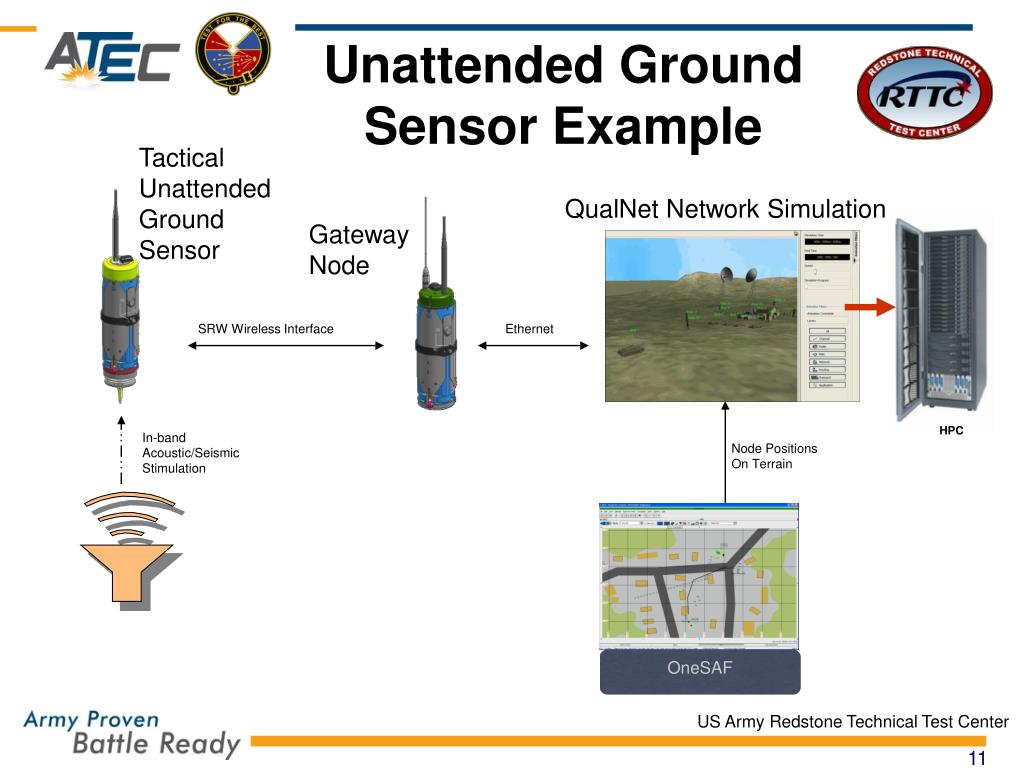
How do temperature sensors work. What are the different types of temperature sensors. Why are temperature sensors important in various industries. How to choose the right temperature sensor for your application. What are the advantages of using thermistors in temperature sensing.
Understanding Temperature Sensors: The Basics
Temperature sensors are crucial components in modern technology, playing a vital role in numerous applications across various industries. These devices are designed to detect and measure thermal energy in a given medium, converting it into an electrical signal for further processing or display. Understanding the fundamentals of temperature sensors is essential for anyone working with or interested in temperature measurement and control systems.
Temperature sensors come in various types, each with its own set of characteristics and advantages. The most common types include:
- Thermistors (NTC and PTC)
- Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
- Digital Temperature Indicators
- Thermocouples
- Infrared sensors
Each type of sensor operates on different principles and offers unique benefits for specific applications. Let’s delve deeper into the world of temperature sensors to explore their functions, applications, and selection criteria.

Thermistors: The Versatile Temperature Sensing Solution
Thermistors are among the most widely used temperature sensors due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and excellent long-term stability. But what exactly are thermistors, and how do they work?
Thermistors are thermally sensitive resistors that exhibit a significant and predictable change in electrical resistance when subjected to temperature variations. There are two main types of thermistors:
- Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors
- Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors
NTC thermistors demonstrate a decrease in electrical resistance as temperature increases, while PTC thermistors show an increase in resistance with rising temperatures. This predictable behavior makes thermistors ideal for a wide range of temperature measurement and control applications.
Advantages of Thermistors
Why are thermistors often preferred over other temperature sensing devices? Thermistors offer several advantages:
- High sensitivity to small temperature changes
- Fast response time
- Wide temperature range
- Excellent long-term stability
- Cost-effectiveness
- Compact size
These characteristics make thermistors suitable for applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial processes, where accurate and reliable temperature measurement is critical.

