How to properly cradle in girls lacrosse. What are the key techniques for effective cradling. Why is cradling crucial for maintaining possession in lacrosse. How can players improve their cradling skills.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Cradling in Girls Lacrosse
Cradling is a fundamental skill in girls lacrosse that allows players to maintain possession of the ball while moving across the field. It involves a rhythmic motion of the stick that keeps the ball securely in the pocket, even during high-speed runs or when facing defensive pressure.
The primary purpose of cradling is to prevent the ball from falling out of the stick’s pocket. This technique is crucial for maintaining control during various game scenarios, including transitioning between offense and defense, evading opponents, and setting up scoring opportunities.
The Importance of Proper Cradling Technique
Mastering the art of cradling is essential for several reasons:
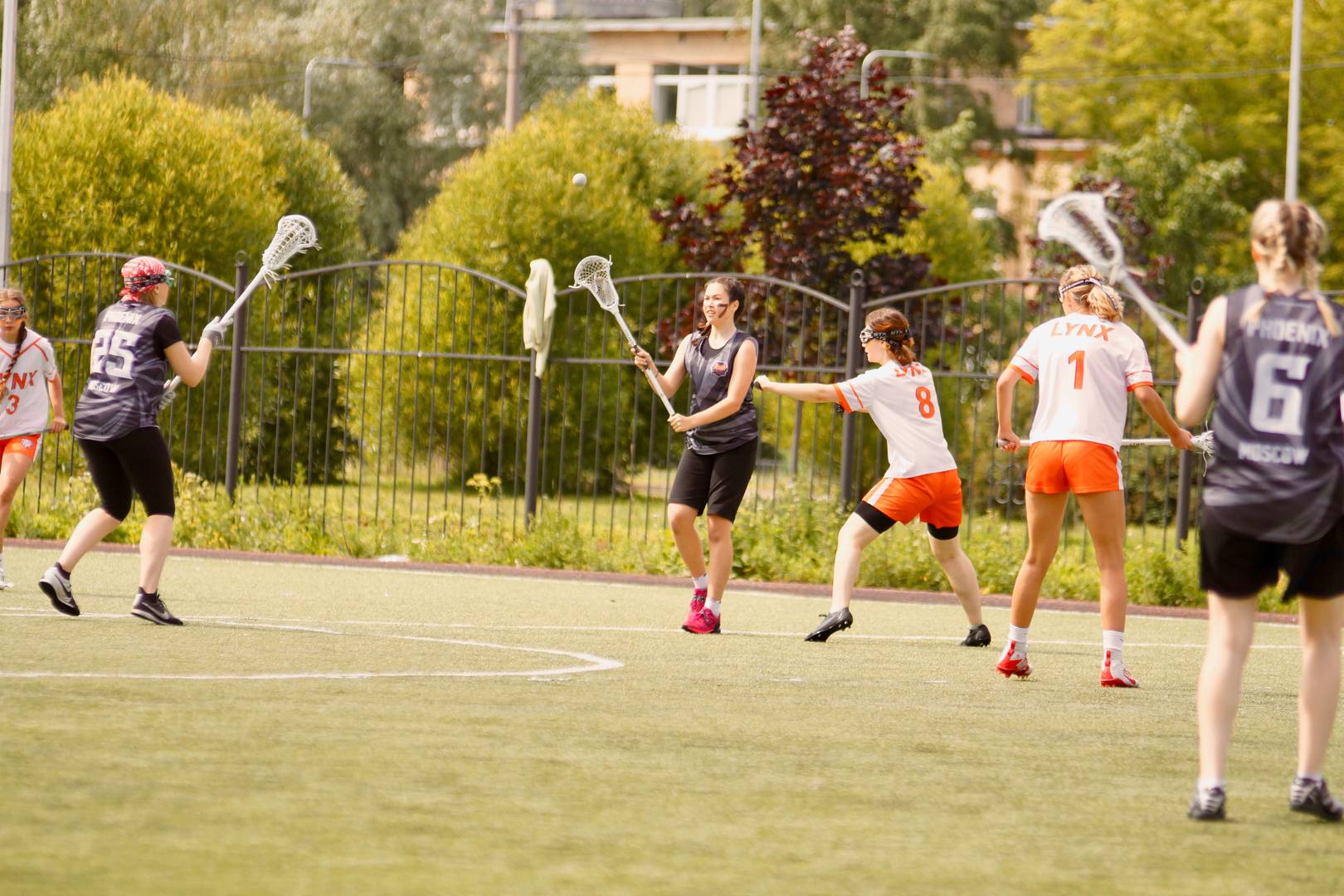
- Ball security: Effective cradling minimizes the risk of turnovers caused by dropping the ball.
- Player confidence: Skilled cradling allows players to focus on strategic play rather than worrying about ball control.
- Game flow: Smooth cradling facilitates faster transitions and more dynamic gameplay.
- Offensive advantage: Proper cradling technique makes it harder for defenders to check the ball away.
Key Components of Effective Cradling in Girls Lacrosse
To execute a proper cradle, players must focus on several key elements:
Hand Placement and Grip
The dominant hand should be placed near the top of the stick, just below the plastic of the head. This hand controls the power and speed of the cradling motion. The non-dominant hand is positioned lower on the shaft, providing stability and support.
Arm and Wrist Movement
The cradling motion primarily comes from the wrists and forearms. Players should aim for a smooth, controlled rotation that keeps the ball nestled in the pocket. Avoid excessive arm movement, as this can lead to less control and make it easier for defenders to disrupt possession.

Body Positioning
Maintain an athletic stance with knees slightly bent and body balanced. This position allows for quick changes in direction and better overall control while cradling.
Common Cradling Techniques in Girls Lacrosse
Players employ various cradling techniques depending on the game situation and their position on the field:
One-Handed Cradle
This technique is often used when running at full speed or when a player needs to keep one hand free for balance or to fend off defenders. The stick is held primarily with the dominant hand, using wrist rotation to maintain ball control.
Two-Handed Cradle
The most common and secure cradling method, two-handed cradling provides maximum control and protection of the ball. Both hands work in unison to create a smooth, rocking motion that keeps the ball in the pocket.
Vertical Cradle
Used when closely guarded by a defender, the vertical cradle involves holding the stick more upright, making it difficult for opponents to check. This technique requires quick wrist action to maintain ball control in a more confined space.

Developing Effective Cradling Skills: Drills and Exercises
Improving cradling technique requires consistent practice and targeted drills. Here are some effective exercises to enhance cradling skills:
- Stationary cradling: Practice cradling in place, focusing on smooth wrist rotation and maintaining proper form.
- Walking cradle: Gradually increase speed while cradling, progressing from a walk to a jog to a sprint.
- Figure-eight drill: Move the stick in a figure-eight pattern while cradling, improving wrist flexibility and control.
- One-handed cradling practice: Alternate between dominant and non-dominant hands to build ambidextrous skills.
- Cradling with distraction: Have a partner try to check the stick while cradling to simulate game-like pressure.
Avoiding Common Cradling Mistakes in Girls Lacrosse
Even experienced players can fall into bad habits when it comes to cradling. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Over-cradling: Excessive motion can actually make it easier to lose control of the ball.
- Cradling too close to the body: This limits a player’s ability to pass or shoot quickly.
- Neglecting off-hand practice: Developing ambidextrous cradling skills is crucial for well-rounded play.
- Focusing solely on the upper body: Proper footwork and body positioning are essential components of effective cradling.
- Ignoring situational awareness: Players should always be ready to pass or shoot, even while cradling.
Advanced Cradling Strategies for Competitive Play
As players progress in their lacrosse careers, they can incorporate more advanced cradling techniques to gain a competitive edge:

Change of Pace Cradling
Varying the speed and intensity of cradling can throw off defenders and create opportunities for quick direction changes or dodges.
