surface temp
- Moving plants out of hot sun to shadier areas
- Using fans to circulate air and improve transpiration
The key is responding before plants show signs of heat damage like wilting or scorched leaves. Your trusty solar thermometer provides the data needed to time protective measures perfectly.
Ideal Thermometer Features for Frost and Heat Protection
To get the most benefit for safeguarding your plants, look for these helpful thermometer features:
- Remote sensor – Place near plants rather than on display unit.
- Min/max temps – Spot temperature swings signaling danger.
- High/low alarms – Get alerts when passing thresholds.
- Wide range – Capture both freezing and hot temps.
- App connectivity – Monitor temps remotely.
- Fast response – Rapidly detect temperature changes.
These capabilities allow responding quickly to shield your plants before they feel the effects of frigid or sweltering weather.
Ideal Thermometer Placement to Monitor Frost and Heat
Proper placement is key for getting the most benefit. Locate your solar thermometer sensor:
- Near vulnerable plants prone to cold/heat damage.
- In different microclimates around your yard.
- In an area that tends to freeze or bake first.
- Under the canopy of fruit trees and dense vegetation.
- In raised planters or containers easier to protect.
Distribute multiple thermometers in different zones for the best coverage. Just be sure they get adequate sun exposure to maintain solar charging.
Recording Temperature Data Alongside Plant Health Observations
To get the most insights from your solar thermometer, be sure to record key details in a garden journal:
- Note daily minimum and maximum temperatures.
- Track any temperature alerts triggered.
- Document when you protected plants from cold or heat.
- Watch for plant damage symptoms correlated to temperatures.
- Identify cold/heat hardy vs. sensitive plants.
Reviewing this temperature and plant health history will help refine your protection methods over time. You’ll learn exactly which plants need help and at what temperatures.
By leveraging solar thermometers to monitor for temperature extremes, you can take proactive steps to protect your vegetation. Avoid losing your carefully tended plants to preventable frost or heat damage!
Best Locations to Place Solar Powered Garden Thermometers
One of the keys to getting the most value from solar powered thermometers is thoughtful placement around your garden. Identifying the right locations allows monitoring the most useful microclimates impacting your plants.
You can mount solar thermometers on walls and fences, stick them in soil, or hang them from branches. Get creative in distributing them throughout your entire landscape. Let’s explore some ideal spots to install solar thermometers in gardens of all sizes and layouts.
Sunny Open Areas
Aim to place at least one solar thermometer in a hot, sunny area of your garden. This could be:
- A vegetable bed getting full sun most of the day.
- An open area with no trees or buildings providing shade.
- Next to sun-loving plants like tomatoes, peppers, and herbs.
- On a south-facing wall or fence absorbing sunlight.
Full sun zones often reach the highest daytime temperatures. Monitoring these locations gives insights into peak heating effects on plants.
Under Trees and Overhangs
It’s also helpful to install a solar thermometer in shadier garden areas, like:
- Beneath shade trees or under the canopy.
- Next to north-facing walls and fences.
- In a planting bed bordered by a shrub or hedge.
- Under the eave overhang of a garden shed or pergola.
Shaded zones typically reach lower temperatures than exposed areas. Comparing sun and shade readings shows the cooling impact of tree cover.
Near Plantings
For monitoring conditions around specific vegetation, place solar thermometers:
- Next to plants prone to cold or heat damage.
- Among delicate transplants that need gradual acclimation.
- Adjoining containers holding moisture-sensitive plants.
- By vegetation you want to baby with extra protection.
The closer the thermometer is to plantings, the better it reflects the microclimate immediately surrounding them.
Microclimates
Take advantage of your yard’s unique microclimates by situating thermometers in areas like:
- Against brick or stone walls that radiate heat.
- Near pools, ponds, or water features cooling the air.
- In a low-lying frost pocket where cold air collects.
- By raised beds, hills, or berms with better drainage.
Identifying and monitoring your garden’s microclimates provides helpful insights on conditions plants experience in each zone.
Inside Greenhouses and Grow Tents
Don’t forget to place solar thermometers:
- On shelving or posts inside a greenhouse.
- Hanging from the ceiling of a grow tent.