RTDs: Precision Temperature Measurement for Specialized Applications
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) represent another important category of temperature sensors, particularly valued for their high accuracy and stability over a wide temperature range. How do RTDs differ from thermistors, and what makes them suitable for specialized applications?
RTDs, particularly those made with platinum (Pt RTDs), exhibit a positive, predictable, and nearly linear change in resistance with temperature variations. This linear response allows for precise temperature measurements across an extensive range, making RTDs ideal for applications requiring high accuracy or involving extreme temperatures.
Key Features of RTDs
- High accuracy (up to 0.06%/0.15°C)
- Wide temperature range (-200°C to 850°C for platinum RTDs)
- Excellent stability over time
- Near-linear response
- Interchangeability between sensors
These characteristics make RTDs particularly suitable for industries such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where precise temperature control is crucial for safety and quality assurance.

Digital Temperature Indicators: The Modern Approach to Temperature Sensing
As technology advances, digital temperature indicators are becoming increasingly popular in various applications. What sets digital temperature indicators apart from their analog counterparts?
Digital temperature indicators provide a direct digital output, eliminating the need for additional signal conditioning in many cases. They typically incorporate a sensing element (often a thermistor or RTD) with integrated circuitry to produce a digital signal proportional to the measured temperature.
Advantages of Digital Temperature Indicators
- Direct digital output for easy integration with control systems
- High accuracy and resolution
- Built-in calibration and linearization
- Reduced susceptibility to noise and interference
- Often include additional features like alarms or data logging
These features make digital temperature indicators particularly useful in applications requiring precise temperature monitoring and control, such as in HVAC systems, industrial processes, and scientific research.

Applications of Temperature Sensors Across Industries
Temperature sensors play a crucial role in numerous industries and applications. How are these devices utilized in different sectors, and what makes them indispensable in modern technology?
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, temperature sensors are essential for monitoring and controlling various systems, including:
- Engine coolant temperature
- Oil temperature
- Exhaust gas temperature
- Battery temperature in electric vehicles
- Cabin climate control
These sensors help optimize engine performance, improve fuel efficiency, and ensure passenger comfort and safety.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
Temperature sensors are critical in medical applications, where accurate temperature measurement can be a matter of life and death. Some key uses include:
- Patient temperature monitoring
- Incubators for premature infants
- Blood and tissue storage
- Sterilization equipment
- Medical imaging devices
The high accuracy and fast response of modern temperature sensors make them invaluable in these sensitive applications.

Industrial Processes
In industrial settings, temperature sensors are used for process control, quality assurance, and safety monitoring. Common applications include:
- Chemical reactors
- Food and beverage processing
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Metal heat treatment
- Environmental monitoring in hazardous areas
The ability to withstand harsh environments and provide accurate measurements makes certain types of temperature sensors ideal for these demanding applications.
Selecting the Right Temperature Sensor for Your Application
Choosing the appropriate temperature sensor is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in your specific application. What factors should be considered when selecting a temperature sensor?
Key Considerations for Sensor Selection
- Temperature range: Ensure the sensor can accurately measure the full range of temperatures expected in your application.
- Accuracy requirements: Determine the level of precision needed for your measurements.
- Response time: Consider how quickly the sensor needs to respond to temperature changes.
- Environmental conditions: Take into account factors such as humidity, vibration, and chemical exposure.
- Size and form factor: Ensure the sensor can be properly integrated into your system or device.
- Cost: Balance performance requirements with budget constraints.
- Compatibility: Consider the sensor’s output signal and how it will interface with your control or monitoring system.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select the most suitable temperature sensor for your specific needs, ensuring reliable and accurate temperature measurement in your application.

Advancements in Temperature Sensing Technology
The field of temperature sensing is continually evolving, with new technologies and improvements emerging to meet the demands of modern applications. What are some of the recent advancements in temperature sensor technology?
Miniaturization and Integration
One significant trend is the miniaturization of temperature sensors, allowing for their integration into increasingly compact devices. This has enabled the development of:
- Wearable health monitoring devices
- Smart home appliances with built-in temperature control
- Micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) based sensors
These advancements have opened up new possibilities for temperature sensing in consumer electronics and IoT devices.