Protected Cradling
Using the body to shield the stick while cradling can provide additional protection against checks and improve ball security in tight spaces.
Deceptive Cradling
Advanced players can use subtle changes in their cradling technique to fake out defenders, creating space for passes or shots.
The Role of Cradling in Overall Lacrosse Strategy
Effective cradling is not just an individual skill; it plays a crucial role in team strategy and game flow. Here’s how cradling impacts various aspects of the game:
Transition Play
Smooth cradling allows for quicker transitions from defense to offense, catching opponents off guard and creating fast-break opportunities.
Ball Possession and Clock Management
In close games, the ability to maintain possession through skilled cradling can be the difference between victory and defeat. Teams can use cradling to control the pace of the game and run down the clock when protecting a lead.

Creating Scoring Opportunities
Confident cradling allows players to navigate through defensive pressure, opening up passing lanes and shooting opportunities that might not otherwise exist.
Adapting Cradling Techniques for Different Positions
While all players need to master cradling, the specific techniques and focus may vary depending on position:
Attackers
Offensive players often need to cradle in tight spaces and under heavy defensive pressure. They should focus on quick, protective cradling techniques that allow for rapid transitions to shooting or passing motions.
Midfielders
As the players covering the most ground, midfielders need versatile cradling skills. They should be proficient in both one-handed and two-handed cradling to adapt to various game situations quickly.
Defenders
While defenders may cradle less frequently, they still need solid technique for clearing the ball and transitioning to offense. Focus on secure, two-handed cradling to minimize the risk of turnovers.

Goalies
Goalkeepers should practice cradling with a longer stick, emphasizing quick transitions from saves to clearing passes. Their cradling technique should prioritize ball security and rapid release.
By understanding and mastering these various aspects of cradling, girls lacrosse players can significantly improve their overall game performance. Remember, effective cradling is not just about keeping the ball in the stick—it’s about creating opportunities, maintaining possession, and ultimately contributing to team success on the field.
cradling tips girls lacrosse|TikTok Search
TikTok
Upload
laxx.girls
laxx.girls
hope this helped! #laxgirls #nunebr15 #15 #lacrosse #cradle #tips #fyp #fyppp #foryou
750 Likes, 65 Comments. TikTok video from laxx.girls (@laxx.girls): “hope this helped! #laxgirls #nunebr15 #15 #lacrosse #cradle #tips #fyp #fyppp #foryou”. Just a Cloud Away – Pharrell Williams.
kingdomheirforcelacrosse
Coach Janel
Lacrosse 101 – Cradling {Join KHF Girls Lacrosse in Port St. Lucie, Fl 🔥 Flash sale is happening now!! Go to KHFLAX.COM ‼️}
Lucie, Fl 🔥 Flash sale is happening now!! Go to KHFLAX.COM ‼️}
682 Likes, 20 Comments. TikTok video from Coach Janel (@kingdomheirforcelacrosse): “Lacrosse 101 – Cradling {Join KHF Girls Lacrosse in Port St. Lucie, Fl 🔥 Flash sale is happening now!! Go to KHFLAX.COM ‼️}”. original sound – Coach Janel.
27coachbritt
Brittany Poist
@kate ⭐️ 8m’s Part 2 #laxcoachbritt #lacrosse #lacrossetok #lacrossetraining #lacrossehighlights #lacrossegirls
5.3K Likes, 78 Comments. TikTok video from Brittany Poist (@27coachbritt): “@kate ⭐️ 8m’s Part 2 #laxcoachbritt #lacrosse #lacrossetok #lacrossetraining #lacrossehighlights #lacrossegirls”. Stuck In The Middle – Tai Verdes.
Stuck In The Middle – Tai Verdes.
that1lacrossecoach
Coach Em 🏳️🌈🥍
Stick brought to you by True Lacrosse. Swag brought to you by finally letting go of other people’s expectations. #lacrossecoach #girlslax
2.3K Likes, 27 Comments. TikTok video from Coach Em 🏳️🌈🥍 (@that1lacrossecoach): “Stick brought to you by True Lacrosse. Swag brought to you by finally letting go of other people’s expectations. #lacrossecoach #girlslax”. Drip Like ME – Kenndog.
lax_tipss
hi
Hope this helps! <3 @givemelaxtips #girlslacrosse #girlslax
65 Likes, 21 Comments. TikTok video from hi (@lax_tipss): “Hope this helps! <3 @givemelaxtips #girlslacrosse #girlslax”.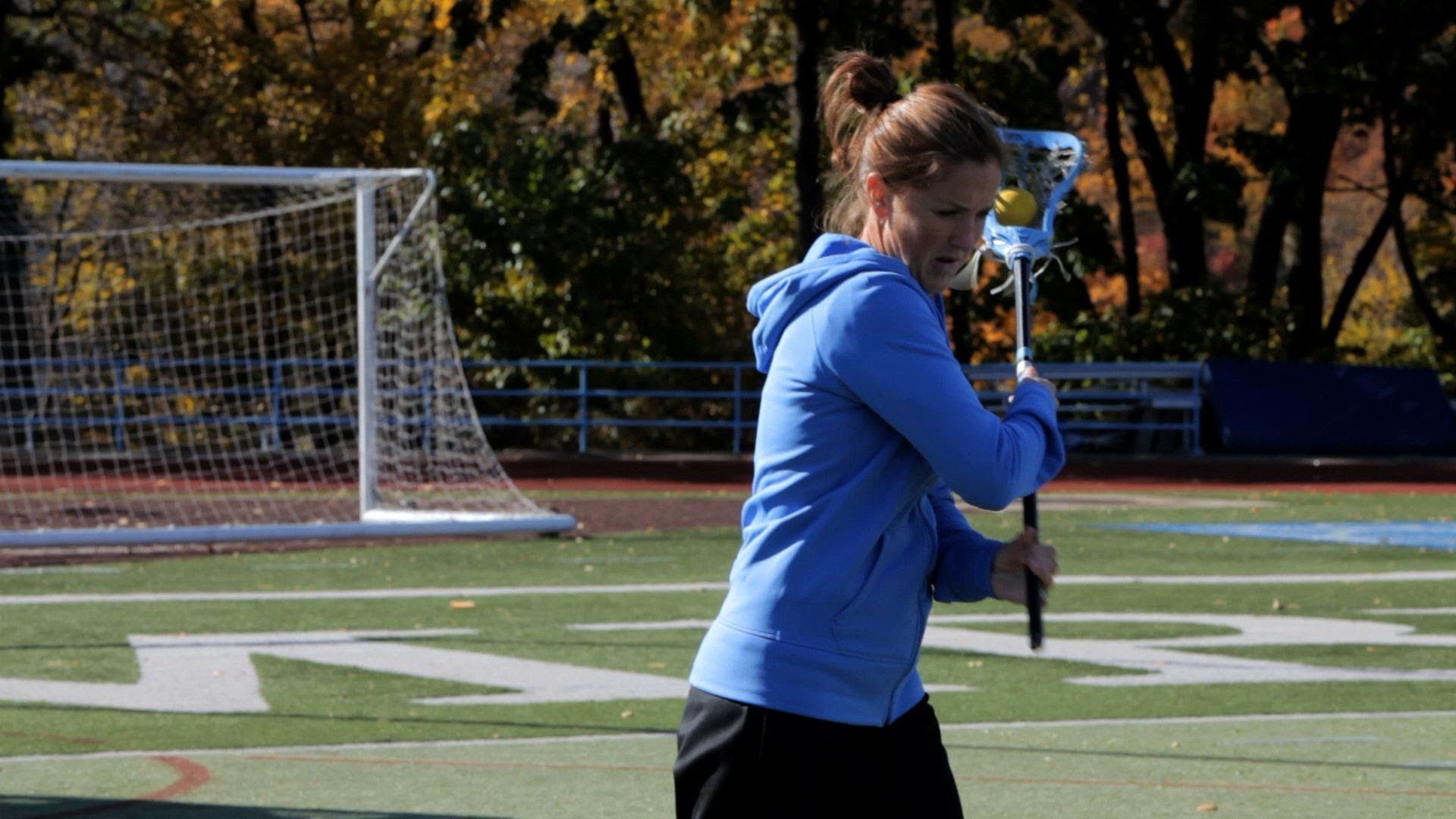 Love You So – The King Khan & BBQ Show.