- On the north and south walls of a cold frame.
Tracking temperatures inside protected structures ensures you aren’t cooking or freezing your plants. Open vents or add a heater as needed.
Care Tips for Placement
When installing solar thermometers, follow these tips:
- Face solar panels south for max sun exposure.
- Consider visibility for easy reading of the display.
- Mount at the same height above ground for comparable data.
- Clean and dry surfaces thoroughly before attachment.
- Use manufacturer’s recommended mounting method.
Distributing thermometers thoughtfully throughout your entire garden ensures you are monitoring the conditions impacting your plants. Observe temperature patterns over time to optimize each unique microclimate.
Solar Thermometers for Greenhouses and Cold Frames
Monitoring temperatures inside protected gardening structures like greenhouses and cold frames is essential. Installing solar powered thermometers provides an easy way to keep tabs on conditions for your plants.
Solar thermometers are ideal for greenhouses and coldframes since they don’t require any wiring. Just mount the display and sensors where needed and the sun powers everything. Let’s look at how solar thermometers help dial in ideal growing environments inside these enclosed spaces.
Benefits Inside a Greenhouse
Adding solar thermometers inside your greenhouse provides:
- Early warning of overheating on hot sunny days
- Ability to monitor nighttime lows during winter
- Insights on zones that are warmer or cooler
- Reminders to vent and control humidity
- Data to determine best placement for plants
- Peace of mind your plants aren’t freezing or cooking
Tracking greenhouse interior temperatures enables making adjustments to ensure your plants thrive in the protected environment.
Optimizing Conditions in Cold Frames
Solar thermometers help create an ideal microclimate inside your cold frame by:
- Measuring heating effectiveness from the sun’s rays
- Warning when interior temps may harm plants
- Indicating when to vent excess heat on sunny days
- Tracking overnight lows and risk of frost
- Letting you safely harden off seedlings
- Extending growing season by months
The data provided by solar thermometers takes the guesswork out of managing your cold frame environment.
Ideal Solar Thermometer Features
Look for these helpful capabilities when selecting models for greenhouses and cold frames:
- Wireless remote sensors to place separately from display
- Min/max temp tracking to catch swings
- Wide temperature range for cold and heat
- High/low alarms to alert when passing thresholds
- Solar recharging so no batteries required
- Waterproof, weatherproof construction
- Easy-mount design with magnets or hangers
Advanced solar thermometers like these provide the functionality needed for closely monitoring protected growing environments.
Ideal Placement Locations

Proper thermometer placement is key. Good locations include:
- On shelving next to plants needing close monitoring
- Hanging from rafters to measure air temperature
- Along the north wall to track cooling overnight
- On southern exposure to monitor daytime solar heating
- Near vent windows to check for overheating
Distribute multiple sensors at different heights for the best coverage. Just ensure they get sun to maintain power.
Using Thermometer Data
Making temperature management adjustments based on your solar thermometer data enables:
- Venting excess heat to prevent plants from wilting
- Adding a heater or moving plants on cold nights
- Providing shade cloth or misting during extreme heat
- Safely hardening off seedlings before transplanting outdoors
- Timing planting and moving plants in and out
Consult your thermometers both morning and night to take appropriate actions for ideal growing temps.
Recording Conditions and Plant Health
To gain the most insights, be sure to log key details like:
- Daily minimum and maximum temperatures
- Adjustments made like adding ventilation
- When plants were moved in and out of the structure
- Any symptoms of plant stress related to temps
Review this history periodically to refine your cold frame or greenhouse temperature regulation strategies.
Installing solar thermometers in protected growing structures takes the guesswork out of maintaining ideal conditions. Monitor temperatures daily and respond quickly to keep plants thriving!
Solar Powered Thermometers for Raised Garden Beds
Raised garden beds create a unique microclimate for your plants. Installing solar powered thermometers allows closely monitoring conditions within your raised bed to ensure ideal growing temps.
Because raised beds sit above ground level, the soil warms up quicker in spring for earlier planting. Beds also drain better, requiring more frequent watering. Tracking temperatures helps provide the perfect environment for your vegetables or flowers. Let’s look at how solar thermometers can optimize your raised bed garden.