Wireless and Smart Sensors
The integration of wireless communication capabilities into temperature sensors has revolutionized remote monitoring and data collection. Smart sensors now offer features such as:
- Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity for easy data transmission
- Cloud-based data storage and analysis
- Real-time alerts and notifications
- Over-the-air firmware updates
These capabilities enhance the flexibility and functionality of temperature monitoring systems across various industries.

Enhanced Durability and Reliability
Advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of more robust and reliable temperature sensors. This includes:
- Sensors capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and harsh environments
- Improved stability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent calibration
- Self-diagnostic capabilities to detect sensor faults or drift
These improvements have expanded the range of applications for temperature sensors, particularly in industrial and aerospace sectors.
The Future of Temperature Sensing: Emerging Trends and Technologies
As we look to the future, several exciting trends are shaping the evolution of temperature sensing technology. What can we expect to see in the coming years?
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms with temperature sensing systems is poised to revolutionize predictive maintenance and process optimization. These advanced technologies can:

- Analyze temperature data patterns to predict equipment failures
- Optimize temperature control in complex systems
- Enhance the accuracy of temperature measurements through intelligent calibration
This convergence of AI and temperature sensing will lead to more efficient and reliable systems across various industries.
Non-Contact and Remote Sensing
Advancements in infrared and fiber optic sensing technologies are expanding the capabilities of non-contact temperature measurement. These developments include:
- High-resolution thermal imaging for precise temperature mapping
- Distributed temperature sensing using fiber optics for long-distance monitoring
- Satellite-based temperature sensing for global climate monitoring
These technologies enable temperature measurement in previously inaccessible or hazardous environments, opening up new applications in fields such as environmental monitoring and industrial safety.
Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensors
The development of energy harvesting technologies is paving the way for self-powered temperature sensors. These innovative devices can:
- Generate power from temperature differentials using thermoelectric effects
- Harvest energy from ambient vibrations or light
- Operate autonomously in remote or hard-to-reach locations
Self-powered sensors will greatly expand the deployment possibilities for temperature monitoring systems, particularly in IoT and environmental sensing applications.
As temperature sensing technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and improved performance in the years to come. From enhancing industrial processes to monitoring global climate change, temperature sensors will play an increasingly critical role in shaping our technological future.
Temperature Sensors – Thermistor – RTDs Probes & Assemblies
- Competitor Cross Reference
Need the Littelfuse equivalent to a competitor part? Enter the competitor part number here.
- Order Sample
Search for the part(s) number you wish to receive samples. Or, visit the sample center page.
- Check Distributor Stock
Check distributor stock levels by entering in full or partial part numbers
- Home
- > Products
- > Temperature Sensors
-
Leaded RTDs -
NTC and PTC Thermistors -
RTD Probes and Assemblies -
Surface Mount Thermistors -
Thermistor Probes and Assemblies -
Digital Temperature Indicators
-
Information Center -
Technical Resources
- The Fundamentals
- Available Styles
- Customizable Options
- Applications
What are Temperature Sensors?
A Temperature Sensor is a device that detects and measures the average heat or thermal energy in a medium and converts it into an electrical signal. A wide variety of temperature sensing devices are available today. Littelfuse offers a broad range of Thermistors, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), Digital Temperature Indicators, and probes and assemblies for temperature sensing applications worldwide.
A wide variety of temperature sensing devices are available today. Littelfuse offers a broad range of Thermistors, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), Digital Temperature Indicators, and probes and assemblies for temperature sensing applications worldwide.
How do Temperature Sensors Work?
Each temperature sensor style has its own set of operating principles, features, benefits, considerations, and limitations for optimal use.
Thermistors (NTCs and PTCs):
- Thermistors are thermally sensitive resistors whose prime function is to exhibit a large, predictable, and precise change in electrical resistance when subjected to a corresponding change in body temperature.
- Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors exhibit a decrease in electrical resistance when subjected to an increase in body temperature.
- Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors exhibit an increase in electrical resistance when subjected to an increase in body temperature.

- Based on the predictable characteristics and their excellent long-term stability, cost-effective thermistors are generally accepted to be the most advantageous sensor for many applications, including temperature measurement and control.
RTDs:
- Platinum Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are temperature sensors that have a positive, predictable, and nearly linear change in resistance when subjected to a corresponding change in their body temperature.