Love You So – The King Khan & BBQ Show.
lacrosse..tips_
Lacrosse 🥍
Reply to @isa40982 As requested, here is how to cradle! Keep requesting more ideas!! #lacrosse #fyp #foryoupage #womanslacrosse
612 Likes, 55 Comments. TikTok video from Lacrosse 🥍 (@lacrosse..tips_): “Reply to @isa40982 As requested, here is how to cradle! Keep requesting more ideas!! #lacrosse #fyp #foryoupage #womanslacrosse”. Theme from “Twilight (Bella’s Lullaby)” – Movie Sounds Unlimited.
lacrossegirliesss
lacrosse girlies!
hope this helps! 🥍 #lax #girlslacrosse #ShowYourJOWO #FORDfortheBuilders #likeabombshell #fyp #lacrossegirls
197 Likes, 48 Comments.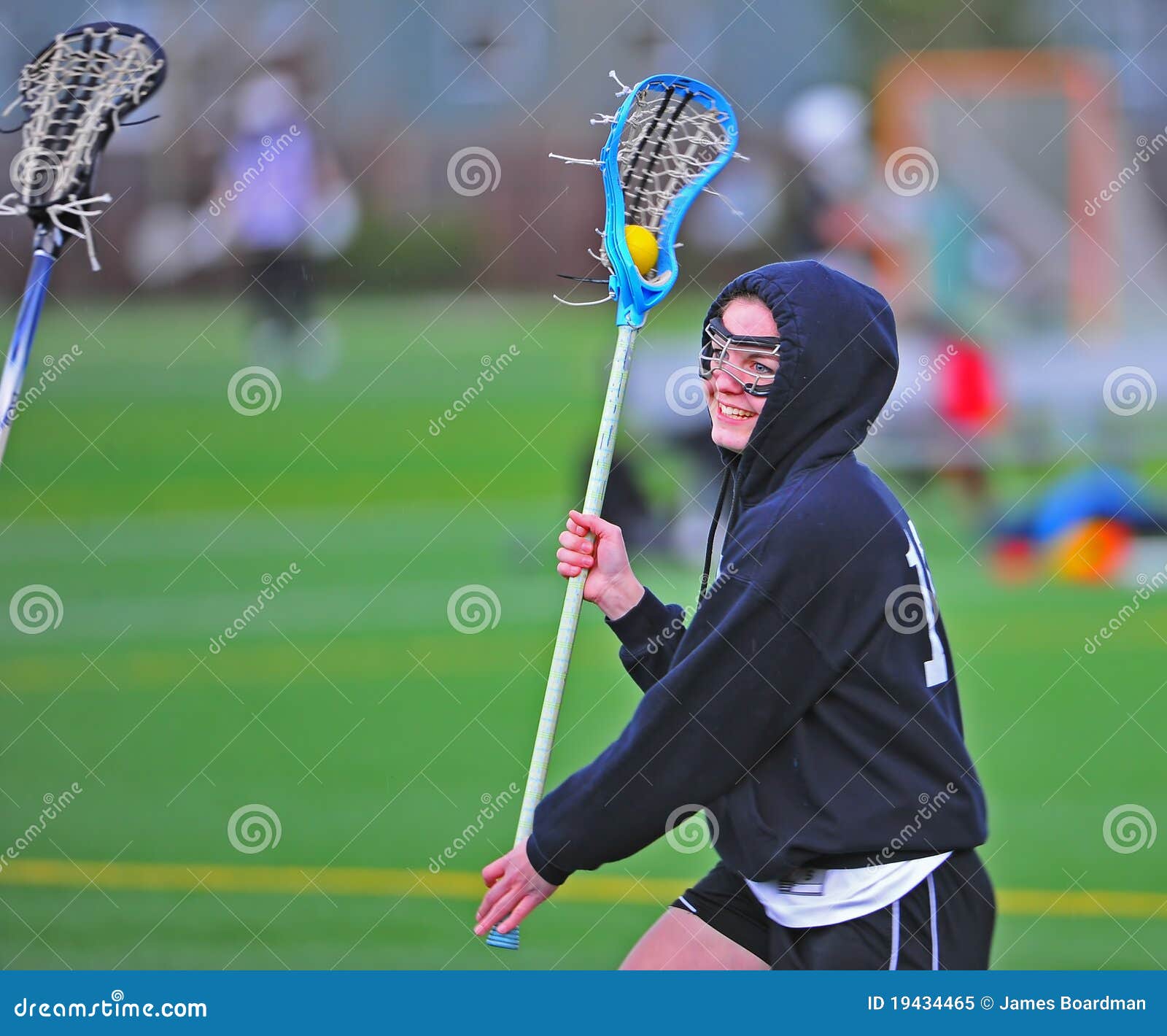 TikTok video from lacrosse girlies! (@lacrossegirliesss): “hope this helps! 🥍 #lax #girlslacrosse #ShowYourJOWO #FORDfortheBuilders #likeabombshell #fyp #lacrossegirls”. As It Was – Harry Styles.
TikTok video from lacrosse girlies! (@lacrossegirliesss): “hope this helps! 🥍 #lax #girlslacrosse #ShowYourJOWO #FORDfortheBuilders #likeabombshell #fyp #lacrossegirls”. As It Was – Harry Styles.
allstar.lax
Caroline
Replying to @hey.itss.zoe the bonus 😜 #lacrossetok #lacrossetips #lacrossegirls #lacrossementality
1.3K Likes, TikTok video from Caroline (@allstar.lax): “Replying to @hey.itss.zoe the bonus 😜 #lacrossetok #lacrossetips #lacrossegirls #lacrossementality”. LACROSSE 101:
Cradling | Hand placement | dominant hand controls power and speed | …Cradling 101 original sound – Caroline.
julesheningburg
Jules
If you are a beginner in Lacrosse, check this out!