Benefits of Solar Thermometers for Raised Beds
Solar powered thermometers offer several advantages for monitoring raised garden beds:
- Fully wireless to install anywhere easily
- No wiring or power required
- Measure soil and ambient air temps
- Low-profile design fits neatly on raised bed edges
- Easy to reposition as beds are rotated or rearranged
- Provide temperature history for analysis
Solar models give freedom to monitor conditions affordably within the unique environment inside your raised beds.
Ideal Raised Bed Placement Locations
Consider these prime spots when installing solar thermometers on raised garden beds:
- On the north side to monitor minimum temps
- Against the south-facing edge to track solar heating
- Next to crops prone to heat or cold damage
- On beds containing heat-loving plants like tomatoes
- Near edges of the bed rather than the center
Distributing thermometers around beds provides a complete view of the temperature variances plants experience.
Typical Temperature Ranges in Raised Beds
Raised beds create a warmer microclimate than at ground level. Typical temperature differences include:
- Daytime highs 5-20°F warmer than surrounding soil
- Overnight lows 3-6° warmer due to better drainage
- Less fluctuation between day and night
- Warms up faster in spring
- Stays workable longer into winter
Monitoring these patterns with solar thermometers enables optimizing planting schedules and frost protection.
Using Thermometer Data
Here are some ways to leverage the temperature data from raised bed thermometers:
- Start seedlings earlier in warmer beds
- Delay first fall frost protection until later
- Choose warm-weather crops for heated beds
- Add shade cloth if beds exceed 85-90°F
- Use floating row covers to trap heat on cold nights
- Adjust watering frequency based on drying rates
The numbers provide actionable insights for tailoring your raised bed conditions perfectly.
Ideal Thermometer Features
Look for these helpful capabilities in solar thermometers for raised beds:
- Detachable soil probe to insert in beds
- Remote wireless sensor to attach on boards
- Min/max readings to monitor temperature swings
- Wide measurement range from -40°F to 140°F
- Large backlit display for easy visibility
- Weatherproof construction rated for outdoors
Advanced models like these deliver all the data needed to dial in your raised bed environment.
Get Started Monitoring Your Raised Beds
Implementing solar thermometers for your raised garden beds is simple:
- Obtain sturdy solar thermometers with min/max readings.
- Position sensors on north and south facing sides of beds.
- Insert soil probes into planting mix in center of beds.
- Check readings daily and record in a garden journal.
- Use data to optimize watering, protection, and planting schedules.
With solar thermometers providing temperature insights, you can leverage the unique microclimate of raised beds to maximize your harvest!
Tips for Reading and Interpreting Solar Thermometer Data
Solar powered thermometers provide a wealth of temperature data for your garden. But that information is only useful if interpreted correctly. Follow these tips to get the most insights from your solar thermometer readings.
Checking your thermometers consistently, recording key details, and watching for patterns will help you leverage the numbers. Let’s explore best practices for gathering, analyzing, and acting on solar thermometer data in your landscape.
Read the Display Fully
Don’t just glance quickly at the solar thermometer display. Take time to note these details:
- Current temperature
- Min/max temperatures for the day
- Any alarm indicators
- Trend arrows showing heating/cooling
- Humidity or other secondary readings
absorbs the full picture of conditions your plants are experiencing, not just the current snapshot.
Check Readings at Consistent Times
Be consistent when checking in on your solar thermometers. Ideal times include:
- First thing in the morning to get minimum overnight temps.
- In late afternoon to observe peak daytime highs.
- Around sunset when cooling begins.
- Before bed to ensure temps aren’t rapidly dropping.
Setting a schedule provides comparable data revealing the day’s temperature swing.
Record Details in a Garden Journal
Don’t just glance at your solar thermometer and walk away. Log key data like:
- Date and time of readings
- Current temp, minimum, and maximum
- Any actions taken based on temps
- Signs of plant stress related to hot or cold
This temperature log coupled with plant health notes provides insights over the season.
Watch for Temperature Trends and Patterns
Over time, noticeable trends will emerge:
- Heating and cooling rates during the day.
- Weather patterns with multi-day heat or cold spells.