- The nearly linear output needed to precisely measure temperature over a very wide range makes RTDs ideal for more-specialized applications requiring very high accuracy (ex. 0.06%/0.15°C) or for applications requiring a lot of precision.
Digital Temperature Indicators:
- Digital Temperature Indicators have a positive relationship between resistance and temperature. The response is very much like a digital signal; below the trip temperature, resistance will be low, above the trip temperature, resistance will be very high.

- This digital response is ideal for applications where knowing the temperature has increased beyond a specific value is required. With the digital response, no analog to digital conversion is necessary, allowing designers to save time and space.
Can I Customize Temperature Sensors?
Modifications are available to existing standard product packages, such as adding connectors or changing wire size or length, as well as offering special resistance-temperature (R-T) curves, R-T curve matching, and custom lead forming and bending to discrete thermistors. In addition, the following options and services are available.
- Complete custom sensor packages, including moisture resistant designs
- Custom resistance-temperature (R-T) characteristics
- Specialized resistance tolerance or temperature accuracy within specified temperature ranges
- Sensing element design for best long-term stability
- Rapid prototyping and quick-turn concept parts including 3D printed parts
- Prototype units using prototype tooling
- Reliability/validation testing options
- Fully designed, production-capable sensor and tooling
Typical Applications for Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors are used in diverse markets, including:
HVAC/R
- Residential & Commercial A/C
- Chilled Water Systems
- Outdoor Temperature Sensors
- Instant Water Heaters
- Condenser, Evaporator & Duct Sensors
Renewable Energy
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Sensors
- Battery Fuel Gauges
- Solar Panel
- Geothermal
- Battery Energy Storage Systems
- Solar Inverters
Appliances
- Oven Temperature Control
- Washing Machines
- Clothes Dryers
- Water Heaters
- Consumer Refrigerators/Freezers
Food Service
- Commercial Coffee Makers
- Hot/Cold Beverage Dispensers
- Food Thermometers
- Walk-in & Reach-in Refrigerators/Freezers
- Temperature Controlled Display Cases
Medical
- Blood Analysis Equipment
- Infant Incubators
- Skin Temperature Monitors
- Blood Dialysis Equipment
- Patient Warming
- View All
- Selection Guides
- Product Literature
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – Chinese | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – German | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – Japanese | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – Russian | |
|
Littelfuse Temperature Sensors Overview – Chinese | |
|
Littelfuse Temperature Sensors Overview – German | |
|
Littelfuse Temperature Sensors Overview – Japanese |
Leaded Thermistors – Temperature Sensors – Interchangeable Leaded Thermistors
- Home
- > Products
- > Temperature Sensors
- > Leaded Thermistors
-
Epoxy Coated Thermistors -
Glass Coated Chip Thermistors -
Glass Encapsulated Thermistors -
Glass Probe Thermistors -
Interchangeable Thermistors
-
Technical Resources
- View All
- Selection Guides
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – German | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – Japanese | |
|
Temperature Sensor Selection Guide – Russian |
Why the United States is installing radiation level sensors in Ukraine
Why is the United States installing radiation level sensors in Ukraine – Gazeta.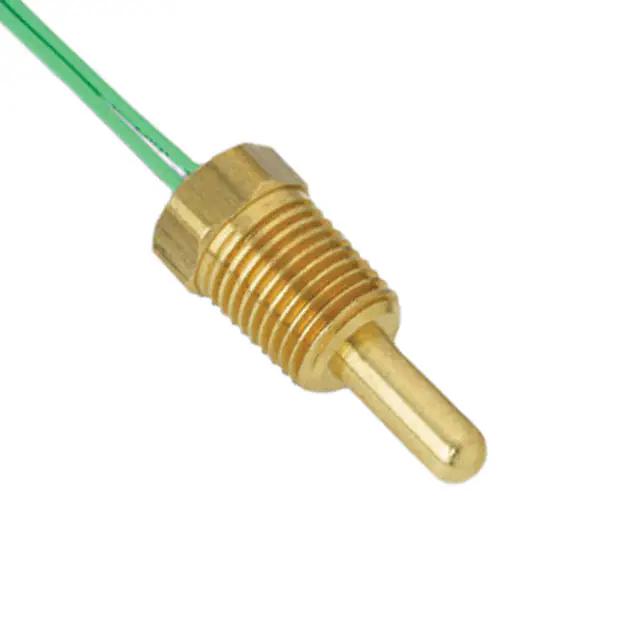 Ru
Ru
Army
Text size
A
A
A
close
100%
The New York Times, citing the US National Nuclear Security Agency, claims that the US is installing sensors in Ukraine that can detect radiation emissions from nuclear weapons and “dirty bombs” and can indicate by whom they were used. The agency notes that such sensors exclude any possibility for Russia to use nuclear weapons in Ukraine and blame Kyiv for this. On April 26, Washington called on Moscow to return to the discussion of the new START-3 treaty – the Russian Foreign Ministry claimed that the Russian Federation would not go “up the ladder of nuclear escalation.”