Cradling is one of the most basic skills in lacrosse, but it isn’t as easy as it seems! #fyp #lacrosseskills #lax #lacrossetraining #lacrosseworkout #lacrosse #sports
50K Likes, 496 Comments.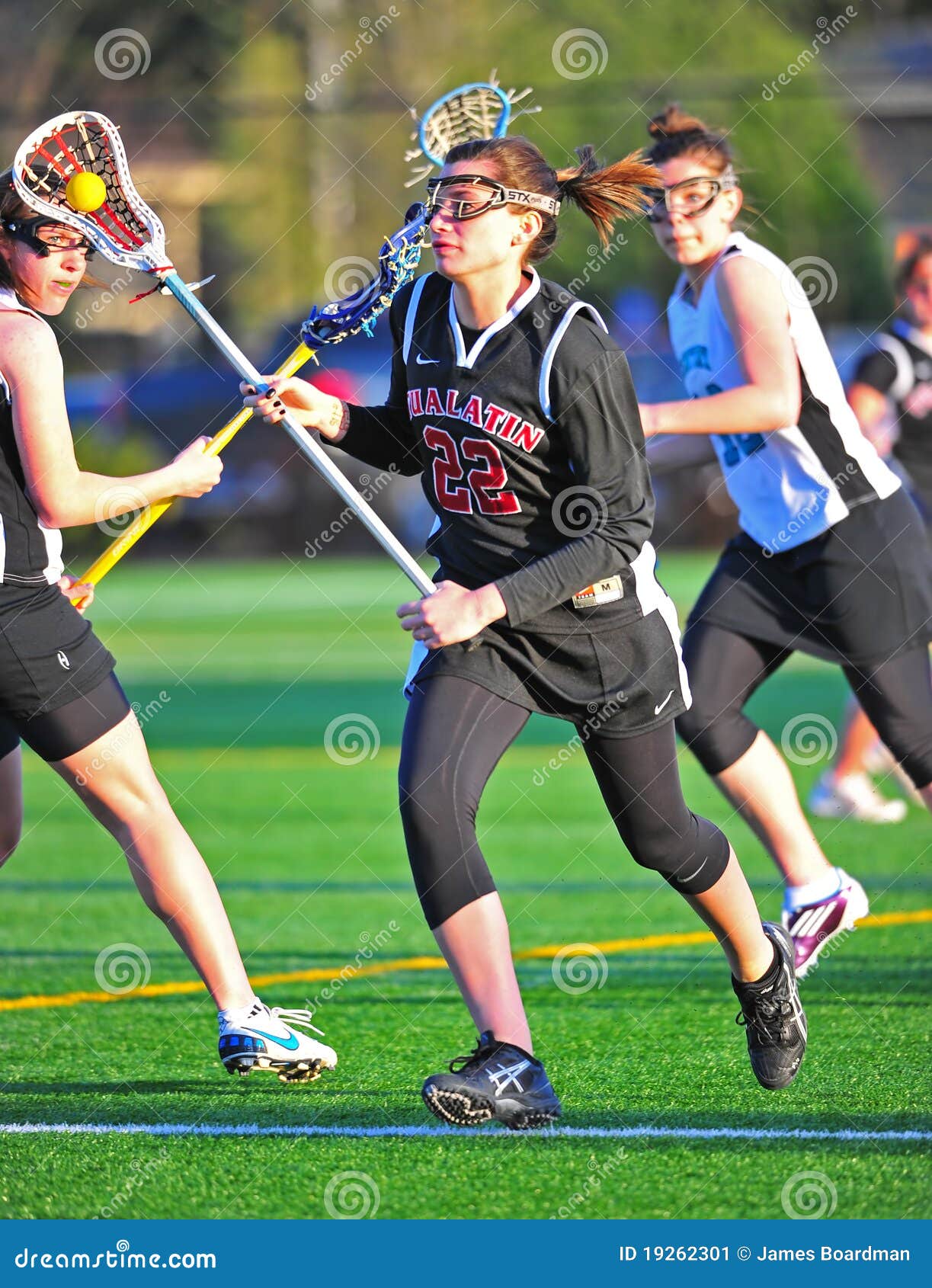 TikTok video from Jules (@julesheningburg): “If you are a beginner in Lacrosse, check this out! Cradling is one of the most basic skills in lacrosse, but it isn’t as easy as it seems! #fyp #lacrosseskills #lax #lacrossetraining #lacrosseworkout #lacrosse #sports”. original sound – Jules.
TikTok video from Jules (@julesheningburg): “If you are a beginner in Lacrosse, check this out! Cradling is one of the most basic skills in lacrosse, but it isn’t as easy as it seems! #fyp #lacrosseskills #lax #lacrossetraining #lacrosseworkout #lacrosse #sports”. original sound – Jules.
Cradling In Lacrosse: The Ultimate Guide
It isn’t easy keeping the ball in your stick while running full speed during a lacrosse match. That is what makes cradling such a crucial skill to learn in the game. Cradling is a technique used to keep the ball in the pocket of your stick. By doing so, your team can maintain possession and ultimately score. With proper form and understanding, you will be able to keep possession while fending off an opposing player.
What is Cradling in Lacrosse?
Lacrosse ball swaying is an essential skill for carrying the ball without dropping it while on the move. A player holds the ball in place during lacrosse play when he weighs the ball.
Cradling puts the ball in a position where it stays in the clubhead’s net when checking, transitioning, and dodging opponents on the field. Most turnovers are caused by the player not knowing how to properly hold his lacrosse stick, which can result in the ball falling onto the grass only to be picked up by the opponent.
What Are Fundamentals Of Cradles In Lacrosse?
It has to be no marvel that turnovers price group games and the worst manner to lose the ball in lacrosse are whilst you are simply cradling them and dropping it. To save you from dropping the ball in lacrosse, the act of cradling enables lacrosse gamers to keep the ball even as shifting and or being checked through a defender. Retaining the lacrosse ball through cradling is maximum useful whilst clearing or dodging in traffic, and being a first-rate lacrosse ball handler irrespective of your lacrosse role can rely upon preserving the ball for your lacrosse stick.
Unlike passing and capturing the lacrosse ball, in which your palms are near together, lacrosse gamers have to preserve their palm’s ways aside whilst cradling. The hand positioning whilst cradling with palms really is once in a while referred to as an “electricity cradle” that will let you avoid via exams, has a hand positioning at the lacrosse stick like that of catching a lacrosse ball. Keeping your palms ways aside offers lacrosse gamers the maximum protection with the lacrosse ball whilst defenders throw stick exams and the maximum balance whilst strolling with the lacrosse ball.
The hand positioning whilst cradling with palms really is once in a while referred to as an “electricity cradle” that will let you avoid via exams, has a hand positioning at the lacrosse stick like that of catching a lacrosse ball. Keeping your palms ways aside offers lacrosse gamers the maximum protection with the lacrosse ball whilst defenders throw stick exams and the maximum balance whilst strolling with the lacrosse ball.
There are different cradles, like cradling in a “triple threat” role or cradling with one hand even as strolling, however beginning with an ordinary -surpassed cradle and gaining knowledge of its miles is the way you start turning into a first-rate lacrosse ball handler.
How to Cradle a Lacrosse Ball
- Hand Positioning:
For the quality manipulation of a lacrosse cradle, your palms want to be in the role of consistent balls even as they may be cradled. When getting to know a way to preserve a lacrosse stick for cradling, your dominant hand has to be close to the pinnacle of the lacrosse shaft and your bottom (non-dominant hand) has to be near the grip on the lowest of the shaft.
- Non-Dominant Hand Grip:
When your palms are in the role of an powerful lacrosse cradle, a right grip guarantees you recognize a way to cradle in lacrosse. Your non-dominant hand has to be an overhand grip, much like the grip used whilst conserving the handlebars even as using a bicycle.
- Dominant Hand Grip:
Your pinnacle hand could be very essential to the stableness of your lacrosse cradle. You have to use an underhand grip close to the pinnacle of the shaft to consistently the cradled ball and be organized to transition backward and forward for protection.
- Stick Positioning:
Once your palms are withinside the right role and you have got discovered a way to preserve a lacrosse stick for a consistent cradle, you may need to put your stick in a manner in order that the lacrosse ball remains withinside the pocket. Your stick has to be parallel in your frame and be at a forty-five to 60-diploma perspective from the ground. Make positive that the open aspect of the pinnacle pocket is going through ahead so the lacrosse ball would not fall out whilst cradled.
Make positive that the open aspect of the pinnacle pocket is going through ahead so the lacrosse ball would not fall out whilst cradled.
What Are Some Effective Lacrosse Ball Cradling Tips?