- Microclimate differences between zones.
- Seasonal shifts as summer transitions to winter.
Spotting these trends helps anticipate upcoming conditions affecting your plants.
Compare Readings to Weather Forecasts
Cross-check your solar thermometer against daily weather forecasts. Differences could indicate:
- Microclimates faring better or worse than expected.
- Radiation heating or cooling surprising your plants.
- Approaching fronts speeding up or slowing temperature swings.
- Your landscape lagging behind or ahead of forecasts.
Comparing your live readings provides ground truth for the forecast.
Take Action Based on Temperature Data
Don’t just observe your solar thermometers – respond! For example:
- Ventilate greenhouses on hot days
- Add water when soil temperature spikes
- Move plants when zones get too hot/cold
- Safeguard vegetation as extremes approach
This protective action is only possible with the advance warning thermometers provide.
Continue Iterating
Learn something new from your solar thermometer data each season:
- Which plants thrive in which microclimates
- Ideal temperature range for each plant
- Refined thresholds for adding insulation/shade
- Adjusted watering frequency based on soil temps
Continuously evaluating your temperature data helps optimize environmental conditions year after year.
Following these simple tips ensures you get maximum benefit from your solar-powered thermometers for healthier, more productive plants!
Compare Different Models of Solar Garden Thermometers
With many options on the market, it can be tricky choosing the right solar thermometer for your garden. Comparing features helps identify models that best fit your needs and budget.
Factors like measurement range, convenience features, and display capabilities distinguish basic economy models from advanced professional-grade units. Evaluate which specifications are most important for your gardening requirements. Let’s look at key variables differentiating solar thermometer models.
Temperature Measurement Range
A wide temperature range allows monitoring both winter lows and summer highs. Look for:
- Limited range like 0°F to 100°F for basic residential use
- Extended range from -40°F up to 140°F for broader conditions
Wider ranges provide early alerts as temperatures begin exceeding plant tolerances.
Single or Dual Channel Readings
Thermometers offer:
- Single sensor displays temperature in one location.
- Dual sensors show indoor and outdoor conditions.
Dual lets you compare ambient and soil or sun and shade temperatures simultaneously.
Current vs. Minimum/Maximum Temps
Basic models show only current temp, while advanced versions track:
- Minimum and maximum high/low readings for the day.
- Time/date stamps for when those extremes occurred.
Min/max gives greater insight into daily temperature fluctuations.
Measurement Accuracy
Accuracy varies based on thermometer technology:
- Liquid-based models are precise to +/- 1°F.
- Digital sensors provide +/- 0.5°F or better accuracy.
More advanced sensors give confidence you’re seeing true conditions.
Display Quality and Size
Evaluate display characteristics:
- LCD screens are inexpensive but can wash out in sunlight.
- OLED displays offer better contrast and visibility.
- Larger formats like 2”x4” are easier to read from a distance.
A highly visible display allows quickly glancing temperatures from anywhere in your yard.
Power Options
Thermometers are powered by:
- Replaceable batteries providing affordable convenience.
- Solar cells for renewable self-charging operation.
Solar power avoids ongoing battery costs while supporting placement anywhere.
Alerts and Alarm Settings
Advanced models offer:
- Programmable alarms to alert when passing high/low thresholds.
- Visual/audio alerts for immediate notification.
Alerts give immediate warning when attention is needed protecting plants.
Remote Monitoring and Connectivity
Added conveniences include:
- Wireless radio transmission between sensors and base.
- Smartphone apps to view data remotely.
- Data logging to track trends over time.
These features allow monitoring conditions from anywhere.
Choosing thermometers based on the capabilities that best match gardening needs and priorities ensures getting the right data to optimize growing conditions.
Extra Features of Advanced Solar Powered Thermometers
Basic solar thermometers simply display current temperatures. But advanced models come packed with extra capabilities to provide enhanced insights into your garden conditions.
Additional sensor types, connectivity options, and convenience features differentiate basic units from higher-end versions. These extras allow customizing thermometers to your specific gardening needs. Let’s explore some of the top extras to look for in advanced solar models.
Multiple Sensor Types
Look for thermometers accommodating various sensor attachments:
- Ambient air sensors for tracking air temps.