The United States installs sensors in Ukraine that detect emissions from nuclear weapons or “dirty bombs”, as well as indicating by whom they were used, writes The New York Times (NYT) with reference to the US National Nuclear Security Agency (NNSA, part of the US Department of Energy). An NNSA spokesman told the newspaper that the sensors can “characterize the size, location and consequences of any nuclear explosion.” It is noted that the installation of this equipment excludes “any opportunity for the Russian Federation to use nuclear weapons in Ukraine” and accuse Kyiv of using it.
An NNSA spokesman told the newspaper that the sensors can “characterize the size, location and consequences of any nuclear explosion.” It is noted that the installation of this equipment excludes “any opportunity for the Russian Federation to use nuclear weapons in Ukraine” and accuse Kyiv of using it.
In addition, US nuclear security experts are helping to train Ukrainian personnel and keep records. It is also noted that the US Department of Energy will spend approximately $160 million this year on nuclear precautions in Ukraine, a similar amount has been requested for 2024.
“If a nuclear emergency occurs in Ukraine, whether it is a release of radiation from a nuclear reactor or the detonation of a nuclear weapon, scientific analysis data will be promptly provided to US government agencies and decision-making centers in Ukraine and the region to make effective, technically sound decisions to protect public health and safety,” the message says.
On April 26, Mikhail Podolyak, adviser to the head of the office of the President of Ukraine, said that the US policy, together with other Western countries, forced Kyiv to abandon nuclear weapons and led to a conflict in the country.
“Unfortunately, the United States, along with a number of Western countries, pushed Ukraine to give up nuclear and other weapons in order to ensure guaranteed security and stability in the region. This erroneous policy was misinterpreted by the aggressor and led to a big war in Europe,”
– says Podolyak.
Also on April 26, the head of the National Nuclear Security Administration at the US Department of Energy, Jill Hruby, called on Moscow to resume contacts on a new nuclear arms limitation treaty.
“We have lost a lot from the suspension of [Moscow’s] participation in this treaty in terms of stabilizing mechanisms. We would certainly like them to return to compliance with the treaty and begin discussions on a new treaty that would limit the number of nuclear weapons, ”she said at a congressional hearing.
Without nuclear missiles, but with submarines. How Biden is going to contain Kim Jong-un
The Presidents of the United States and South Korea agreed to sign the Washington Declaration following the meeting. This is a new…
This is a new…
April 27 02:37
On April 27, US Ambassador to Moscow Lynn Tracy said that Washington remains committed to the implementation of START-3 and is ready for contacts with Moscow on this issue. “We will continue to strive for a world without wars, including through an expanded strategic dialogue with Russia, whenever possible,” she stressed.
At the same time, in a interview with newspaper Kommersant, Tracy stated that the United States continues to observe a complete moratorium on nuclear weapons test explosions and calls on all countries possessing nuclear weapons to declare or observe this moratorium.
In turn, on April 27, Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova said that Moscow did not intend to follow the path of nuclear escalation. Zakharova also indicated that she “does not recommend” doubting Russia’s determination and testing it “in practice.”
“American strategists are also under illusions about the hypothetical nuclear escalation ladder, as experts call it. And we will do everything to prevent the development of events according to the worst scenario, as the Russian leadership has repeatedly said,” the diplomat said.
And we will do everything to prevent the development of events according to the worst scenario, as the Russian leadership has repeatedly said,” the diplomat said.
On April 28, Russian presidential spokesman Dmitry Peskov commented on Tracy’s call to continue observing the moratorium on test explosions of such weapons: “At present, everyone adheres to the moratorium. There’s nothing more to say here.”
Subscribe to Gazeta.Ru in News, Zen and Telegram.