If you’re just learning the game of lacrosse, it’s important to master the cradle technique. The above steps describe the most basic method of weighing in lacrosse and are the building blocks of advanced lacrosse weighing techniques. Before delving into the more difficult forms of the lacrosse cradle, consider using the following cradle ball tips to improve your technique.
- Making a bag:
Creating the perfect bag to weigh in lacrosse is key to balancing a strong bag with compliance with the rules of lacrosse equipment. The ideal bag for safely weighing lacrosse balls should be deep enough to allow the top of the lacrosse ball to extend slightly beyond the edge of the bag. Men’s lacrosse and women’s lacrosse have different pocket depths, so the women’s lacrosse cradle pocket is shallower than the men’s lacrosse stick pocket, which is deeper.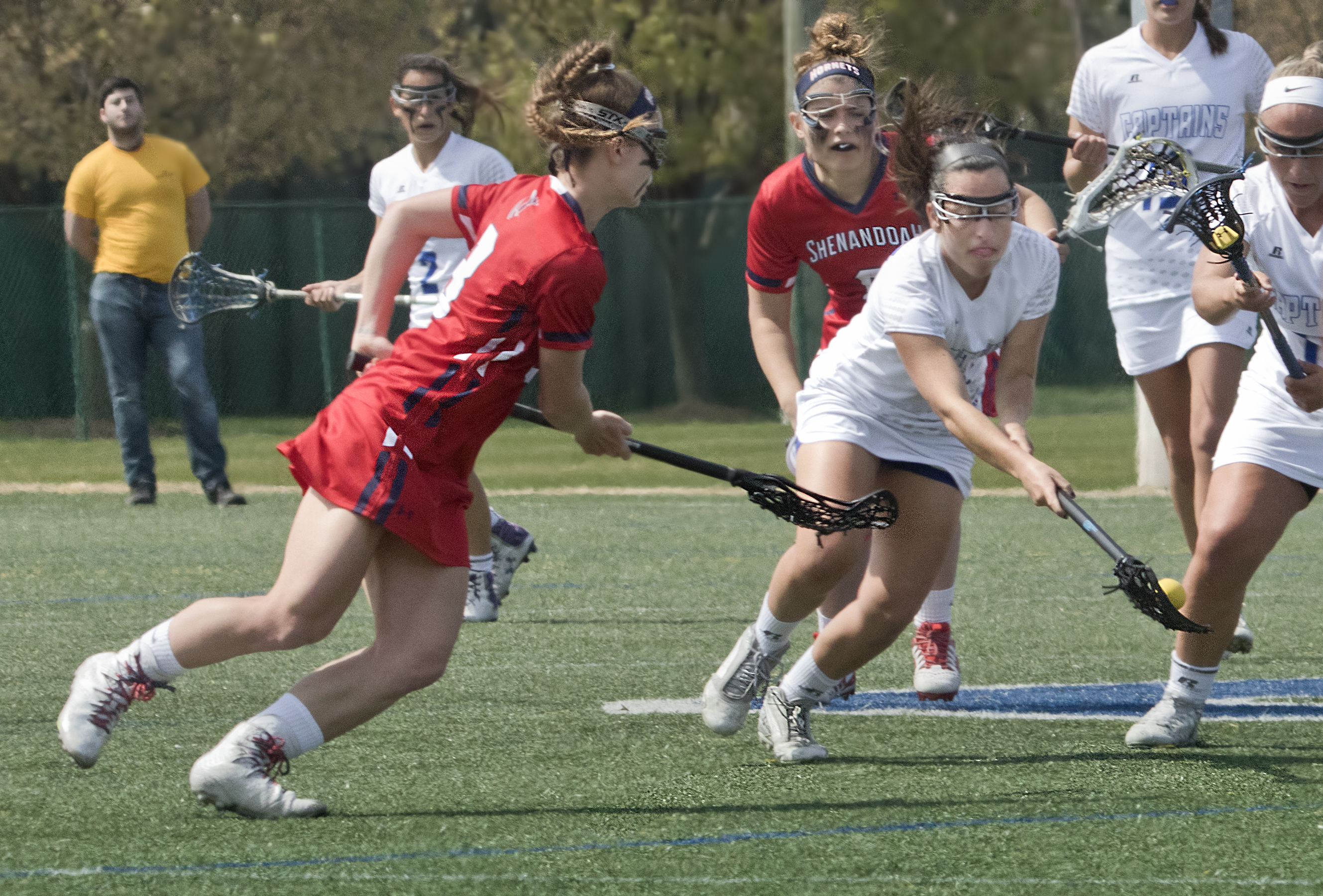
- Side change:
Swinging the ball over the same shoulder can lead to turnovers if you haven’t learned how to keep the lacrosse stick moving while switching sides. To effectively switch sides while holding the lacrosse ball, start by keeping your head as vertical as possible to keep the lacrosse ball from rolling out of your pocket. With your feet off, swing the racquet head down in his V-shaped motion, making sure the cradle of the ball is pointing up. During the backswing, take your bottom hand off the grip and switch positions with your top hand to place the lacrosse cradle over your opposite shoulder. One hand weighing:
Using the one-handed lacrosse cradle allows for faster movement as you run across the field to position your attack. If you’re thinking of your lacrosse stick as a one-handed cradle, you’ll need to twist your wrist slightly to match your stride so the ball is held securely in the cradle. The one-handed cradle is effective for quick movements but slows transitions to shots and passes.
- Passing and shooting from the cradle:
Passing and shooting from a lacrosse stick holder begins with a simple sequence of hand movements from securing the holder to shooting or passing the lacrosse ball. Start by bending the head of the lacrosse stick toward the target. While loading the shot, slide your upper hand down the shaft and gently rock the head of the club to pass or shoot.
Conclusion
The weight helps to hold the ball and protect it from defenders. One way he does this is by holding a stick between his shoulders.
Skills help you move around the field and allow you to focus on the sport’s more advanced techniques.
Olympic Games. History of the Olympic Games. Modern Olympic Games. Paralympic Games | Article on physical education:
History of the Olympic Games
The Olympic Games, the Games of the Olympiad are the largest international complex sports competitions of our time, which are held every four years.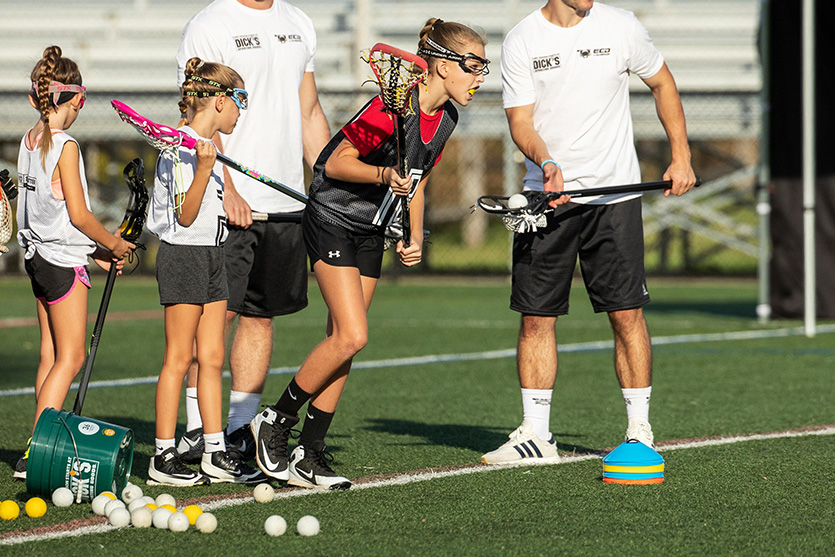 The tradition that existed in ancient Greece was revived at the end of the 19th century by the French public figure Pierre de Coubertin. The Olympic Games, also known as the Summer Olympics, have been held every four years since 1896, except for the years that fell on the world wars. In 1924, the Winter Olympic Games were established, which were originally held in the same year as the summer ones. However, since 1994 the time of the Winter Olympic Games has been shifted by two years from the time of the Summer Games.