- Soil probes to monitor ground temperature.
- Waterproof sensors for water features.
- Humidity sensors to measure moisture levels.
Multiple sensor inputs give a complete picture of the microclimate conditions impacting plants.
Min/Max Temperature Tracking
Advanced units record:
- Daily highs and lows beyond just current temp.
- Time/date stamps for when extremes occurred.
This min/max data reveals hidden temperature swings plants experience.
User-Programmable Alarm Thresholds

- Set high and low temp limits to trigger alerts.
- Receive visual/audio alerts when exceeding limits.
Alarms provide immediate notification when action is required protecting plants.
Smartphone Connectivity and Apps
Advanced thermometers offer:
- Bluetooth and WiFi connectivity to sync data to devices.
- Companion apps to view readings from anywhere.
Wireless connectivity allows monitoring from indoors or on the go.
Web Portals and Data Logging
Some models provide:
- Cloud storage to maintain temperature history.
- Web portals to access data for analysis.
Logged readings reveal temperature trends over time.
Weather Forecasting Displays
Added display features include:
- Weather icons indicating forecast conditions.
- Rainfall tracking with tipping bucket sensors.
These provide at-a-glance insights beyond just temperature.
Rugged and Waterproof Construction
Look for:
- Commercial grade materials for professional use.
- Weatherproof ratings like IP65 or NEMA 4X.
Heavy duty construction allows permanent installation in any outdoor environment.
Expanded Power Options
Advanced models offer:
- Solar and battery power for installation anywhere.
- AC power adapters for continuous indoor operation.
Flexible power choices support versatility across many applications.
Seeking out thermometers with these extra capabilities provides the features and customization needed to monitor garden conditions. Advanced solar models are an investment that pays dividends through healthier plants and bigger yields!
Solar Powered Thermometers Allow Hands-Free Temperature Monitoring
One of the key benefits of solar thermometers is the ability to monitor temperatures completely hands-free. Thanks to solar power and wireless transmission, these devices run themselves without any work required on your part.
Once in place, solar thermometers provide continuous remote readings to keep close tabs on conditions in your yard and garden. Let’s look at how the set-and-forget nature of solar thermometers makes temperature tracking effortless.
No Wiring Needed

Solar power means:
- No electrical outlets or extensions cords needed.
- Sensors can be freely placed anywhere outdoors.
- Units operate off-grid using free solar energy.
Wireless solar operation enables positioning thermometers where they’re needed most.
No Battery Hassles
- Costly battery replacement.
- Loss of power from dead batteries.
- Exposure damage from removing/reinstalling batteries.
Uninterrupted solar power removes a frequent headache with temperature monitoring.
No Manual Data Logging
- No manually checking and writing down temperatures.
- All data is automatically retained for review.
- Apps and software collect and analyze readings for you.
Automated data history provides insights without effort on your part.
No Direct Visual Checks Needed
- Remote smartphone monitoring of readings.
- Alerts that notify you when attention is needed.
- Web dashboards to view data anywhere.
Automated monitoring means no need for frequent visual inspection.
Simple Do-It-Yourself Installation
- Pre-paired wireless sensors.
- Magnets, hooks, and stands for no-tool mounting.
- Step-by-step manuals and video instructions.
Hands-free temperature tracking starts the moment your solar thermometers are in place.
Self-Contained Design
- All-in-one units with no loose parts.
- Waterproof, weatherproof enclosures.
- Vandal-proof construction for public areas.
Minimal maintenance ensures maximum uptime for uninterrupted data collection.
Flexible Expandability
- Starting small and adding sensors over time.
- Positioning sensors in multiple locations as needed.
- Upgrading capabilities without replacing entire system.
Expandability enables customizing your setup with minimal added effort.
Hassle-Free Accuracy You Can Trust
- Lab-certified accuracy for reliable readings.
- NIST-traceable calibration for dependable performance.
- Quality components resistant to drift and degradation.
Top-tier accuracy guarantees data you can count on with confidence.
By leveraging self-contained solar thermometers, you remove the hassle from temperature monitoring. Let automated systems do the watching and recording so you can focus on growing!