To report a bug, select the text and press Ctrl+Enter
News
Zen
Telegram
Georgy Bovt
A four-day work week in Russia: dreams and reality
Why a four-day work week does not shine for us
Anastasia Mironova
For an abortion: how many women in Russia terminate a pregnancy
We have fewer abortions than in religious Poland, leave behind our women
Evgeny Zaramenskikh
Why does Russia need its own drones?
Where drones are most actively used in Russia
Dmitry Samoilov
The history of the Russian dacha
Why country rest is so popular in Russia
Artur Muradyan
Is it worth vacationing in Turkey and Egypt in the summer of 2023?
About holidays in popular foreign destinations
The United States handed over to Ukraine sensors for detecting nuclear explosions – RBC
adv.rbc.ru
adv. rbc.ru
rbc.ru
Hide banners
What is your location ?
YesChoose other
Categories
Euro exchange rate on July 25
EUR CB: 100.36
(-0.29)
Investments, 24 Jul, 18:07
Dollar exchange rate on July 25
USD CB: 90.49
(+0.1)
Investments, 24 Jul, 18:07
Siluanov predicted a GDP deficit in 2023 at the level of 2-2.5%
Economy, 06:40
In Snigirevka announced the preparation of the Armed Forces of Ukraine to storm the Dnieper
Politics, 06:10
Doctors spoke about the risks of heat stress threatening Europeans
Society, 06:00
adv. rbc.ru
rbc.ru
adv.rbc.ru
IAEA experts found anti-personnel mines on the outer perimeter of ZNPP
Politics, 05:40
The Ministry of Defense announced 10 attempts to attack the Armed Forces of Ukraine in the DPR
Politics, 05:30
Bastrykin considered unacceptable non-payment of taxes with millions in income
Politics, 05:09
The President of Venezuela boarded the Russian ship Perekop
Society, 05:05
Do you see a competitor in ChatGPT?
Learn how to turn a neural network into an assistant in the new intensive RBC Pro
Buy intensive
Bastrykin declared the lack of moral principles of the Ukrainian authorities
Politics, 04:19
Russians named the most dangerous countries for tourism
Society, 04:00
One person died after a boat capsized near Kronstadt
Society, 03:53
10 police officers injured at protests in Tel Aviv
Politics, 03:33
Oleg Deripaska sued Elizabeth Osetinskaya and Olga Romanova
Society, 03:32
Kommersant announced the initiation of a terrorism case after a drone attack
Politics, 03:24
Bloomberg learned about Disney’s plans to postpone premieres due to strike
Society, 02:59
adv. rbc.ru
rbc.ru
adv.rbc.ru
adv.rbc.ru
Sensors capable of capturing data on the size and location of a nuclear explosion and describing its effects, as well as providing data to help identify the party that used such weapons , writes The New York Times (NYT) with reference to the US National Nuclear Security Agency (NNSA), which is a structure of the US Department of Energy.
Sensors can “characterize the size, location and effects of any nuclear explosion,” NNSA said. Their presence, according to the agency, excludes “any possibility [for Russia] to use nuclear weapons in Ukraine without giving reasons,” including blaming Kyiv itself for its use.
“Should a nuclear emergency occur in Ukraine, whether it be a release of radiation from a nuclear reactor or the detonation of a nuclear weapon, scientific analysis will be promptly provided to U.S. government agencies and decision-making centers in Ukraine and the region to make actionable, technically sound decisions to protect public health and safety,” the statement said.
adv.rbc.ru
In addition to installing sensors, a team of nuclear experts helps train staff and monitor data.
adv.rbc.ru
Last autumn, Moscow repeatedly stated that Kyiv was planning to use a “dirty bomb” (a type of attack using radioactive material, such as undermining a non-military installation). The Ukrainian side denied such accusations.
Russia has also stated that Ukraine is ready to deploy NATO nuclear weapons on its territory. Kyiv abandoned his at 1994, by signing the Budapest Memorandum (other signatories are Great Britain, Russia, the USA). In exchange for this, Ukraine received guarantees of security and territorial integrity. Shortly before the outbreak of hostilities, President of Ukraine Volodymyr Zelensky said that the country wants to hold a summit of the countries participating in the memorandum, and if it does not take place or Kiev does not receive security guarantees again, then Ukraine will abandon all points of the agreement.