The tradition that existed in ancient Greece was revived at the end of the 19th century by the French public figure Pierre de Coubertin. The Olympic Games, also known as the Summer Olympics, have been held every four years since 1896, except for the years that fell on the world wars. In 1924, the Winter Olympic Games were established, which were originally held in the same year as the summer ones. However, since 1994 the time of the Winter Olympic Games has been shifted by two years from the time of the Summer Games.
OLYMPIA – THE CRADE OF THE OLYMPIC GAMES
The Olympic Games, as we know them now, have a long history dating back to ancient times. It all started in the Peloponnese, Greece, about 3,000 years ago.
Sports competitions were held in Olympia and took their name from the venue of the Olympic Games. No one knows exactly when they began, but the first written mention dates back to 776 BC.
The Games were held in the same place every four years. This four-year period was called the Olympiad and was used as a reckoning system: time was measured in Olympiads, not in years.
Initially, the program of the Olympic Games was limited to the stadium – running one stage. Then the program began to expand: competitions were introduced in running for two stages, running for the 24th stage, running with weapons, then pentathlon appeared – pentathlon (running, jumping, discus and spear throwing, wrestling), wrestling and fisticuffs, chariot racing. From 632 BC competitions for children began to be included in the Games.
No matter how the program of the Olympic Games expanded, the one-stage race remained the most revered. The winner in the stadium was given the right to light a fire on the altar of Zeus, he became the main character of the Games.
The main award for the winner of the Olympic Games – Olympionics was an olive branch. She was cut with a golden ritual knife from an old tree, which, it was believed, was planted by Hercules. The name of the athlete was carved on a marble slab, and monuments were erected to those who were especially outstanding. But it was, so to speak, a moral encouragement. The inhabitants of the city, which was represented by the winner, presented him with expensive gifts, exempted him from taxes, and provided him with a free place in the theater.
But it was, so to speak, a moral encouragement. The inhabitants of the city, which was represented by the winner, presented him with expensive gifts, exempted him from taxes, and provided him with a free place in the theater.
The return of the winner to his homeland turned into a truly triumphal procession; all the inhabitants greeted him joyfully.
The Olympic Games essentially lost their significance with the advent of the Romans. After Christianity became the official religion, the games began to be seen as a manifestation of paganism, and in 394 A.D. e. they were banned by the emperor
Modern Olympic Games
The principles, rules and regulations of the Olympic Games are defined by the Olympic Charter, the foundations of which were approved by the International Sports Congress in Paris in 1894, who, at the suggestion of the French educator and public figure Pierre de Coubertin, decided to organize the Games on the model of the ancient ones and to create the International Olympic Committee (IOC).
According to the charter of the Games, the Olympiad “…unite amateur athletes of all countries in fair and equal competitions. In relation to countries and individuals, no discrimination is allowed on racial, religious or political grounds … “. Games are held in the first year of the Olympiad (4-year period between games). Olympiads have been counted since 1896, when the first Olympic Games took place (I Olympiad – 1896-99). The Olympiad also receives its number in cases where games are not held (for example, VI – in 1916-19, XII-1940-43, XIII – 1944-47). The symbol of the Olympic Games is five fastened rings, symbolizing the unification of the five parts of the world in the Olympic movement, the so-called. Olympic rings. The color of the rings in the top row is blue for Europe, black for Africa, red for America, in the bottom row yellow for Asia, green for Australia. In addition to Olympic sports, the Organizing Committee has the right to include demonstration competitions in 1-2 sports that are not recognized by the IOC. In the same year as the Olympics, from 1924 Winter Olympic Games are held, which have their own numbering. Since 1994, the dates for the Winter Olympic Games have been shifted by 2 years relative to the summer ones. The venue of the Olympics is chosen by the IOC, the right to organize them is granted to the city, not the country. Duration no more than 15 days (winter games – no more than 10).
In the same year as the Olympics, from 1924 Winter Olympic Games are held, which have their own numbering. Since 1994, the dates for the Winter Olympic Games have been shifted by 2 years relative to the summer ones. The venue of the Olympics is chosen by the IOC, the right to organize them is granted to the city, not the country. Duration no more than 15 days (winter games – no more than 10).
The Olympic movement has its own emblem and flag, approved by the IOC at the suggestion of Coubertin in 1913. The emblem is the Olympic rings. The motto is Citius, Altius, Fortius (faster, higher, stronger). The flag is a white cloth with the Olympic rings, from 1920 goes up in all Games.
The Olympic Games, like any strictly organized event, have their own traditions and rituals
– solemn passage through the central stadium of athletes and members of delegations. Athletes from each country go in separate groups in alphabetical order of country names in the language of the country in which the Games are held, or in the official language of the IOC (English or French).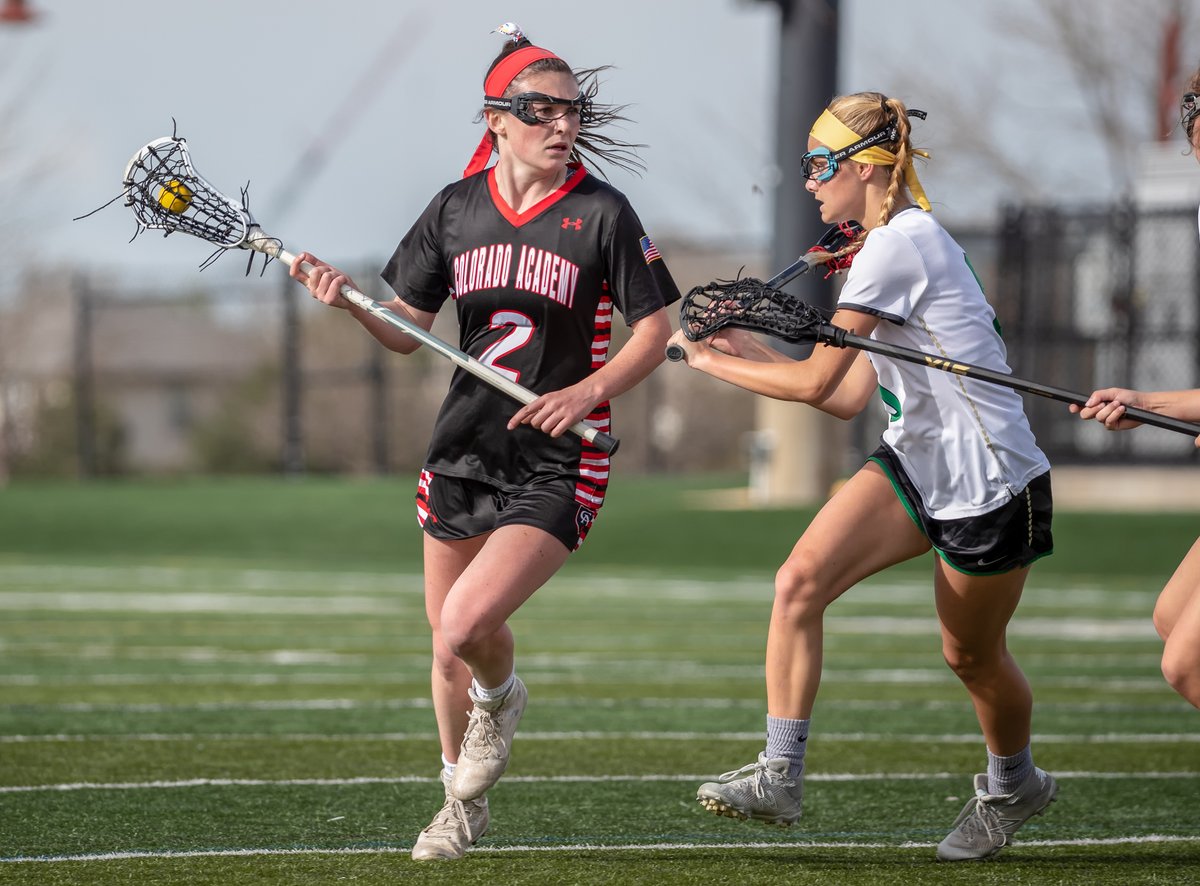 Each group is preceded by a representative of the host country who carries a sign with the name of the respective country. He is followed by a flag bearer carrying the flag of his country. This very honorable mission, as a rule, is granted to the most respected and titled athletes;
Each group is preceded by a representative of the host country who carries a sign with the name of the respective country. He is followed by a flag bearer carrying the flag of his country. This very honorable mission, as a rule, is granted to the most respected and titled athletes;
– It is mandatory for the President of the International Olympic Committee to make welcoming speeches. Also, the speech is delivered by the head of state in which the Games are held;
– the flag of Greece is raised as the country in which the Olympic Games originated. Her national anthem is played;
– the flag of the country in which the Games are held is raised and its national anthem is also played; – one of the outstanding athletes of the host country of the Games takes an oath on behalf of all participants about a fair fight and competition that will comply with all the principles and rules of sports;
– the opening ceremony ends with the lighting and “relay” of the Olympic flame. The initial part of the relay passes through the cities of Greece, the final part – through the cities of the country in which the games are held. The torch with fire is delivered to the city that organizes the Games on the opening day. The fire burns until the closing ceremony of the Olympic Games;
The initial part of the relay passes through the cities of Greece, the final part – through the cities of the country in which the games are held. The torch with fire is delivered to the city that organizes the Games on the opening day. The fire burns until the closing ceremony of the Olympic Games;
– The Closing Ceremony is also accompanied by theatrical performances, the speech of the IOC President, the passage of participants, etc. The President of the IOC announces the closing of the Olympics, followed by the performance of the national anthem, the anthem of the Olympic Games, the lowering of the flags. At the end of the ceremony, the Olympic flame goes out.
Each country participating in the Olympic Games develops its own official emblem and mascot of the Games, which become part of the souvenirs.
Olympic sports
Summer sports
Badminton. Basketball. Boxing. Wrestling: Greco-Roman wrestling, freestyle wrestling. Cycling: BMX cycling, road cycling, track cycling, mountain bike cycling. Water sports: swimming, synchronized swimming, diving, water polo, open water, water skiing. Volleyball: volleyball, beach volleyball. Handball. Gymnastics: artistic gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastics, trampolining. Rowing is academic. Rowing in kayaks and canoes. Judo. Horseback Riding. Athletics. Table tennis. Sailing. Modern pentathlon. Archery. Shooting: bullet shooting, trap shooting. Tennis. Triathlon. Taekwondo. Weightlifting. Fencing. Football. Field hockey.
Water sports: swimming, synchronized swimming, diving, water polo, open water, water skiing. Volleyball: volleyball, beach volleyball. Handball. Gymnastics: artistic gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastics, trampolining. Rowing is academic. Rowing in kayaks and canoes. Judo. Horseback Riding. Athletics. Table tennis. Sailing. Modern pentathlon. Archery. Shooting: bullet shooting, trap shooting. Tennis. Triathlon. Taekwondo. Weightlifting. Fencing. Football. Field hockey.
Winter Sports
Biathlon Bobsleigh: Bobsleigh, Skeleton Speed Skating: Speed Skating, Figure Skating, Short Track Curling Skiing: Alpine Skiing, Nordic Combined, Cross Country Skiing, Ski Jumping, Snowboarding, Freestyle Sun sports Hockey with puck.
Sports excluded from the Olympic program
Golf (1900, 1904). Speedboat racing (1908). Jeu-de-paume (1908). Cricket (1900). Croquet (1900). Lacrosse (1904, 1908). Basque pelota (1900). Tug of war (1900, 1904, 1908, 1912, 1920). Polo (game) or Chovgan (national game) (1900, 1908, 1920, 1924, 1936). Rackets (1908). Rugby (1900, 1908, 1920, 1924). Rock (sport) (1904). Roller Hockey (1992). Baseball. Softball. 3.4 Candidates for inclusion in the Olympic program. Rugby 7. Golf. Squash. Karate. Roller sports. Speed skiing (downhill skiing). Hockey with a ball. Orientation. Billiards. Chapter
Rackets (1908). Rugby (1900, 1908, 1920, 1924). Rock (sport) (1904). Roller Hockey (1992). Baseball. Softball. 3.4 Candidates for inclusion in the Olympic program. Rugby 7. Golf. Squash. Karate. Roller sports. Speed skiing (downhill skiing). Hockey with a ball. Orientation. Billiards. Chapter
The Paralympic Movement. Paralympic Games
The Paralympic Games (Paralympic Games) are international sports competitions for people with disabilities. Traditionally held after the Olympic Games, starting from the Summer Paralympic Games 1988 years – at the same sports facilities; in 2001, this practice was enshrined in an agreement between the IOC and the International Paralympic Committee (IPC). The Summer Paralympic Games have been held since 1960, the Winter Paralympic Games since 1976. The emergence of sports in which disabled people can participate is associated with the name of the English neurosurgeon Ludwig Guttmann, who, overcoming age-old stereotypes in relation to people with physical disabilities, introduced sports into the process of rehabilitation of patients with spinal cord injuries. He proved in practice that sport for people with physical disabilities creates the conditions for successful life, restores mental balance, allows you to return to a full life regardless of physical disabilities, strengthens the physical strength necessary to manage a wheelchair. The name was originally associated with the term paraplegia paralysis of the lower extremities, since these competitions were held among people with diseases of the spine, but with the beginning of the participation of athletes in the games and with other diseases, it was rethought as “nearby, outside the Olympics”; this refers to the parallelism and equality of the Paralympic competitions with the Olympic ones. The spelling “Paralympic” is recorded in the academic “Russian Spelling Dictionary” and other dictionaries. The spelling “Paralympic” is non-normative and is not noted in dictionaries and is used only in official documents of state authorities, being a tracing-paper from the official name (IOC) in English – Paralympic Games.
He proved in practice that sport for people with physical disabilities creates the conditions for successful life, restores mental balance, allows you to return to a full life regardless of physical disabilities, strengthens the physical strength necessary to manage a wheelchair. The name was originally associated with the term paraplegia paralysis of the lower extremities, since these competitions were held among people with diseases of the spine, but with the beginning of the participation of athletes in the games and with other diseases, it was rethought as “nearby, outside the Olympics”; this refers to the parallelism and equality of the Paralympic competitions with the Olympic ones. The spelling “Paralympic” is recorded in the academic “Russian Spelling Dictionary” and other dictionaries. The spelling “Paralympic” is non-normative and is not noted in dictionaries and is used only in official documents of state authorities, being a tracing-paper from the official name (IOC) in English – Paralympic Games.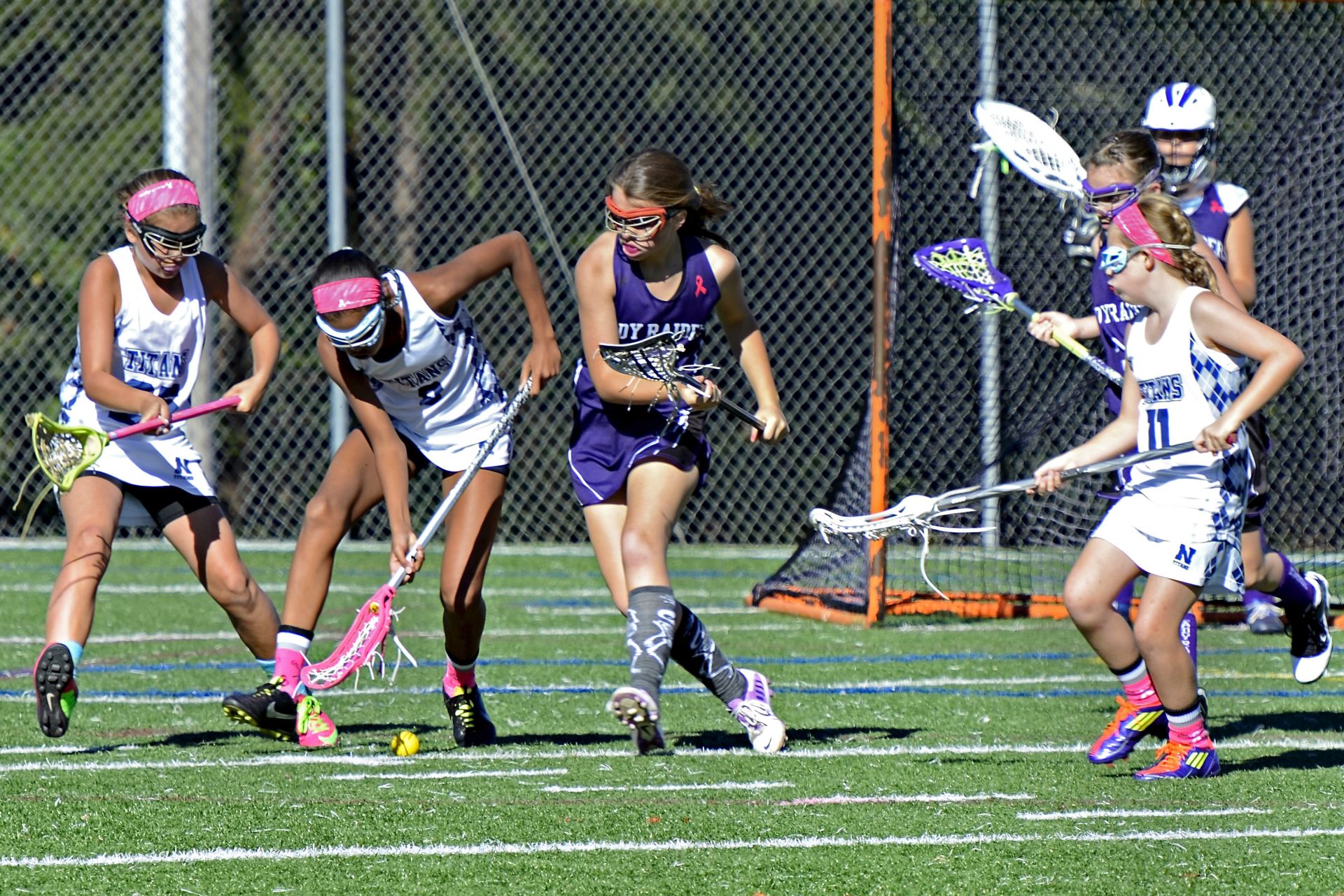 At first, the term “Paralympic Games” was applied informally. Games 19For 60 years they were officially called the “Ninth International Stoke Mandeville Games” and only in 1984 they were given the status of the first Paralympic Games. The first games to which the term “Paralympics” was officially applied were the 1964 games. However, in a number of games up to the 1980 Games, the term “Olympic Games for the Disabled” was used, in 1984 – “International Games of the Disabled”. The term “Paralympic” was finally officially fixed, starting with the 1988 Games. Since 2005, a system has been introduced that allows participants to perform not only with the disease, but also with deafness.
At first, the term “Paralympic Games” was applied informally. Games 19For 60 years they were officially called the “Ninth International Stoke Mandeville Games” and only in 1984 they were given the status of the first Paralympic Games. The first games to which the term “Paralympics” was officially applied were the 1964 games. However, in a number of games up to the 1980 Games, the term “Olympic Games for the Disabled” was used, in 1984 – “International Games of the Disabled”. The term “Paralympic” was finally officially fixed, starting with the 1988 Games. Since 2005, a system has been introduced that allows participants to perform not only with the disease, but also with deafness.
Summer sports: rowing; wheelchair basketball; kayaking; judo; Athletics; table tennis; paratriathlon; sailing; swimming; bullet shooting; wheelchair rugby; seated volleyball; archery; wheelchair tennis; Weightlifting; wheelchair fencing; football 5×5; football 7×7.
Winter sports: Alpine skiing; wheelchair curling; ski race; biathlon; sledge hockey (a team sports game on ice, an analogue of ice hockey for people with disabilities; it consists in a confrontation between two teams on special sledges, which, passing the puck with sticks, seek to throw it as many times as possible into the opponent’s goal and not let it into their own; the team that scores the most goals in the opponent’s goal wins.
Conclusion
Since ancient times, the Olympic Games have been the main sporting event of all time. In the days of the Olympiads, harmony and reconciliation reigned throughout the earth. Wars stopped, and all strong and worthy people competed in a fair fight for the title of the best. Over the centuries, the Olympic movement has overcome many obstacles, oblivion and alienation. But despite everything, the Olympic Games are alive to this day. Of course, these are no longer the competitions in which naked youths took part and the winner of which entered the city through a hole in the wall. Today, the Olympics are one of the biggest events in the world. Games are equipped with the latest technology – computers and television cameras monitor the results, the time is determined to the nearest thousandth of a second, the athletes and their results largely depend on the technical equipment. In recent years, the Olympic movement has acquired a huge scale and the capitals of the games for the duration of the games become the capitals of the world. Sport plays an increasingly important role in people’s lives! Nothing ennobles the human soul like art. And nothing is closer to art than a real pure sport. “Art,” said Coubertin, “must coexist with sports, must be associated with the practice of sports.” This close unity, as the founder of the modern Olympic Games believed, will help the development of the human personality. At his suggestion, art competitions were included in the program of the Olympic Games, as was done at the ancient Greek Games. Such contests have been held since 1912 to 1948. The IOC then decided to replace the “artistic battles” with extensive cultural programs. And now the Olympic Games are decorated with concerts, exhibitions, theatrical performances. Another useful thing is various creative contests, events where the main theme is sport, its masculinity and beauty. The Russian Olympic Committee, celebrating the 100th anniversary of the formation of the International Olympic Committee and the 100th anniversary of the modern Olympic Games, organized competitions for the best work on a sports theme in the field of literature, journalism, cinematography, theater and fine arts.
Sport plays an increasingly important role in people’s lives! Nothing ennobles the human soul like art. And nothing is closer to art than a real pure sport. “Art,” said Coubertin, “must coexist with sports, must be associated with the practice of sports.” This close unity, as the founder of the modern Olympic Games believed, will help the development of the human personality. At his suggestion, art competitions were included in the program of the Olympic Games, as was done at the ancient Greek Games. Such contests have been held since 1912 to 1948. The IOC then decided to replace the “artistic battles” with extensive cultural programs. And now the Olympic Games are decorated with concerts, exhibitions, theatrical performances. Another useful thing is various creative contests, events where the main theme is sport, its masculinity and beauty. The Russian Olympic Committee, celebrating the 100th anniversary of the formation of the International Olympic Committee and the 100th anniversary of the modern Olympic Games, organized competitions for the best work on a sports theme in the field of literature, journalism, cinematography, theater and fine arts.